Abstract
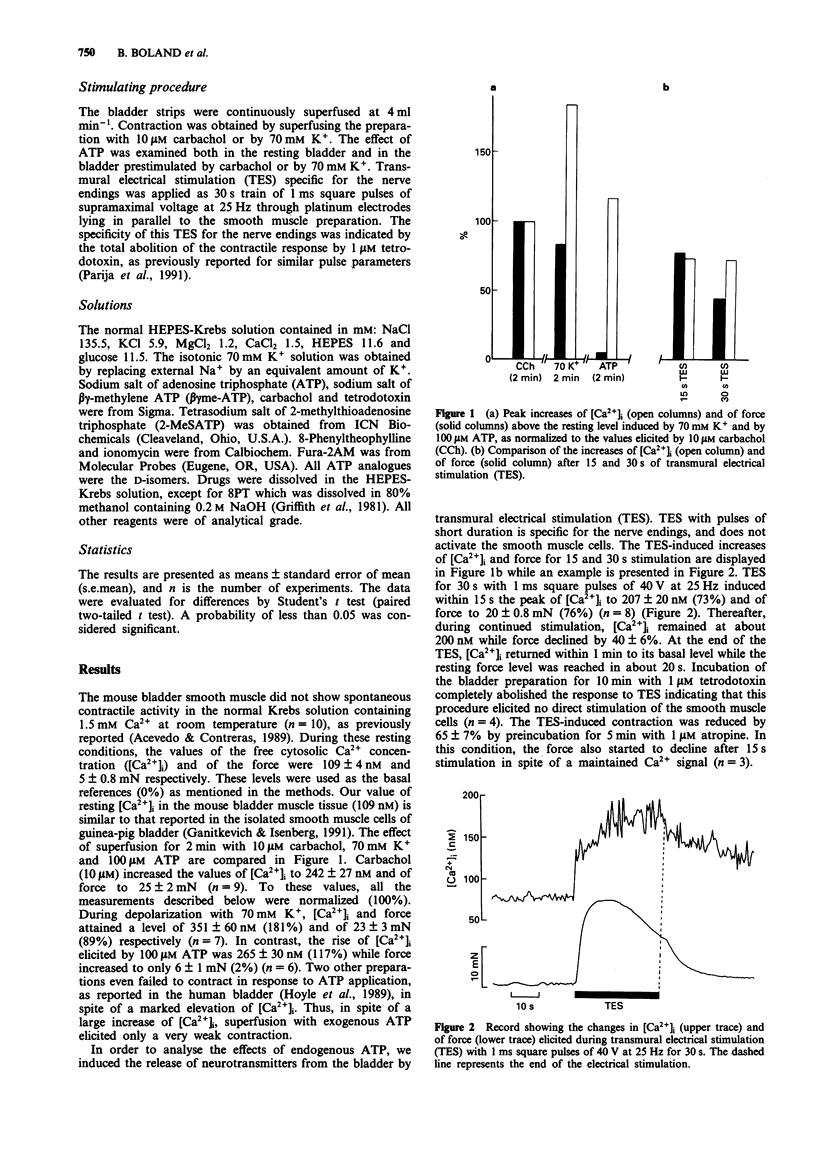
1. The effect of adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) on the free cytosolic Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]i) as measured with the fluorescent Ca(2+)-indicator fura-2, and on force was investigated in the intact smooth muscle strips of the mouse urinary bladder. 2. ATP elicited, when exogenously applied, a large increase of [Ca2+]i with limited force development resulting in a marked Ca(2+)-force dissociation. 3. Release of endogenous neurotransmitters by transmural electrical stimulation (TES) for 30 s induced a steady increase of [Ca2+]i and a peak contraction, followed within 15 s by a relaxation. 4. In carbachol-prestimulated preparations, ATP elicited an initial rise of [Ca2+]i followed by a return to the initial precontraction Ca(2+)-level. Force in contrast presented a biphasic pattern, i.e. an initial contraction was followed by a sustained relaxation. 5. In the K(+)-depolarized precontracted preparation, ATP elicited a slight initial rise of [Ca2+]i. The partial relaxation of the force during depolarization was not preceded by a transient contraction. 6. The ATP-induced relaxation of the K(+)-prestimulated preparations was not inhibited by 8-phenyltheophylline, a potent P1-purinoceptor antagonist. 7. The order of potency for relaxation of the ATP analogues was 2-MeSATP > ATP > beta gamma Me-ATP, which is characteristic for P2y-purinoceptors. 8. These results indicate that, besides its activating effect, ATP also relaxes the mouse urinary bladder. It is suggested that the relaxant effect, mediated through P2y-purinoceptors, is mainly responsible for the low contractile potency of ATP in the bladder.
