Abstract
1. The binding of [3H]-idazoxan in the presence of 10(-6) M (-)-adrenaline was used to quantitate non-adrenoceptor idazoxan binding sites (NAIBS) in the rat brain after treatment with various psychotropic drugs. 2. Chronic treatment (14 days) with the monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors clorgyline (0.3-10 mg kg-1, i.p.) and pargyline (10 mg kg-1, i.p.), but not with Ro 41-1049 (1 mg kg-1, i.p.), markedly decreased (30-50%) the density of NAIBS in the cerebral cortex without any apparent change in the affinity of the radioligand. 3. Acute (1 day) and/or chronic treatments (14 days) with other psychotropic drugs such as desipramine (3 mg kg-1, i.p.), cocaine (10 mg kg-1, i.p.), reserpine (0.12 mg kg-1, s.c.), haloperidol (1 mg kg-1, i.p.) and diazepam (10 mg kg-1, i.p.) did not alter the density of NAIBS in the cerebral cortex. 4. In vitro, the propargylamines clorgyline, pargyline and deprenyl displaced the binding of [3H]-idazoxan to NAIBS from two distinct sites, but only clorgyline displayed an apparent very high affinity for a relevant population of NAIBS (KiH = 40 pM; KiL = 10.6 microM). The structurally diverse MAO inhibitors Ro 16-6491 (selective for MAO-B) and Ro 41-1049 (selective for MAO-A), as well as the other psychotropic drugs (desipramine, cocaine, reserpine and haloperidol) displaced the binding of [3H]-idazoxan to NAIBS monophasically and with very low potencies.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

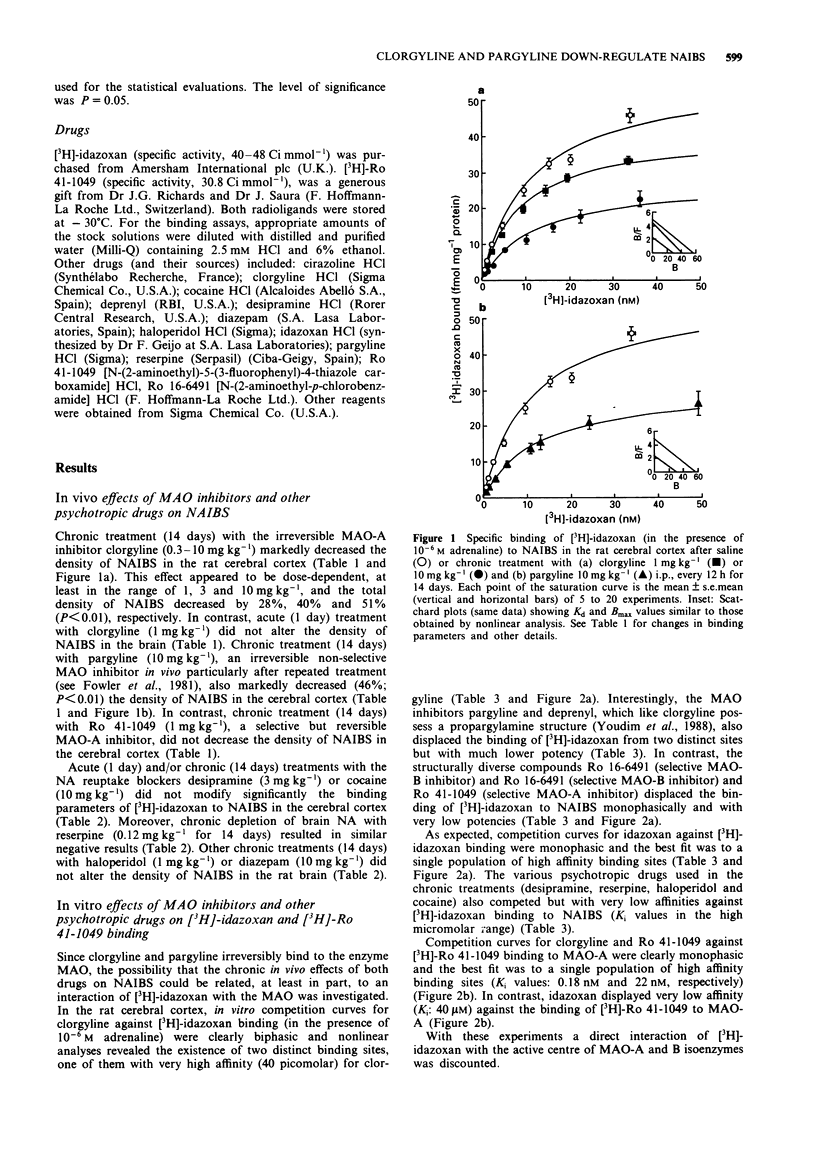
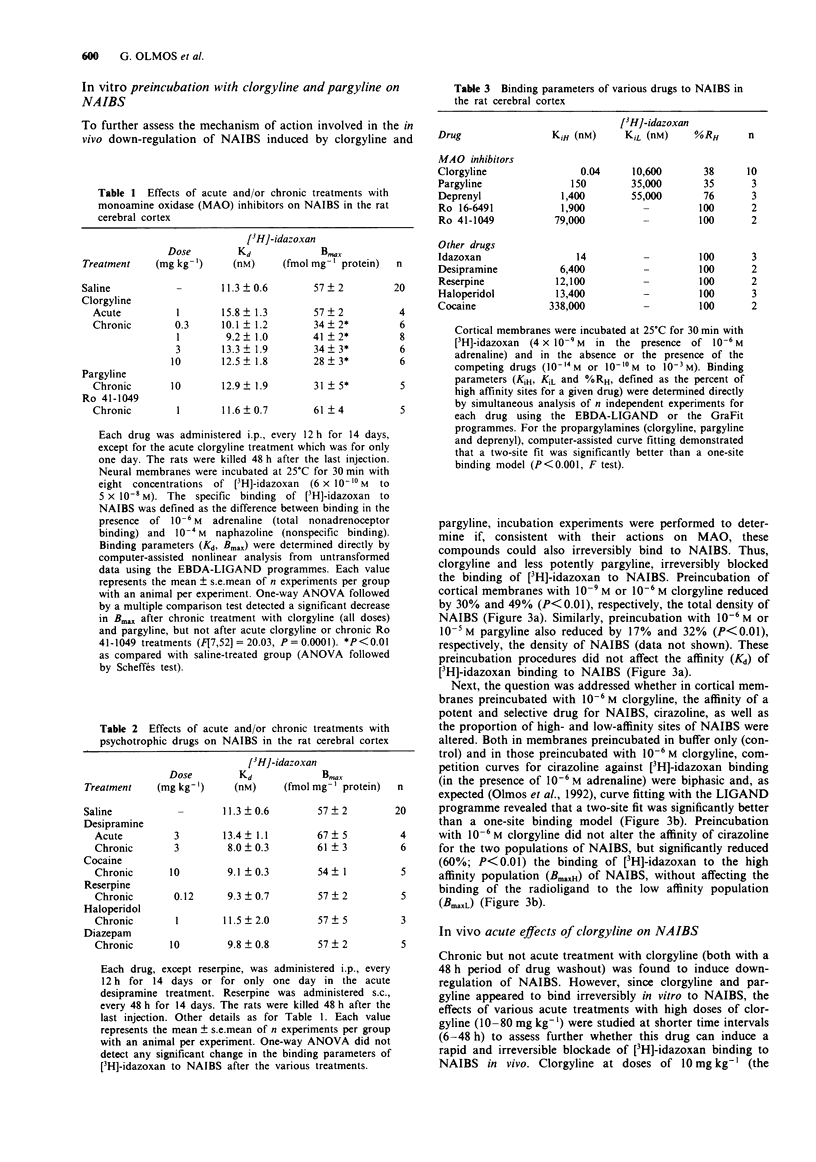



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atlas D. Clonidine-displacing substance (CDS) and its putative imidazoline receptor. New leads for further divergence of alpha 2-adrenergic receptor activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Jun 1;41(11):1541–1549. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90152-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes J. M., Barnes N. M., Barber P. C., Champaneria S., Costall B., Hornsby C. D., Ironside J. W., Naylor R. J. Pharmacological comparison of the sigma recognition site labelled by [3H]haloperidol in human and rat cerebellum. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1992 Feb;345(2):197–202. doi: 10.1007/BF00165736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyajian C. L., Loughlin S. E., Leslie F. M. Anatomical evidence for alpha-2 adrenoceptor heterogeneity: differential autoradiographic distributions of [3H]rauwolscine and [3H]idazoxan in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Jun;241(3):1079–1091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F., Lawson-Wendling K., Pugsley T. A. A rapid filtration assay for soluble receptors using polyethylenimine-treated filters. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):74–81. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90427-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cesura A. M., Bös M., Galva M. D., Imhof R., Da Prada M. Characterization of the binding of [3H]Ro 41-1049 to the active site of human monoamine oxidase-A. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;37(3):358–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cesura A. M., Imhof R., Muggli-Maniglio D., Picotti G. B., Da Prada M. Characterization of [3H]Ro 16-6491 binding to digitonin solubilized monoamine oxidase-B and purification of the enzyme from human platelets by affinity chromatography. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Jan 1;39(1):216–220. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90670-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cesura A. M., Imhof R., Takacs B., Galva M. D., Picotti G. B., Da Prada M. [3H]Ro 16-6491, a selective probe for affinity labelling of monoamine oxidase type B in human brain and platelet membranes. J Neurochem. 1988 Apr;50(4):1037–1043. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb10570.