Abstract
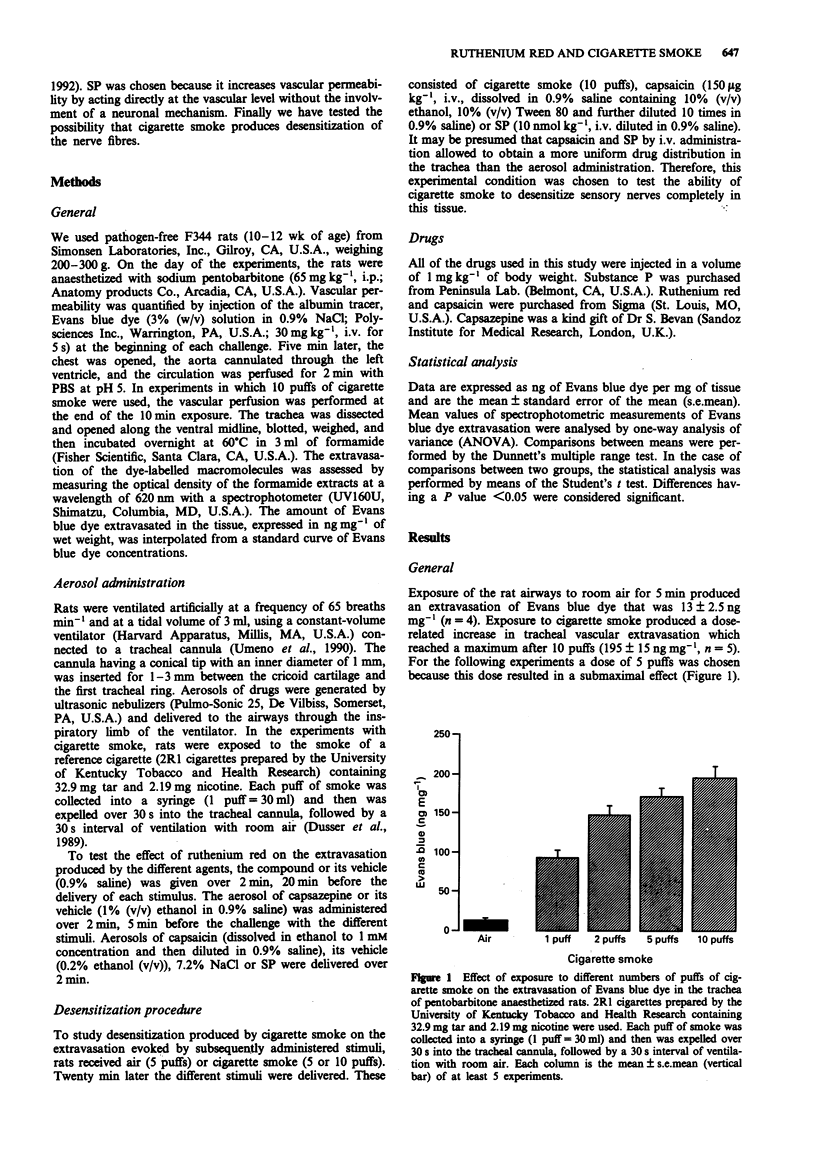
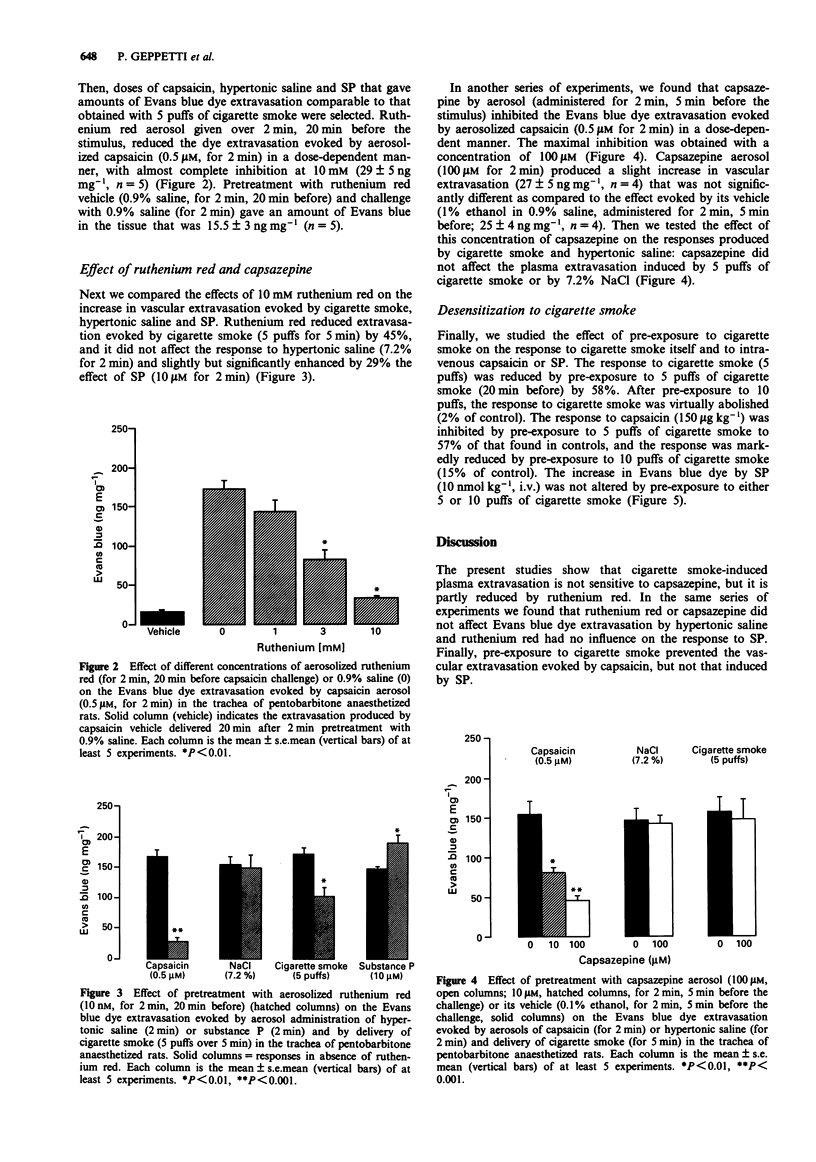
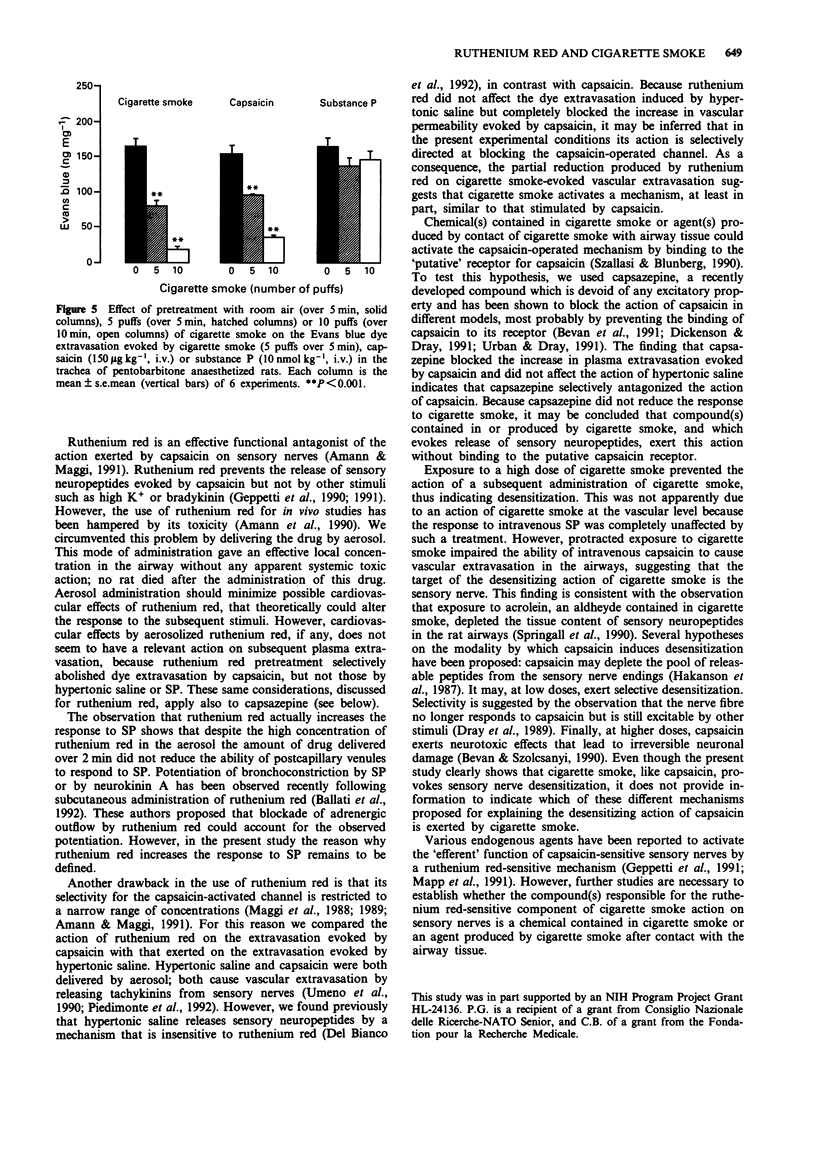
1. Cigarette smoke increases vascular permeability in rat airways by activating release of tachykinin from capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerves. However, the mechanism by which cigarette smoke induces secretion of sensory neuropeptides is unknown. Here we hypothesized that cigarette smoke activates sensory nerve endings via a mechanism similar to that of capsaicin. 2. We studied the effects of ruthenium red, an inorganic dye which blocks the cation influx promoted by capsaicin and of the capsaicin antagonist capsazepine on the increase in vascular permeability produced by cigarette smoke, capsaicin, hypertonic saline and substance P in the trachea of pentobarbitone anaesthetized rats. We also investigated the ability of cigarette smoke to desensitize sensory nerve fibres. 3. Ruthenium red (10 mM) by aerosol blocked the increase in vascular permeability induced by capsaicin (0.5 microM) and reduced the response to cigarette smoke (5 puffs) but did not affect responses evoked by hypertonic saline (7.2%) or by substance P (10 microM) (all given by aerosol). Aerosols of capsazepine (0.1 mM) prevented extravasation by capsaicin, but did not inhibit response to cigarette smoke, hypertonic saline or substance P. Finally, pre-exposure to a high dose of cigarette smoke (10 puffs) prevented the extravasation caused by cigarette smoke (5 puffs) itself and by intravenous capsaicin (150 micrograms kg-1), but not that by intravenous substance P (10 nmol kg-1).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amann R., Donnerer J., Maggi C. A., Giuliani S., DelBianco E., Weihe E., Lembeck F. Capsaicin desensitization in vivo is inhibited by ruthenium red. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Sep 21;186(2-3):169–175. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90430-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amann R., Maggi C. A. Ruthenium red as a capsaicin antagonist. Life Sci. 1991;49(12):849–856. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90169-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballati L., Maggi C. A., Evangelista S. Effect of ruthenium red on the bronchoconstriction induced by capsaicin and by selective tachykinin receptor agonists in anaesthetized guinea-pig. J Auton Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;12(5):369–375. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1992.tb00385.