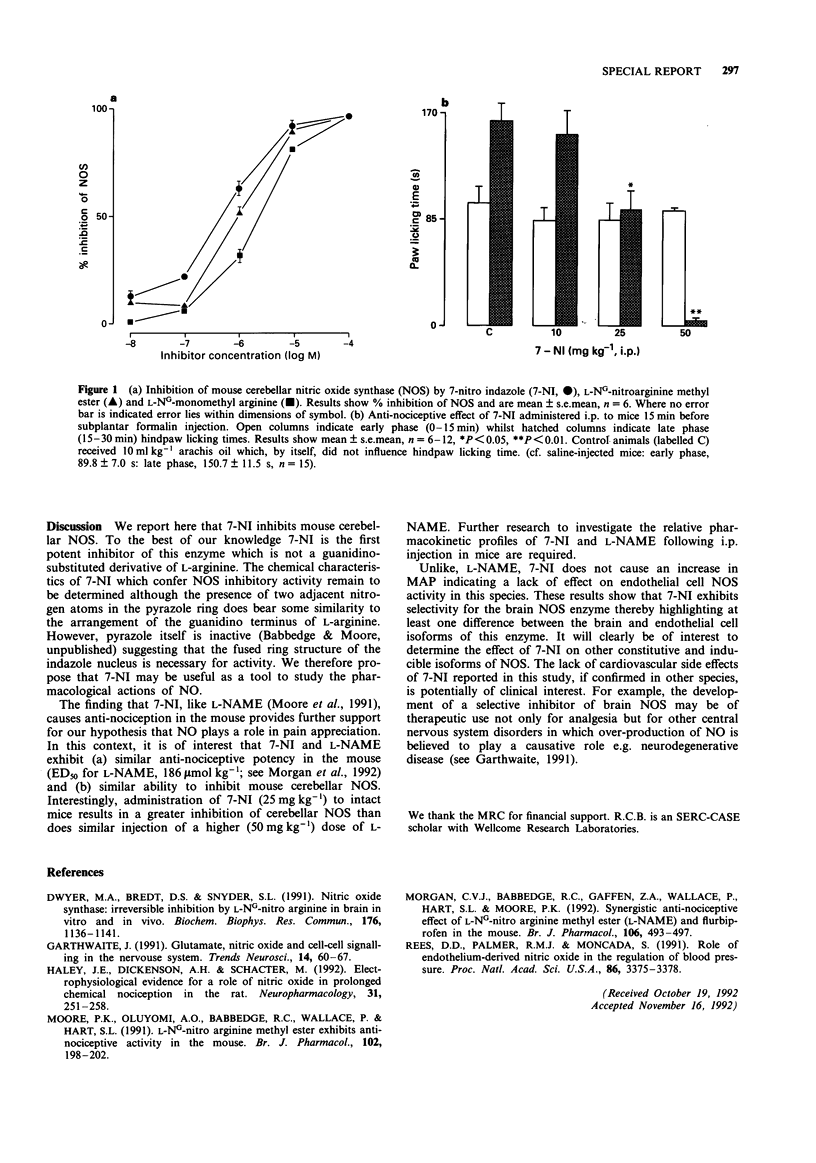
Abstract
7-Nitro indazole (7-NI) inhibits mouse cerebellar nitric oxide synthase (NOS) in vitro with an IC50 of 0.47 microM. Following i.p. administration in mice, 7-NI (10-50 mg kg-1) produces dose-related anti-nociception as evidenced by an inhibition of late phase (15-30 min) but not early phase (0-5 min) hindpaw licking time following subplantar injection of formalin (10 microliters, 5% v/v). The ED50 for this effect was 26 mg kg-1 (equivalent to 159.5 mumol kg-1). Similar i.p. administration of 7-NI (20 and 80 mg kg-1) in urethane-anaesthetized mice failed to increase MAP. Thus, 7-NI is a novel inhibitor of NOS which exhibits selectivity for the brain enzyme. Accordingly, 7-NI may be a useful starting point for the development of selective, centrally acting NOS inhibitors devoid of cardiovascular side effects and as a tool to study the central pharmacological effects of nitric oxide (NO).
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dwyer M. A., Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Nitric oxide synthase: irreversible inhibition by L-NG-nitroarginine in brain in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 May 15;176(3):1136–1141. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90403-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite J. Glutamate, nitric oxide and cell-cell signalling in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1991 Feb;14(2):60–67. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(91)90022-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley J. E., Dickenson A. H., Schachter M. Electrophysiological evidence for a role of nitric oxide in prolonged chemical nociception in the rat. Neuropharmacology. 1992 Mar;31(3):251–258. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(92)90175-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. K., Oluyomi A. O., Babbedge R. C., Wallace P., Hart S. L. L-NG-nitro arginine methyl ester exhibits antinociceptive activity in the mouse. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jan;102(1):198–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12153.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan C. V., Babbedge R. C., Gaffen Z., Wallace P., Hart S. L., Moore P. K. Synergistic anti-nociceptive effect of L-NG-nitro arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) and flurbiprofen in the mouse. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Jun;106(2):493–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14362.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Role of endothelium-derived nitric oxide in the regulation of blood pressure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3375–3378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


