Abstract
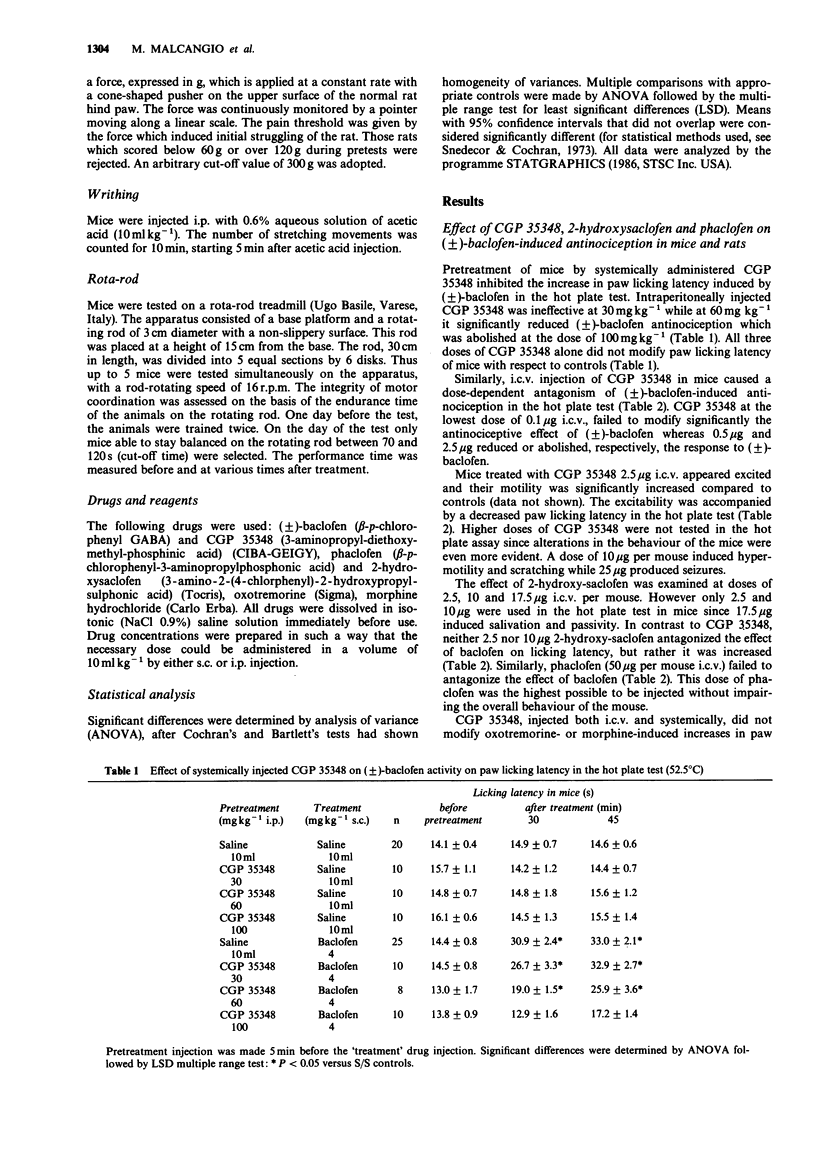
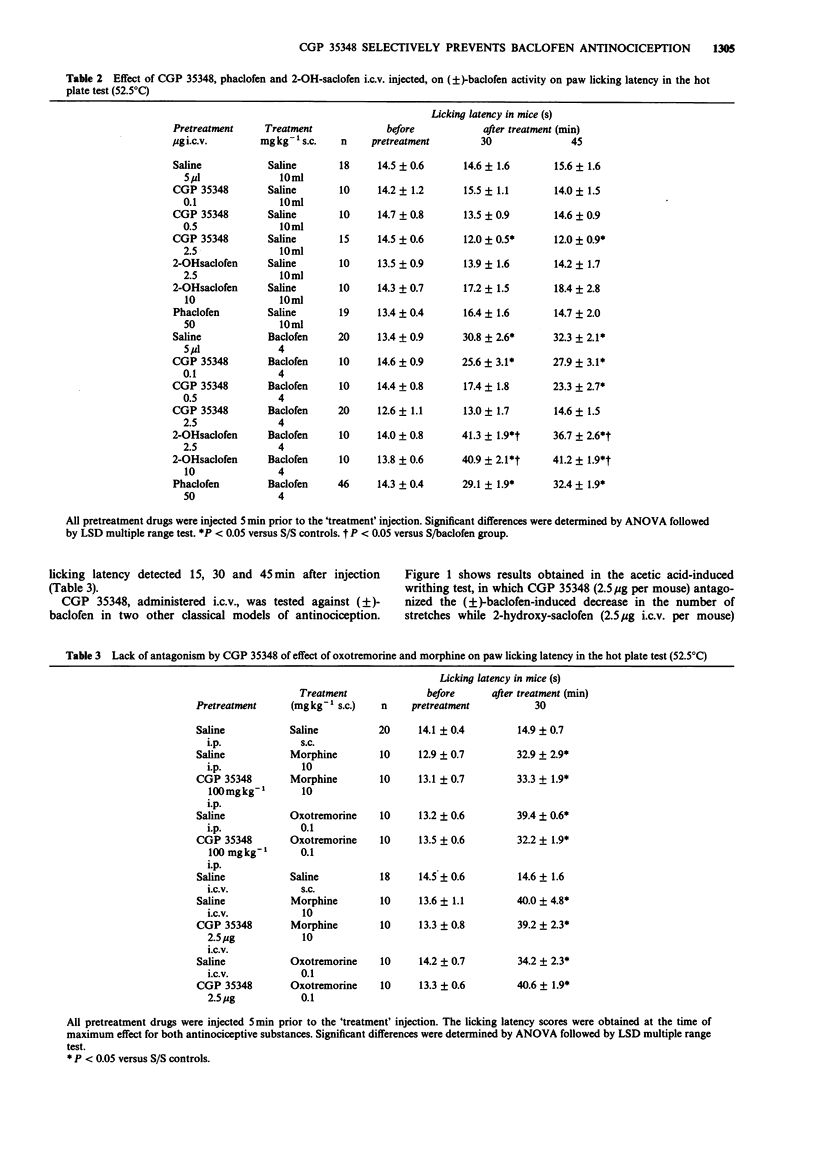
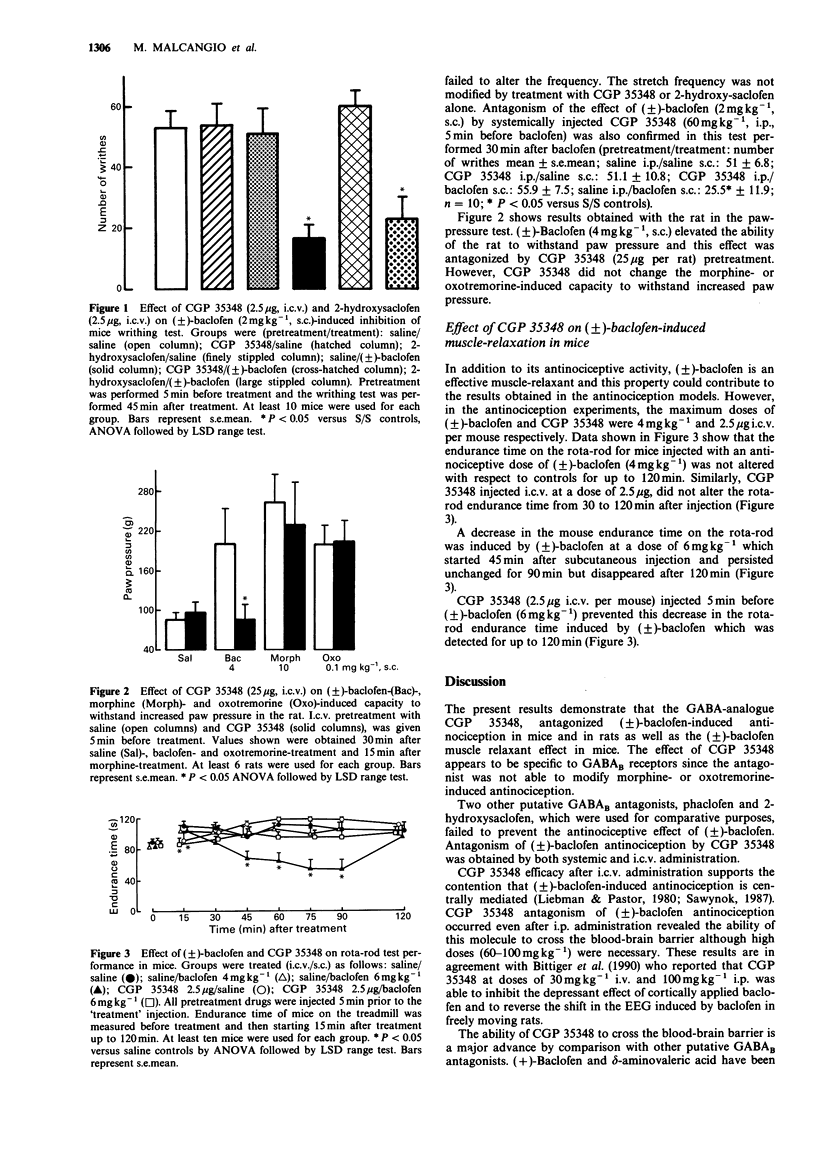
1. CGP 35348, a new GABAB antagonist, was examined on antinociception induced by (+/-)-baclofen by use of the hot plate and writhing tests in mice and the paw pressure test in rats. CGP 35348 was also studied in mice on (+/-)-baclofen-induced impairment of rota-rod performance. 2. CGP 35348, injected either i.p. (60-100 mg kg-1 in mouse) or intracerebroventricularly (i.c.v.) (0.5-2.5 micrograms per mouse; 25 micrograms per rat) prevented (+/-)-baclofen-induced antinociception. 3. CGP 35348 did not modify oxotremorine- and morphine-induced antinociception in mice and rats. 4. CGP 35348 (2.5 micrograms i.c.v. per mouse) also prevented (+/-)-baclofen-induced impairment of the rota-rod test. 5. Two other GABAB antagonists, phaclofen (50 micrograms i.c.v. per mouse) and 2-OH-saclofen (2.5 micrograms-10 micrograms i.c.v. per mouse) did not modify (+/-)-baclofen-induced antinociception. 7. These results suggest that, at present, CGP 35348 is the only compound able to antagonize (+/-)-baclofen-induced antinociception.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowery N. GABAB receptors and their significance in mammalian pharmacology. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Oct;10(10):401–407. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corli O., Roma G., Bacchini M., Battagliarin G., De Lorenzi P. P. Il Baclofen come analgesico negli interventi di dilatazione, aspirazione e curettage uterino. Minerva Anestesiol. 1984 Jul-Aug;50(7-8):401–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutting D. A., Jordan C. C. Alternative approaches to analgesia: baclofen as a model compound. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Jun;54(2):171–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb06926.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutar P., Nicoll R. A. A physiological role for GABAB receptors in the central nervous system. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):156–158. doi: 10.1038/332156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giuliani S., Evangelista S., Borsini F., Meli A. Intracerebroventricular phaclofen antagonizes baclofen antinociceptive activity in hot plate test with mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep 13;154(2):225–226. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALEY T. J., MCCORMICK W. G. Pharmacological effects produced by intracerebral injection of drugs in the conscious mouse. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Mar;12(1):12–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb01354.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond D. L., Drower E. J. Effects of intrathecally administered THIP, baclofen and muscimol on nociceptive threshold. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Aug 3;103(1-2):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90197-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill R. C., Maurer R., Buescher H. H., Roemer D. Analgesic properties of the GABA-mimetic THIP. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jan 16;69(2):221–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90419-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang A. S., Wilcox G. L. Baclofen, gamma-aminobutyric acidB receptors and substance P in the mouse spinal cord. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Mar;248(3):1026–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr D. I., Ong J., Johnston G. A., Abbenante J., Prager R. H. 2-Hydroxy-saclofen: an improved antagonist at central and peripheral GABAB receptors. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Sep 23;92(1):92–96. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90748-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr D. I., Ong J., Prager R. H., Gynther B. D., Curtis D. R. Phaclofen: a peripheral and central baclofen antagonist. Brain Res. 1987 Mar 3;405(1):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90999-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R. A., Proudfit H. K. Analgesia produced by microinjection of baclofen and morphine at brain stem sites. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Jul 15;57(1):43–55. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90102-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R. A., Proudfit H. K. The analgesic action of baclofen [beta-(4-chlorophenyl)-gamma-aminobutyric acid]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1977 Aug;202(2):437–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebman J. M., Pastor G. Antinociceptive effects of baclofen and muscimol upon intraventricular administration. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Feb 8;61(3):225–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90124-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olpe H. R., Karlsson G., Pozza M. F., Brugger F., Steinmann M., Van Riezen H., Fagg G., Hall R. G., Froestl W., Bittiger H. CGP 35348: a centrally active blocker of GABAB receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Oct 2;187(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90337-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson T. N., Cross A. J., Green A. R., Toczek J. M., Boar B. R. Effects of the putative antagonists phaclofen and delta-aminovaleric acid on GABAB receptor biochemistry. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):833–840. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14612.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawynok J. Baclofen activates two distinct receptors in the rat spinal cord and guinea pig ileum. Neuropharmacology. 1986 Jul;25(7):795–798. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(86)90098-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawynok J., Dickson C. D-Baclofen is an antagonist at baclofen receptors mediating antinociception in the spinal cord. Pharmacology. 1985;31(5):248–259. doi: 10.1159/000138129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawynok J., Dickson C. Evidence for the involvement of descending noradrenergic pathways in the antinociceptive effect of baclofen. Brain Res. 1985 May 27;335(1):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90279-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawynok J. GABAergic mechanisms of analgesia: an update. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1987 Feb;26(2):463–474. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(87)90148-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawynok J., LaBella F. S. On the involvement of GABA in the analgesia produced by baclofen, muscimol and morphine. Neuropharmacology. 