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belvisi M. G., Miura M., Stretton D., Barnes P. J. Capsazepine as a selective antagonist of capsaicin-induced activation of C-fibres in guinea-pig bronchi. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 May 14;215(2-3):341–344. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan S., Szolcsányi J. Sensory neuron-specific actions of capsaicin: mechanisms and applications. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Aug;11(8):330–333. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delay-Goyet P., Lundberg J. M. Cigarette smoke-induced airway oedema is blocked by the NK1 antagonist, CP-96,345. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Oct 2;203(1):157–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90808-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickenson A. H., Dray A. Selective antagonism of capsaicin by capsazepine: evidence for a spinal receptor site in capsaicin-induced antinociception. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;104(4):1045–1049. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12547.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dray A., Bettaney J., Forster P. Capsaicin desensitization of peripheral nociceptive fibres does not impair sensitivity to other noxious stimuli. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Apr 24;99(1-2):50–54. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90263-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dray A., Forbes C. A., Burgess G. M. Ruthenium red blocks the capsaicin-induced increase in intracellular calcium and activation of membrane currents in sensory neurones as well as the activation of peripheral nociceptors in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 1990 Mar 2;110(1-2):52–59. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(90)90786-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dusser D. J., Djokic T. D., Borson D. B., Nadel J. A. Cigarette smoke induces bronchoconstrictor hyperresponsiveness to substance P and inactivates airway neutral endopeptidase in the guinea pig. Possible role of free radicals. J Clin Invest. 1989 Sep;84(3):900–906. doi: 10.1172/JCI114251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geppetti P., Del Bianco E., Patacchini R., Santicioli P., Maggi C. A., Tramontana M. Low pH-induced release of calcitonin gene-related peptide from capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerves: mechanism of action and biological response. Neuroscience. 