Abstract
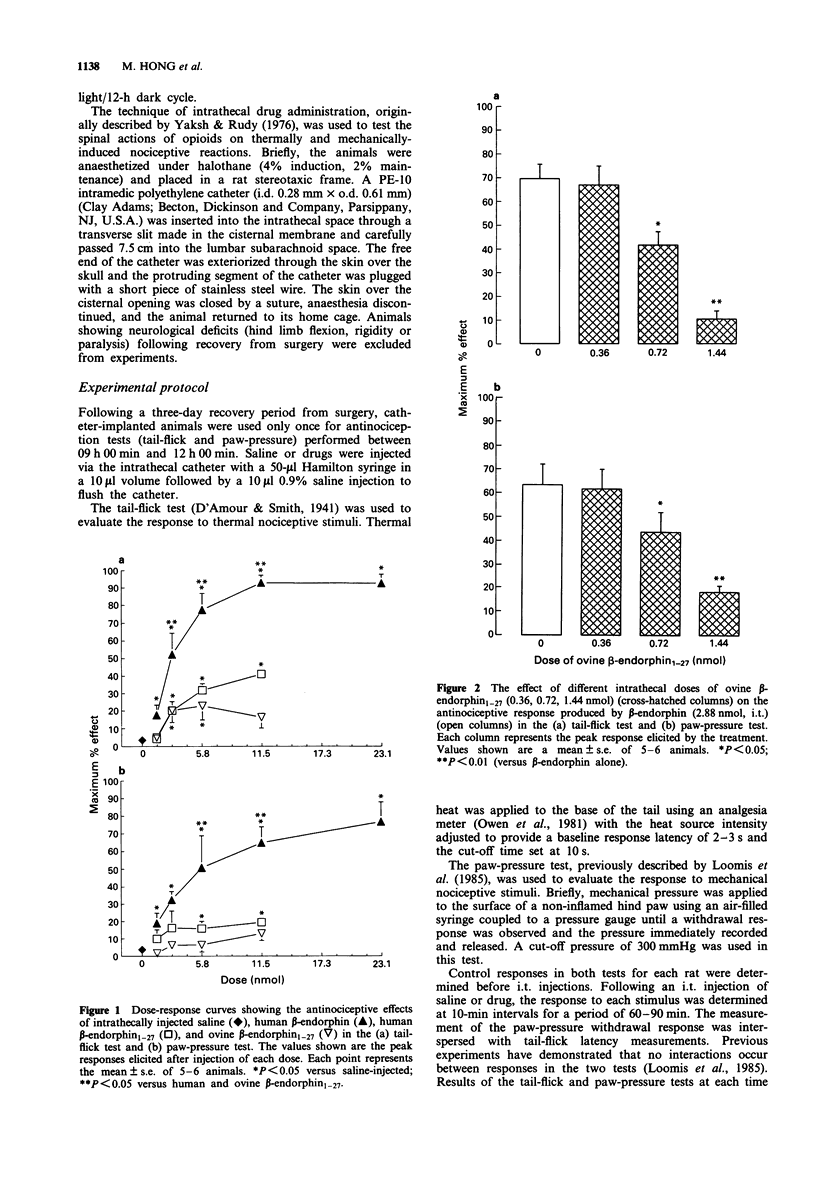
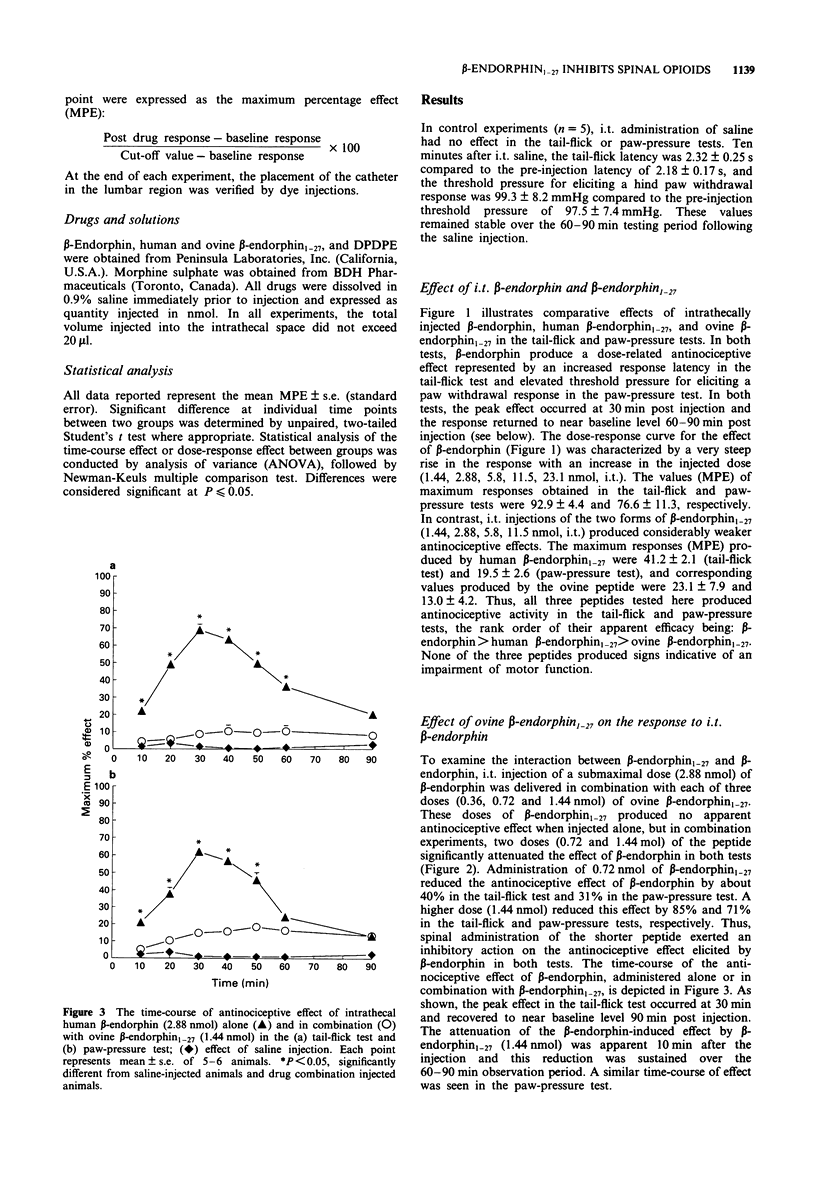
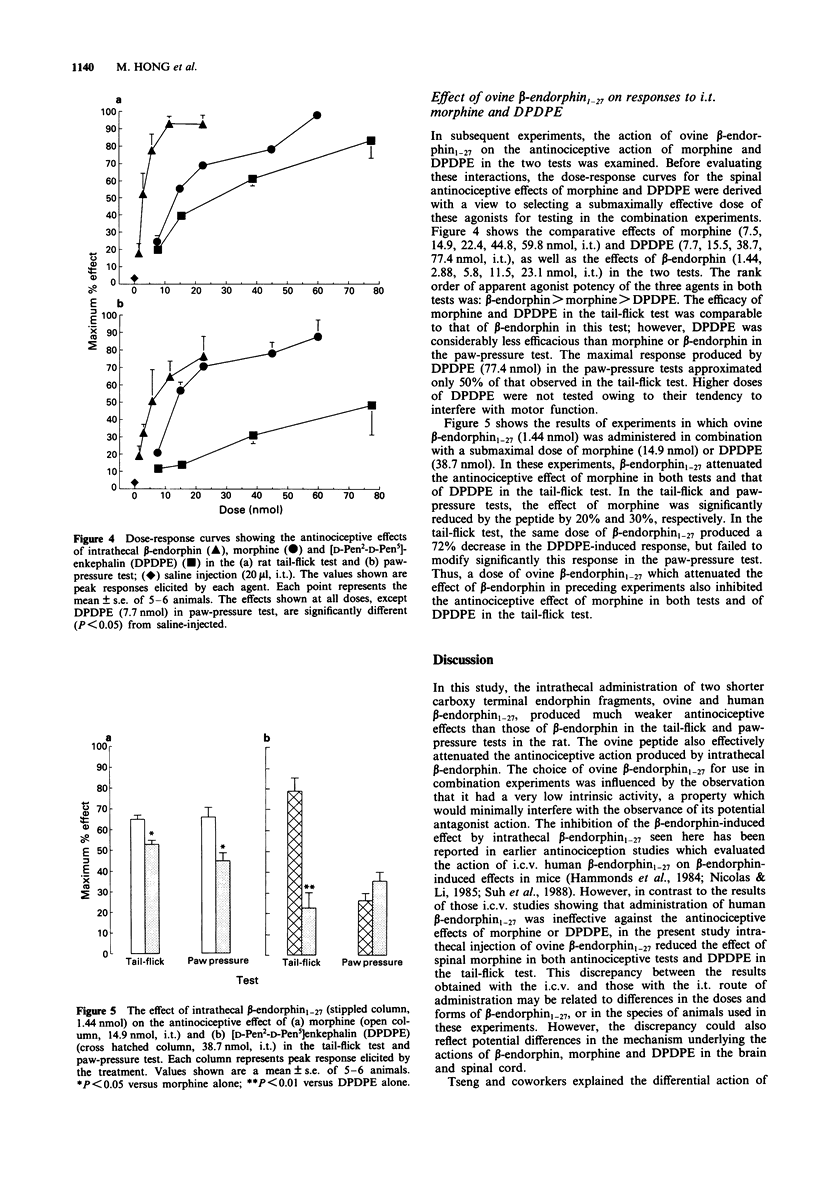
1. The effects of intrathecal (i.t.) administration of beta-endorphin and two shorter fragments, human and ovine beta-endorphin1-27, were examined for antinociceptive activity in the tail-flick and paw-pressure tests in the rat. Additionally, the ability of ovine beta-endorphin1-27 to influence the action of i.t. beta-endorphin, morphine and [D-Pen2-D-Pen5]enkephalin (DPDPE) was also examined in these tests. 2. After i.t. injection, beta-endorphin produced potent dose-related antinociception in the tail-flick and paw-pressure tests. Shorter endorphins produced much weaker effects. The order of antinociceptive efficacy was beta-endorphin > human beta-endorphin1-27 > ovine beta-endorphin1-27. 3. Administration of ovine beta-endorphin1-27 (0.72, 1.44 nmol, i.t.) significantly attenuated the antinociceptive effect of beta-endorphin (2.88 nmol, i.t.) in the tail-flick and paw-pressure tests. 4. Both i.t. morphine and DPDPE produced dose-related antinociception in the tail-flick and paw-pressure tests. The potency of DPDPE was lower than that of morphine in both tests; however, the effect of DPDPE was weaker in the paw-pressure test. 5. Administration of ovine beta-endorphin1-27 (1.44 nmol, i.t.) significantly attenuated the antinociceptive effect of morphine (14.9 nmol, i.t.) in both tests and the effect of DPDPE (38.7 nmol) in the tail-flick test. 6. The results show that beta-endorphin1-27 acts as an opioid antagonist at the spinal level in the rat. Its ability to inhibit the action of morphine and DPDPE suggests that it may attenuate beta-endorphin action by an interaction with mu- and/or delta-opioid receptors.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bals-Kubik R., Herz A., Shippenberg T. S. Beta-endorphin-(1-27) is a naturally occurring antagonist of the reinforcing effects of opioids. