Abstract
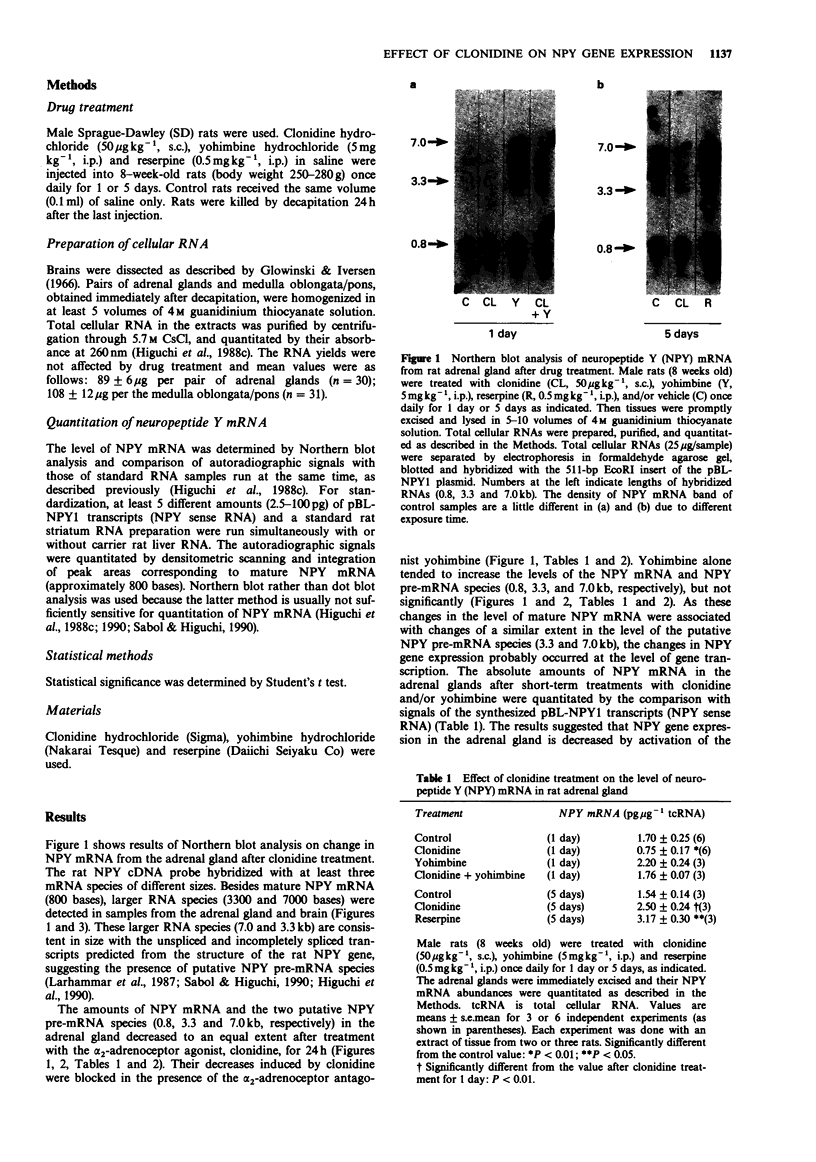
1 The mechanism of regulation of the neuropeptide Y (NPY) gene by pharmacological treatment with the alpha 2-adrenenoceptor agonist, clonidine, was investigated by quantitative Northern blot analysis of the effects of this drug on the NPY mRNA levels in rat adrenal gland and medulla oblongata/pons. 2 In the adrenal gland, clonidine-treatment (50 microgram kg-1, s.c., once daily) resulted in decrease in the amount of NPY mRNA to 44 +/- 10% of the control level in 24 h and then its increase to 162 +/- 16% of the control level after 5 days. Concomitant changes in putative NPY pre-mRNA species (7.0 and 3.3 kb) were observed, probably due to changes at the level of NPY gene transcription. 3 The short-term (24 h) effect of clonidine was blocked by yohimbine (5 mg kg-1, i.p., once daily). Yohimbine alone tended to increase the NPY mRNA level after 24h. 4 The recovery/increase in the NPY mRNA level in the adrenal gland after 5 days treatment with clonidine was similar to its increase after treatment with reserpine (0.5 mg kg-1, i.p., once daily). 5 NPY gene expression in the medulla oblongata/pons was not changed by short- or long-term treatment with clonidine. 6 These results suggest that clonidine suppresses NPY gene expression in the adrenal gland, probably at the level of transcription, by activation of the alpha 2-adrenoceptor.