1991;41(1):295–301. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90218-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geppetti P., Tramontana M., Santicioli P., Del Bianco E., Giuliani S., Maggi C. A. Bradykinin-induced release of calcitonin gene-related peptide from capsaicin-sensitive nerves in guinea-pig atria: mechanism of action and calcium requirements. Neuroscience. 1990;38(3):687–692. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer P. Capsaicin: cellular targets, mechanisms of action, and selectivity for thin sensory neurons. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Jun;43(2):143–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Håkanson R., Beding B., Ekman R., Heilig M., Wahlestedt C., Sundler F. Multiple tachykinin pools in sensory nerve fibres in the rabbit iris. Neuroscience. 1987 Jun;21(3):943–950. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Martling C. R., Saria A., Folkers K., Rosell S. Cigarette smoke-induced airway oedema due to activation of capsaicin-sensitive vagal afferents and substance P release. Neuroscience. 1983 Dec;10(4):1361–1368. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Saria A. Capsaicin-induced desensitization of airway mucosa to cigarette smoke, mechanical and chemical irritants. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):251–253. doi: 10.1038/302251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Patacchini R., Santicioli P., Giuliani S., Del Bianco E., Geppetti P., Meli A. The 'efferent' function of capsaicin-sensitive nerves: ruthenium red discriminates between different mechanisms of activation. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov 7;170(3):167–177. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90537-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Santicioli P., Geppetti P., Parlani M., Astolfi M., Pradelles P., Patacchini R., Meli A. The antagonism induced by ruthenium red of the actions of capsaicin on the peripheral terminals of sensory neurons: further studies. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep 1;154(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90356-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mapp C. E., Boniotti A., Graf P. D., Chitano P., Fabbri L. M., Nadel J. A. Bronchial smooth muscle responses evoked by toluene diisocyanate are inhibited by ruthenium red and by indomethacin. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 23;200(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90667-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh S. J., Stansfeld C. E., Brown D. A., Davey R., McCarthy D. The mechanism of action of capsaicin on sensory C-type neurons and their axons in vitro. Neuroscience. 1987 Oct;23(1):275–289. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90289-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springall D. R., Edginton J. A., Price P. N., Swanston D. W., Noel C., Bloom S. R., Polak J. M. Acrolein depletes the neuropeptides CGRP and substance P in sensory nerves in rat respiratory tract. Environ Health Perspect. 1990 Apr;85:151–157. doi: 10.1289/ehp.85-1568331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stedman R. L. The chemical composition of tobacco and tobacco smoke. Chem Rev. 1968 Apr;68(2):153–207. doi: 10.1021/cr60252a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szallasi A., Blumberg P. M. Specific binding of resiniferatoxin, an ultrapotent capsaicin analog, by dorsal root ganglion membranes. Brain Res. 1990 Jul 30;524(1):106–111. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90498-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tramontana M., Cecconi R., Del Bianco E., Santicioli P., Maggi C. A., Alessandri M., Geppetti P. Hypertonic media produce Ca(2+)-dependent release of calcitonin gene-related peptide from capsaicin-sensitive nerve fibres in the rat urinary bladder. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Mar 11;124(1):79–82. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90826-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umeno E., McDonald D. M., Nadel J. A. Hypertonic saline increases vascular permeability in the rat trachea by producing neurogenic inflammation. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1905–1908. doi: 10.1172/JCI114652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban L., Dray A. Capsazepine, a novel capsaicin antagonist, selectively antagonises the effects of capsaicin in the mouse spinal cord in vitro. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Dec 16;134(1):9–11. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90496-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. N., Winter J., James I. F., Rang H. P., Yeats J., Bevan S. Capsaicin-induced ion fluxes in dorsal root ganglion cells in culture. J Neurosci. 1988 Sep;8(9):3208–3220. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-09-03208.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


