Abstract
1. Flexor withdrawal reflexes to noxious mechanical pinch stimuli were recorded as single motor unit activity in alpha-chloralose anaesthetized rats, by means of tungsten bipolar electrodes inserted percutaneously into hindlimb flexor muscles. The relative spinal and supraspinal contributions to mu- and kappa-opioid agonists in inhibiting these spinal reflexes, together with possible potency changes elicited by surgical trauma, were examined by comparing their relative potencies in spinally unoperated, sham spinalized and spinalized rats. 2. The noxious stimuli, which were of comparable intensity in the three groups, elicited similar mean firing rates of the motor units in all groups. This indicates that the excitability levels in the reflex pathway were not greatly affected by either sham or actual spinalization. 3. The mu-agonists morphine and fentanyl, and the kappa-agonist U-50,488H, inhibited the reflexes in a dose-dependent manner, when administered intravenously in a log2 cumulative dose regime. 4. The surgery of sham spinalization had little effect on the potency of morphine and fentanyl, whereas it doubled the potency of U-50,488. 5. Spinalization did not affect the potency of morphine. In contrast it decreased the potency of fentanyl 2-4 fold and that of U-50,488 approximately 6 fold. 6. The effects of all agonists were antagonized by naloxone. Dose-dependence studies indicating that antagonism of U-50,488H required about 5 times the dose of naloxone that antagonized morphine. 7. The data suggest that surgical trauma to the spinal column and/or dura mater triggers supraspinal mechanisms that significantly enhance the potency of kappa- but not mu-agonists.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

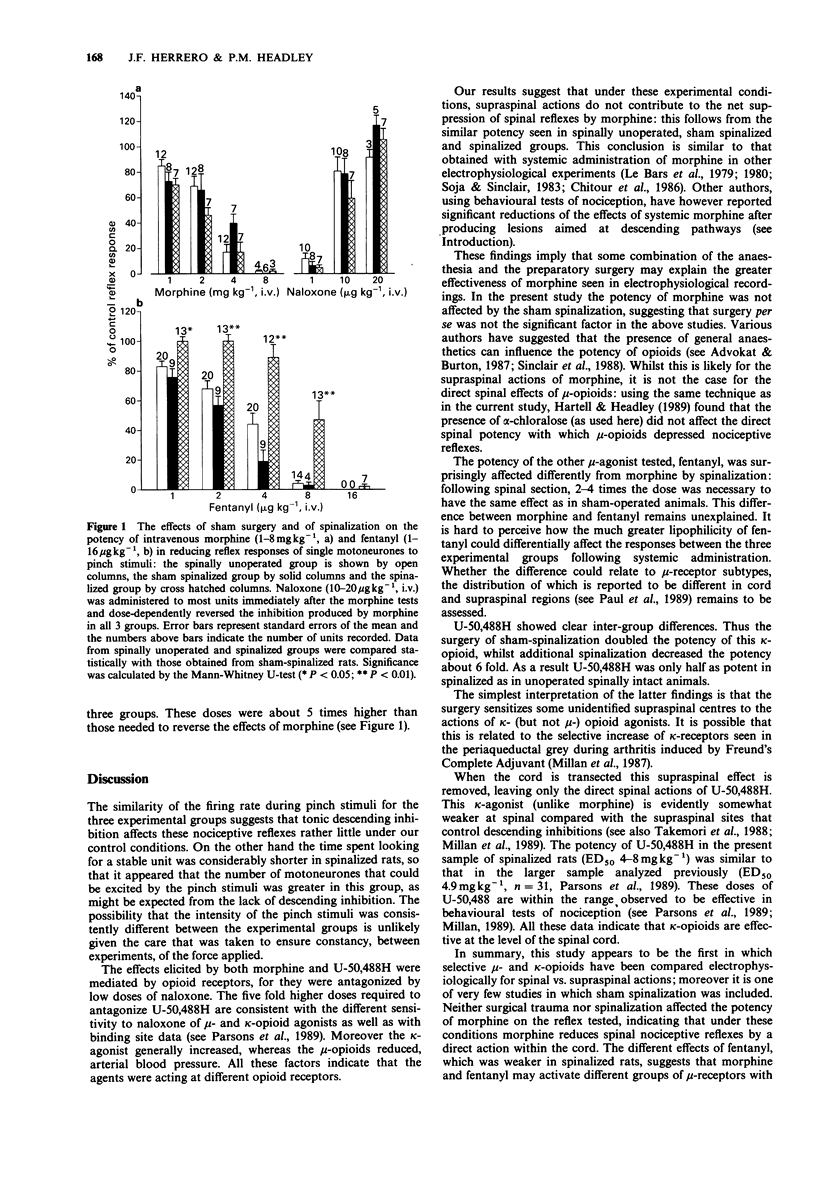
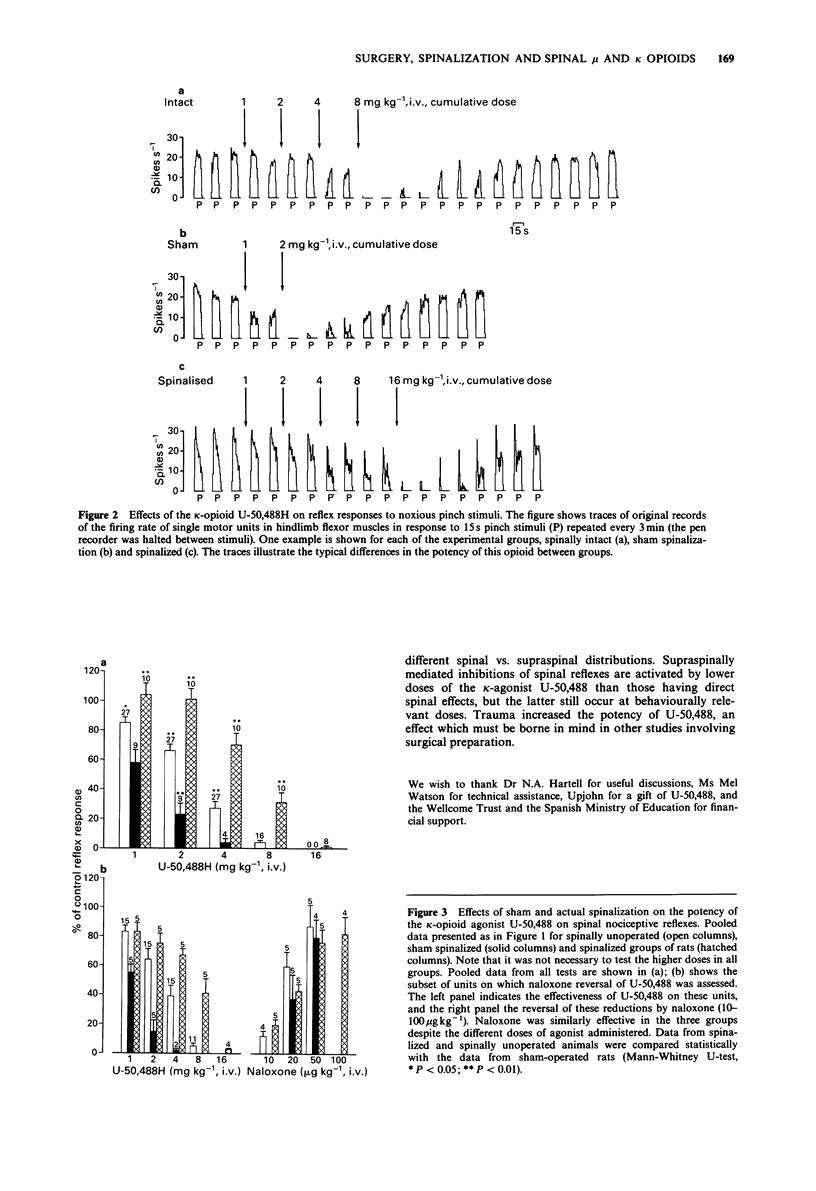

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Advokat C., Burton P. Antinociceptive effect of systemic and intrathecal morphine in spinally transected rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jul 23;139(3):335–343. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90591-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton C., Basbaum A. I., Fields H. L. Dissociation of supraspinal and spinal actions of morphine: a quantitative evaluation. Brain Res. 1980 Apr 28;188(2):487–498. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basbaum A. I., Marley N. J., O'Keefe J., Clanton C. H. Reversal of morphine and stimulus-produced analgesia by subtotal spinal cord lesions. Pain. 1977 Feb;3(1):43–56. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(77)90034-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calthrop J., Hill R. G. The action of K-agonists on the nociceptive responses of neurones in the medullary dorsal horn of the anaesthetized rat. Life Sci. 1983;33 (Suppl 1):541–544. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90560-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chitour D., Villanueva L., Le Bars D. Lesions of dorsolateral funiculi (DLF) do not affect the depressive effects of systemic morphine upon dorsal horn convergent neuronal activities related to pain in the rat. Brain Res. 1986 Jul 9;377(2):397–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90889-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong X. W., Parsons C. G., Headley P. M. Effects of intravenous mu and kappa opioid receptor agonists on sensory responses of convergent neurones in the dorsal horn of spinalized rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 May;103(1):1230–1236. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12329.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartell N. A., Headley P. M. Spinal effects of four injectable anaesthetics on nociceptive reflexes in rats: a comparison of electrophysiological and behavioural measurements. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):563–568. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14121.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes R. L., Price D. D., Bennett G. J., Wilcox G. L., Mayer D. J. Differential effects of spinal cord lesions on narcotic and non-narcotic suppression of nociceptive reflexes: further evidence for the physiologic multiplicity of pain modulation. Brain Res. 1978 Oct 20;155(1):91–101. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90307-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope P. J., Fleetwood-Walker S. M., Mitchell R. Distinct antinociceptive actions mediated by different opioid receptors in the region of lamina I and laminae III-V of the dorsal horn of the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Oct;101(2):477–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12733.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knox R. J., Dickenson A. H. Effects of selective and non-selective kappa-opioid receptor agonists on cutaneous C-fibre-evoked responses of rat dorsal horn neurones. Brain Res. 1987 Jul 7;415(1):21–29. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90265-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bars D., Guilbaud G., Chitour D., Besson J. M. Does systemic morphine increase descending inhibitory controls of dorsal horn neurones involved in nociception? Brain Res. 1980 Nov 24;202(1):223–228. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90659-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bars D., Rivot J. P., Guilbaud G., Menetrey D., Besson J. M. The depressive effects of morphine on the C fibre response of dorsal horn neurones in the spinal rat pretreated or not by pCPA. Brain Res. 1979 Nov 2;176(2):337–353. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90988-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leighton G. E., Rodriguez R. E., Hill R. G., Hughes J. kappa-Opioid agonists produce antinociception after i.v. and i.c.v. but not intrathecal administration in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Mar;93(3):553–560. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb10310.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millan M. J., Członkowski A., Lipkowski A., Herz A. Kappa-opioid receptor-mediated antinociception in the rat. II. Supraspinal in addition to spinal sites of action. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Oct;251(1):342–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millan M. J. Kappa-opioid receptor-mediated antinociception in the rat. I. Comparative actions of mu- and kappa-opioids against noxious thermal, pressure and electrical stimuli. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Oct;251(1):334–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millan M. J. Kappa-opioid receptors and analgesia. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Feb;11(2):70–76. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90321-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millan M. J., Morris B. J., Colpaert F. C., Herz A. A model of chronic pain in the rat: high-resolution neuroanatomical approach identifies alterations in multiple opioid systems in the periaqueductal grey. Brain Res. 1987 Jul 28;416(2):349–353. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90917-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons C. G., Headley P. M. Spinal antinociceptive actions of mu- and kappa-opioids: the importance of stimulus intensity in determining 'selectivity' between reflexes to different modalities of noxious stimulus. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;98(2):523–532. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12626.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons C. G., West D. C., Headley P. M. Spinal antinociceptive actions and naloxone reversibility of intravenous mu- and kappa-opioids in spinalized rats: potency mismatch with values reported for spinal administration. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;98(2):533–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12627.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul D., Bodnar R. J., Gistrak M. A., Pasternak G. W. Different mu receptor subtypes mediate spinal and supraspinal analgesia in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Sep 22;168(3):307–314. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90792-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmauss C., Yaksh T. L. In vivo studies on spinal opiate receptor systems mediating antinociception. II. Pharmacological profiles suggesting a differential association of mu, delta and kappa receptors with visceral chemical and cutaneous thermal stimuli in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Jan;228(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair J. G., Main C. D., Lo G. F. Spinal vs. supraspinal actions of morphine on the rat tail-flick reflex. Pain. 1988 Jun;33(3):357–362. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(88)90296-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soja P. J., Sinclair J. G. Spinal vs supraspinal actions of morphine on cat spinal cord multireceptive neurons. Brain Res. 1983 Aug 22;273(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91087-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens C. W., Yaksh T. L. Dynorphin A and related peptides administered intrathecally in the rat: a search for putative kappa opiate receptor activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Sep;238(3):833–838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemori A. E., Ho B. Y., Naeseth J. S., Portoghese P. S. Nor-binaltorphimine, a highly selective kappa-opioid antagonist in analgesic and receptor binding assays. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Jul;246(1):255–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaksh T. L. Multiple opioid receptor systems in brain and spinal cord: Part 2. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 1984 Sep;1(3):201–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaksh T. L., Noueihed R. The physiology and pharmacology of spinal opiates. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1985;25:433–462. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.25.040185.002245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaksh T. L., Rudy T. A. Studies on the direct spinal action of narcotics in the production of analgesia in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Aug;202(2):411–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