Full text
PDF
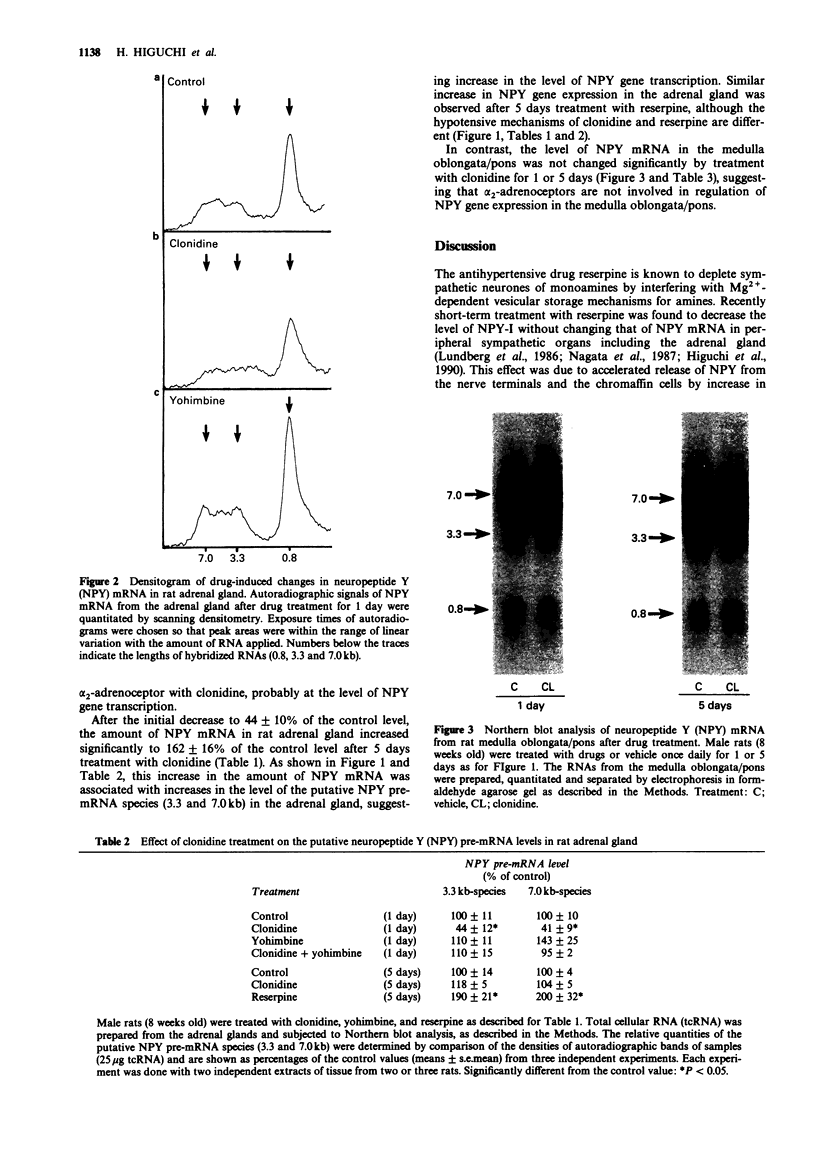


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. M., Bircham P. M., Bloom S. R., Edwards A. V. Release of neuropeptide Y in response to splanchnic nerve stimulation in the conscious calf. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:401–408. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. M., Bircham P. M., Edwards A. V., Tatemoto K., Bloom S. R. Neuropeptide Y (NPY) reduces myocardial perfusion and inhibits the force of contraction of the isolated perfused rabbit heart. Regul Pept. 1983 Jul;6(3):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(83)90143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlöf C., Dahlöf P., Lundberg J. M. Alpha 2-adrenoceptor-mediated inhibition of nerve stimulation-evoked release of neuropeptide Y (NPY)-like immunoreactivity in the pithed guinea-pig. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Nov 19;131(2-3):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90583-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlöf C., Dahlöf P., Lundberg J. M. Neuropeptide Y (NPY): enhancement of blood pressure increase upon alpha-adrenoceptor activation and direct pressor effects in pithed rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb 26;109(2):289–292. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90433-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblad E., Edvinsson L., Wahlestedt C., Uddman R., Håkanson R., Sundler F. Neuropeptide Y co-exists and co-operates with noradrenaline in perivascular nerve fibers. Regul Pept. 1984 Apr;8(3):225–235. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(84)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everitt B. J., Hökfelt T., Terenius L., Tatemoto K., Mutt V., Goldstein M. Differential co-existence of neuropeptide Y (NPY)-like immunoreactivity with catecholamines in the central nervous system of the rat. Neuroscience. 1984 Feb;11(2):443–462. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco-Cereceda A., Nagata M., Svensson T. H., Lundberg J. M. Differential effects of clonidine and reserpine treatment on neuropeptide Y content in some sympathetically innervated tissues of the guinea-pig. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Oct 13;142(2):267–273. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90116-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuxe K., Agnati L. F., Härfstrand A., Zini I., Tatemoto K., Pich E. M., Hökfelt T., Mutt V., Terenius L. Central administration of neuropeptide Y induces hypotension bradypnea and EEG synchronization in the rat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1983 Jun;118(2):189–192. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1983.tb07261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glowinski J., Iversen L. L. Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain. I. The disposition of [3H]norepinephrine, [3H]dopamine and [3H]dopa in various regions of the brain. J Neurochem. 1966 Aug;13(8):655–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb09873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray T. S., Morley J. E. Neuropeptide Y: anatomical distribution and possible function in mammalian nervous system. Life Sci. 1986 Feb 3;38(5):389–401. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90061-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haeusler G. Clonidine-induced inhibition of sympathetic nerve activity: no indication for a central presynaptic or an indirect sympathomimetic mode of action. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1974;286(1):07–111. doi: 10.1007/BF00499107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi H., Costa E., Yang H. Y. Neuropeptide Y inhibits the nicotine-mediated release of catecholamines from bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Feb;244(2):468–474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi H., Iwasa A., Yoshida H., Miki N. Long lasting increase in neuropeptide Y gene expression in rat adrenal gland with reserpine treatment: positive regulation of transsynaptic activation and membrane depolarization. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;38(5):614–623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi H., Yang H. Y., Costa E. Age-related bidirectional changes in neuropeptide Y peptides in rat adrenal glands, brain, and blood. J Neurochem. 1988 Jun;50(6):1879–1886. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb02492.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi H., Yang H. Y., Sabol S. L. Rat neuropeptide Y precursor gene expression. mRNA structure, tissue distribution, and regulation by glucocorticoids, cyclic AMP, and phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6288–6295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi H., Yang H. Y. Splanchnic nerve transection abolishes the age-dependent increase of neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactivity in rat adrenal gland. J Neurochem. 1986 May;46(5):1658–1660. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb01792.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi H. [Neuropeptide Y (NPY): functions and biosynthesis as a peptidergic neurotransmitter and the regulation of neuron-specific expression of NPY gene]. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi. 1989 Apr;93(4):203–218. doi: 10.1254/fpj.93.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Håkanson R., Wahlestedt C., Ekblad E., Edvinsson L., Sundler F. Neuropeptide Y: coexistence with noradrenaline. Functional implications. Prog Brain Res. 1986;68:279–287. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)60244-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larhammar D., Ericsson A., Persson H. Structure and expression of the rat neuropeptide Y gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):2068–2072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.2068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Al-Saffar A., Saria A., Theodorsson-Norheim E. Reserpine-induced depletion of neuropeptide Y from cardiovascular nerves and adrenal gland due to enhanced release. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Feb;332(2):163–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00511407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Terenius L., Hökfelt T., Martling C. R., Tatemoto K., Mutt V., Polak J., Bloom S., Goldstein M. Neuropeptide Y (NPY)-like immunoreactivity in peripheral noradrenergic neurons and effects of NPY on sympathetic function. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Dec;116(4):477–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majane E. A., Alho H., Kataoka Y., Lee C. H., Yang H. Y. Neuropeptide Y in bovine adrenal glands: distribution and characterization. Endocrinology. 1985 Sep;117(3):1162–1168. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-3-1162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAuley M. A., Macrae I. M., Reid J. L. The cardiovascular actions of clonidine and neuropeptide-Y in the ventrolateral medulla of the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug;97(4):1067–1074. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12563.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata M., Franco-Cereceda A., Saria A., Amann R., Lundberg J. M. Reserpine-induced depletion of neuropeptide Y in the guinea-pig: tissue-specific effects and mechanisms of action. J Auton Nerv Syst. 1987 Oct;20(3):257–263. doi: 10.1016/0165-1838(87)90154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata M., Franco-Cereceda A., Svensson T. H., Lundberg J. M. Clonidine treatment elevates content of neuropeptide Y in cardiac nerves. Acta Physiol Scand. 