Abstract
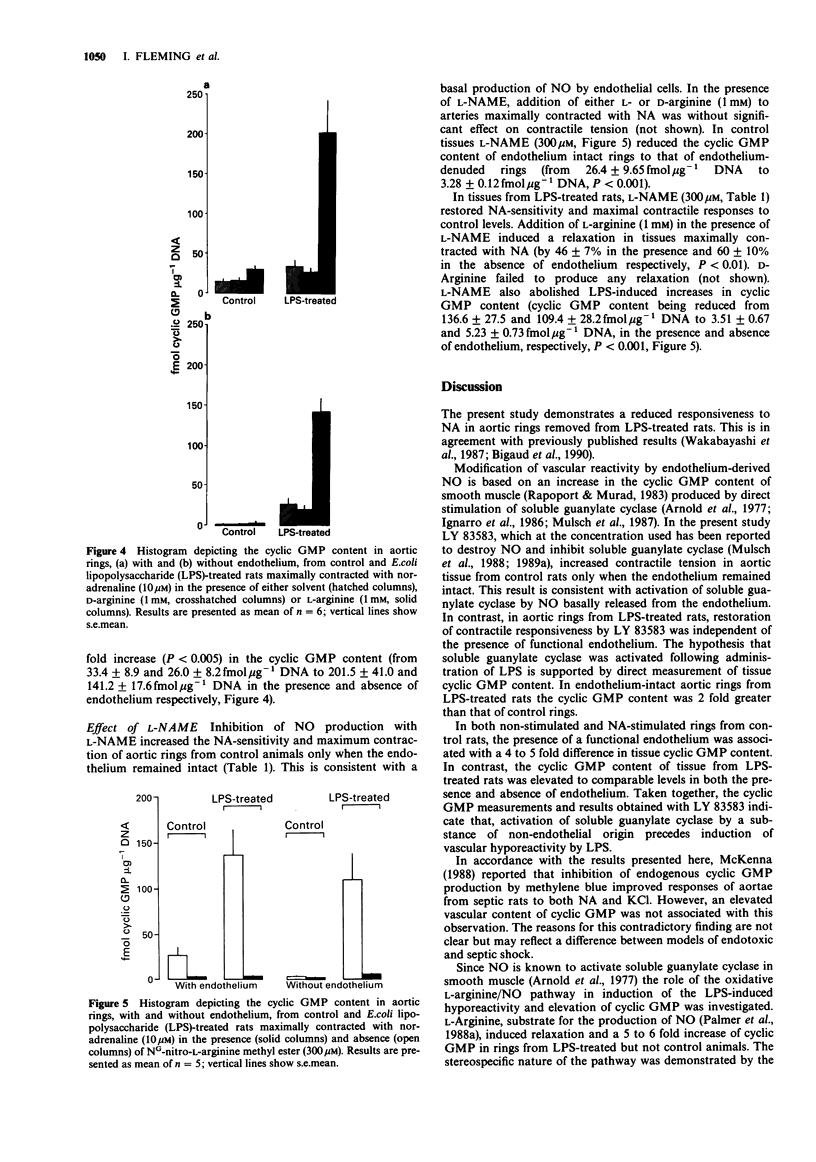
1. The aim of this investigation was to study the relationship between contractile responsiveness, activation of the L-arginine pathway and tissue levels of guanosine 3':5'cyclic monophosphate (cylic GMP) in aortic rings removed from rats 4 h after intraperitoneal administration of bacterial endotoxin (E. coli. lipopolysaccharide, LPS, 20 mg kg-1). 2. LPS-treatment resulted in a reduction of the sensitivity and maximal contractile response to noradrenaline (NA). 3. Depression of the maximal contractile response was restored to control by 6-anilo-5,8-quinolinedione (LY 83583, 10 microM), which prevents activation of soluble guanylate cyclase. 4. Cyclic GMP levels in tissue from LPS-treated rats were 2 fold greater than cyclic GMP levels detected in tissue from control (saline-treated) rats. The LPS-induced increase in cyclic GMP content was observed both in the presence and absence of functional endothelium. 5. Addition of L-arginine 1 mM) to maximally contracted aortic rings produced significantly relaxation of rings from LPS-treated rats but not rings from control animals. In the LPS-treated group, addition of L-arginine was also associated with a significant increase in cyclic GMP content. L-Arginine had no effect on the cyclic GMP content of control rings. D-Arginine (1 mM) was without effect. 6. In rings from LPS-treated rats, NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME, 300 microM), an inhibitor of nitric oxide (NO) production, increased the contractile response to NA and prevented the LPS-induced increase in cyclic GMP content.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold W. P., Mittal C. K., Katsuki S., Murad F. Nitric oxide activates guanylate cyclase and increases guanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate levels in various tissue preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3203–3207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beasley D. Interleukin 1 and endotoxin activate soluble guanylate cyclase in vascular smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jul;259(1 Pt 2):R38–R44. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1990.259.1.R38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biguad M., Julou-Schaeffer G., Parratt J. R., Stoclet J. C. Endotoxin-induced impairment of vascular smooth muscle contractions elicited by different mechanisms. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 6;190(1-2):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94125-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunk C. F., Jones K. C., James T. W. Assay for nanogram quantities of DNA in cellular homogenates. Anal Biochem. 1979 Jan 15;92(2):497–500. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90690-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draznin M. B., Rapoport R. M., Murad F. Myosin light chain phosphorylation in contraction and relaxation of intact rat thoracic aorta. Int J Biochem. 1986;18(10):917–928. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(86)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink M. P., Homer L. D., Fletcher J. R. Diminished pressor response to exogenous norepinephrine and angiotensin II in septic, unanesthetized rats: evidence for a prostaglandin-mediated effect. J Surg Res. 1985 Apr;38(4):335–342. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(85)90046-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming I., Gray G. A., Julou-Schaeffer G., Parratt J. R., Stoclet J. C. Incubation with endotoxin activates the L-arginine pathway in vascular tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 14;171(2):562–568. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91183-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudenberg N., Riese K. H. Characterization of cells of the normal aortic endothelium of adult rats and changes due to endotoxin shock. I. Communication: light microscopy, autoradiography, DNA cytophotometry, and enzyme histochemistry. Beitr Pathol. 1976 Nov;159(2):125–142. doi: 10.1016/s0005-8165(76)80001-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs J. B., Jr, Taintor R. R., Vavrin Z., Rachlin E. M. Nitric oxide: a cytotoxic activated macrophage effector molecule. