Abstract
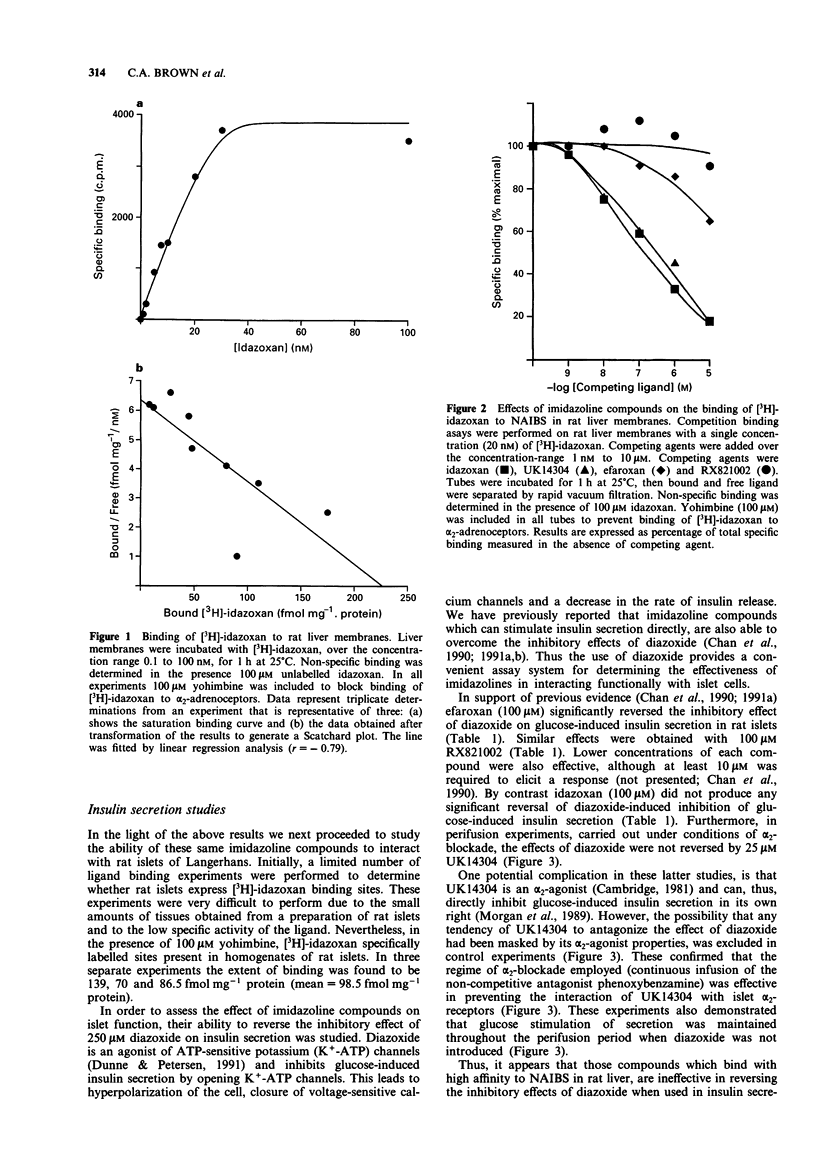
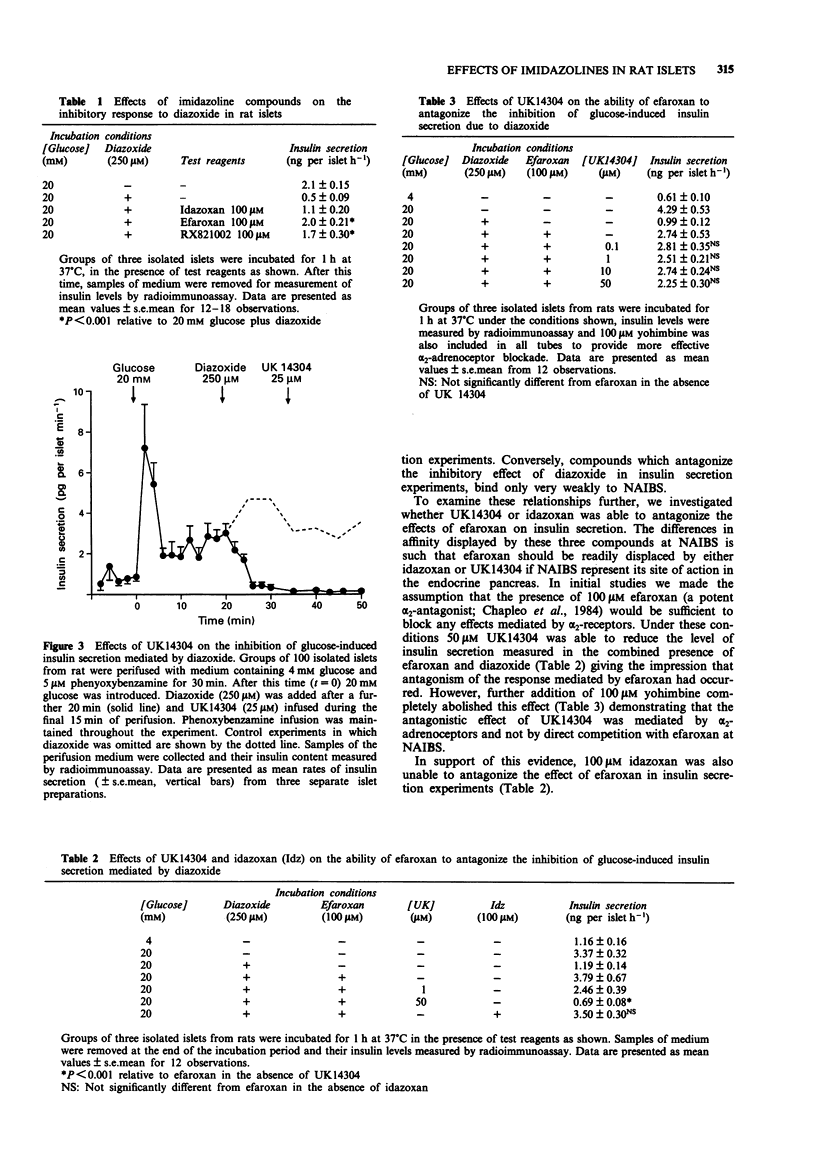
1. The potency of interaction of several imidazoline compounds with non-adrenoceptor idazoxan binding sites (NAIBS) in rat liver membranes was compared with their ability to alter insulin secretion from rat pancreatic islets. 2. NAIBS could be labelled specifically with [3H]-idazoxan in both rat liver membranes and in rat islet homogenates. Liver binding sites exhibited a KD for [3H]-idazoxan of 24 nM and a Bmax of 264 fmol mg-1 protein. 3. Binding of [3H]-idazoxan to NAIBS in rat liver membranes was displaced effectively by unlabelled idazoxan (IC50 0.1 microM) and by UK14304 (IC50 0.5 microM). However, two other imidazoline compounds efaroxan and RX821002, which are related in structure to idazoxan, were much less effective as displacers. 4. In insulin secretion experiments, the ATP-sensitive potassium channel agonist diazoxide (250 microM) was able to suppress the rise in insulin secretion induced by 20 mM glucose. Both efaroxan and RX821002 (100 microM) antagonized the inhibitory effect of diazoxide on glucose-induced insulin secretion. By contrast, neither idazoxan (100 microM) nor UK14304 (50 microM), was able to overcome significantly the inhibitory effect of diazoxide. 5. The ability of 100 microM efaroxan to antagonize the suppression of insulin secretion mediated by diazoxide, was not prevented by idazoxan (up to 100 microM) or by UK14304 (up to 50 microM). 6. The results indicate that the stimulatory effects of imidazoline compounds on insulin secretion are not due to interaction with NAIBS similar to those present in rat liver.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atlas D. Clonidine-displacing substance (CDS) and its putative imidazoline receptor. New leads for further divergence of alpha 2-adrenergic receptor activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Jun 1;41(11):1541–1549. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90152-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadstone V. L., Pfeifer M. A., Bajaj V., Stagner J. I., Samols E. Alpha-adrenergic blockade improves glucose-potentiated insulin secretion in non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1987 Aug;36(8):932–937. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.8.932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambridge D. UK-14,304, a potent and selective alpha2-agonist for the characterisation of alpha-adrenoceptor subtypes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul 10;72(4):413–415. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90588-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. L., Dunne M. J., Stillings M. R., Morgan N. G. The alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonist efaroxan modulates K+ATP channels in insulin-secreting cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Oct 29;204(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90833-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. L., Morgan N. G. Stimulation of insulin secretion by efaroxan may involve interaction with potassium channels. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jan 25;176(1):97–101. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90137-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. L., Stillings M. R., Morgan N. G. Mechanisms involved in stimulation of insulin secretion by the hypoglycaemic alpha-adrenergic antagonist, DG-5128. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 15;176(3):1545–1551. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90463-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapleo C. B., Myers P. L., Butler R. C., Davis J. A., Doxey J. C., Higgins S. D., Myers M., Roach A. G., Smith C. F., Stillings M. R. Alpha-adrenoreceptor reagents. 2. Effects of modification of the 1,4-benzodioxan ring system on alpha-adrenoreceptor activity. J Med Chem. 1984 May;27(5):570–576. doi: 10.1021/jm00371a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coupry I., Podevin R. A., Dausse J. P., Parini A. Evidence for imidazoline binding sites in basolateral membranes from rabbit kidney. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 30;147(3):1055–1060. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80177-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J. Block of ATP-regulated potassium channels by phentolamine and other alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;103(4):1847–1850. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12340.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunne M. J., Petersen O. H. Potassium selective ion channels in insulin-secreting cells: physiology, pharmacology and their role in stimulus-secretion coupling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 7;1071(1):67–82. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90012-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrino M. G., Henquin J. C. B cell adrenoceptors and sulphonylurea-induced insulin release in mouse islets. Diabetologia. 1990 Mar;33(3):145–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00404040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göthert M., Molderings G. J. Involvement of presynaptic imidazoline receptors in the alpha 2-adrenoceptor-independent inhibition of noradrenaline release by imidazoline derivatives. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;343(3):271–282. doi: 10.1007/BF00251126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton C. A., Reid J. L., Yakubu M. A. [3H]yohimbine and [3H]idazoxan bind to different sites on rabbit forebrain and kidney membranes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Feb 9;146(2-3):345–348. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90314-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameda K. Y., Koyama I., Abiko Y. Comparative study on the effects of a hypoglycemic 2-substituted-2-imidazoline derivative (DG-5128) and tolbutamide on insulin secretion from and insulin synthesis in the isolated rat pancreatic islets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Oct 12;677(2):263–268. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90094-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameda K., Ono S., Koyama I., Abiko Y. Insulin releasing action of 2-[2-(4,5-dihydro-1H-imadazol-2-yl)-1-phenylethyl] pyridine dihydrochloride sesquihydrate (DG-5128), a new, orally effective hypoglycaemic agent. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1982 Mar;99(3):410–415. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0990410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawazu S., Suzuki M., Negishi K., Watanabe T., Ishii J. Studies of midaglizole (DG-5128). A new type of oral hypoglycemic drug in healthy subjects. Diabetes. 1987 Feb;36(2):216–220. doi: 10.2337/diab.36.2.216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick A. T., Brown C. C., Mackinnon A. C. Non-alpha 2-adrenoceptor idazoxan binding sites; a new target for drug development. Biochem Soc Trans. 1992 Feb;20(1):113–118. doi: 10.1042/bst0200113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer J., Panten U., Zielmann S. Effects of alpha-adrenoceptor antagonists on clonidine-induced inhibition of insulin secretion by isolated pancreatic islets. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):415–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11014.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langin D., Lafontan M. [3H]idazoxan binding at non-alpha 2-adrenoceptors in rabbit adipocyte membranes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Jan 10;159(2):199–203. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90707-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A., Angus J. A. Phentolamine and structurally related compounds selectively antagonize the vascular actions of the K+ channel opener, cromromakalim. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;97(3):941–949. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12035.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montague W., Taylor K. W. Pentitols and insulin release by isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Biochem J. 1968 Sep;109(3):333–339. doi: 10.1042/bj1090333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan N. G., Montague W. Stimulation of insulin secretion from isolated rat islets of Langerhans by melittin. Biosci Rep. 1984 Aug;4(8):665–671. doi: 10.1007/BF01121020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan N. G., Montague W. Studies on the mechanism of inhibition of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion by noradrenaline in rat islets of Langerhans. Biochem J. 1985 Mar 1;226(2):571–576. doi: 10.1042/bj2260571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmos G., Miralles A., Barturen F., Garcia-Sevilla J. A. Characterization of brain imidazoline receptors in normotensive and hypertensive rats: differential regulation by chronic imidazoline drug treatment. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Mar;260(3):1000–1007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parini A., Coupry I., Graham R. M., Uzielli I., Atlas D., Lanier S. M. Characterization of an imidazoline/guanidinium receptive site distinct from the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11874–11878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant T. D., Henquin J. C. Phentolamine and yohimbine inhibit ATP-sensitive K+ channels in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Sep;101(1):115–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12099.