Abstract
Involvement of protein kinase C in receptor-operated Ca2+ sensitization of cell shortening was investigated by use of alpha-toxin-permeabilized smooth muscle cells from the fundus of the guinea-pig. Most of the isolated cells responded to 0.6 microM Ca2+ with a maximal shortening to approximately 65% of the resting cell length. Addition of acetylcholine (ACh) at a maximal concentration (10 microM) resulted in a marked decrease in the concentration of Ca2+ required to trigger a threshold response from 0.6 microM to 0.2 microM. The augmentation of Ca2+ sensitivity by ACh was not inhibited by specific protein kinase C inhibitors, calphostin C and K-252b at a concentration of 1 microM. These findings suggest that protein kinase C is not involved in the muscarinic receptor-operated augmentation of Ca2+ sensitivity.
Full text
PDF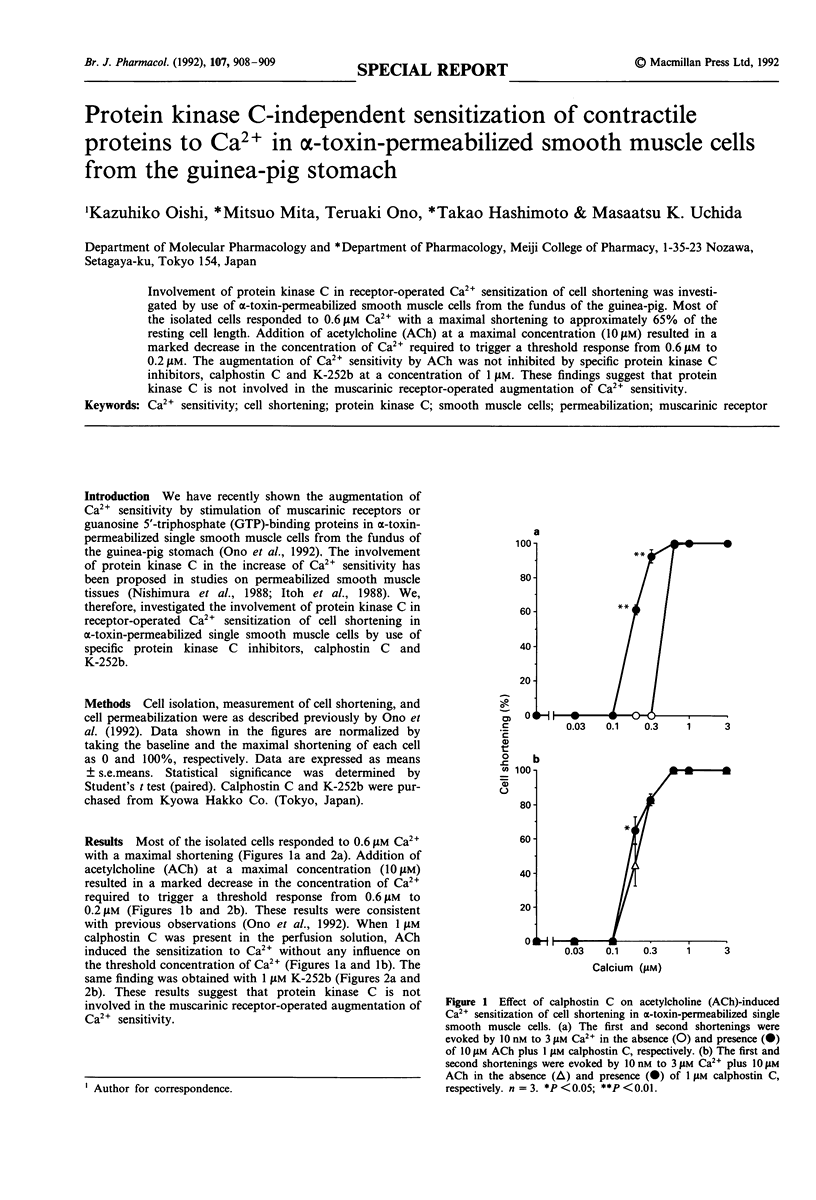

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Freissmuth M., Casey P. J., Gilman A. G. G proteins control diverse pathways of transmembrane signaling. FASEB J. 1989 Aug;3(10):2125–2131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata K., Kikuchi A., Sasaki T., Kuroda S., Kaibuchi K., Matsuura Y., Seki H., Saida K., Takai Y. Involvement of rho p21 in the GTP-enhanced calcium ion sensitivity of smooth muscle contraction. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):8719–8722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Kubota Y., Kuriyama H. Effects of a phorbol ester on acetylcholine-induced Ca2+ mobilization and contraction in the porcine coronary artery. J Physiol. 1988 Mar;397:401–419. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara Y., Kawata M., Sunako M., Araki S., Koide M., Tsuda T., Fukuzaki H., Takai Y. Identification of a major GTP-binding protein in bovine aortic smooth muscle cytosol as the rhoA gene product. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 31;170(2):673–683. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)92144-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathanson N. M. Molecular properties of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1987;10:195–236. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.10.030187.001211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura J., Kolber M., van Breemen C. Norepinephrine and GTP-gamma-S increase myofilament Ca2+ sensitivity in alpha-toxin permeabilized arterial smooth muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 15;157(2):677–683. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80303-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono T., Mita M., Suga O., Hashimoto T., Oishi K., Uchida M. K. Receptor-coupled shortening of alpha-toxin-permeabilized single smooth muscle cells from the guinea-pig stomach. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Jul;106(3):539–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14371.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson H. F., Self A. J., Garrett M. D., Just I., Aktories K., Hall A. Microinjection of recombinant p21rho induces rapid changes in cell morphology. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1001–1007. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