Full text
PDF
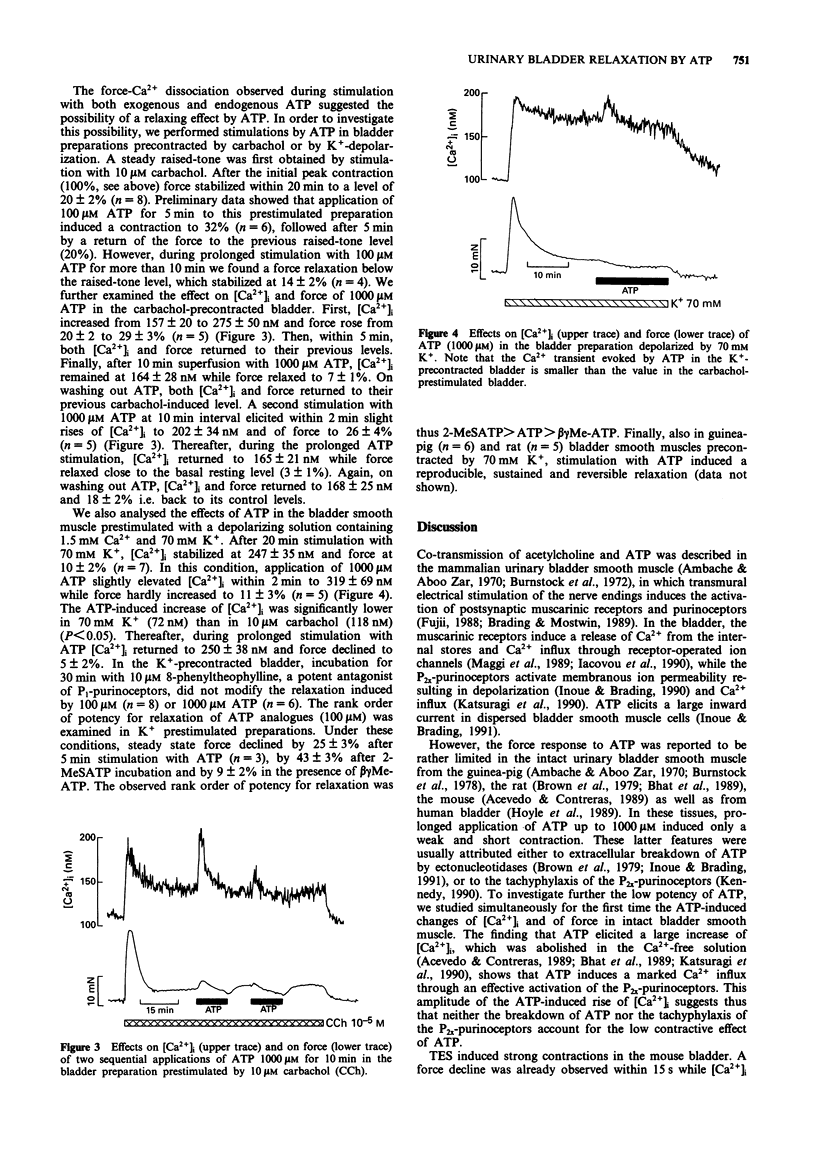


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acevedo C. G., Contreras E. Effect of extracellular calcium and calcium channel antagonists on ATP and field stimulation induced contractions of the mouse urinary bladder. Gen Pharmacol. 1989;20(6):811–815. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(89)90334-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambache N., Zar M. A. Non-cholinergic transmission by post-ganglionic motor neurones in the mammalian bladder. J Physiol. 1970 Oct;210(3):761–783. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat M. B., Mishra S. K., Raviprakash V. Sources of calcium for ATP-induced contractions in rat urinary bladder smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 2;164(1):163–166. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90244-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boland B., Himpens B., Vincent M. F., Gillis J. M., Casteels R. ATP activates P2x-contracting and P2y-relaxing purinoceptors in the smooth muscle of mouse vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;107(4):1152–1158. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb13422.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brading A. F., Mostwin J. L. Electrical and mechanical responses of guinea-pig bladder muscle to nerve stimulation. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;98(4):1083–1090. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12651.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. M., Burnstock G. The structural conformation of the polyphosphate chain of the ATP molecule is critical for its promotion of prostaglandin biosynthesis. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jan 5;69(1):81–86. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90604-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C., Burnstock G., Cocks T. Effects of adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) and beta-gamma-methylene ATP on the rat urinary bladder. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Jan;65(1):97–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb17337.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Cocks T., Crowe R., Kasakov L. Purinergic innervation of the guinea-pig urinary bladder. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 May;63(1):125–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb07782.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Dumsday B., Smythe A. Atropine resistant excitation of the urinary bladder: the possibility of transmission via nerves releasing a purine nucleotide. Br J Pharmacol. 1972 Mar;44(3):451–461. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1972.tb07283.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Kennedy C. Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptor? Gen Pharmacol. 1985;16(5):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(85)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedan J. S., Hogaboom G. K., Westfall D. P., O'Donnell J. P. Comparison of contractions of the smooth muscle of the guinea-pig vas deferens induced by ATP and related nucleotides. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Jul 9;81(2):193–204. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90437-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friel D. D. An ATP-sensitive conductance in single smooth muscle cells from the rat vas deferens. J Physiol. 1988 Jul;401:361–380. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii K. Evidence for adenosine triphosphate as an excitatory transmitter in guinea-pig, rabbit and pig urinary bladder. J Physiol. 1988 Oct;404:39–52. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganitkevich V Y. a., Isenberg G. Depolarization-mediated intracellular calcium transients in isolated smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig urinary bladder. J Physiol. 1991 Apr;435:187–205. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L. Extracellular ATP: effects, sources and fate. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):309–319. doi: 10.1042/bj2330309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith S. G., Meghji P., Moody C. J., Burnstock G. 8-phenyltheophylline: a potent P1-purinoceptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Oct 15;75(1):61–64. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90346-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himpens B., Kitazawa T., Somlyo A. P. Agonist-dependent modulation of Ca2+ sensitivity in rabbit pulmonary artery smooth muscle. Pflugers Arch. 1990 Sep;417(1):21–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00370764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himpens B., Somlyo A. P. Free-calcium and force transients during depolarization and pharmacomechanical coupling in guinea-pig smooth muscle. J Physiol. 1988 Jan;395:507–530. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp016932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle C. H., Chapple C., Burnstock G. Isolated human bladder: evidence for an adenine dinucleotide acting on P2X-purinoceptors and for purinergic transmission. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec 12;174(1):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90881-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacovou J. W., Hill S. J., Birmingham A. T. Agonist-induced contraction and accumulation of inositol phosphates in the guinea-pig detrusor: evidence that muscarinic and purinergic receptors raise intracellular calcium by different mechanisms. J Urol. 1990 Sep;144(3):775–779. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)39590-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue R., Brading A. F. Human, pig and guinea-pig bladder smooth muscle cells generate similar inward currents in response to purinoceptor activation. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;103(4):1840–1841. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12338.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue R., Brading A. F. The properties of the ATP-induced depolarization and current in single cells isolated from the guinea-pig urinary bladder. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;100(3):619–625. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15856.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsuragi T., Usune S., Furukawa T. Antagonism by nifedipine of contraction and Ca2(+)-influx evoked by ATP in guinea-pig urinary bladder. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jun;100(2):370–374. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15811.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy C. P1- and P2-purinoceptor subtypes--an update. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1990 Jan-Feb;303:30–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre R. A., Burnstock G. Effect of adenosine triphosphate and related purines in the rat gastric fundus. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1990 Jan-Feb;303:199–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Giuliani S., Patacchini R., Turini D., Barbanti G., Giachetti A., Meli A. Multiple sources of calcium for contraction of the human urinary bladder muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):1021–1031. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14634.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzini S., Maggi C. A., Meli A. Further evidence for involvement of adenosine-5'-triphosphate in non-adrenergic non-cholinergic relaxation of the isolated rat duodenum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jul 31;113(3):399–408. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90088-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody C. J., Meghji P., Burnstock G. Stimulation of P1-purinoceptors by ATP depends partly on its conversion to AMP and adenosine and partly on direct action. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Jan 13;97(1-2):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90511-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls J., Hourani S. M., Kitchen I. The ontogeny of purinoceptors in rat urinary bladder and duodenum. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):874–878. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14107.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parija S. C., Raviprakash V., Mishra S. K. Adenosine- and alpha,beta-methylene ATP-induced differential inhibition of cholinergic and non-cholinergic neurogenic responses in rat urinary bladder. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;102(2):396–400. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12185.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralevic V., Burnstock G. Roles of P2-purinoceptors in the cardiovascular system. Circulation. 1991 Jul;84(1):1–14. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.84.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restrepo D., Kozody D. J., Spinelli L. J., Knauf P. A. pH homeostasis in promyelocytic leukemic HL60 cells. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Oct;92(4):489–507. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.4.489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sneddon P., Westfall D. P. Pharmacological evidence that adenosine triphosphate and noradrenaline are co-transmitters in the guinea-pig vas deferens. J Physiol. 1984 Feb;347:561–580. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witt P. A., Kramer T. H., Burks T. F. Norepinephrine and ATP are synergistic in the mouse vas deferens preparation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Nov 5;204(2):149–155. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90699-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


