Abstract
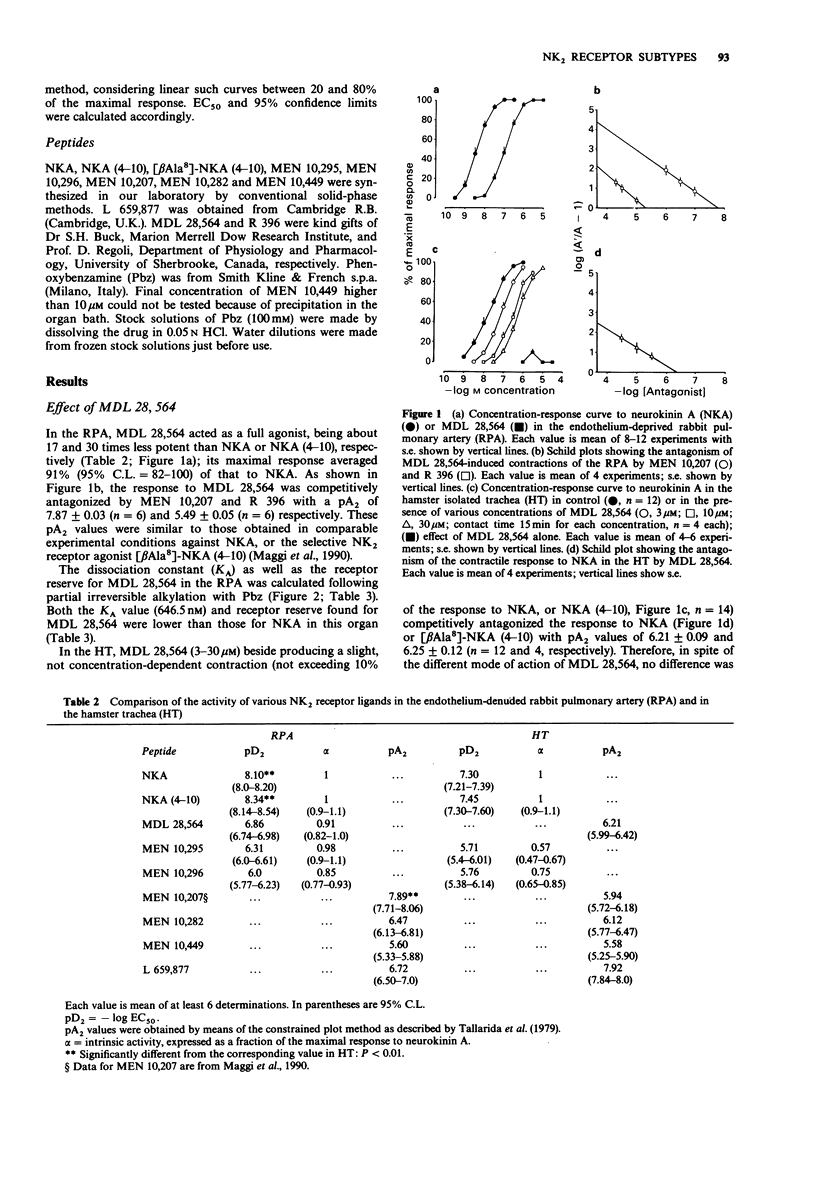
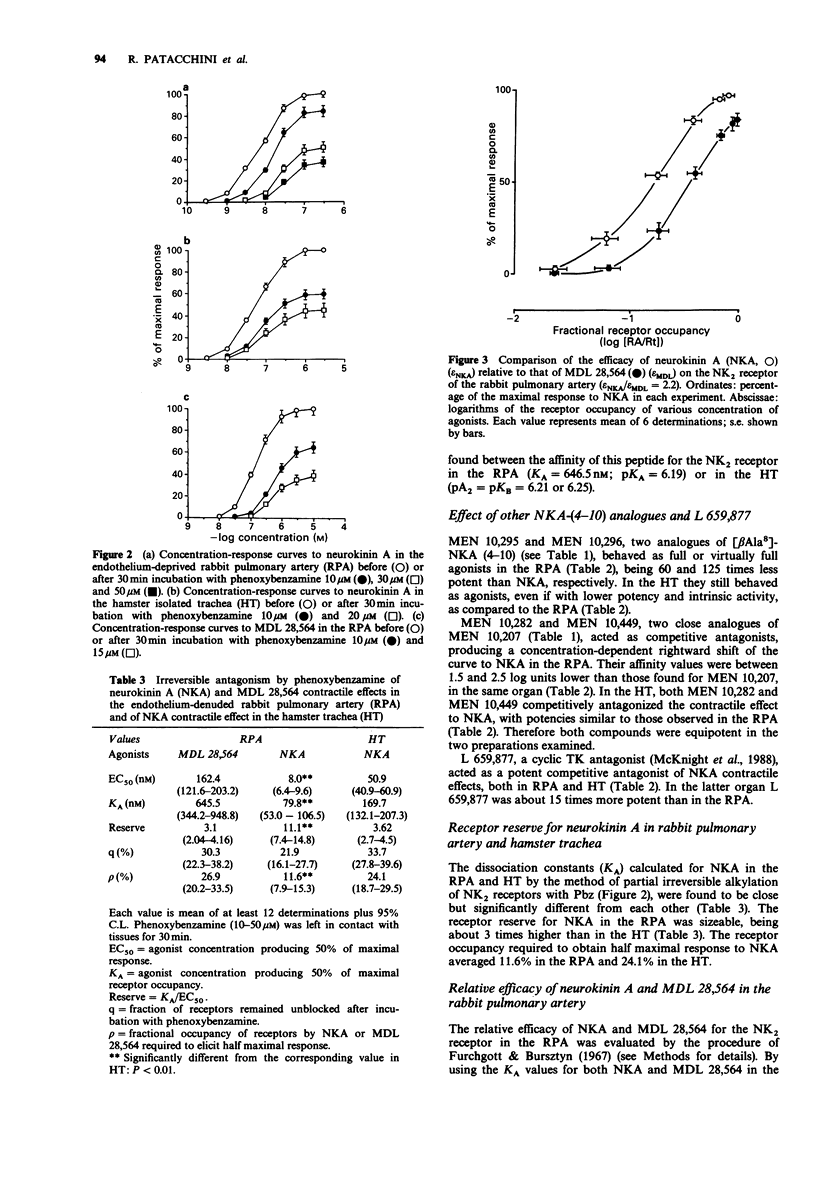
1. We have evaluated the biological activity of a number of neurokinin A (4-10), (NKA (4-10)) analogues in the endothelium-deprived rabbit isolated pulmonary artery (RPA) and hamster isolated trachea (HT), two tissues rich in different NK2 receptor subtypes. 2. MDL 28,564, a pseudopeptide selective for NK2 receptor sites, behaved as a full agonist in the RPA, while in the HT it competitively antagonized NKA or [beta Ala8]-NKA (4-10) contractile effects. 3. The peculiar behaviour of MDL 28,564 in the RPA and HT may be explained neither by a difference in receptor reserve between the two organs (the reserve being three times greater in RPA than in the HT) nor by a different affinity for the two receptor subtypes (identical dissociation constants, pKA or pKB, calculated in the RPA and in the HT). On the other hand, MDL 28,564 displayed a very different intrinsic efficacy for the two receptor subtypes. 4. The novel peptides MEN 10,295 ([Trp7, beta Ala8]-NKA-(4-10)) and MEN 10,296 ([Tyr5, Trp7, beta Ala8]-NKA-(4-10] behaved as weaker agonists than MDL 28,564 in the RPA, but retained appreciable agonist activity also in the HT. 5. The novel peptides: MEN 10,282 ([Tyr5, D-Trp6,8, Trp9, Arg10]-NKA-(4-10], MEN 10,449 ([diI-Try5, D-Trp6,8,9, Arg10]-NKA-(4-10] and the cyclic hexapeptide L 659,877 (cyclo [Leu-Met-Gln-Trp-Phe-Gly]) behaved as competitive antagonists against NKA contractile effects both in the RPA and HT. MEN 10,282 and MEN 10,449 were unable to distinguish between the NK2 receptor subtypes, having almost the same affinity in the two organs.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck S. H., Burcher E. Differential sensitivity to phenoxybenzamine alkylation among types of neurokinin binding sites. Neuropeptides. 1987 Jan;9(1):33–39. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(87)90029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck S. H., Burcher E., Shults C. W., Lovenberg W., O'Donohue T. L. Novel pharmacology of substance K-binding sites: a third type of tachykinin receptor. Science. 1984 Nov 23;226(4677):987–989. doi: 10.1126/science.6095447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck S. H., Pruss R. M., Krstenansky J. L., Robinson P. J., Stauderman K. A. A tachykinin peptide receptor joins an elite club. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Jan;9(1):3–5. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Orléans-Juste P., Dion S., Drapeau G., Regoli D. Different receptors are involved in the endothelium-mediated relaxation and the smooth muscle contraction of the rabbit pulmonary artery in response to substance P and related neurokinins. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Jun 5;125(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90081-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dion S., D'Orléans-Juste P., Drapeau G., Rhaleb N. E., Rouissi N., Tousignant C., Regoli D. Characterization of neurokinin receptors in various isolated organs by the use of selective agonists. Life Sci. 1987 Nov 16;41(20):2269–2278. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90538-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drapeau G., D'Orléans-Juste P., Dion S., Rhaleb N. E., Rouissi N. E., Regoli D. Selective agonists for substance P and neurokinin receptors. Neuropeptides. 1987 Jul;10(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(87)90088-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey A. D., Krause J. E. Molecular characterization of a functional cDNA encoding the rat substance P receptor. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):958–962. doi: 10.1126/science.2154852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. M., Campbell N. J., Williams B. J., Iversen L. L. Multiple tachykinin binding sites in peripheral tissues and in brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Nov 4;130(3):209–217. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90270-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. W., Musacchio J. M. The determination of dissociation constants for substance P and substance P analogues in the guinea pig ileum by pharmacological procedures. Mol Pharmacol. 1983 May;23(3):558–562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Giuliani S., Santicioli P., Regoli D., Meli A. Peripheral effects of neurokinins: functional evidence for the existence of multiple receptors. J Auton Pharmacol. 1987 Mar;7(1):11–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1987.tb00130.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Patacchini R., Giuliani S., Rovero P., Dion S., Regoli D., Giachetti A., Meli A. Competitive antagonists discriminate between NK2 tachykinin receptor subtypes. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;100(3):589–592. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb15851.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maggi C. A., Patacchini R., Rovero P., Meli A. The hamster isolated trachea: a new preparation for studying NK-2 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug 3;166(3):435–440. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90356-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masu Y., Nakayama K., Tamaki H., Harada Y., Kuno M., Nakanishi S. cDNA cloning of bovine substance-K receptor through oocyte expression system. 