Abstract
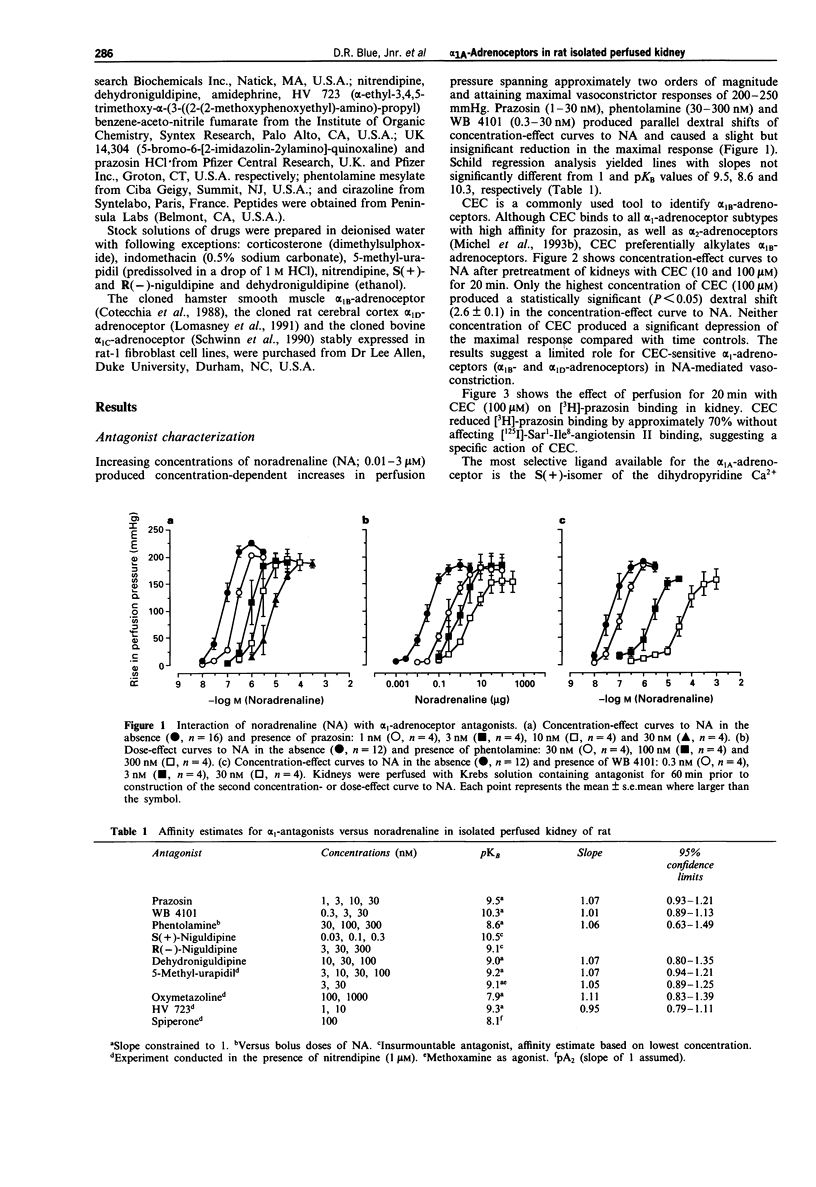
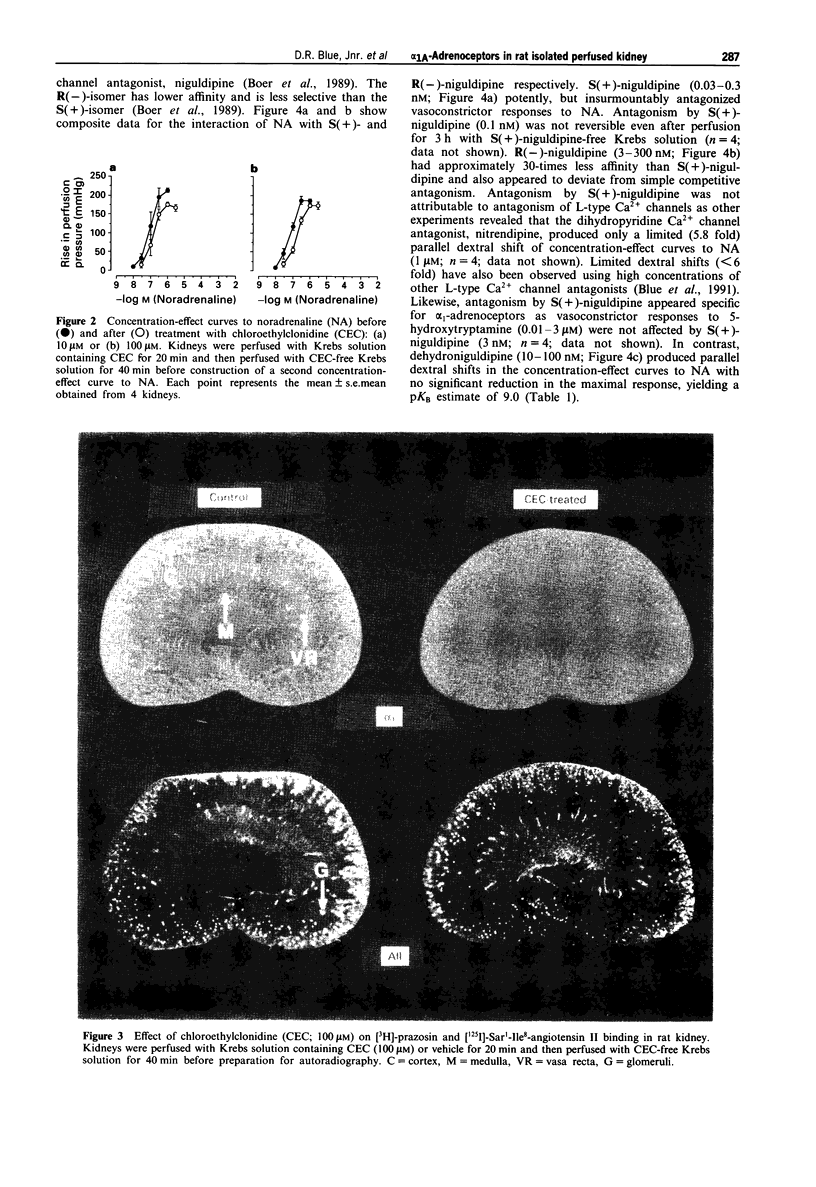
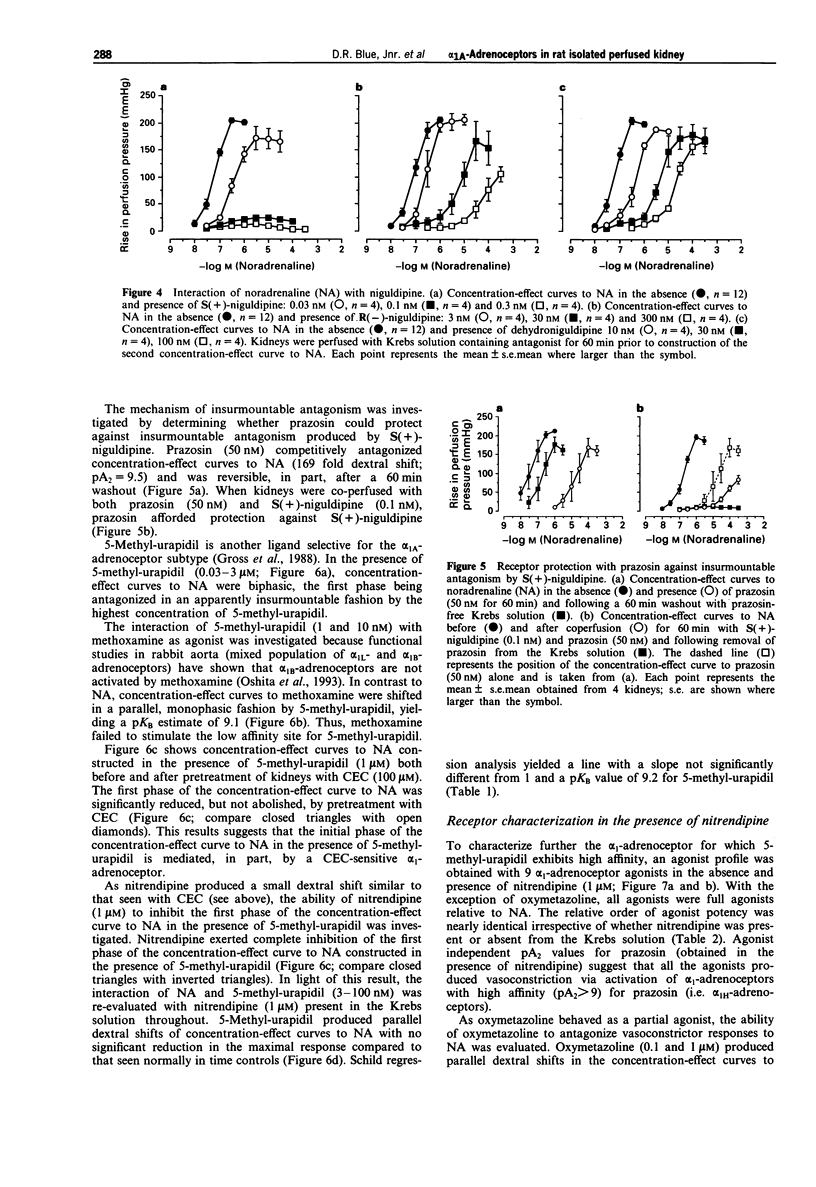
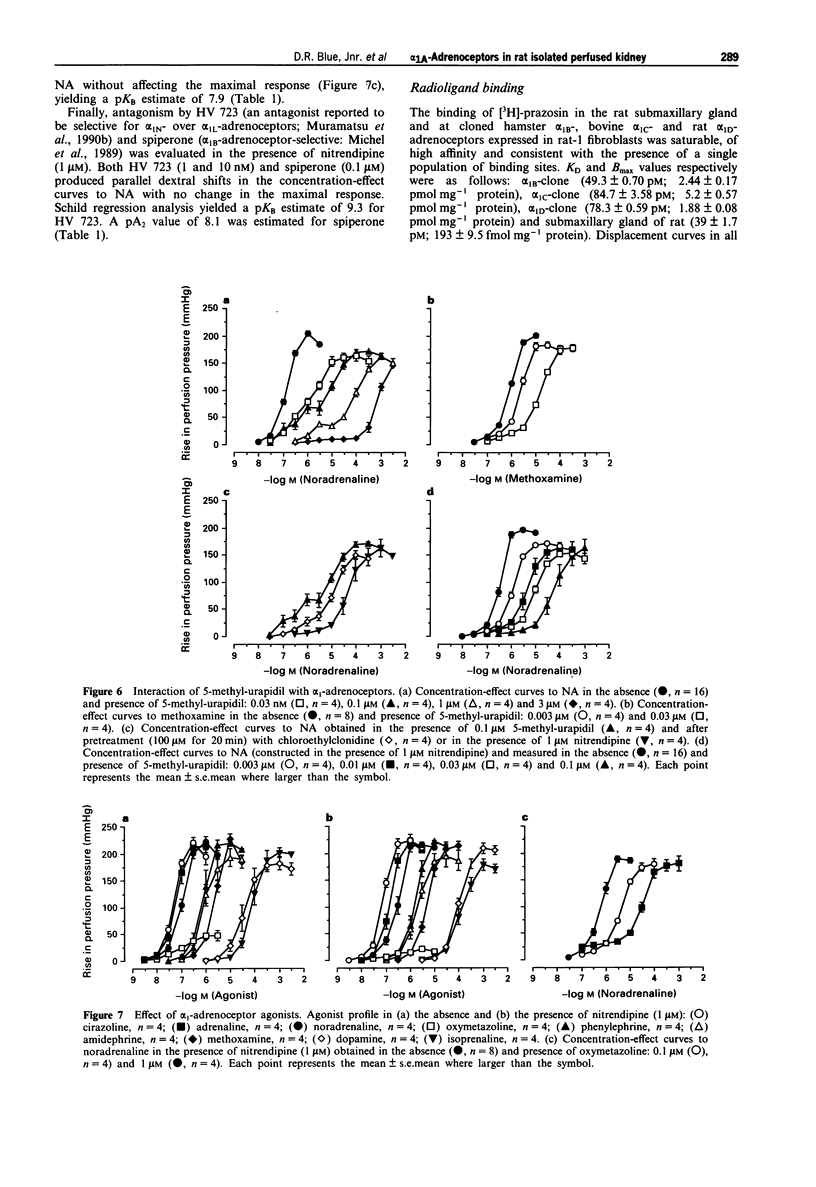
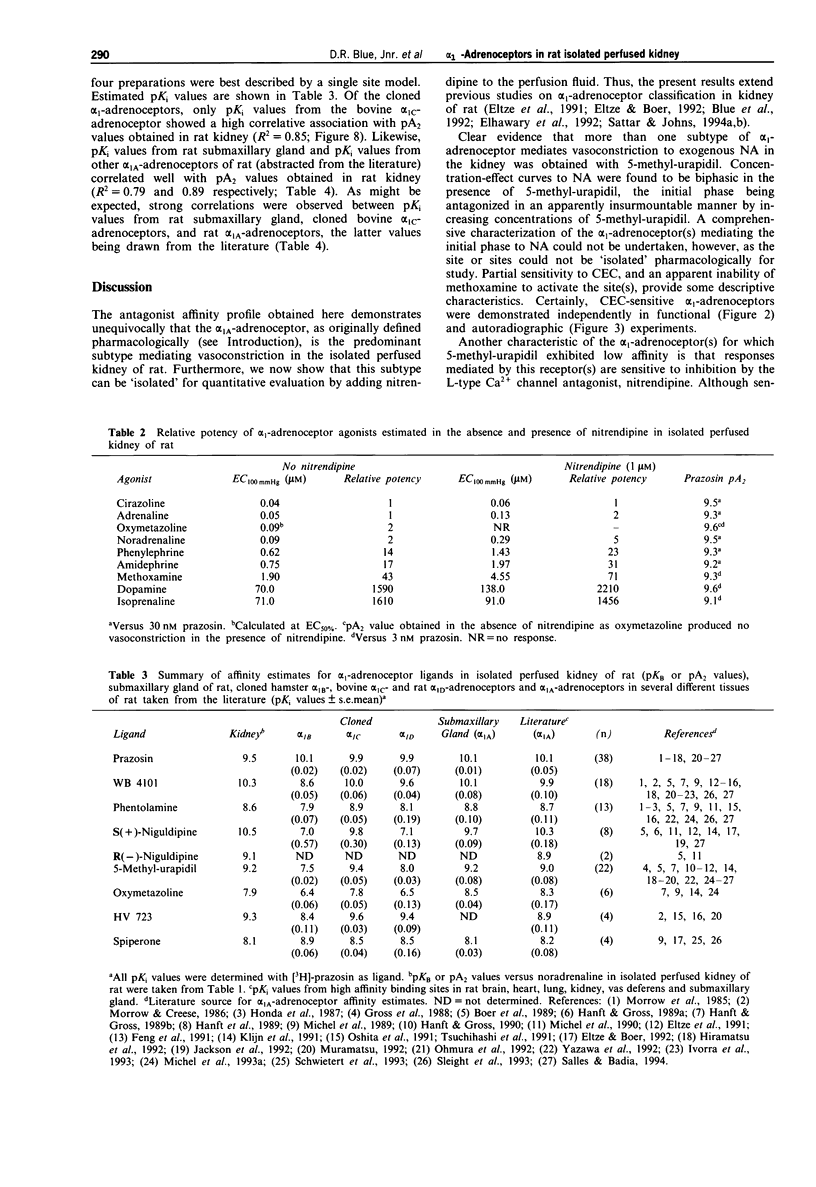
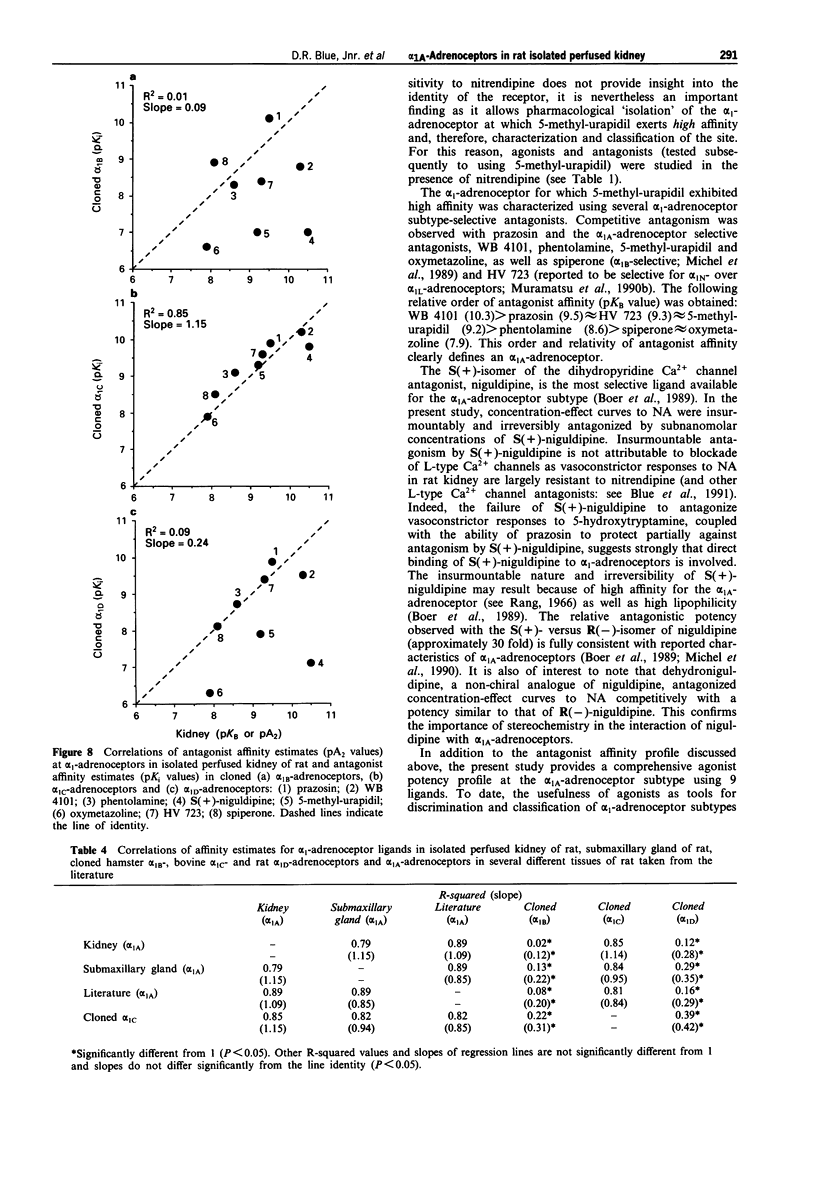
1. The present study characterizes and classifies alpha 1-adrenoceptor-mediated vasoconstriction in the isolated perfused kidney of rat using quantitative receptor pharmacology and compares the results to radioligand binding studies (made in cloned alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes, native alpha 1A-adrenoceptors in submaxillary gland of rat, and alpha 1A-adrenoceptors in several other tissues of rat). 2. Concentration-effect curves to noradrenaline in the presence of 5-methyl-urapidil were biphasic, indicating alpha 1-adrenoceptor heterogeneity. The alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtype mediating the first phase (low affinity for 5-methyl-urapidil) could not be 'isolated' for detailed pharmacological characterization but was defined by a sensitivity to inhibition by chloroethylclonidine and an inability of methoxamine to activate the site. Additionally, vasoconstriction mediated by this alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtype or subtypes was abolished by nitrendipine (1 microM), thereby allowing characterization of the second, high affinity site for 5-methyl-urapidil. 3. The following antagonists interacted competitively with noradrenaline at the alpha 1-adrenoceptor for which 5-methyl-urapidil exhibits high affinity (pKB value): WB 4101 (10.3) > prazosin (9.5) approximately HV 723 (9.3) approximately 5-methyl-urapidil (9.2) > phenotolamine (8.6) > spiperone (pA2 = 8.1) approximately oxymetazoline (7.9). In contrast, insurmountable antagonism was seen with S(+)- and R(-)-niguldipine, the S(+)-isomer being approximately 30 fold more potent than the R(-)-isomer. Receptor protection experiments indicated that S(+)-niguldipine interacted directly with alpha 1-adrenoceptors. Dehydroniguldipine acted as a competitive antagonist (pKB = 9.0). Thus, the results with antagonists define the alpha 1-adrenoceptor as an alpha 1A-adrenoceptor. 4. An agonist 'fingerprint' was constructed in the presence of nitrendipine to define further the alpha 1A-adrenoceptor. The following order and relativity of agonist potency was obtained: cirazoline (1) approximately adrenaline (2) > noradrenaline (5) > phenylephrine (23) approximately amidephrine (31) > methoxamine (71) >> isoprenaline (1456) approximately dopamine (2210). 5. A high correlative association was shown between the affinity of antagonists obtained functionally in the isolated perfused kidney of rat and pKi values obtained from binding experiments with the cloned bovine alpha 1C-adrenoceptor (R2 = 0.85), native alpha 1A-adrenoceptors in submaxillary gland of rat (R2 = 0.79), and alpha 1A-adrenoceptors from several other tissues of rat (values taken from the literature, R2 = 0.89). 