Abstract
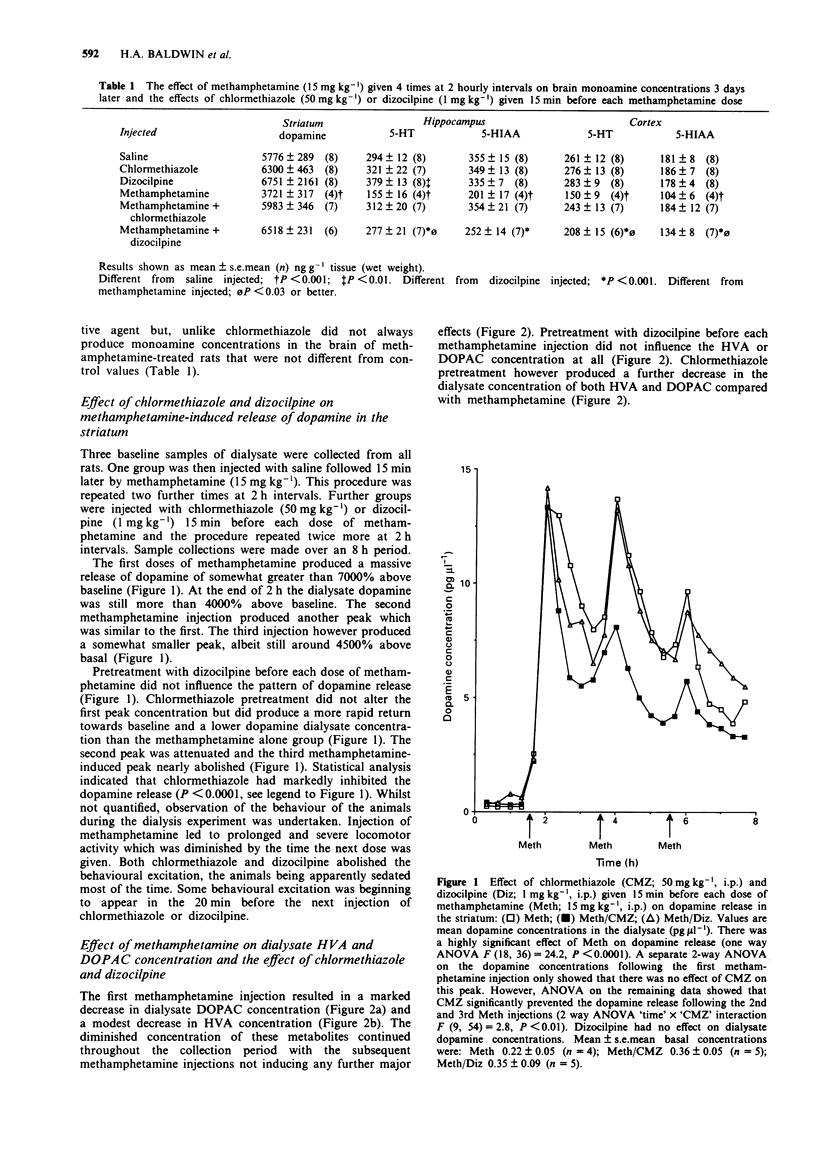
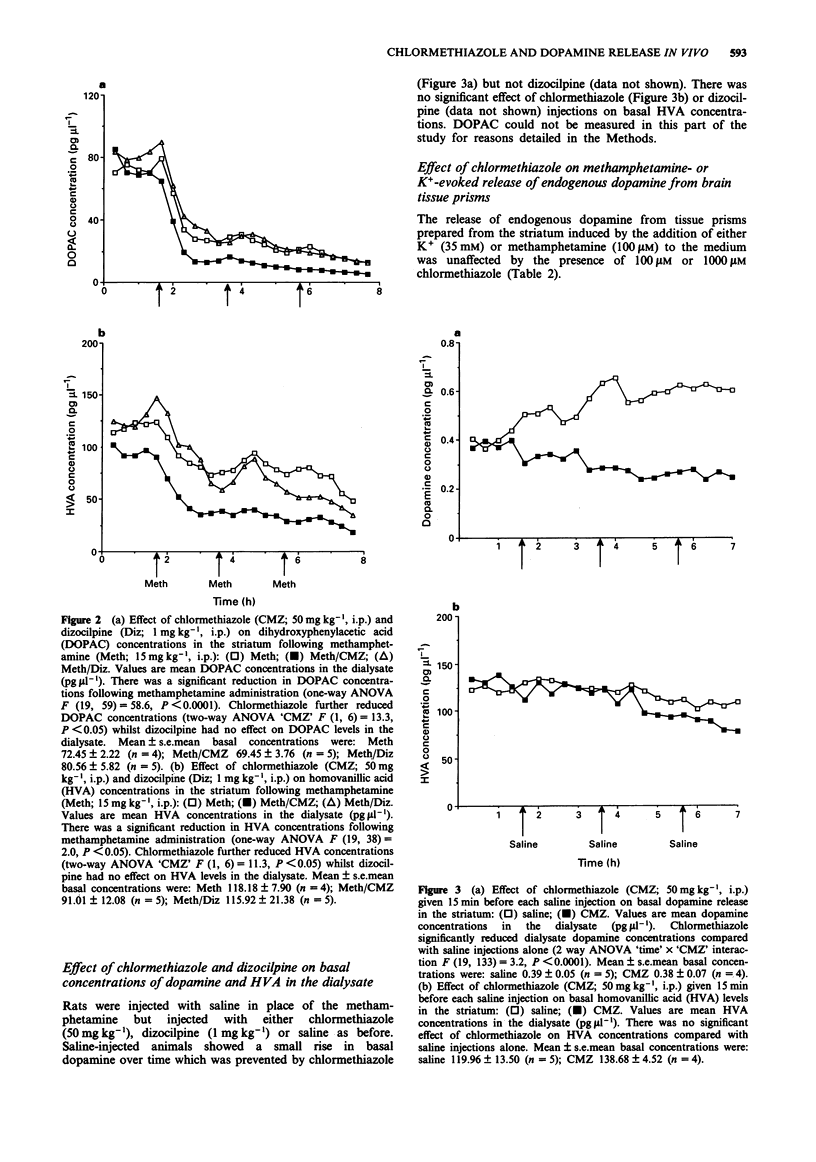
1. Administration to rats of methamphetamine (15 mg kg-1, i.p.) every 2 h to a total of 4 doses resulted in a neurotoxic loss of striatal dopamine of 36% and of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) in the cortex (43%) and hippocampus (47%) 3 days later. 2. Administration of chlormethiazole (50 mg kg-1, i.p.) 15 min before each dose of methamphetamine provided complete protection against the neurotoxic loss of monoamines while administration of dizocilpine (1 mg kg-1, i.p.) using the same dose schedule provided substantial protection. 3. Measurement of dopamine release in the striatum by in vivo microdialysis revealed that methamphetamine produced an approximate 7000% increase in dopamine release after the first injection. The enhanced release response was somewhat diminished after the third injection but still around 4000% above baseline. Dizocilpine (1 mg kg-1, i.p.) did not alter this response but chlormethiazole (50 mg kg-1, i.p.) attenuated the methamphetamine-induced release by approximately 40%. 4. Dizocilpine pretreatment did not influence the decrease in the dialysate concentration of the dopamine metabolites dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (DOPAC) and homovanillic acid (HVA) produced by administration of methamphetamine while chlormethiazole pretreatment decreased the dialysate concentration of these metabolites still further. 5. The concentration of dopamine in the dialysate during basal conditions increased modestly during the course of the experiment. This increase did not occur in chlormethiazole-treated rats. HVA concentrations were unaltered by chlormethiazole administration. 6. Chlormethiazole (100-1000 microM) did not alter methamphetamine (100 microM) or K+ (35 mM)-evoked release of endogenous dopamine from striatal prisms in vitro.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auerbach S., Lipton P. Regulation of serotonin release from the in vitro rat hippocampus: effects of alterations in levels of depolarization and in rates of serotonin metabolism. J Neurochem. 1985 Apr;44(4):1116–1130. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb08733.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin H. A., De Souza R. J., Sarna G. S., Murray T. K., Green A. R., Cross A. J. Measurements of tacrine and monoamines in brain by in vivo microdialysis argue against release of monoamines by tacrine at therapeutic doses. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;103(4):1946–1950. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12357.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowyer J. F., Scallet A. C., Holson R. R., Lipe G. W., Slikker W., Jr, Ali S. F. Interactions of MK-801 with glutamate-, glutamine- and methamphetamine-evoked release of [3H]dopamine from striatal slices. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Apr;257(1):262–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buening M. K., Gibb J. W. Influence of methamphetamine and neuroleptic drugs on tyrosine hydroxylase activity. Eur J Pharmacol. 1974 Apr;26(1):30–34. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(74)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colado M. I., Murray T. K., Green A. R. 5-HT loss in rat brain following 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA), p-chloroamphetamine and fenfluramine administration and effects of chlormethiazole and dizocilpine. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;108(3):583–589. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12846.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. J., Jones J. A., Baldwin H. A., Green A. R. Neuroprotective activity of chlormethiazole following transient forebrain ischaemia in the gerbil. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;104(2):406–411. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12443.