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Da Prada M., Kettler R., Keller H. H., Cesura A. M., Richards J. G., Saura Marti J., Muggli-Maniglio D., Wyss P. C., Kyburz E., Imhof R. From moclobemide to Ro 19-6327 and Ro 41-1049: the development of a new class of reversible, selective MAO-A and MAO-B inhibitors. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1990;29:279–292. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-9050-0_27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamant S., Eldar-Geva T., Atlas D. Imidazoline binding sites in human placenta: evidence for heterogeneity and a search for physiological function. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 May;106(1):101–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14300.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris C. D., Hirsch D. J., Brooks B. P., Snyder S. H. Sigma receptors: from molecule to man. J Neurochem. 1991 Sep;57(3):729–737. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler C. J., Oreland L., Callingham B. A. The acetylenic monoamine oxidase inhibitors clorgyline, deprenyl, pargyline and J-508: their properties and applications. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1981 Jun;33(6):341–347. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1981.tb13800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavish M., Katz Y., Bar-Ami S., Weizman R. Biochemical, physiological, and pathological aspects of the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor. J Neurochem. 1992 May;58(5):1589–1601. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giralt M. T., García-Sevilla J. A. Acute and long-term regulation of brain alpha 2-adrenoceptors after manipulation of noradrenergic transmission in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 30;164(3):455–466. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90253-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göthert M., Molderings G. J. Involvement of presynaptic imidazoline receptors in the alpha 2-adrenoceptor-independent inhibition of noradrenaline release by imidazoline derivatives. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;343(3):271–282. doi: 10.1007/BF00251126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieble J. P., Ruffolo R. R., Jr Imidazoline receptors: historical perspective. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1992;6 (Suppl 1):7S–13S. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.1992.tb00136.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itzhak Y., Alerhand S. Differential regulation of sigma and PCP receptors after chronic administration of haloperidol and phencyclidine in mice. FASEB J. 1989 May;3(7):1868–1872. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.7.2541039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itzhak Y., Kassim C. O. Clorgyline displays high affinity for sigma binding sites in C57BL/6 mouse brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jan 25;176(1):107–108. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90139-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen K. L., Elliot M., Leslie R. A. sigma receptors in rat brain and testes show similar reductions in response to chronic haloperidol. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Apr 22;214(2-3):281–283. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90131-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick A. T., Brown C. C., Mackinnon A. C. Non-alpha 2-adrenoceptor idazoxan binding sites; a new target for drug development. Biochem Soc Trans. 1992 Feb;20(1):113–118. doi: 10.1042/bst0200113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallard N. J., Hudson A. L., Nutt D. J. Characterization and autoradiographical localization of non-adrenoceptor idazoxan binding sites in the rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Aug;106(4):1019–1027. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14450.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A. Analysis of radioligand binding experiments. A collection of computer programs for the IBM PC. J Pharmacol Methods. 