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plant T. D., Jonas J. C., Henquin J. C. Clonidine inhibits ATP-sensitive K+ channels in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;104(2):385–390. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12440.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remaury A., Paris H. The insulin-secreting cell line, RINm5F, expresses an alpha-2D adrenoceptor and nonadrenergic idazoxan-binding sites. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jan;260(1):417–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. P., Halter J. B., Porte D., Jr A role for alpha-adrenergic receptors in abnormal insulin secretion in diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar;57(3):791–795. doi: 10.1172/JCI108338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz A., Hasselblatt A. An insulin-releasing property of imidazoline derivatives is not limited to compounds that block alpha-adrenoceptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;340(3):321–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00168517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz A., Hasselblatt A. Phentolamine, a deceptive tool to investigate sympathetic nervous control of insulin release. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;337(6):637–643. doi: 10.1007/BF00175789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M., Furman B. L. Augmentation of glucose induced insulin secretion by pertussis vaccine, phentolamine and benextramine: involvement of mechanisms additional to prevention of the inhibitory actions of catecholamines in rats. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1988 May;118(1):89–95. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.1180089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. K., Krohn R. I., Hermanson G. T., Mallia A. K., Gartner F. H., Provenzano M. D., Fujimoto E. K., Goeke N. M., Olson B. J., Klenk D. C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem. 1985 Oct;150(1):76–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillings M. R., Chapleo C. B., Butler R. C., Davis J. A., England C. D., Myers M., Myers P. L., Tweddle N., Welbourn A. P., Doxey J. C. Alpha-adrenoreceptor reagents. 3. Synthesis of some 2-substituted 1,4-benzodioxans as selective presynaptic alpha 2-adrenoreceptor antagonists. J Med Chem. 1985 Aug;28(8):1054–1062. doi: 10.1021/jm00146a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikberg J. E., Uhlén S., Chhajlani V. Medetomidine stereoisomers delineate two closely related subtypes of idazoxan (imidazoline) I-receptors in the guinea pig. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Feb 14;193(3):335–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90148-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zonnenchein R., Diamant S., Atlas D. Imidazoline receptors in rat liver cells: a novel receptor or a subtype of alpha 2-adrenoceptors? Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 6;190(1-2):203–215. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94127-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


