Abstract
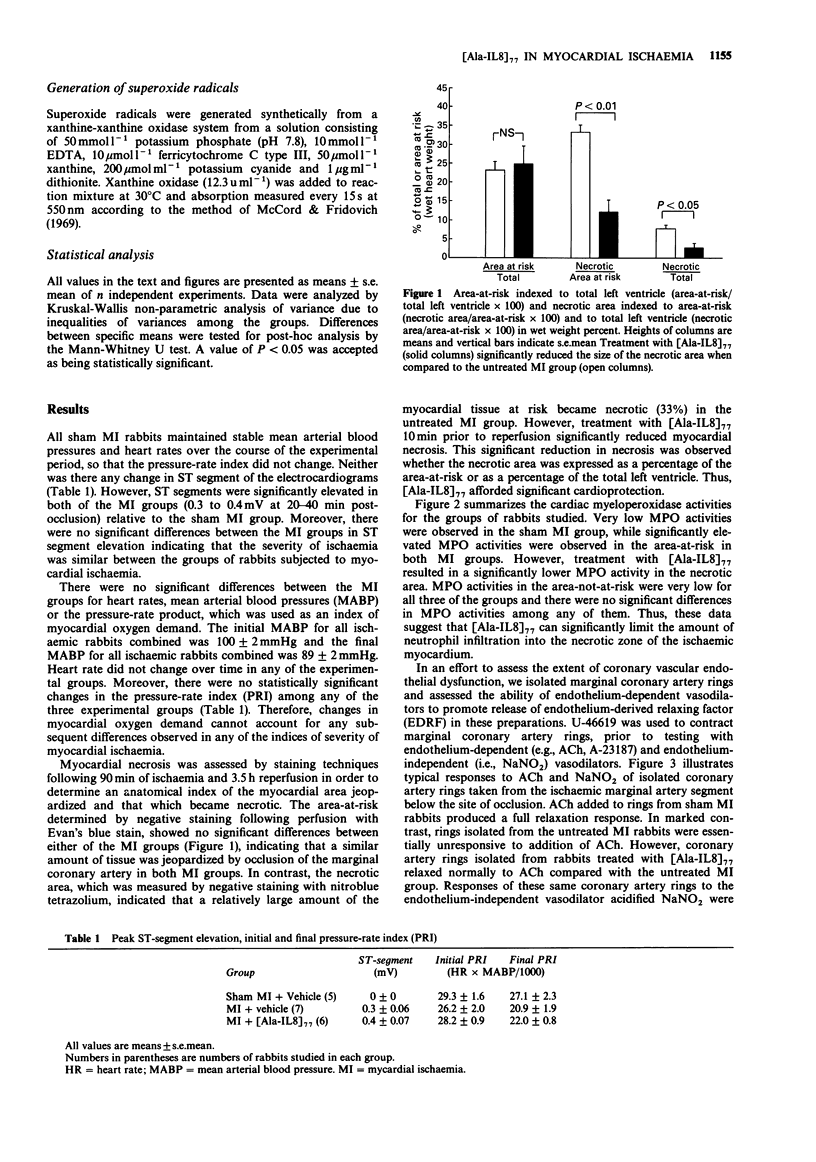
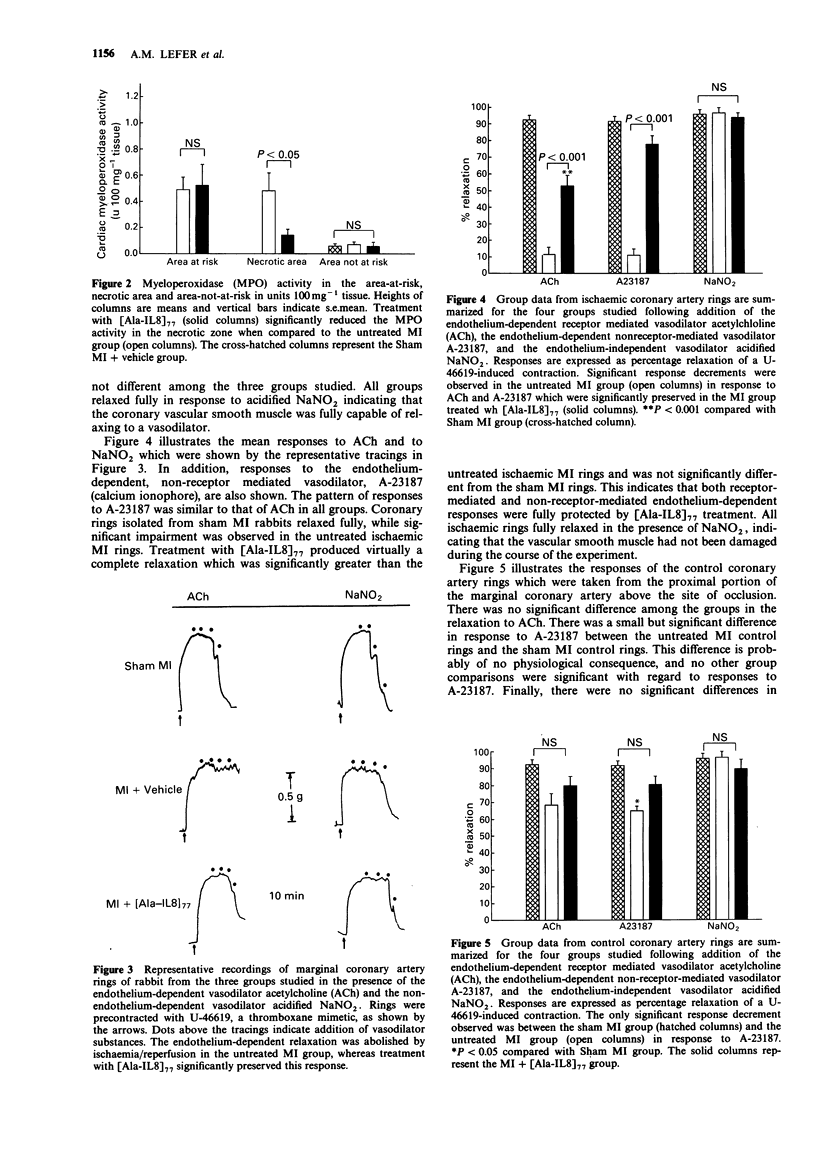
1 We studied the effects of a form of interleukin-8 (i.e., [Ala-IL8]77) on endothelial dysfunction and myocardial injury in rabbits. Pentobarbitone-anaesthetized rabbits were subjected to 1.5 h occlusion of the marginal coronary artery and 3.5 h reperfusion. [Ala-IL8]77 (50 micrograms or its vehicle) was given i.v. as a bolus 10 min prior to reperfusion. [Ala-IL8]77 was also studied in isolated perfused hearts of rabbits. 2 Myocardial ischaemia plus reperfusion in untreated rabbits produced severe endothelial dysfunction and myocardial injury, including marked myocardial necrosis, elevated cardiac myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity in ischaemic cardiac tissue, and loss of response of marginal coronary rings to the endothelium-dependent vasodilators, acetylcholine (ACh) and A23187. 3 Administration of [Ala-IL8]77 10 min prior to reperfusion resulted in significant protective effects in post-ischaemic reperfusion. Compared with untreated rabbits, [Ala-IL8]77 caused a reduced necrotic zone (P less than 0.01), lower MPO activity in the necrotic zone (P less than 0.05), and significantly preserved vasorelaxant responses of marginal coronary artery rings to endothelium-dependent vasodilators, ACh (P less than 0.001) and A23187 (P less than 0.001). 4 These results indicate that myocardial ischaemia and reperfusion result in a severe endothelial dysfunction and myocardial injury which involved the interaction of neutrophils and endothelial cells. However, [Ala-IL8]77 did not appear to exert a direct endothelial protective effect in the absence of neutrophils in rabbit isolated perfused hearts. 5 Inhibition of neutrophil accumulation in the myocardium, perhaps by prevention of endothelial dysfunction resulting from [Ala-IL8]77, leads to significant protective effects in ischaemia and reperfusion in rabbits.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoki N., Siegfried M., Lefer A. M. Anti-EDRF effect of tumor necrosis factor in isolated, perfused cat carotid arteries. Am J Physiol. 1989 May;256(5 Pt 2):H1509–H1512. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.256.5.H1509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bednar M., Smith B., Pinto A., Mullane K. M. Nafazatrom-induced salvage of ischemic myocardium in anesthetized dogs is mediated through inhibition of neutrophil function. Circ Res. 1985 Jul;57(1):131–141. doi: 10.1161/01.res.57.1.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Mendrick D. L., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Identification of an inducible endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9238–9242. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley P. P., Priebat D. A., Christensen R. D., Rothstein G. Measurement of cutaneous inflammation: estimation of neutrophil content with an enzyme marker. J Invest Dermatol. 1982 Mar;78(3):206–209. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12506462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunwald E., Kloner R. A. Myocardial reperfusion: a double-edged sword? J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1713–1719. doi: 10.1172/JCI112160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engler R. L., Dahlgren M. D., Morris D. D., Peterson M. A., Schmid-Schönbein G. W. Role of leukocytes in response to acute myocardial ischemia and reflow in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1986 Aug;251(2 Pt 2):H314–H323. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1986.251.2.H314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forman M. B., Virmani R., Puett D. W. Mechanisms and therapy of myocardial reperfusion injury. Circulation. 