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. J., Stirling J. M., Robinson T. N., Bowen D. M., Francis P. T., Green A. R. The modulation by chlormethiazole of the GABAA-receptor complex in rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;98(1):284–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb16893.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibb J. W., Johnson M., Stone D., Hanson G. R. MDMA: historical perspectives. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;600:601–612. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb16913.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibb J. W., Kogan F. J. Influence of dopamine synthesis on methamphetamine-induced changes in striatal and adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase activity. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Dec;310(2):185–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00500283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill R., Foster A. C., Woodruff G. N. MK-801 is neuroprotective in gerbils when administered during the post-ischaemic period. Neuroscience. 1988 Jun;25(3):847–855. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90040-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill R., Foster A. C., Woodruff G. N. Systemic administration of MK-801 protects against ischemia-induced hippocampal neurodegeneration in the gerbil. J Neurosci. 1987 Oct;7(10):3343–3349. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-10-03343.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Globus M. Y., Busto R., Dietrich W. D., Martinez E., Valdes I., Ginsberg M. D. Effect of ischemia on the in vivo release of striatal dopamine, glutamate, and gamma-aminobutyric acid studied by intracerebral microdialysis. J Neurochem. 1988 Nov;51(5):1455–1464. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A. R., De Souza R. J., Williams J. L., Murray T. K., Cross A. J. The neurotoxic effects of methamphetamine on 5-hydroxytryptamine and dopamine in brain: evidence for the protective effect of chlormethiazole. Neuropharmacology. 1992 Apr;31(4):315–321. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(92)90062-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison N. L., Simmonds M. A. Two distinct interactions of barbiturates and chlormethiazole with the GABAA receptor complex in rat cuneate nucleus in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Oct;80(2):387–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10045.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotchkiss A. J., Gibb J. W. Long-term effects of multiple doses of methamphetamine on tryptophan hydroxylase and tyrosine hydroxylase activity in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Aug;214(2):257–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M., Hanson G. R., Gibb J. W. Effect of MK-801 on the decrease in tryptophan hydroxylase induced by methamphetamine and its methylenedioxy analog. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Jun 20;165(2-3):315–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90728-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson G., Nwanze E. Selective (+)-amphetamine neurotoxicity on striatal dopamine nerve terminals in the mouse. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Oct;77(2):335–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09303.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalant H., Khanna J. M. Metabolic and functional aspects of tolerance to chlormethiazole and cross-tolerance to ethanol in the rat. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 1986;329:45–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1986.tb10535.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashihara K., Okumura K., Onishi M., Otsuki S. MK-801 fails to modify the effect of methamphetamine on dopamine release in the rat striatum. Neuroreport. 1991 May;2(5):236–238. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199105000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koda L. Y., Gibb J. W. Adrenal and striatal tyrosine hydroxylase activity after methamphetamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Apr;185(1):42–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna D. J., Peroutka S. J. Neurochemistry and neurotoxicity of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, "ecstasy"). J Neurochem. 