Abstract
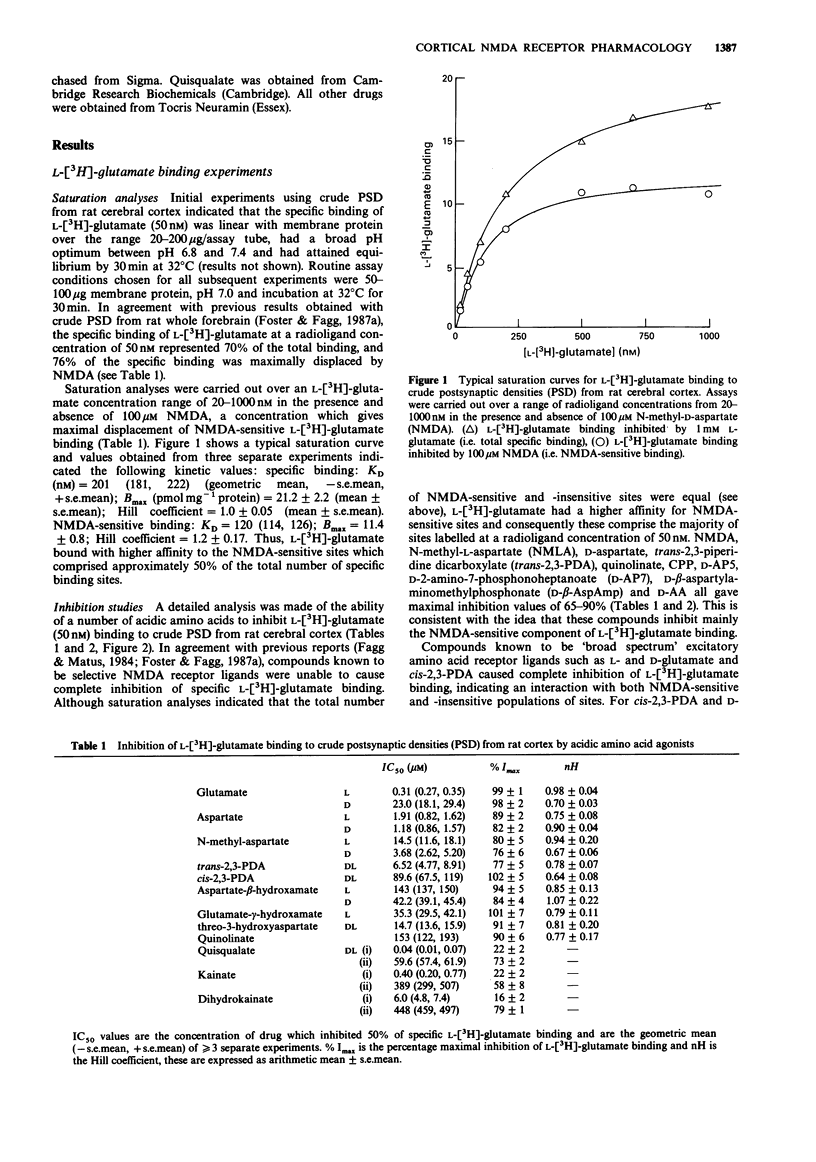
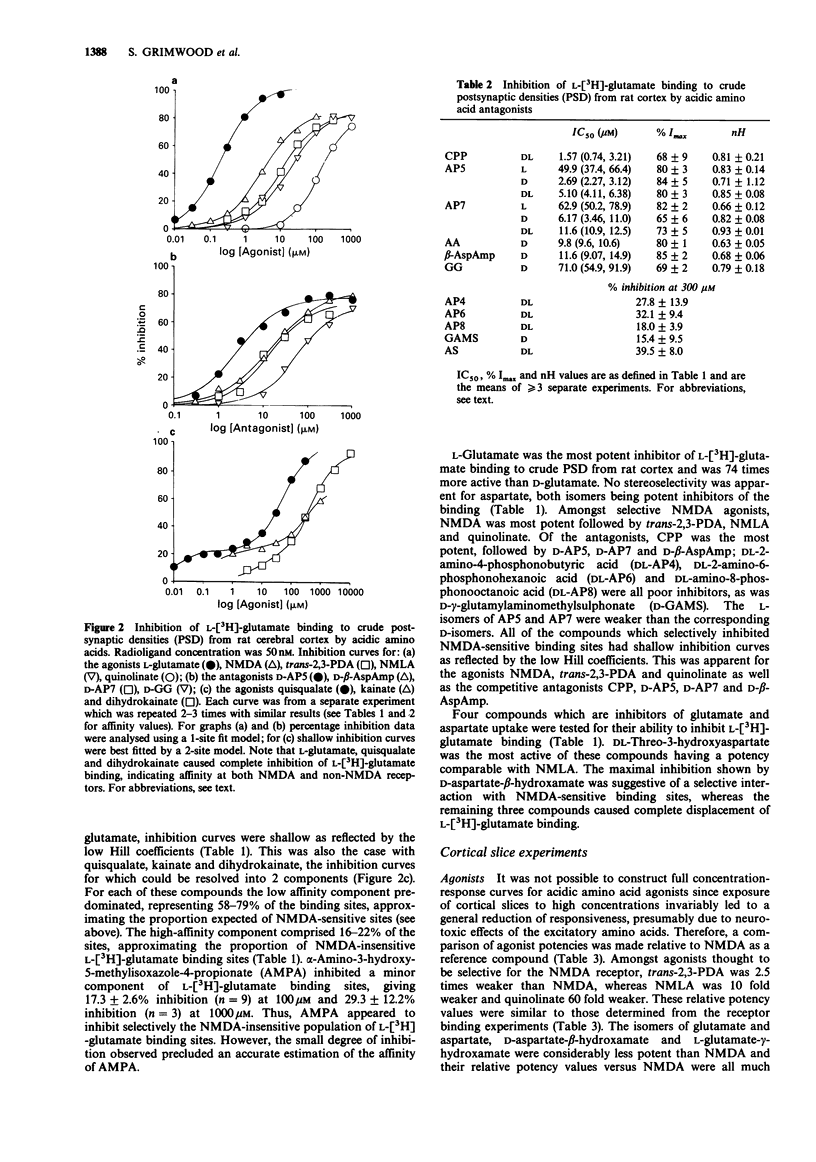
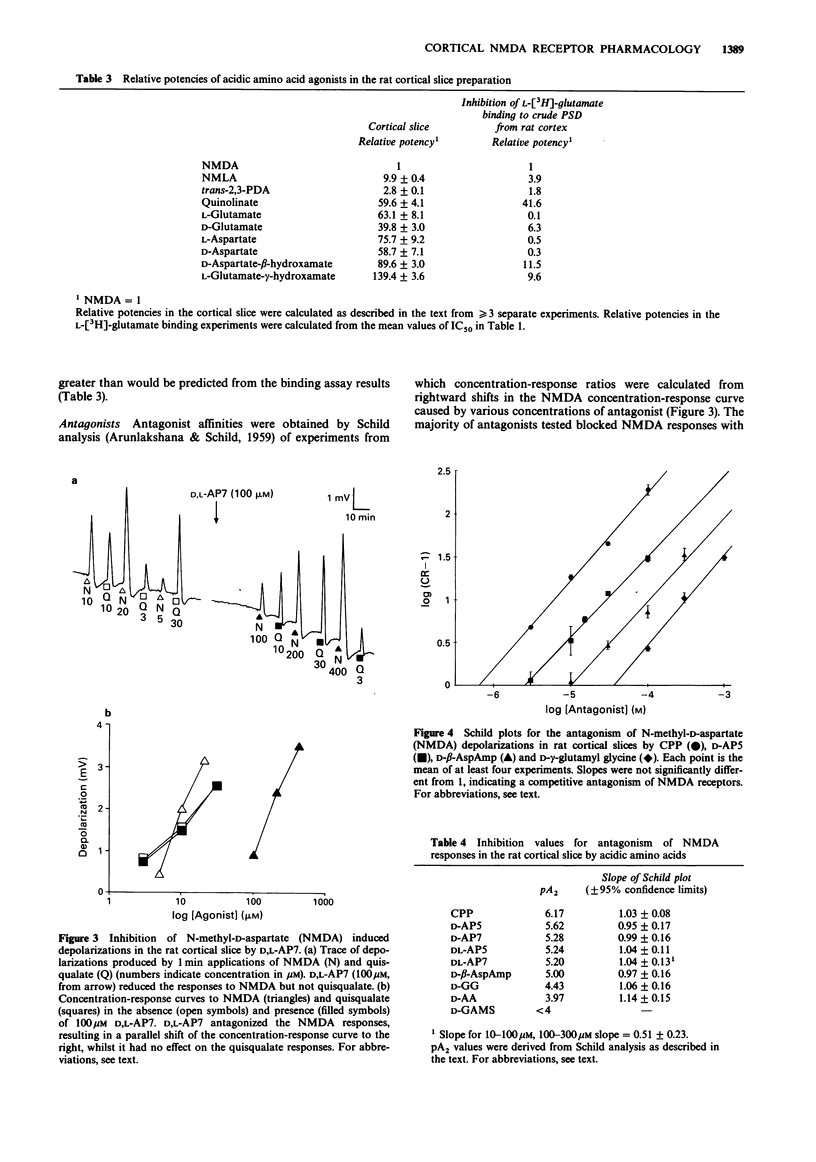
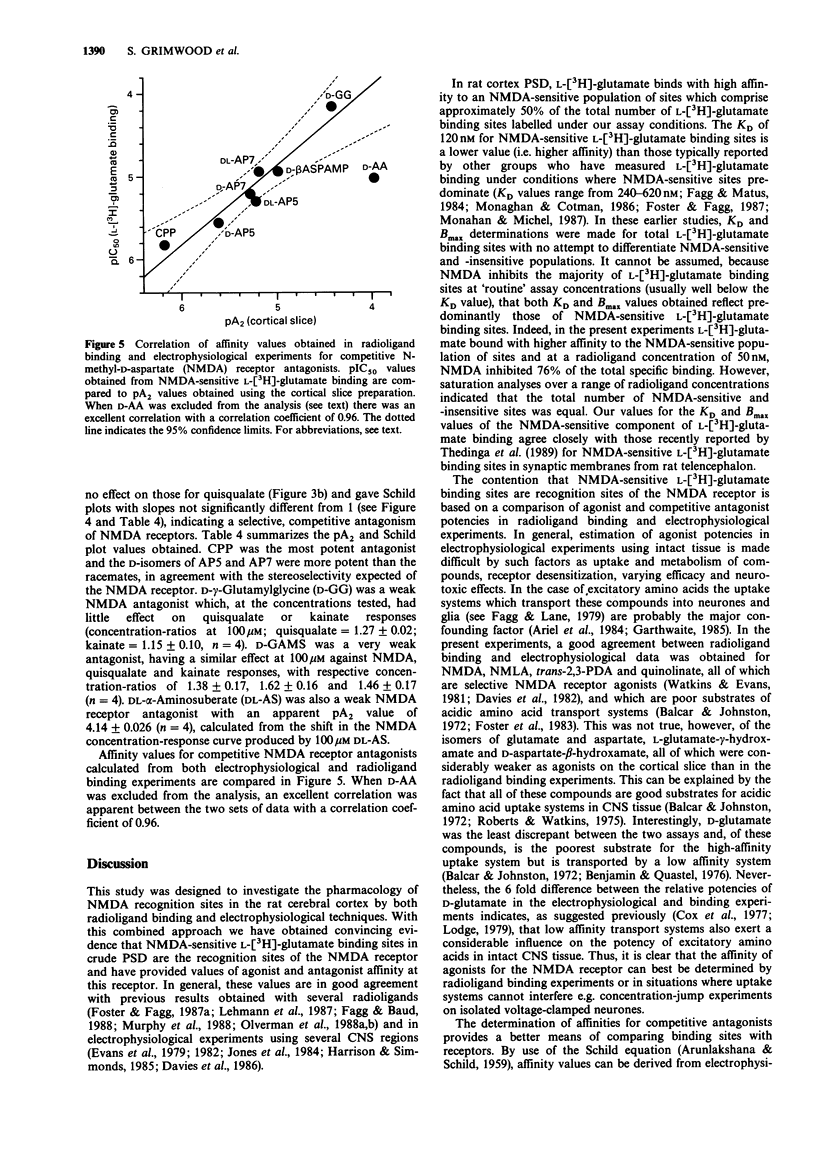
1. The pharmacological specificity of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors has been investigated in the rat cerebral cortex by use of radioligand binding and electrophysiological techniques. 2. A comparison was made between a functional assay (NMDA-induced depolarizations in a rat cortical slice preparation) and NMDA-sensitive L-[3H]-glutamate binding in the same brain region and species, to provide accurate affinity values for agonists and antagonists at the NMDA recognition site. 3. In a preparation of crude postsynaptic densities (PSD) from rat cortex, L-[3H]-glutamate bound with high affinity to an NMDA-sensitive population of sites with KD (geometric mean (-s.e.mean. + s.e. mean) = 120 (114, 126) nM, Bmax (mean +/- s.e.mean) = 11.4 +/- 0.8 pmol mg-1 protein and Hill coefficient (mean +/- s.e.mean) = 1.2 +/- 0.17 (n = 3). 4. There was a good agreement between the relative affinities in radioligand binding and electrophysiological assays for the receptor agonists NMDA, N-methyl-L-aspartate, quinolinate and trans-2,3-piperidine dicarboxylate, which are poor substrates of acidic amino acid transport systems. However, agonists which are good substrates for high affinity uptake systems (L- and D-glutamate, L- and D-aspartate, D-aspartate-beta-hydroxamate and L-glutamate-gamma-hydroxamate) were much weaker in the electrophysiological experiments.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ariel M., Lasater E. M., Mangel S. C., Dowling J. E. On the sensitivity of H1 horizontal cells of the carp retina to glutamate, aspartate and their agonists. Brain Res. 1984 Mar 12;295(1):179–183. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90828-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balcar V. J., Johnston G. A. The structural specificity of the high affinity uptake of L-glutamate and L-aspartate by rat brain slices. J Neurochem. 1972 Nov;19(11):2657–2666. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1972.tb01325.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin A. M., Quastel J. H. Cerebral uptakes and exchange diffusion in vitro of L- and D-glutamates. J Neurochem. 1976 Mar;26(3):431–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1976.tb01493.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles A. K., Chang Y. F. Uptake, release, and metabolism of D- and L-alpha-aminoadipate by rat cerebral cortex. J Neurochem. 