1987 Oct 29-Nov 4Nature. 329(6142):836–838. doi: 10.1038/329836a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Drapeau G., Dion S., Couture R. New selective agonists for neurokinin receptors: pharmacological tools for receptor characterization. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Aug;9(8):290–295. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Drapeau G., Dion S., D'Orléans-Juste P. Pharmacological receptors for substance P and neurokinins. Life Sci. 1987 Jan 12;40(2):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(87)90349-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoli D., Drapeau G., Dion S., D'Orléans-Juste P. Receptors for substance P and related neurokinins. Pharmacology. 1989;38(1):1–15. doi: 10.1159/000138512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovero P., Pestellini V., Maggi C. A., Patacchini R., Regoli D., Giachetti A. A highly selective NK-2 tachykinin receptor antagonist containing D-tryptophan. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jan 3;175(1):113–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovero P., Pestellini V., Patacchini R., Giuliani S., Santicioli P., Maggi C. A., Meli A., Giachetti A. A potent and selective agonist for NK-2 tachykinin receptor. Peptides. 1989 May-Jun;10(3):593–595. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(89)90148-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tallarida R. J., Cowan A., Adler M. W. pA2 and receptor differentiation: a statistical analysis of competitive antagonism. Life Sci. 1979 Aug 20;25(8):637–654. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90505-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaught J. L., Scott R. W., Jacoby H. I. A differentiation between peripheral and central neurokinin receptors using phenoxybenzamine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Jun 24;125(3):325–331. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90788-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota Y., Sasai Y., Tanaka K., Fujiwara T., Tsuchida K., Shigemoto R., Kakizuka A., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Molecular characterization of a functional cDNA for rat substance P receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17649–17652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Giersbergen P. L., Shatzer S. A., Henderson A. K., Lai J., Nakanishi S., Yamamura H. I., Buck S. H. Characterization of a tachykinin peptide NK2 receptor transfected into murine fibroblast B82 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1661–1665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