1982 May;21(5):397–403. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(82)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawynok J. Monoamines as mediators of the antinociceptive effect of baclofen. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;323(1):54–57. doi: 10.1007/BF00498828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawynok J., Moochhala S. M., Pillay D. J. Substance P, injected intrathecally, antagonizes the spinal antinociceptive effect of morphine, baclofen and noradrenaline. Neuropharmacology. 1984 Jul;23(7A):741–747. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(84)90106-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawynok J. The 1988 Merck Frosst Award. The role of ascending and descending noradrenergic and serotonergic pathways in opioid and non-opioid antinociception as revealed by lesion studies. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;67(9):975–988. doi: 10.1139/y89-154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirling J. M., Cross A. J., Robinson T. N., Green A. R. The effects of GABAB receptor agonists and antagonists on potassium-stimulated [Ca2+]i in rat brain synaptosomes. Neuropharmacology. 1989 Jul;28(7):699–704. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(89)90153-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaught J. L., Pelley K., Costa L. G., Setler P., Enna S. J. A comparison of the antinociceptive responses to the GABA-receptor agonists THIP and baclofen. Neuropharmacology. 1985 Mar;24(3):211–216. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(85)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M. Y., Dun N. J. Phaclofen-insensitive presynaptic inhibitory action of (+/-)-baclofen in neonatal rat motoneurones in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;99(2):413–421. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14718.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. R., Yaksh T. L. Baclofen is antinociceptive in the spinal intrathecal space of animals. Eur J Pharmacol. 1978 Oct 15;51(4):323–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(78)90423-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