6. The present study demonstrates that the alpha 1A-adrenoceptor is the predominant alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtype mediating vasoconstrictor responses to exogenously administered noradrenaline in the isolated perfused kidney of rat.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdul Sattar M., Johns E. J. Alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes mediating adrenergic vasoconstriction in kidney, one-clip Goldblatt and deoxycorticosterone acetate-salt hypertensive rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1994 Sep;24(3):420–428. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199409000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alonso-Llamazares A., Zamanillo D., Fernández A., Chinchetru M. A., Calvo P. Differential expression of the alpha 1c adrenergic receptor subtype in rat tissues. Neuroreport. 1993 Sep 10;4(11):1266–1268. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199309000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blue D. R., Jr, Vimont R. L., Clarke D. E. Evidence for a noradrenergic innervation to alpha 1A-adrenoceptors in rat kidney. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;107(2):414–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb12760.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boer R., Grassegger A., Schudt C., Glossmann H. (+)-Niguldipine binds with very high affinity to Ca2+ channels and to a subtype of alpha 1-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 11;172(2):131–145. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(89)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond R. A., Ornstein A. G., Clarke D. E. Unsurmountable antagonism to 5-hydroxytryptamine in rat kidney results from pseudoirreversible inhibition rather than multiple receptors or allosteric receptor modulation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 May;249(2):401–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B. Heterogeneity of alpha-2 adrenergic receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1985 May;22(5):835–843. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(85)90536-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotecchia S., Schwinn D. A., Randall R. R., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G., Kobilka B. K. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for the hamster alpha 1-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7159–7163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M. What do antagonists tell us about alpha-adrenoceptors? Clin Sci (Lond) 1985;68 (Suppl 10):15s–19s. doi: 10.1042/cs068s015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn W. R., McGrath J. C., Wilson V. G. Expression of functional postjunctional alpha 2-adrenoceptors in rabbit isolated distal saphenous artery--a permissive role for angiotensin II? Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Feb;96(2):259–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11810.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elhawary A. M., Pettinger W. A., Wolff D. W. Subtype-selective alpha-1 adrenoceptor alkylation in the rat kidney and its effect on the vascular pressor response. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Feb;260(2):709–713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eltze M., Boer R., Sanders K. H., Kolassa N. Vasodilatation elicited by 5-HT1A receptor agonists in constant-pressure-perfused rat kidney is mediated by blockade of alpha 1A-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Sep 4;202(1):33–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90250-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eltze M., Boer R. The adrenoceptor agonist, SDZ NVI 085, discriminates between alpha 1A- and alpha 1B-adrenoceptor subtypes in vas deferens, kidney and aorta of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec 2;224(2-3):125–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90796-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eltze M. Characterization of the alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtype mediating contraction of guinea-pig spleen. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Aug 1;260(2-3):211–220. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(94)90339-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faure C., Pimoule C., Arbilla S., Langer S. Z., Graham D. Expression of alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes in rat tissues: implications for alpha 1-adrenoceptor classification. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Jul 15;268(2):141–149. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90183-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng F., Pettinger W. A., Abel P. W., Jeffries W. B. Regional distribution of alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes in rat kidney. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Jul 1;258(1):263–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford A. P., Williams T. J., Blue D. R., Clarke D. E. Alpha 1-adrenoceptor classification: sharpening Occam's razor. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Jun;15(6):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forray C., Bard J. A., Wetzel J. M., Chiu G., Shapiro E., Tang R., Lepor H., Hartig P. R., Weinshank R. L., Branchek T. A. The alpha 1-adrenergic receptor that mediates smooth muscle contraction in human prostate has the pharmacological properties of the cloned human alpha 1c subtype. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Apr;45(4):703–708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross G., Hanft G., Mehdorn H. M. Demonstration of alpha 1A- and alpha 1B-adrenoceptor binding sites in human brain tissue. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Oct 10;169(2-3):325–328. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90032-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross G., Hanft G., Rugevics C. 5-Methyl-urapidil discriminates between subtypes of the alpha 1-adrenoceptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 7;151(2):333–335. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90819-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C. D., Wilson K. M., Minneman K. P. Alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes and formation of inositol phosphates in dispersed hepatocytes and renal cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Jun;37(6):903–910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C., Abel P. W., Minneman K. P. Alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes linked to different mechanisms for increasing intracellular Ca2+ in smooth muscle. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):333–335. doi: 10.1038/329333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanft G., Gross G., Beckeringh J. J., Korstanje C. Alpha 1-adrenoceptors: the ability of various agonists and antagonists to discriminate between two distinct [3H]prazosin binding sites. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1989 Oct;41(10):714–716. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1989.tb06348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanft G., Gross G. Subclassification of alpha 1-adrenoceptor recognition sites by urapidil derivatives and other selective antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;97(3):691–700. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12005.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanft G., Gross G. The effect of reserpine, desipramine and thyroid hormone on alpha 1a- and alpha 1b-adrenoceptor binding sites: evidence for a subtype-specific regulation. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1990;30 (Suppl 1):125S–127S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1990.tb05482.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiramatsu Y., Muraoka R., Kigoshi S., Muramatsu I. 5-Methylurapidil may discriminate between alpha 1-adrenoceptors with a high affinity for WB4101 in rat lung. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Jan;105(1):6–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14200.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holck M. I., Jones C. H., Haeusler G. Differential interactions of clonidine and methoxamine with the postsynaptic alpha-adrenoceptor of rabbit main pulmonary artery. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1983 Mar-Apr;5(2):240–248. doi: 10.1097/00005344-198303000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda K., Nakagawa C., Terai M. Further studies on (+/-)-YM-12617, a potent and selective alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist and its individual optical enantiomers. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1987 Sep;336(3):295–302. doi: 10.1007/BF00172681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivorra D., Gascón S., Vila E., Badia A. Alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes and inositol phosphates production in heart ventricles of spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1993 Jun;21(6):931–936. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199306000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. A., Michel M. C., Insel P. A. Expression of renal alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes in established hypertension. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1992 Jun;19(6):857–862. doi: 10.1097/00005344-199206000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. D., Minneman K. P. Differentiation of alpha 1-adrenergic receptors linked to phosphatidylinositol turnover and cyclic AMP accumulation in rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1987 Mar;31(3):239–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klijn K., Slivka S. R., Bell K., Insel P. A. Renal alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes: MDCK-D1 cells, but not rat cortical membranes possess a single population of receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;39(3):407–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko F. N., Guh J. H., Yu S. M., Hou Y. S., Wu Y. C., Teng C. M. (-)-Discretamine, a selective alpha 1D-adrenoceptor antagonist, isolated from Fissistigma glaucescens. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Aug;112(4):1174–1180. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13207.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohno Y., Saito H., Takita M., Kigoshi S., Muramatsu I. Heterogeneity of alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes involved in adrenergic contractions of dog blood vessels. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Aug;112(4):1167–1173. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13206.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laz T. M., Forray C., Smith K. E., Bard J. A., Vaysse P. J., Branchek T. A., Weinshank R. L. The rat homologue of the bovine alpha 1c-adrenergic receptor shows the pharmacological properties of the classical alpha 1A subtype. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Sep;46(3):414–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomasney J. W., Cotecchia S., Lorenz W., Leung W. Y., Schwinn D. A., Yang-Feng T. L., Brownstein M., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for the alpha 1A-adrenergic receptor. The gene for which is located on human chromosome 5. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6365–6369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. C., Brown C. M., Wilson V. G. Alpha-adrenoceptors: a critical review. Med Res Rev. 1989 Oct-Dec;9(4):407–533. doi: 10.1002/med.2610090403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel A. D., Loury D. N., Whiting R. L. Identification of a single alpha 1-adrenoceptor corresponding to the alpha 1A-subtype in rat submaxillary gland. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):883–889. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14617.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Büscher R., Kerker J., Kraneis H., Erdbrügger W., Brodde O. E. Alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtype affinities of drugs for the treatment of prostatic hypertrophy. Evidence for heterogeneity of chloroethylclonidine-resistant rat renal alpha 1-adrenoceptor. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1993 Oct;348(4):385–395. doi: 10.1007/BF00171338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Hanft G., Gross G. Alpha 1 B- but not alpha 1 A-adrenoceptors mediate inositol phosphate generation. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Apr;341(4):385–387. doi: 10.1007/BF00180666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Insel P. A. Comparison of cloned and pharmacologically defined rat tissue alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1994 Aug;350(2):136–142. doi: 10.1007/BF00241087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Kerker J., Branchek T. A., Forray C. Selective irreversible binding of chloroethylclonidine at alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenoceptor subtypes. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;44(6):1165–1170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow A. L., Battaglia G., Norman A. B., Creese I. Identification of subtypes of [3H]prazosin-labelled alpha 1 receptor binding sites in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb 26;109(2):285–287. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90432-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow A. L., Creese I. Characterization of alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes in rat brain: a reevaluation of [3H]WB4104 and [3H]prazosin binding. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;29(4):321–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu I., Kigoshi S., Oshita M. Two distinct alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes involved in noradrenaline contraction of the rabbit thoracic aorta. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):662–666. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14137.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu I., Ohmura T., Kigoshi S., Hashimoto S., Oshita M. Pharmacological subclassification of alpha 1-adrenoceptors in vascular smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jan;99(1):197–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14678.