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Nov 30;157(1):87–94. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80015-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs A. J., Gibson A. L-NG-nitro-arginine and its methyl ester are potent inhibitors of non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic transmission in the rat anococcygeus. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):749–752. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14086.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzmann S. Endothelium-induced relaxation by acetylcholine associated with larger rises in cyclic GMP in coronary arterial strips. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1982;8(6):409–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Harbison R. G., Wood K. S., Kadowitz P. J. Activation of purified soluble guanylate cyclase by endothelium-derived relaxing factor from intrapulmonary artery and vein: stimulation by acetylcholine, bradykinin and arachidonic acid. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Jun;237(3):893–900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julou-Schaeffer G., Gray G. A., Fleming I., Schott C., Parratt J. R., Stoclet J. C. Loss of vascular responsiveness induced by endotoxin involves L-arginine pathway. Am J Physiol. 1990 Oct;259(4 Pt 2):H1038–H1043. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.4.H1038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kai H., Kanaide H., Matsumoto T., Nakamura M. 8-Bromoguanosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate decreases intracellular free calcium concentrations in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells from rat aorta. FEBS Lett. 1987 Sep 14;221(2):284–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80941-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marletta M. A., Yoon P. S., Iyengar R., Leaf C. D., Wishnok J. S. Macrophage oxidation of L-arginine to nitrite and nitrate: nitric oxide is an intermediate. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8706–8711. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer B., Schmidt K., Humbert P., Böhme E. Biosynthesis of endothelium-derived relaxing factor: a cytosolic enzyme in porcine aortic endothelial cells Ca2+-dependently converts L-arginine into an activator of soluble guanylyl cyclase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Oct 31;164(2):678–685. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91513-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna T. M. Enhanced vascular effects of cyclic GMP in septic rat aorta. Am J Physiol. 1988 Mar;254(3 Pt 2):R436–R442. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1988.254.3.R436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada S., Palmer R. M., Higgs E. A. Biosynthesis of nitric oxide from L-arginine. A pathway for the regulation of cell function and communication. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Jun 1;38(11):1709–1715. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90403-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mülsch A., Bassenge E., Busse R. Nitric oxide synthesis in endothelial cytosol: evidence for a calcium-dependent and a calcium-independent mechanism. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;340(6 Pt 2):767–770. doi: 10.1007/BF00169688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mülsch A., Busse R., Liebau S., Förstermann U. LY 83583 interferes with the release of endothelium-derived relaxing factor and inhibits soluble guanylate cyclase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Oct;247(1):283–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mülsch A., Böhme E., Busse R. Stimulation of soluble guanylate cyclase by endothelium-derived relaxing factor from cultured endothelial cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Mar 17;135(2):247–250. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90620-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mülsch A., Lückhoff A., Pohl U., Busse R., Bassenge E. LY 83583 (6-anilino-5,8-quinolinedione) blocks nitrovasodilator-induced cyclic GMP increases and inhibition of platelet activation. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;340(1):119–125. doi: 10.1007/BF00169217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ashton D. S., Moncada S. Vascular endothelial cells synthesize nitric oxide from L-arginine. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):664–666. doi: 10.1038/333664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Rees D. D., Ashton D. S., Moncada S. L-arginine is the physiological precursor for the formation of nitric oxide in endothelium-dependent relaxation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 30;153(3):1251–1256. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81362-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radomski M. W., Palmer R. M., Moncada S. An L-arginine/nitric oxide pathway present in human platelets regulates aggregation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(13):5193–5197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.13.5193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport R. M., Murad F. Agonist-induced endothelium-dependent relaxation in rat thoracic aorta may be mediated through cGMP. Circ Res. 1983 Mar;52(3):352–357. doi: 10.1161/01.res.52.3.352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Hodson H. F., Moncada S. A specific inhibitor of nitric oxide formation from L-arginine attenuates endothelium-dependent relaxation. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Feb;96(2):418–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11833.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimele T. J., Sturm R. J., Adams L. M., Henry D. E., Heaslip R. J., Weichman B. M., Grimes D. Interaction of neutrophils with vascular smooth muscle: identification of a neutrophil-derived relaxing factor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Apr;245(1):102–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakuma I., Stuehr D. J., Gross S. S., Nathan C., Levi R. Identification of arginine as a precursor of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8664–8667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvemini D., Korbut R., Anggård E., Vane J. R. Lipopolysaccharide increases release of a nitric oxide-like factor from endothelial cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov 14;171(1):135–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90437-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvemini D., Korbut R., Anggård E., Vane J. Immediate release of a nitric oxide-like factor from bovine aortic endothelial cells by Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2593–2597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvemini D., Masini E., Anggard E., Mannaioni P. F., Vane J. Synthesis of a nitric oxide-like factor from L-arginine by rat serosal mast cells: stimulation of guanylate cyclase and inhibition of platelet aggregation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jun 15;169(2):596–601. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90372-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller M. D., Waeber B., Nussberger J., Brunner H. R. Angiotensin II, vasopressin, and sympathetic activity in conscious rats with endotoxemia. Am J Physiol. 1985 Dec;249(6 Pt 2):H1086–H1092. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1985.249.6.H1086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuehr D. J., Kwon N. S., Gross S. S., Thiel B. A., Levi R., Nathan C. F. Synthesis of nitrogen oxides from L-arginine by macrophage cytosol: requirement for inducible and constitutive components. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jun 15;161(2):420–426. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92615-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi I., Hatake K., Kakishita E., Nagai K. Diminution of contractile response of the aorta from endotoxin-injected rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep 2;141(1):117–122. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90417-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood K. S., Buga G. M., Byrns R. E., Ignarro L. J. Vascular smooth muscle-derived relaxing factor (MDRF) and its close similarity to nitric oxide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 16;170(1):80–88. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91243-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