1981 Mar;36(3):1127–1136. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1981.tb01709.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. S., Blomberg F., Berzins K., Siekevitz P. The structure of postsynaptic densities isolated from dog cerebral cortex. I. Overall morphology and protein composition. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jul;74(1):181–203. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.1.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox D. W., Headley M. H., Watkins J. C. Actions of L- and D-homocysteate in rat CNS: a correlation between low-affinity uptake and the time courses of excitation by microelectrophoretically applied L-glutamate analogues. J Neurochem. 1977 Sep;29(3):579–588. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb10707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. J., Skan W. J., Slater P. The association of [3H]D-aspartate binding and high-affinity glutamate uptake in the human brain. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Jan 16;63(2):121–124. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90047-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Evans R. H., Herrling P. L., Jones A. W., Olverman H. J., Pook P., Watkins J. C. CPP, a new potent and selective NMDA antagonist. Depression of central neuron responses, affinity for [3H]D-AP5 binding sites on brain membranes and anticonvulsant activity. Brain Res. 1986 Sep 10;382(1):169–173. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90127-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J., Evans R. H., Jones A. W., Smith D. A., Watkins J. C. Differential activation and blockade of excitatory amino acid receptors in the mammalian and amphibian central nervous systems. Comp Biochem Physiol C. 1982;72(2):211–224. doi: 10.1016/0306-4492(82)90086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Hunt K., Oakes D. J., Watkins J. C. Antagonism of excitatory amino acid-induced responses and of synaptic excitation in the isolated spinal cord of the frog. Br J Pharmacol. 1979 Dec;67(4):591–603. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1979.tb08706.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. H., Francis A. A., Jones A. W., Smith D. A., Watkins J. C. The effects of a series of omega-phosphonic alpha-carboxylic amino acids on electrically evoked and excitant amino acid-induced responses in isolated spinal cord preparations. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;75(1):65–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb08758.