1990 Mar;81(3 Suppl):IV69–IV78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Obin M. S., Brock A. F., Luis E. A., Hass P. E., Hébert C. A., Yip Y. K., Leung D. W., Lowe D. G., Kohr W. J. Endothelial interleukin-8: a novel inhibitor of leukocyte-endothelial interactions. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1601–1603. doi: 10.1126/science.2688092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. M. Neutrophil-mediated vascular injury. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1987;715:123–129. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1987.tb09912.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess M. L., Manson N. H. Molecular oxygen: friend and foe. The role of the oxygen free radical system in the calcium paradox, the oxygen paradox and ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1984 Nov;16(11):969–985. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(84)80011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G., 3rd, Furlan L. E., Aoki N., Lefer A. M. Endothelium and myocardial protecting actions of taprostene, a stable prostacyclin analogue, after acute myocardial ischemia and reperfusion in cats. Circ Res. 1990 May;66(5):1362–1370. doi: 10.1161/01.res.66.5.1362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloner R. A., Ganote C. E., Jennings R. B. The "no-reflow" phenomenon after temporary coronary occlusion in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1974 Dec;54(6):1496–1508. doi: 10.1172/JCI107898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefer A. M., Tsao P., Aoki N., Palladino M. A., Jr Mediation of cardioprotection by transforming growth factor-beta. Science. 1990 Jul 6;249(4964):61–64. doi: 10.1126/science.2164258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucchesi B. R., Werns S. W., Fantone J. C. The role of the neutrophil and free radicals in ischemic myocardial injury. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1989 Dec;21(12):1241–1251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(89)90670-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase. An enzymic function for erythrocuprein (hemocuprein). J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6049–6055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCord J. M. Oxygen-derived free radicals in postischemic tissue injury. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 17;312(3):159–163. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501173120305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehta J. L., Nichols W. W., Donnelly W. H., Lawson D. L., Thompson L., ter Riet M., Saldeen T. G. Protection by superoxide dismutase from myocardial dysfunction and attenuation of vasodilator reserve after coronary occlusion and reperfusion in dog. Circ Res. 1989 Nov;65(5):1283–1295. doi: 10.1161/01.res.65.5.1283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullane K. M., Kraemer R., Smith B. Myeloperoxidase activity as a quantitative assessment of neutrophil infiltration into ischemic myocardium. J Pharmacol Methods. 1985 Nov;14(3):157–167. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(85)90029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romson J. L., Hook B. G., Kunkel S. L., Abrams G. D., Schork M. A., Lucchesi B. R. Reduction of the extent of ischemic myocardial injury by neutrophil depletion in the dog. Circulation. 1983 May;67(5):1016–1023. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.67.5.1016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romson J. L., Hook B. G., Rigot V. H., Schork M. A., Swanson D. P., Lucchesi B. R. The effect of ibuprofen on accumulation of indium-111-labeled platelets and leukocytes in experimental myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1982 Nov;66(5):1002–1011. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.66.5.1002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubanyi G. M., Vanhoutte P. M. Oxygen-derived free radicals, endothelium, and responsiveness of vascular smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1986 May;250(5 Pt 2):H815–H821. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1986.250.5.H815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOMMERS H. M., JENNINGS R. B. EXPERIMENTAL ACUTE MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION; HISTOLOGIC AND HISTOCHEMICAL STUDIES OF EARLY MYOCARDIAL INFARCTS INDUCED BY TEMPORARY OR PERMANENT OCCLUSION OF A CORONARY ARTERY. Lab Invest. 1964 Dec;13:1491–1503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder J. M., Christophers E. Secretion of novel and homologous neutrophil-activating peptides by LPS-stimulated human endothelial cells. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):244–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P. J., Mickelson J., Fantone J. C., Gallagher K. P., Lucchesi B. R. Reduction of experimental canine myocardial infarct size with prostaglandin E1: inhibition of neutrophil migration and activation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Feb;244(2):619–624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P. J., Mitsos S. E., Ventura A., Gallagher K. P., Fantone J. C., Abrams G. D., Schork M. A., Lucchesi B. R. Prostacyclin protects ischemic reperfused myocardium in the dog by inhibition of neutrophil activation. Am Heart J. 1987 Jan;113(1):129–137. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(87)90020-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P. J., Todd R. F., 3rd, Fantone J. C., Mickelson J. K., Griffin J. D., Lucchesi B. R. Reduction of experimental canine myocardial reperfusion injury by a monoclonal antibody (anti-Mo1, anti-CD11b) that inhibits leukocyte adhesion. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):624–629. doi: 10.1172/JCI113364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strieter R. M., Kunkel S. L., Showell H. J., Remick D. G., Phan S. H., Ward P. A., Marks R. M. Endothelial cell gene expression of a neutrophil chemotactic factor by TNF-alpha, LPS, and IL-1 beta. Science. 1989 Mar 17;243(4897):1467–1469. doi: 10.1126/science.2648570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao P. S., Aoki N., Lefer D. J., Johnson G., 3rd, Lefer A. M. Time course of endothelial dysfunction and myocardial injury during myocardial ischemia and reperfusion in the cat. Circulation. 1990 Oct;82(4):1402–1412. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.82.4.1402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VanBenthuysen K. M., McMurtry I. F., Horwitz L. D. Reperfusion after acute coronary occlusion in dogs impairs endothelium-dependent relaxation to acetylcholine and augments contractile reactivity in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jan;79(1):265–274. doi: 10.1172/JCI112793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler M. E., Luscinskas F. W., Bevilacqua M. P., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Cultured human endothelial cells stimulated with cytokines or endotoxin produce an inhibitor of leukocyte adhesion. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1211–1218. doi: 10.1172/JCI113718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweier J. L. Measurement of superoxide-derived free radicals in the reperfused heart. Evidence for a free radical mechanism of reperfusion injury. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1353–1357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