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;338(4):392–396. doi: 10.1007/BF00172115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dores R. M., Jain M., Akil H. Characterization of the forms of beta-endorphin and alpha-MSH in the caudal medulla of the rat and guinea pig. Brain Res. 1986 Jul 9;377(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90866-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianoulakis C., Angelogianni P. Characterization of beta-endorphin peptides in the spinal cord of the rat. Peptides. 1989 Sep-Oct;10(5):1049–1054. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(89)90189-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammonds R. G., Jr, Li C. H. Studies on opioid receptor selectivity of beta-endorphin antagonists. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1985 Aug;26(2):118–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1985.tb03188.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammonds R. G., Jr, Nicolas P., Li C. H. beta-endorphin-(1-27) is an antagonist of beta-endorphin analgesia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1389–1390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis C. W., Cervenko F. W., Jhamandas K., Sutak M., Milne B. Analgesia and autonomic function following intrathecal administration of morphine and norepinephrine to the rat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1985 Jun;63(6):656–662. doi: 10.1139/y85-109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight A. T., Corbett A. D., Kosterlitz H. W. Increase in potencies of opioid peptides after peptidase inhibition. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan 21;86(3-4):393–402. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90189-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas P., Li C. H. Beta-endorphin-(1-27) is a naturally occurring antagonist to etorphine-induced analgesia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3178–3181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen J. A., Milne B., Jhamandas K., Nakatsu K. Assembly of an inexpensive tail flick analgesia meter. J Pharmacol Methods. 