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmura T., Oshita M., Kigoshi S., Muramatsu I. Identification of alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes in the rat vas deferens: binding and functional studies. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Nov;107(3):697–704. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14509.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshita M., Kigoshi S., Muramatsu I. Pharmacological characterization of two distinct alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes in rabbit thoracic aorta. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Apr;108(4):1071–1076. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13507.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshita M., Kigoshi S., Muramatsu I. Three distinct binding sites for [3H]-prazosin in the rat cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;104(4):961–965. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12533.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. T., Chari R. S., Berkowitz D. E., Meyers W. C., Schwinn D. A. Expression of alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtype mRNA in rat tissues and human SK-N-MC neuronal cells: implications for alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtype classification. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Aug;46(2):221–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P. The kinetics of action of acetylcholine antagonists in smooth muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1966 Apr 19;164(996):488–510. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1966.0045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees S. A., Curtis M. J. Selective IK blockade as an antiarrhythmic mechanism: effects of UK66,914 on ischaemia and reperfusion arrhythmias in rat and rabbit hearts. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jan;108(1):139–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13453.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rokosh D. G., Bailey B. A., Stewart A. F., Karns L. R., Long C. S., Simpson P. C. Distribution of alpha 1C-adrenergic receptor mRNA in adult rat tissues by RNase protection assay and comparison with alpha 1B and alpha 1D. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 May 16;200(3):1177–1184. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sallés J., Badia A. Selective enrichment with alpha 1A- and alpha 1B-adrenoceptor subtypes in rat brain cortical membranes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Feb 15;266(3):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90140-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattar M. A., Johns E. J. Evidence for an alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtype mediating adrenergic vasoconstriction in Wistar normotensive and stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rat kidney. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1994 Feb;23(2):232–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J. M., Graham R. M., Sagalowsky A., Pettinger W. A. Renal alpha-1 and alpha-2 adrenergic receptors: biochemical and pharmacological correlations. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Nov;219(2):400–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwinn D. A., Lomasney J. W., Lorenz W., Szklut P. J., Fremeau R. T., Jr, Yang-Feng T. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Cotecchia S. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for a novel alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtype. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8183–8189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwinn D. A., Lomasney J. W. Pharmacologic characterization of cloned alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes: selective antagonists suggest the existence of a fourth subtype. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec 1;227(4):433–436. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(92)90162-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleight A. J., Koek W., Bigg D. C. Binding of antipsychotic drugs at alpha 1A- and alpha 1B-adrenoceptors: risperidone is selective for the alpha 1B-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul 20;238(2-3):407–410. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90876-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchihashi H., Maruyama K., Baba S., Mano F., Kinami J., Nagatomo T. Comparison of alpha 1-adrenoceptors between rat brain and spleen. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;56(4):523–530. doi: 10.1254/jjp.56.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T. J., Clarke D. E. Characterization of alpha 1-adrenoceptors mediating vasoconstriction to noradrenaline and nerve stimulation in the isolated perfused mesentery of rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Jan;114(2):531–536. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb13259.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. M., Minneman K. P. Different pathways of [3H]inositol phosphate formation mediated by alpha 1a- and alpha 1b-adrenergic receptors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17601–17606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yazawa H., Takanashi M., Sudoh K., Inagaki O., Honda K. Characterization of [3H]YM617, R-(-)-5-[2-[[2[ethoxyring(n)-3H](o-ethoxyphenoxy)ethyl]amino]- propyl]-2-methoxybenzenesulfonamide HCl, a potent and selective alpha-1 adrenoceptor radioligand. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Oct;263(1):201–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]