1990 Jan;54(1):14–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb13277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody E. J., Skolnick P. Chlormethiazole: neurochemical actions at the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor complex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 2;164(1):153–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogren S. O. Chlormethiazole--mode of action. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 1986;329:13–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricaurte G. A., Guillery R. W., Seiden L. S., Schuster C. R., Moore R. Y. Dopamine nerve terminal degeneration produced by high doses of methylamphetamine in the rat brain. Brain Res. 1982 Mar 4;235(1):93–103. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90198-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson T. N., De Souza R. J., Cross A. J., Green A. R. The mechanism of tetrahydroaminoacridine-evoked release of endogenous 5-hydroxytryptamine and dopamine from rat brain tissue prisms. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;98(4):1127–1136. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12656.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt C. J., Kehne J. H. Neurotoxicity of MDMA: neurochemical effects. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;600:665–681. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb16917.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt C. J., Ritter J. K., Sonsalla P. K., Hanson G. R., Gibb J. W. Role of dopamine in the neurotoxic effects of methamphetamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Jun;233(3):539–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonsalla P. K., Nicklas W. J., Heikkila R. E. Role for excitatory amino acids in methamphetamine-induced nigrostriatal dopaminergic toxicity. Science. 1989 Jan 20;243(4889):398–400. doi: 10.1126/science.2563176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonsalla P. K., Riordan D. E., Heikkila R. E. Competitive and noncompetitive antagonists at N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors protect against methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic damage in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Feb;256(2):506–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone D. M., Johnson M., Hanson G. R., Gibb J. W. Role of endogenous dopamine in the central serotonergic deficits induced by 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Oct;247(1):79–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone D. M., Stahl D. C., Hanson G. R., Gibb J. W. The effects of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) and 3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA) on monoaminergic systems in the rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Aug 22;128(1-2):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90555-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincens M., Enjalbert A., Lloyd K. G., Paillard J. J., Thuret F., Kordon C., Lechat P. Evidence that clomethiazole interacts with the macromolecular GABA A-receptor complex in the central nervous system and in the anterior pituitary gland. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Apr;339(4):397–402. doi: 10.1007/BF00736053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weihmuller F. B., O'Dell S. J., Cole B. N., Marshall J. F. MK-801 attenuates the dopamine-releasing but not the behavioral effects of methamphetamine: an in vivo microdialysis study. Brain Res. 1991 May 24;549(2):230–235. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90462-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weihmuller F. B., O'Dell S. J., Marshall J. F. MK-801 protection against methamphetamine-induced striatal dopamine terminal injury is associated with attenuated dopamine overflow. Synapse. 1992 Jun;11(2):155–163. doi: 10.1002/syn.890110209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