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagg G. E., Foster A. C., Mena E. E., Cotman C. W. Chloride and calcium ions separate L-glutamate receptor populations in synaptic membranes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Mar 18;88(1):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90397-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagg G. E., Lane J. D. The uptake and release of putative amino acid neurotransmitters. Neuroscience. 1979;4(8):1015–1036. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(79)90185-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagg G. E., Matus A. Selective association of N-methyl aspartate and quisqualate types of L-glutamate receptor with brain postsynaptic densities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6876–6880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster A. C., Collins J. F., Schwarcz R. On the excitotoxic properties of quinolinic acid, 2,3-piperidine dicarboxylic acids and structurally related compounds. Neuropharmacology. 1983 Dec;22(12A):1331–1342. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(83)90221-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster A. C., Fagg G. E. Comparison of L-[3H]glutamate, D-[3H]aspartate, DL-[3H]AP5 and [3H]NMDA as ligands for NMDA receptors in crude postsynaptic densities from rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jan 20;133(3):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster A. C., Fagg G. E. Neurobiology. Taking apart NMDA receptors. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):395–396. doi: 10.1038/329395a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garthwaite J. Cellular uptake disguises action of L-glutamate on N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. With an appendix: diffusion of transported amino acids into brain slices. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 May;85(1):297–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08860.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison N. L., Simmonds M. A. Quantitative studies on some antagonists of N-methyl D-aspartate in slices of rat cerebral cortex. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb;84(2):381–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb12922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. W., Smith D. A., Watkins J. C. Structure-activity relations of dipeptide antagonists of excitatory amino acids. Neuroscience. 1984 Oct;13(2):573–581. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90250-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann J., Schneider J., McPherson S., Murphy D. E., Bernard P., Tsai C., Bennett D. A., Pastor G., Steel D. J., Boehm C. CPP, a selective N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)-type receptor antagonist: characterization in vitro and in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Mar;240(3):737–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodge D. L-histidine: effects on sensitivity of cat spinal neurones to amino acids. Neurosci Lett. 1979 Oct;14(2-3):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(79)96143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matus A. I., Taff-Jones D. H. Morphology and molecular composition of isolated postsynaptic junctional structures. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1978 Dec 4;203(1151):135–151. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1978.0097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Cotman C. W. Identification and properties of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in rat brain synaptic plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7532–7536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Holets V. R., Toy D. W., Cotman C. W. Anatomical distributions of four pharmacologically distinct 3H-L-glutamate binding sites. Nature. 1983 Nov 10;306(5939):176–179. doi: 10.1038/306176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Olverman H. J., Nguyen L., Watkins J. C., Cotman C. W. Two classes of N-methyl-D-aspartate recognition sites: differential distribution and differential regulation by glycine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9836–9840. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monahan J. B., Michel J. Identification and characterization of an N-methyl-D-aspartate-specific L-[3H]glutamate recognition site in synaptic plasma membranes. J Neurochem. 1987 Jun;48(6):1699–1708. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb05726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. E., Hutchison A. J., Hurt S. D., Williams M., Sills M. A. Characterization of the binding of [3H]-CGS 19755: a novel N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonist with nanomolar affinity in rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;95(3):932–938. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11723.