Abstract
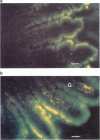
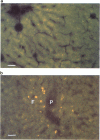
1. The somatostatin octapeptide-analogue octreotide was absorbed as an intact peptide from the gastro-intestinal tract with an absolute bioavailability of about 0.3% in rats. Administration of octreotide in the presence of polyoxyethylene (24)-cholesterol-ether (POECE) resulted in an about 23 fold increase of bioavailability. 2. In vitro studies with Caco-2 cells showed a dose-dependent increase in octreotide permeation with increasing doses of coadministered POECE. The use of [3H]-polyethyleneglycol (PEG) 4000 as an extracellular marker also indicated that higher doses of POECE may partly enhance paracellular transport of macromolecules. 3. By means of fluorescence microscopy it was shown that transepithelial transport of the fluorescent octreotide analogue (4-nitrobenzo-2-oxa-1,3-diazol [NBD] labelled octreotide) was enhanced by the addition of POECE. Besides an increased enterocyte uptake, there was evidence of enhanced partition of NBD-octreotide into the intercellular space between enterocytes after co-administration of POECE. In addition, there appeared to be changes in the hepatic topographic disposition of NBD-octreotide when it was given together with POECE compared with its administration alone. 4. In a study in healthy volunteers, 16 mg POECE significantly enhanced by 8 fold the absorption of octreotide after oral administration.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Battershill P. E., Clissold S. P. Octreotide. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic potential in conditions associated with excessive peptide secretion. Drugs. 1989 Nov;38(5):658–702. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198938050-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis W. W., Pfeiffer R. R., Quay J. F. Normal and promoted gastrointestinal absorption of water-soluble substances. I. Induced rapidly reversible hyperabsorptive state in the canine fundic stomach pouch. J Pharm Sci. 1970 Jul;59(7):960–963. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600590708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donovan M. D., Flynn G. L., Amidon G. L. Absorption of polyethylene glycols 600 through 2000: the molecular weight dependence of gastrointestinal and nasal absorption. Pharm Res. 1990 Aug;7(8):863–868. doi: 10.1023/a:1015921101465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franz J. M., Vonderscher J. P. Enhancement of the intestinal absorption of ergot peptide alkaloids in the rat by micellar solutions of polyoxyethylene-24-cholesteryl ether. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1981 Sep;33(9):565–568. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1981.tb13867.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricker G., Bruns C., Munzer J., Briner U., Albert R., Kissel T., Vonderscher J. Intestinal absorption of the octapeptide SMS 201-995 visualized by fluorescence derivatization. Gastroenterology. 1991 Jun;100(6):1544–1552. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90651-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricker G., Drewe J., Vonderscher J., Kissel T., Beglinger C. Enteral absorption of octreotide. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;105(4):783–786. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09057.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuessl H. S., Domin J., Bloom S. R. Oral absorption of the somatostatin analogue SMS 201-995: theoretical and practical implications. Clin Sci (Lond) 1987 Feb;72(2):255–257. doi: 10.1042/cs0720255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo I. J., Borchardt R. T. Transport of a large neutral amino acid (phenylalanine) in a human intestinal epithelial cell line: Caco-2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Sep 21;1028(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90261-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo I. J., Borchardt R. T. Transport of a large neutral amino acid (phenylalanine) in a human intestinal epithelial cell line: Caco-2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Sep 21;1028(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90261-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo I. J., Borchardt R. T. Transport of bile acids in a human intestinal epithelial cell line, Caco-2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jul 20;1035(1):97–103. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(90)90179-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo I. J., Raub T. J., Borchardt R. T. Characterization of the human colon carcinoma cell line (Caco-2) as a model system for intestinal epithelial permeability. Gastroenterology. 1989 Mar;96(3):736–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz M. D., Erstad B. L. Octreotide, a new somatostatin analogue. Clin Pharm. 1989 Apr;8(4):255–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler E., Duberow-Drewe M., Drewe J., Ribes G., Loubatiéres-Mariani M. M., Mazer N., Gyr K., Beglinger C. Absorption of an aqueous solution of a new synthetic somatostatin analogue administered to man by gavage. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1987;33(2):167–171. doi: 10.1007/BF00544562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marbach P., Neufeld M., Pless J. Clinical applications of somatostatin analogs. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1985;188:339–353. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-7886-4_19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus S. N., Schteingart C. D., Marquez M. L., Hofmann A. F., Xia Y., Steinbach J. H., Ton-Nu H. T., Lillienau J., Angellotti M. A., Schmassmann A. Active absorption of conjugated bile acids in vivo. Kinetic parameters and molecular specificity of the ileal transport system in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1991 Jan;100(1):212–221. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90603-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimoto K., Akatsuchi H., Morisaka K., Kamada A. Effect of non-ionic surfactants in a polyacrylic acid gel base on the rectal absorption of [Asu1,7]-eel calcitonin in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1985 Oct;37(10):759–760. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1985.tb04963.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touitou E., Donbrow M., Rubinstein A. Effective intestinal absorption of insulin in diabetic rats using a new formulation approach. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1980 Feb;32(2):108–110. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1980.tb12863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]