Abstract
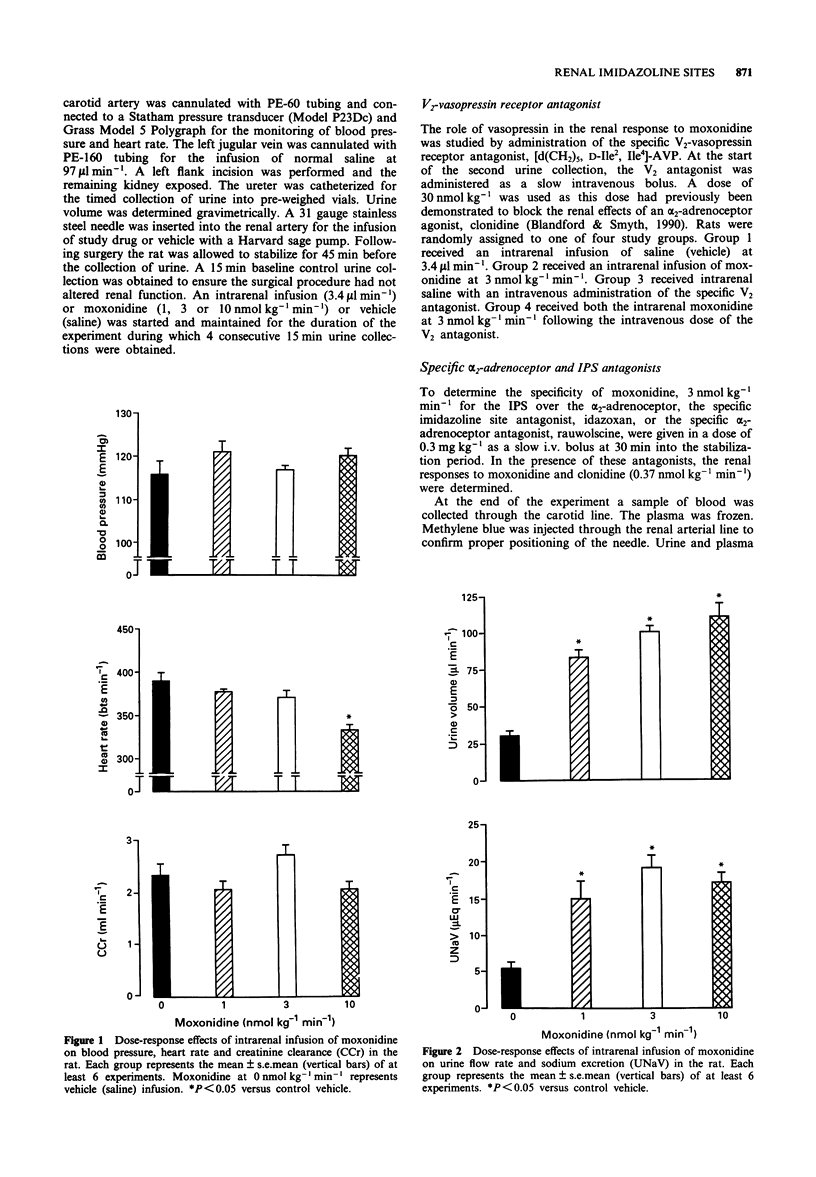
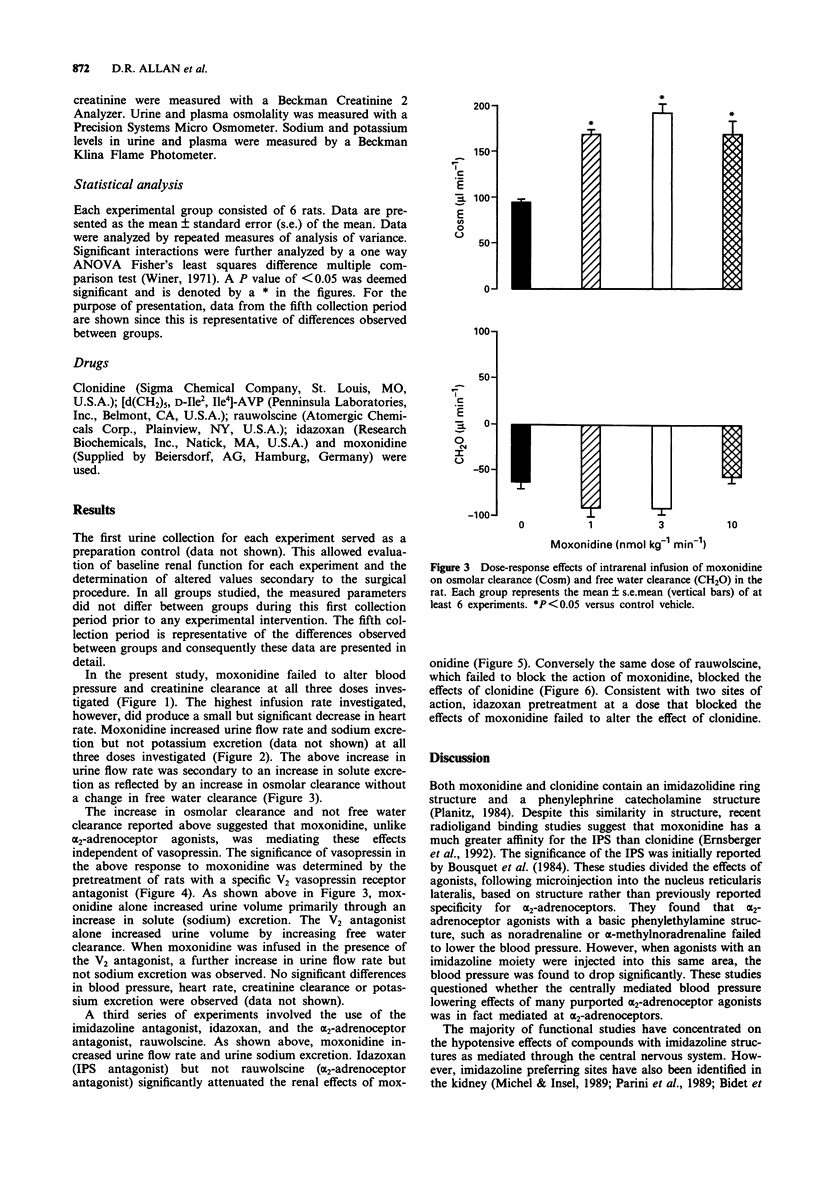
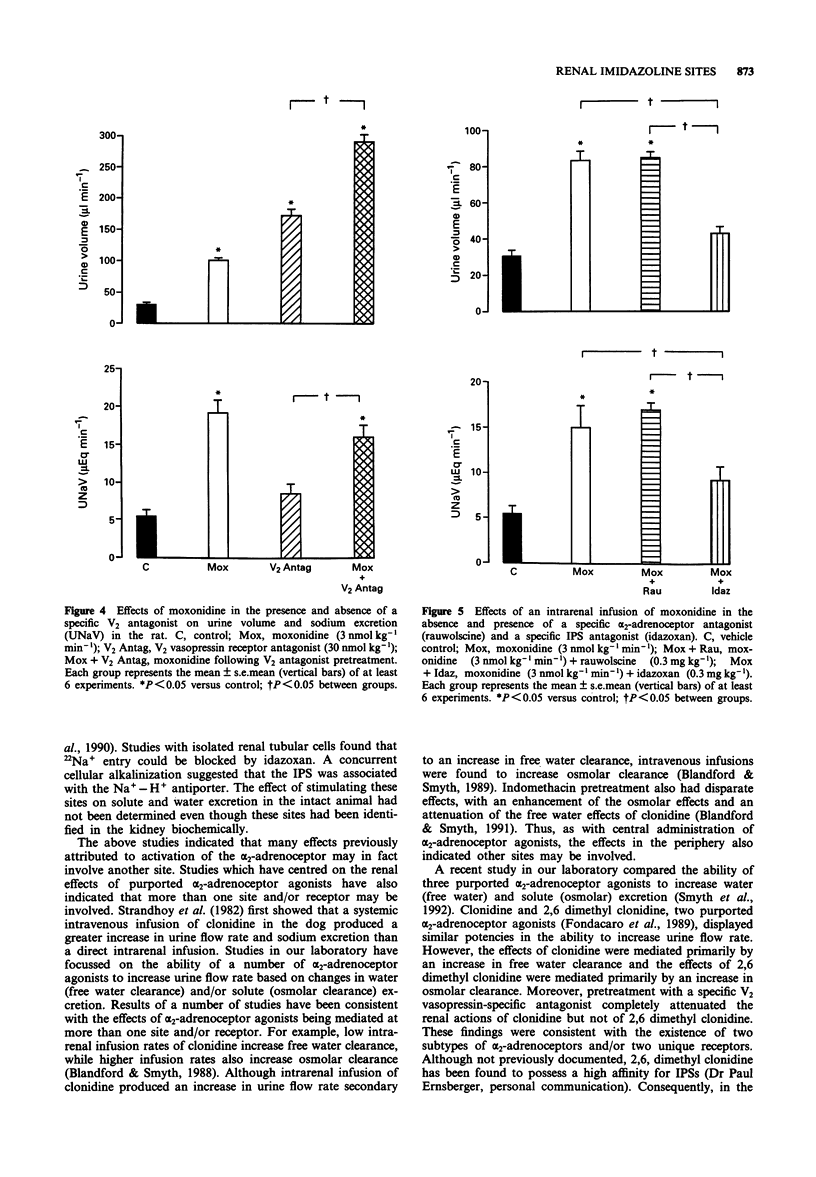
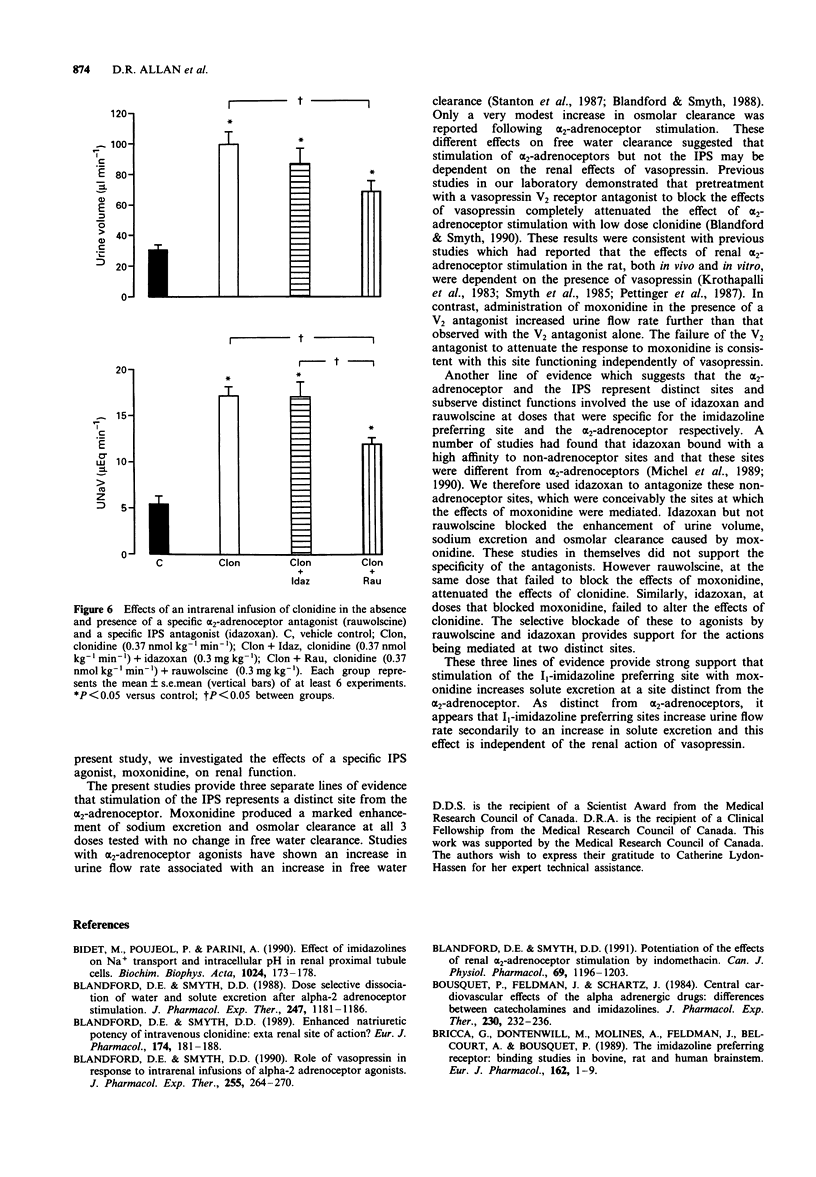
1. Moxonidine has been found to have an approximately 600 fold greater affinity for I1 imidazoline preferring sites as compared to alpha 2-adrenoceptors in the rat kidney. The effects of an intrarenal infusion of moxonidine in an anaesthetized rat preparation were investigated and contrasted with the effects previously reported for alpha 2-adrenoceptor stimulation. 2. An intrarenal infusion of moxonidine (1, 3 and 10 nmol kg-1 min-1) produced an increase in urine flow rate and sodium excretion. Moxonidine increased urine volume through an increase in osmolar clearance rather than an increase in free water clearance as previously reported for alpha 2-adrenoceptor stimulation. 3. The effects of moxonidine also appeared to be unique from the effects of alpha 2-adrenoceptor stimulation. An imidazoline preferring site specific blocking dose of idazoxan (0.3 mg kg-1), but not an alpha 2-adrenoceptor specific blocking dose of rauwolscine (0.3 mg kg-1) attenuated the renal effects of moxonidine (3 nmol kg-1 min-1). Moreover, unlike alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonists, the effects of moxonidine were not altered by prior treatment with a V2 vasopressin receptor antagonist. 4. These results indicate differences between stimulation of alpha 2-adrenoceptors and I1 imidazoline preferring sites in the rat kidney and suggest a direct physiological function of renal imidazoline preferring sites.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bidet M., Poujeol P., Parini A. Effect of imidazolines on Na+ transport and intracellular pH in renal proximal tubule cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 9;1024(1):173–178. