Abstract
1. The objective of the present study was to assess whether inhibition of nitric oxide (NO) production could modulate vascular permeability in the coronary circulation in conscious rats. 2. Intravenous injection of NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME, 2 mg kg-1) resulted in a slowly developing hypertension and evoked twofold increases in vascular permeability in the left ventricle and right atrium as measured by the extravasation of Evans blue dye. Maintenance of mean arterial blood pressure at the level observed following L-NAME injection by infusion of noradrenaline (620-820 ng kg-1 min-1) did not induce significant protein extravasation in the coronary circulation. 3. L-NAME treatment markedly enhanced (up to 490%) protein extravasation both in the left ventricle and right atrium in response to platelet-activating factor (PAF, 1.9 nmol kg-1, i.v.) and endothelin-1 (1 nmol kg-1, i.v.). Noradrenaline infusion potentiated (up to 69%) endothelin-1-induced protein extravasation. The permeability effect of PAF was only slightly enhanced by noradrenaline. 4. The present findings indicate that inhibition of endogenous NO synthesis leads to an increase in protein extravasation and to potentiation of the permeability effects of PAF and endothelin-1 in the coronary circulation. These results also suggest that NO may be an important regulator of vascular permeability under physiological and pathological conditions.
Full text
PDF
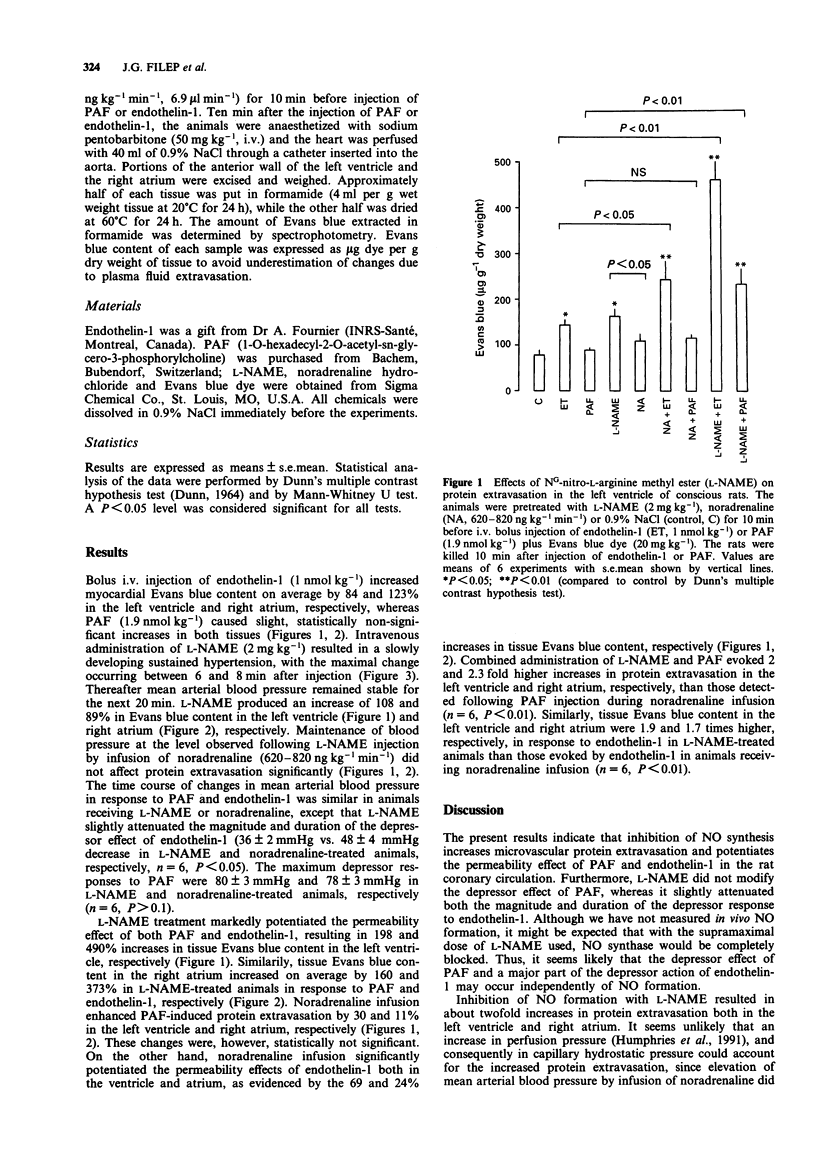
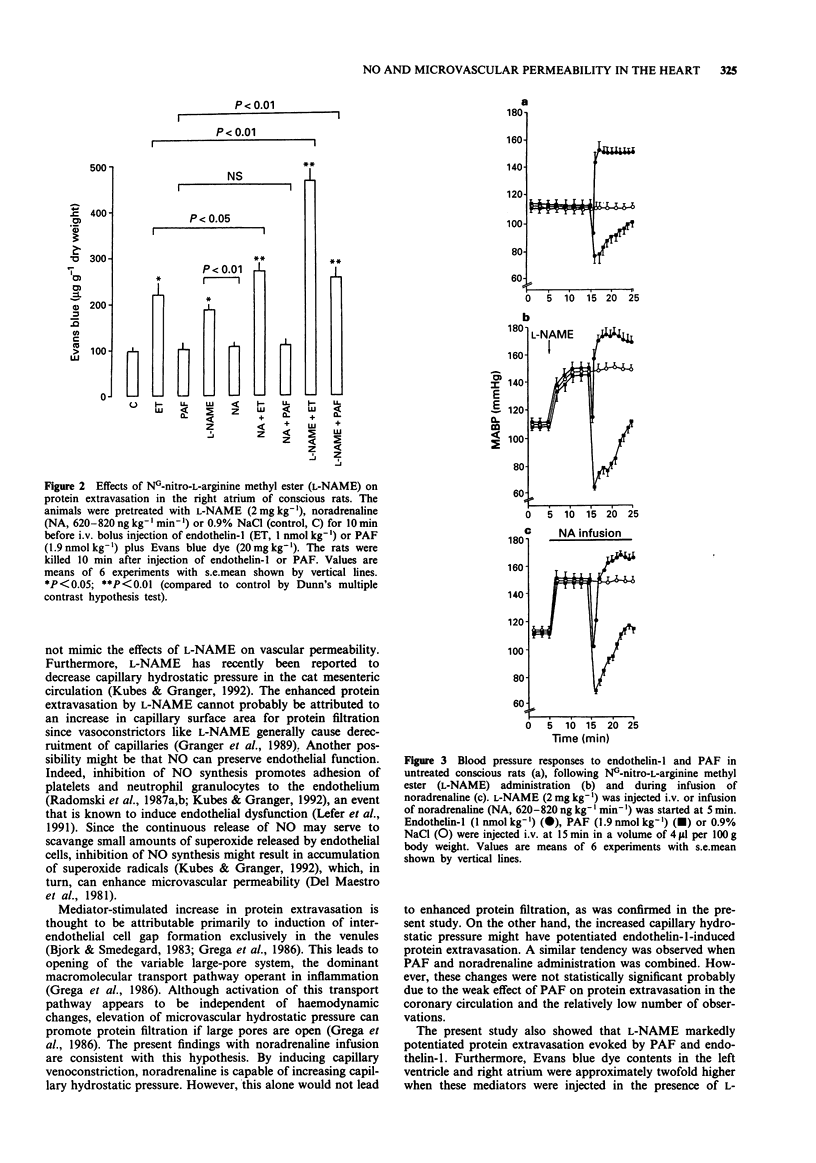

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Björk J., Smedegård G. Acute microvascular effects of PAF-acether, as studied by intravital microscopy. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Dec 9;96(1-2):87–94. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90532-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braquet P., Paubert-Braquet M., Koltai M., Bourgain R., Bussolino F., Hosford D. Is there a case for PAF antagonists in the treatment of ischemic states? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Jan;10(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90103-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Maestro R. F., Björk J., Arfors K. E. Increase in microvascular permeability induced by enzymatically generated free radicals. I. In vivo study. Microvasc Res. 1981 Nov;22(3):239–254. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(81)90095-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filep J. G., Sirois M. G., Rousseau A., Fournier A., Sirois P. Effects of endothelin-1 on vascular permeability in the conscious rat: interactions with platelet-activating factor. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;104(4):797–804. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12509.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filep J., Földes-Filep E., Frölich J. C. Vascular responses to leukotriene B4, C4 and D4 following FPL 55712, indomethacin, saralasin, phentolamine and verapamil in the conscious rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Feb;90(2):431–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb08973.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filep J., Hermán F., Braquet P., Mózes T. Increased levels of platelet-activating factor in blood following intestinal ischemia in the dog. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 31;158(2):353–359. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80055-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner S. M., Compton A. M., Bennett T., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Control of regional blood flow by endothelium-derived nitric oxide. Hypertension. 1990 May;15(5):486–492. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.15.5.486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grega G. J., Adamski S. W., Dobbins D. E. Physiological and pharmacological evidence for the regulation of permeability. Fed Proc. 1986 Feb;45(2):96–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries R. G., Carr R. D., Nicol A. K., Tomlinson W., O'Connor S. E. Coronary vasoconstriction in the conscious rabbit following intravenous infusion of L-NG-nitro-arginine. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):565–566. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12212.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J. Biological actions and properties of endothelium-derived nitric oxide formed and released from artery and vein. Circ Res. 1989 Jul;65(1):1–21. doi: 10.1161/01.res.65.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Buga G. M., Wood K. S., Byrns R. E., Chaudhuri G. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor produced and released from artery and vein is nitric oxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9265–9269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubes P., Granger D. N. Nitric oxide modulates microvascular permeability. Am J Physiol. 1992 Feb;262(2 Pt 2):H611–H615. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1992.262.2.H611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefer A. M., Tsao P. S., Lefer D. J., Ma X. L. Role of endothelial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of reperfusion injury after myocardial ischemia. FASEB J. 1991 Apr;5(7):2029–2034. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.7.2010056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montrucchio G., Alloatti G., Tetta C., De Luca R., Saunders R. N., Emanuelli G., Camussi G. Release of platelet-activating factor from ischemic-reperfused rabbit heart. Am J Physiol. 1989 Apr;256(4 Pt 2):H1236–H1246. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.256.4.H1236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ashton D. S., Moncada S. Vascular endothelial cells synthesize nitric oxide from L-arginine. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):664–666. doi: 10.1038/333664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radomski M. W., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Comparative pharmacology of endothelium-derived relaxing factor, nitric oxide and prostacyclin in platelets. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep;92(1):181–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11310.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Role of endothelium-derived nitric oxide in the regulation of blood pressure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3375–3378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Schulz R., Hodson H. F., Moncada S. Characterization of three inhibitors of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vitro and in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):746–752. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14151.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegfried M. R., Erhardt J., Rider T., Ma X. L., Lefer A. M. Cardioprotection and attenuation of endothelial dysfunction by organic nitric oxide donors in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Feb;260(2):668–675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenbergen C., Hill M. L., Jennings R. B. Volume regulation and plasma membrane injury in aerobic, anaerobic, and ischemic myocardium in vitro. Effects of osmotic cell swelling on plasma membrane integrity. Circ Res. 1985 Dec;57(6):864–875. doi: 10.1161/01.res.57.6.864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tranum-Jensen J., Janse M. J., Fiolet W. T., Krieger W. J., D'Alnoncourt C. N., Durrer D. Tissue osmolality, cell swelling, and reperfusion in acute regional myocardial ischemia in the isolated porcine heart. Circ Res. 1981 Aug;49(2):364–381. doi: 10.1161/01.res.49.2.364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Suzuki N., Shimamoto N., Fujino M., Imada A. Contribution of endogenous endothelin to the extension of myocardial infarct size in rats. Circ Res. 1991 Aug;69(2):370–377. doi: 10.1161/01.res.69.2.370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


