Abstract
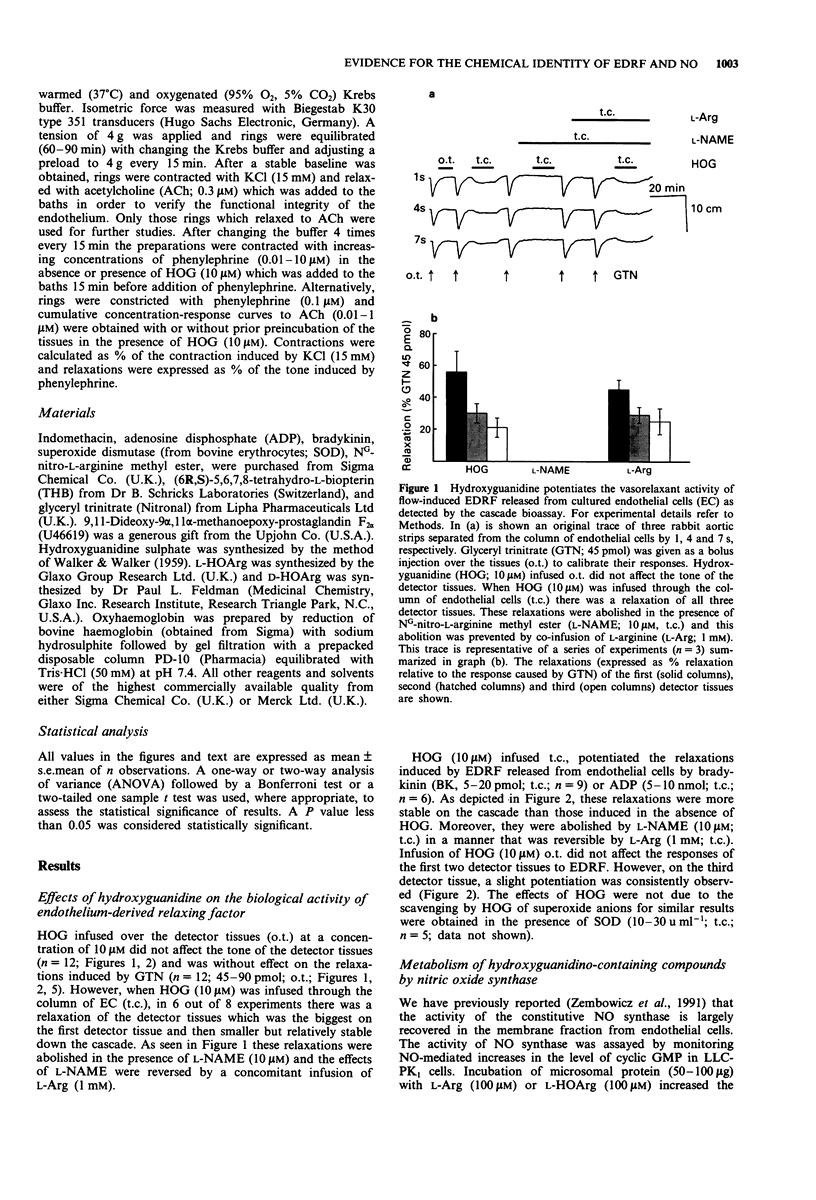
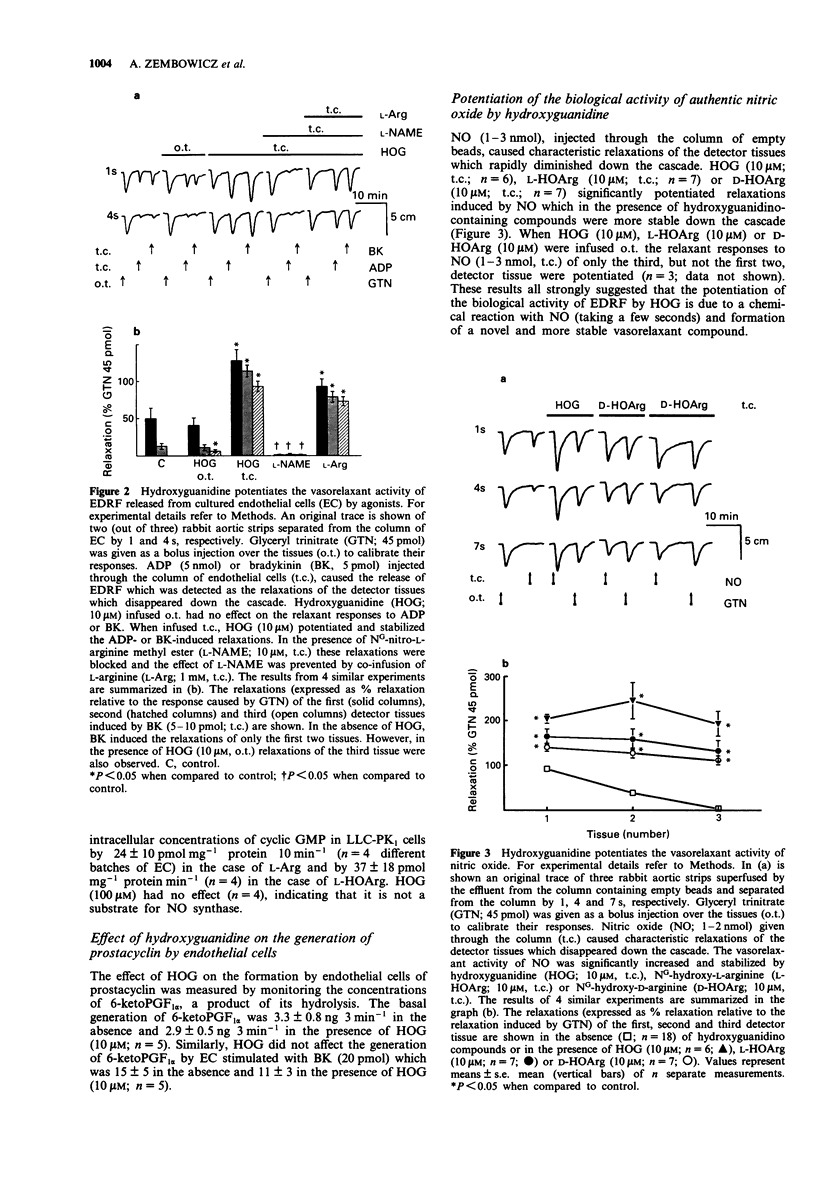
1. We recently demonstrated that NG-hydroxy-L-arginine (L-HOArg) is a substrate for the constitutive nitric oxide (NO) synthase present in bovine aortic endothelial cells cultured on microcarrier beads (EC). Furthermore, L-HOArg reacts chemically with NO released from these cells to form a potent and more stable vasodilator. This is most likely through a reaction with the hydroxyguanidino group. 2. Here, we studied the interaction of a simpler molecule, hydroxyguanidine (HOG) with NO. 3. HOG (10 microM), like L-HOArg (10 microM) or NG-hydroxy-D-arginine (D-HOArg, 10 microM), potentiated and stabilized the relaxant activity of authentic NO. 4. When NO was bubbled through the solution of HOG, a new compound was formed. It had similar physicochemical properties to those of the previously described L-HOArg/NO adduct. It was also a potent vasodilator and its action was inhibited by oxyhaemoglobin (10 microM), indicating formation of a NO-containing substance. 5. Moreover, HOG (10 microM) was not a substrate for the constitutive NO synthase present in the microsomal fraction of EC and did not affect the flow-induced or bradykinin-stimulated generation of prostacyclin, as measured by 6-keto-PGF1 alpha. 6. We also studied the effect of HOG on the endothelium-derived relaxing factor (EDRF) released from the column of EC. HOG (10 microM) potentiated and stabilized the relaxations of rabbit aortic strips induced by EDRF released by bradykinin (5-20 pmol) or ADP (5-10 nmol). These relaxations were inhibited by NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME, 10 microM) and L-arginine (L-Arg, 1 mM) reversed the inhibitory effects of L-NAME.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Billiar T. R., Curran R. D., Stuehr D. J., Stadler J., Simmons R. L., Murray S. A. Inducible cytosolic enzyme activity for the production of nitrogen oxides from L-arginine in hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 May 16;168(3):1034–1040. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91133-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Isolation of nitric oxide synthetase, a calmodulin-requiring enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):682–685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busse R., Mülsch A. Induction of nitric oxide synthase by cytokines in vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 1990 Nov 26;275(1-2):87–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81445-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feelisch M., Kelm M. Biotransformation of organic nitrates to nitric oxide by vascular smooth muscle and endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Oct 15;180(1):286–293. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81290-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förstermann U., Pollock J. S., Schmidt H. H., Heller M., Murad F. Calmodulin-dependent endothelium-derived relaxing factor/nitric oxide synthase activity is present in the particulate and cytosolic fractions of bovine aortic endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1788–1792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryglewski R. J., Moncada S., Palmer R. M. Bioassay of prostacyclin and endothelium-derived relaxing factor (EDRF) from porcine aortic endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;87(4):685–694. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb14586.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. F., Brooker G. Femtomole sensitive radioimmunoassay for cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP after 2'0 acetylation by acetic anhydride in aqueous solution. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;1(4):207–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutcheson I. R., Griffith T. M. Release of endothelium-derived relaxing factor is modulated both by frequency and amplitude of pulsatile flow. Am J Physiol. 1991 Jul;261(1 Pt 2):H257–H262. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.261.1.H257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson P. J., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Comparative pharmacology of EDRF and nitric oxide on vascular strips. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep 23;141(3):445–451. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90563-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon N. S., Nathan C. F., Gilker C., Griffith O. W., Matthews D. E., Stuehr D. J. L-citrulline production from L-arginine by macrophage nitric oxide synthase. The ureido oxygen derives from dioxygen. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13442–13445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marletta M. A., Yoon P. S., Iyengar R., Leaf C. D., Wishnok J. S. Macrophage oxidation of L-arginine to nitrite and nitrate: nitric oxide is an intermediate. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8706–8711. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers P. R., Guerra R., Jr, Harrison D. G. Release of NO and EDRF from cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Apr;256(4 Pt 2):H1030–H1037. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.256.4.H1030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers P. R., Minor R. L., Jr, Guerra R., Jr, Bates J. N., Harrison D. G. Vasorelaxant properties of the endothelium-derived relaxing factor more closely resemble S-nitrosocysteine than nitric oxide. Nature. 1990 May 10;345(6271):161–163. doi: 10.1038/345161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mülsch A., Busse R. NG-nitro-L-arginine (N5-[imino(nitroamino)methyl]-L-ornithine) impairs endothelium-dependent dilations by inhibiting cytosolic nitric oxide synthesis from L-arginine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Jan-Feb;341(1-2):143–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00195071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Hibbs J. B., Jr Role of nitric oxide synthesis in macrophage antimicrobial activity. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Feb;3(1):65–70. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(91)90079-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ashton D. S., Moncada S. Vascular endothelial cells synthesize nitric oxide from L-arginine. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):664–666. doi: 10.1038/333664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radomski M. W., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Comparative pharmacology of endothelium-derived relaxing factor, nitric oxide and prostacyclin in platelets. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep;92(1):181–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11310.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radomski M. W., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Glucocorticoids inhibit the expression of an inducible, but not the constitutive, nitric oxide synthase in vascular endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):10043–10047. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.10043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Schulz R., Hodson H. F., Moncada S. Characterization of three inhibitors of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vitro and in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):746–752. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14151.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmon J. A. A radioimmunoassay for 6-keto-prostaglandin F1alpha. Prostaglandins. 1978 Mar;15(3):383–397. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(78)90122-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvemini D., Mollace V., Pistelli A., Anggard E., Vane J. Metabolism of glyceryl trinitrate to nitric oxide by endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells and its induction by Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):982–986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H., Bredt D. S. Nitric oxide as a neuronal messenger. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Apr;12(4):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90526-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Kwon N. S., Nathan C. F., Griffith O. W., Feldman P. L., Wiseman J. N omega-hydroxy-L-arginine is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of nitric oxide from L-arginine. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6259–6263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vane J. R., Anggård E. E., Botting R. M. Regulatory functions of the vascular endothelium. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 5;323(1):27–36. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007053230106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALKER J. B., WALKER M. S. The enzymatic reduction of hydroxyguanidine. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jun;234(6):1481–1484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zembowicz A., Hecker M., Macarthur H., Sessa W. C., Vane J. R. Nitric oxide and another potent vasodilator are formed from NG-hydroxy-L-arginine by cultured endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11172–11176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Nucci G., Gryglewski R. J., Warner T. D., Vane J. R. Receptor-mediated release of endothelium-derived relaxing factor and prostacyclin from bovine aortic endothelial cells is coupled. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2334–2338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


