Abstract
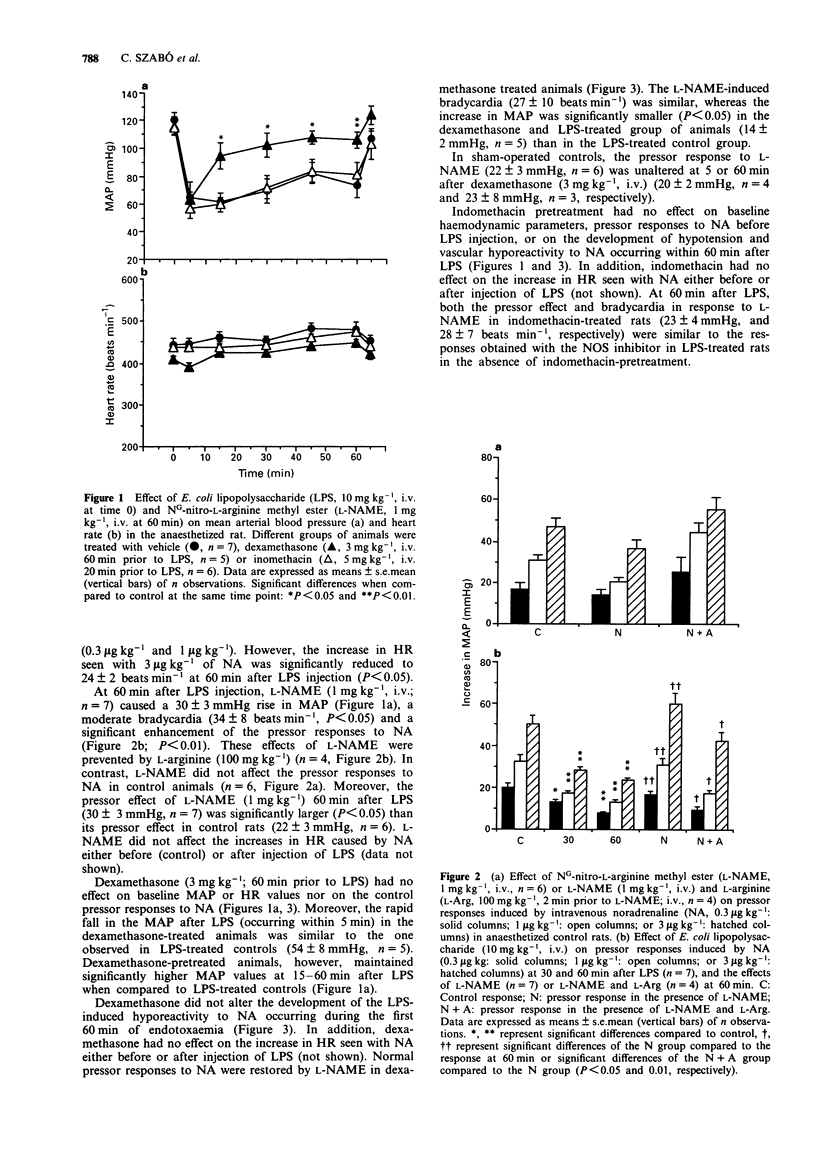
1. The role of an enhanced formation of nitric oxide (NO) and the relative importance of the constitutive and inducible NO synthase (NOS) for the development of immediate (within 60 min) and delayed (at 180 min) vascular hyporeactivity to noradrenaline was investigated in a model of circulatory shock induced by endotoxin (lipopolysaccharide; LPS) in the rat. 2. Male Wistar rats were anaesthetized and instrumented for the measurement of mean arterial blood pressure (MAP) and heart rate. In addition, the calcium-dependent and calcium-independent NOS activity was measured ex vivo by the conversion of [3H]-arginine to [3H]-citrulline in homogenates from several organs obtained from vehicle- and LPS-treated rats. 3. E. coli LPS (10 mg kg-1, i.v. bolus) caused a rapid (within 5 min) and sustained fall in MAP. At 30 and 60 min after LPS, pressor responses to noradrenaline (0.3, 1 or 3 micrograms kg-1, i.v.) were significantly reduced. The pressor responses were restored by NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME, 1 mg kg-1, i.v. at 60 min), a potent inhibitor of NO synthesis. In contrast, L-NAME did not potentiate the noradrenaline-induced pressor responses in control animals. 4. Dexamethasone (3 mg kg-1, i.v., 60 min prior to LPS), a potent inhibitor of the induction of NOS, did not alter initial MAP or pressor responses to noradrenaline in control rats, but significantly attenuated the LPS-induced fall in MAP at 15 to 60 min after LPS. Dexamethasone did not influence the development of the LPS-induced immediate (within 60 min) hyporeactivity to noradrenaline.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benyó Z., Kiss G., Szabó C., Csáki C., Kovách A. G. Importance of basal nitric oxide synthesis in regulation of myocardial blood flow. Cardiovasc Res. 1991 Aug;25(8):700–703. doi: 10.1093/cvr/25.8.700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braquet P., Touqui L., Shen T. Y., Vargaftig B. B. Perspectives in platelet-activating factor research. Pharmacol Rev. 1987 Jun;39(2):97–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredt D. S., Snyder S. H. Isolation of nitric oxide synthetase, a calmodulin-requiring enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):682–685. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busse R., Mülsch A. Induction of nitric oxide synthase by cytokines in vascular smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 1990 Nov 26;275(1-2):87–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81445-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerstein G., Dimicco J. A., Ramu A., Kopin I. J. Effect of indomethacin on the blood pressure and plasma catecholamine responses to acute endotoxaemia. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1981 Sep;33(9):576–579. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1981.tb13869.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J., Blackwell G. J. Anti-inflammatory steroids induce biosynthesis of a phospholipase A2 inhibitor which prevents prostaglandin generation. Nature. 1979 Mar 29;278(5703):456–459. doi: 10.1038/278456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu J. Y., Masferrer J. L., Seibert K., Raz A., Needleman P. The induction and suppression of prostaglandin H2 synthase (cyclooxygenase) in human monocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16737–16740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förstermann U., Schmidt H. H., Pollock J. S., Sheng H., Mitchell J. A., Warner T. D., Nakane M., Murad F. Isoforms of nitric oxide synthase. Characterization and purification from different cell types. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Oct 24;42(10):1849–1857. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90581-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner S. M., Compton A. M., Bennett T., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Control of regional blood flow by endothelium-derived nitric oxide. Hypertension. 1990 May;15(5):486–492. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.15.5.486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross S. S., Jaffe E. A., Levi R., Kilbourn R. G. Cytokine-activated endothelial cells express an isotype of nitric oxide synthase which is tetrahydrobiopterin-dependent, calmodulin-independent and inhibited by arginine analogs with a rank-order of potency characteristic of activated macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Aug 15;178(3):823–829. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)90965-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryglewski R. J., Botting R. M., Vane J. R. Mediators produced by the endothelial cell. Hypertension. 1988 Dec;12(6):530–548. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.12.6.530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt D. E., White J. G., Craddock P. R., Jacob H. S. Corticosteroids inhibit complement-induced granulocyte aggregation. A possible mechanism for their efficacy in shock states. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):798–803. doi: 10.1172/JCI109365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecker M., Mitchell J. A., Harris H. J., Katsura M., Thiemermann C., Vane J. R. Endothelial cells metabolize NG-monomethyl-L-arginine to L-citrulline and subsequently to L-arginine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Mar 30;167(3):1037–1043. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90627-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries R. G., Carr R. D., Nicol A. K., Tomlinson W., O'Connor S. E. Coronary vasoconstriction in the conscious rabbit following intravenous infusion of L-NG-nitro-arginine. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;102(3):565–566. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12212.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julou-Schaeffer G., Gray G. A., Fleming I., Schott C., Parratt J. R., Stoclet J. C. Loss of vascular responsiveness induced by endotoxin involves L-arginine pathway. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 2):H1038–H1043. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.4.H1038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katori M., Majima M., Odoi-Adome R., Sunahara N., Uchida Y. Evidence for the involvement of a plasma kallikrein-kinin system in the immediate hypotension produced by endotoxin in anaesthetized rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;98(4):1383–1391. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12688.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbourn R. G., Gross S. S., Jubran A., Adams J., Griffith O. W., Levi R., Lodato R. F. NG-methyl-L-arginine inhibits tumor necrosis factor-induced hypotension: implications for the involvement of nitric oxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3629–3632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilbourn R. G., Jubran A., Gross S. S., Griffith O. W., Levi R., Adams J., Lodato R. F. Reversal of endotoxin-mediated shock by NG-methyl-L-arginine, an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):1132–1138. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91565-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. G., Merrett M., Salter M., Moncada S. Differential induction of brain, lung and liver nitric oxide synthase by endotoxin in the rat. Biochem J. 1990 Sep 15;270(3):833–836. doi: 10.1042/bj2700833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles R. G., Salter M., Brooks S. L., Moncada S. Anti-inflammatory glucocorticoids inhibit the induction by endotoxin of nitric oxide synthase in the lung, liver and aorta of the rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):1042–1048. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91551-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marletta M. A., Tayeh M. A., Hevel J. M. Unraveling the biological significance of nitric oxide. Biofactors. 1990 Oct;2(4):219–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masferrer J. L., Seibert K., Zweifel B., Needleman P. Endogenous glucocorticoids regulate an inducible cyclooxygenase enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3917–3921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. A., Sheng H., Förstermann U., Murad F. Characterization of nitric oxide synthases in non-adrenergic non-cholinergic nerve containing tissue from the rat anococcygeus muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;104(2):289–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12422.