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90221-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blandford D. E., Smyth D. D. Dose selective dissociation of water and solute excretion after renal alpha-2 adrenoceptor stimulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Dec;247(3):1181–1186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blandford D. E., Smyth D. D. Enhanced natriuretic potency of intravenous clonidine: extrarenal site of action? Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec 19;174(2-3):181–188. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blandford D. E., Smyth D. D. Potentiation of the natriuretic effect of clonidine following indomethacin in the rat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;69(8):1196–1203. doi: 10.1139/y91-175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blandford D. E., Smyth D. D. Role of vasopressin in response to intrarenal infusions of alpha-2 adrenoceptor agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Oct;255(1):264–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bousquet P., Feldman J., Schwartz J. Central cardiovascular effects of alpha adrenergic drugs: differences between catecholamines and imidazolines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Jul;230(1):232–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bricca G., Dontenwill M., Molines A., Feldman J., Belcourt A., Bousquet P. The imidazoline preferring receptor: binding studies in bovine, rat and human brainstem. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Mar 14;162(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90597-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernsberger P., Giuliano R., Willette R. N., Granata A. R., Reis D. J. Hypotensive action of clonidine analogues correlates with binding affinity at imidazole and not alpha-2-adrenergic receptors in the rostral ventrolateral medulla. J Hypertens Suppl. 1988 Dec;6(4):S554–S557. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198812040-00174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernsberger P., Giuliano R., Willette R. N., Reis D. J. Role of imidazole receptors in the vasodepressor response to clonidine analogs in the rostral ventrolateral medulla. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Apr;253(1):408–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernsberger P., Meeley M. P., Mann J. J., Reis D. J. Clonidine binds to imidazole binding sites as well as alpha 2-adrenoceptors in the ventrolateral medulla. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jan 28;134(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90125-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernsberger P., Meeley M. P., Reis D. J. An endogenous substance with clonidine-like properties: selective binding to imidazole sites in the ventrolateral medulla. Brain Res. 1988 Feb 16;441(1-2):309–318. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91409-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fondacaro J. D., McCafferty G. P., Kolpak D. C., Smith P. L. Antidiarrheal activity of alpha-2 adrenoceptor agonist SK&F 35886. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Apr;249(1):221–228. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesek F. A., Strandhoy J. W. Dual interactions between alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonists and the proximal Na(+)-H+ exchanger. Am J Physiol. 1990 Mar;258(3 Pt 2):F636–F642. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.258.3.F636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krothapalli R. K., Duffy W. B., Senekjian H. O., Suki W. N. Modulation of the hydro-osmotic effect of vasopressin on the rabbit cortical collecting tubule by adrenergic agents. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):287–294. doi: 10.1172/JCI110968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Brodde O. E., Schnepel B., Behrendt J., Tschada R., Motulsky H. J., Insel P. A. [3H]idazoxan and some other alpha 2-adrenergic drugs also bind with high affinity to a nonadrenergic site. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Mar;35(3):324–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Insel P. A. Are there multiple imidazoline binding sites? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Sep;10(9):342–344. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Regan J. W., Gerhardt M. A., Neubig R. R., Insel P. A., Motulsky H. J. Nonadrenergic [3H]idazoxan binding sites are physically distinct from alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Jan;37(1):65–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parini A., Coupry I., Graham R. M., Uzielli I., Atlas D., Lanier S. M. Characterization of an imidazoline/guanidinium receptive site distinct from the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11874–11878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettinger W. A., Umemura S., Smyth D. D., Jeffries W. B. Renal alpha 2-adrenoceptors and the adenylate cyclase-cAMP system: biochemical and physiological interactions. Am J Physiol. 1987 Feb;252(2 Pt 2):F199–F208. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.252.2.F199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plänitz V. Crossover comparison of moxonidine and clonidine in mild to moderate hypertension. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1984;27(2):147–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00544037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis D. J., Regunathan S., Wang H., Feinstein D. L., Meeley M. P. Imidazoline receptors in the nervous system. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1992;6 (Suppl 1):23S–29S. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.1992.tb00138.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth D. D., Li P., Blandford D. E., Penner S. B. Opposite rank order of potency for alpha-2 adrenoceptor agonists on water and solute excretion in the rat: two sites and/or receptors? J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Jun;261(3):1080–1086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth D. D., Umemura S., Pettinger W. A. Renal nerve stimulation causes alpha 1-adrenoceptor-mediated sodium retention but not alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonism of vasopressin. Circ Res. 1985 Aug;57(2):304–311. doi: 10.1161/01.res.57.2.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton B., Puglisi E., Gellai M. Localization of alpha 2-adrenoceptor-mediated increase in renal Na+, K+, and water excretion. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jun;252(6 Pt 2):F1016–F1021. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.252.6.F1016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strandhoy J. W., Morris M., Buckalew V. M., Jr Renal effects of the antihypertensive, guanabenz, in the dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 May;221(2):347–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