1985 Nov;14(3):213–228. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(85)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meana J. J., Barturen F., García-Sevilla J. A. Alpha 2-adrenoceptors in the brain of suicide victims: increased receptor density associated with major depression. Biol Psychiatry. 1992 Mar 1;31(5):471–490. doi: 10.1016/0006-3223(92)90259-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Insel P. A. Are there multiple imidazoline binding sites? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Sep;10(9):342–344. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molderings G. J., Hentrich F., Göthert M. Pharmacological characterization of the imidazoline receptor which mediates inhibition of noradrenaline release in the rabbit pulmonary artery. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;344(6):630–638. doi: 10.1007/BF00174746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmos G., Miralles A., Barturen F., Garcia-Sevilla J. A. Characterization of brain imidazoline receptors in normotensive and hypertensive rats: differential regulation by chronic imidazoline drug treatment. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Mar;260(3):1000–1007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piletz J. E., Halaris A., Saran A., Marler M. R. Desipramine lowers tritiated para-aminoclonidine binding in platelets of depressed patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1991 Sep;48(9):813–820. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1991.01810330037006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piletz J. E., Halaris A., Saran A., Marler M. Elevated 3H-para-aminoclonidine binding to platelet purified plasma membranes from depressed patients. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1990 Jun;3(3):201–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirion R., Bowen W. D., Itzhak Y., Junien J. L., Musacchio J. M., Rothman R. B., Su T. P., Tam S. W., Taylor D. P. A proposal for the classification of sigma binding sites. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Mar;13(3):85–86. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(92)90030-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samovilova N. N., Vinogradov V. A. Subcellular distribution of (+)-[3H]SKF 10,047 binding sites in rat liver. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan 14;225(1):69–74. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(92)90041-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saura J., Kettler R., Da Prada M., Richards J. G. Quantitative enzyme radioautography with 3H-Ro 41-1049 and 3H-Ro 19-6327 in vitro: localization and abundance of MAO-A and MAO-B in rat CNS, peripheral organs, and human brain. J Neurosci. 1992 May;12(5):1977–1999. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-05-01977.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesson F., Parini A. Identification of an imidazoline-guanidinium receptive site in mitochondria from rabbit cerebral cortex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Sep 12;208(1):81–83. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(91)90055-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesson F., Prip-Buus C., Lemoine A., Pegorier J. P., Parini A. Subcellular distribution of imidazoline-guanidinium-receptive sites in human and rabbit liver. Major localization to the mitochondrial outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 5;266(1):155–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikberg J. E., Uhlén S., Chhajlani V. Evidence that drug binding to non-adrenergic [3H]-idazoxan binding sites (I-receptors) occurs to interacting or interconvertible affinity forms of the receptor. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1992 Mar;70(3):208–219. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1992.tb00459.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