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):109–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore P. K., al-Swayeh O. A., Chong N. W., Evans R. A., Gibson A. L-NG-nitro arginine (L-NOARG), a novel, L-arginine-reversible inhibitor of endothelium-dependent vasodilatation in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;99(2):408–412. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14717.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mózes T., Zijlstra F. J., Heiligers J. P., Tak C. J., Ben-Efraim S., Bonta I. L., Saxena P. R. Sequential release of tumour necrosis factor, platelet activating factor and eicosanoids during endotoxin shock in anaesthetized pigs: protective effects of indomethacin. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;104(3):691–699. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12490.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parratt J. R., Sturgess R. M. The effect of indomethacin on the cardiovascular and metabolic responses to E. coli endotoxin in the cat. Br J Pharmacol. 1974 Feb;50(2):177–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1974.tb08559.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radomski M. W., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Glucocorticoids inhibit the expression of an inducible, but not the constitutive, nitric oxide synthase in vascular endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):10043–10047. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.10043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. Role of endothelium-derived nitric oxide in the regulation of blood pressure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3375–3378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter M., Knowles R. G., Moncada S. Widespread tissue distribution, species distribution and changes in activity of Ca(2+)-dependent and Ca(2+)-independent nitric oxide synthases. FEBS Lett. 1991 Oct 7;291(1):145–149. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81123-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvemini D., Korbut R., Anggård E., Vane J. Immediate release of a nitric oxide-like factor from bovine aortic endothelial cells by Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2593–2597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skubitz K. M., Craddock P. R., Hammerschmidt D. E., August J. T. Corticosteroids block binding of chemotactic peptide to its receptor on granulocytes and cause disaggregation of granulocyte aggregates in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1981 Jul;68(1):13–20. doi: 10.1172/JCI110228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiemermann C., Mustafa M., Mester P. A., Mitchell J. A., Hecker M., Vane J. R. Inhibition of the release of endothelium-derived relaxing factor in vitro and in vivo by dipeptides containing NG-nitro-L-arginine. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Sep;104(1):31–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12380.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiemermann C., Vane J. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis reduces the hypotension induced by bacterial lipopolysaccharides in the rat in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul 17;182(3):591–595. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90062-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walder C. E., Thiemermann C., Vane J. R. The involvement of endothelium-derived relaxing factor in the regulation of renal cortical blood flow in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Apr;102(4):967–973. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12285.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. E., Rees D. D., Moncada S. Protective and pathological roles of nitric oxide in endotoxin shock. Cardiovasc Res. 1992 Jan;26(1):48–57. doi: 10.1093/cvr/26.1.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