1986 Oct;128(2):321–322. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1986.tb07982.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pernow J., Thorén P., Millberg B. I., Lundberg J. M. Renal sympathetic nerve activation in relation to reserpine-induced depletion of neuropeptide Y in the kidney of the rat. Acta Physiol Scand. 1988 Sep;134(1):53–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1988.tb08458.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabol S. L., Higuchi H. Transcriptional regulation of the neuropeptide Y gene by nerve growth factor: antagonism by glucocorticoids and potentiation by adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and phorbol ester. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Mar;4(3):384–392. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-3-384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalling M., Dagerlind A., Brené S., Hallman H., Djurfeldt M., Persson H., Terenius L., Goldstein M., Schlesinger D., Hökfelt T. Coexistence and gene expression of phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase, tyrosine hydroxylase, and neuropeptide tyrosine in the rat and bovine adrenal gland: effects of reserpine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8306–8310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalling M., Franco-Cereceda A., Hökfelt T., Persson H., Lundberg J. M. Increased neuropeptide Y messenger RNA and peptide in sympathetic ganglia after reserpine pretreatment. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov 8;156(3):419–420. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90289-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalling M., Seroogy K., Hökfelt T., Chai S. Y., Hallman H., Persson H., Larhammar D., Ericsson A., Terenius L., Graffi J. Neuropeptide tyrosine in the rat adrenal gland--immunohistochemical and in situ hybridization studies. Neuroscience. 1988 Jan;24(1):337–349. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90335-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun M. K., Guyenet P. G. Effects of vasopressin and other neuropeptides on rostral medullary sympathoexcitatory neurons 'in vitro'. Brain Res. 1989 Jul 17;492(1-2):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90909-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson T. H. Stress, central neurotransmitters, and the mechanism of action of alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonists. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1987;10 (Suppl 12):S88–S92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K. Neuropeptide Y: complete amino acid sequence of the brain peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5485–5489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng C. J., Mosqueda-Garcia R., Appalsamy M., Robertson D. Cardiovascular effects of neuropeptide Y in rat brainstem nuclei. Circ Res. 1989 Jan;64(1):55–61. doi: 10.1161/01.res.64.1.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward-Routledge C., Marsden C. A. Adrenaline in the CNS and the action of antihypertensive drugs. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Jun;9(6):209–214. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90087-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Quidt M. E., Emson P. C. Neuropeptide Y in the adrenal gland: characterization, distribution and drug effects. Neuroscience. 1986 Nov;19(3):1011–1022. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90313-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]