1981 Aug;6(1):33–37. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(81)90081-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porreca F., Heyman J. S., Mosberg H. I., Omnaas J. R., Vaught J. L. Role of mu and delta receptors in the supraspinal and spinal analgesic effects of [D-Pen2, D-Pen5]enkephalin in the mouse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 May;241(2):393–400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shook J. E., Kazmierski W., Wire W. S., Lemcke P. K., Hruby V. J., Burks T. F. Opioid receptor selectivity of beta-endorphin in vitro and in vivo: mu, delta and epsilon receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Sep;246(3):1018–1025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh H. H., Tseng L. F. Intrathecal beta-funaltrexamine antagonizes intracerebroventricular beta-endorphin- but not morphine-induced analgesia in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 May;245(2):587–593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh H. H., Tseng L. F., Li C. H. Beta-endorphin-(1-27) antagonizes beta-endorphin- but not morphine-, D-Pen2-D-Pen5-enkephalin- and U50, 488H-induced analgesia in mice. Neuropharmacology. 1988 Sep;27(9):957–963. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(88)90124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh H. H., Tseng L. F., Li C. H. Beta-endorphin-(1-27) antagonizes beta-endorphin-induced hypothermia in mice. Peptides. 1987 Jan-Feb;8(1):123–126. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(87)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng L. F., Fujimoto J. M. Differential actions of intrathecal naloxone on blocking the tail-flick inhibition induced by intraventricular beta-endorphin and morphine in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Jan;232(1):74–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng L. F., Higgins M. J., Hong J. S., Hudson P. M., Fujimoto J. M. Release of immunoreactive Met-enkephalin from the spinal cord by intraventricular beta-endorphin but not morphine in anesthetized rats. Brain Res. 1985 Sep 16;343(1):60–69. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91158-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng L. F., Li C. H. beta-Endorphin-(1-27) inhibits the spinal beta-endorphin-induced release of Met-enkephalin. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1986 Apr;27(4):394–397. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1986.tb01033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng L. F., Towell J. F., Fujimoto J. M. Spinal release of immunoreactive Met-enkephalin by intraventricular beta-endorphin and its analogs in anesthetized rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Apr;237(1):65–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsou K., Khachaturian H., Akil H., Watson S. J. Immunocytochemical localization of pro-opiomelanocortin-derived peptides in the adult rat spinal cord. Brain Res. 1986 Jul 16;378(1):28–35. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90283-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüster M., Schulz R., Herz A. Specificity of opioids towards the mu-, delta- and epsilon-opiate receptors. Neurosci Lett. 1979 Dec;15(2-3):193–198. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(79)96112-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaksh T. L., Henry J. L. Antinociceptive effects of intrathecally administered human beta-endorphin in the rat and cat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1978 Oct;56(5):754–759. doi: 10.1139/y78-120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaksh T. L., Rudy T. A. Chronic catheterization of the spinal subarachnoid space. Physiol Behav. 1976 Dec;17(6):1031–1036. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(76)90029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakarian S., Smyth D. G. Distribution of beta-endorphin-related peptides in rat pituitary and brain. Biochem J. 1982 Mar 15;202(3):561–571. doi: 10.1042/bj2020561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