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy D. E., Schneider J., Boehm C., Lehmann J., Williams M. Binding of [3H]3-(2-carboxypiperazin-4-yl)propyl-1-phosphonic acid to rat brain membranes: a selective, high-affinity ligand for N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Mar;240(3):778–784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olverman H. J., Jones A. W., Mewett K. N., Watkins J. C. Structure/activity relations of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor ligands as studied by their inhibition of [3H]D-2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid binding in rat brain membranes. Neuroscience. 1988 Jul;26(1):17–31. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90124-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olverman H. J., Jones A. W., Watkins J. C. L-glutamate has higher affinity than other amino acids for [3H]-D-AP5 binding sites in rat brain membranes. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):460–462. doi: 10.1038/307460a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olverman H. J., Jones A. W., Watkins J. C. [3H]D-2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoate as a ligand for N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the mammalian central nervous system. Neuroscience. 1988 Jul;26(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90123-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olverman H. J., Monaghan D. T., Cotman C. W., Watkins J. C. [3H]CPP, a new competitive ligand for NMDA receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Nov 12;131(1):161–162. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90533-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pin J. P., Bockaert J., Recasesn M. The Ca2+/C1- dependent L-[3H]glutamate binding: a new receptor or a particular transport process? FEBS Lett. 1984 Sep 17;175(1):31–36. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80563-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts P. J., Watkins J. C. Structural requirements for the inhibition for L-glutamate uptake by glia and nerve endings. Brain Res. 1975 Feb 21;85(1):120–125. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)91016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thedinga K. H., Benedict M. S., Fagg G. E. The N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor complex: a stoichiometric analysis of radioligand binding domains. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Sep 25;104(1-2):217–222. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90357-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. C., Evans R. H. Excitatory amino acid transmitters. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1981;21:165–204. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.21.040181.001121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


