Abstract
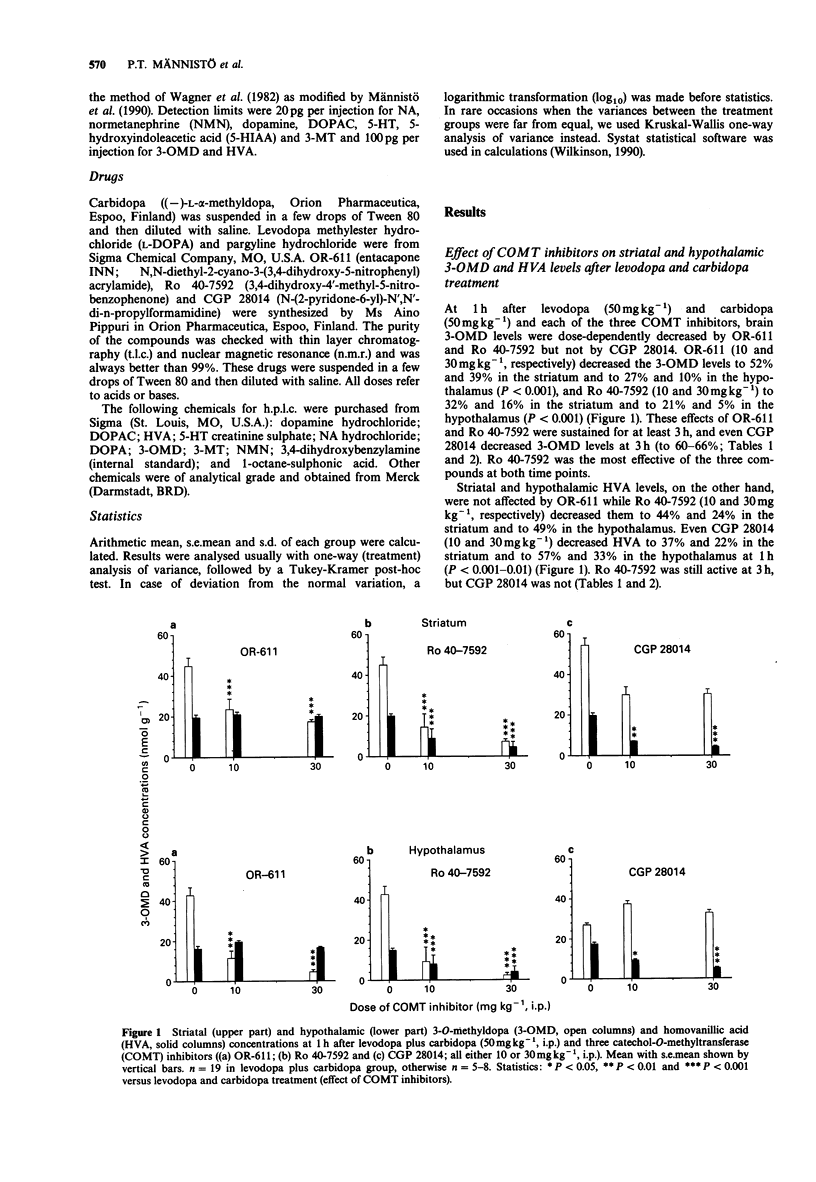
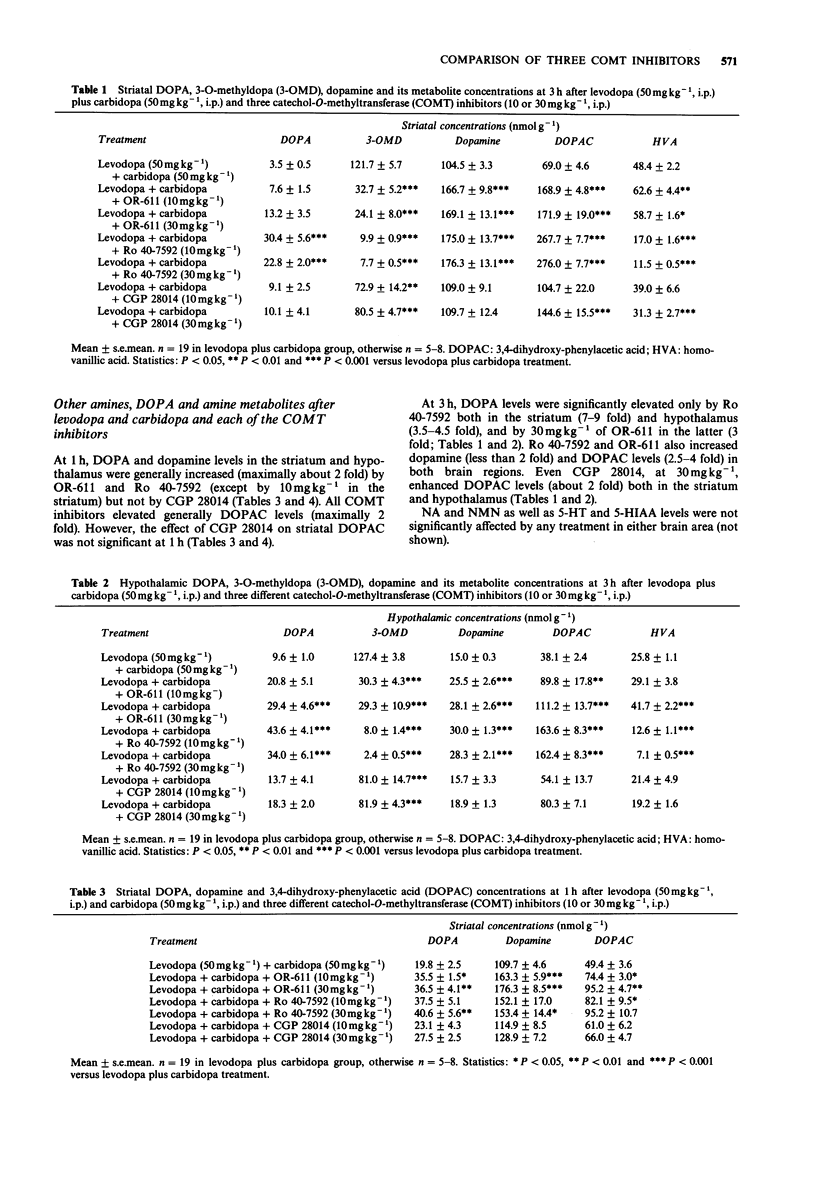
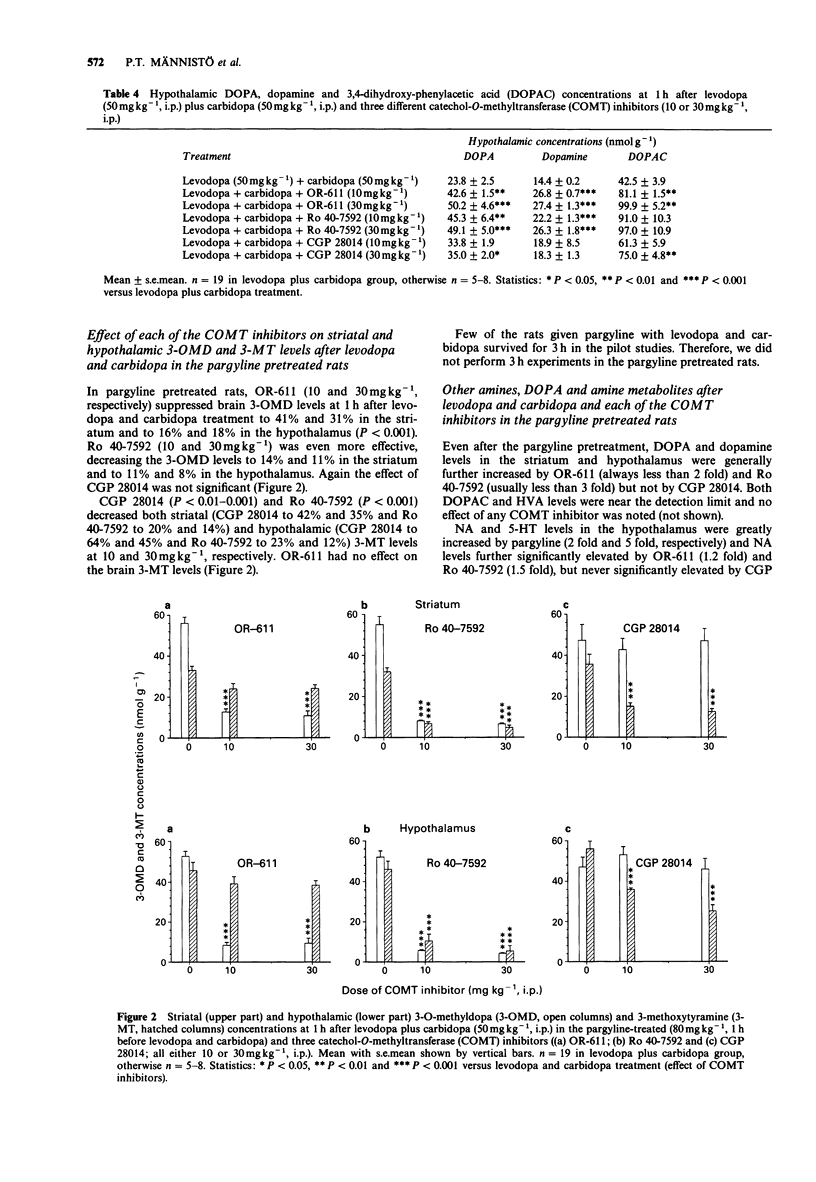
1. We compared three new catechol O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitors (OR-611, Ro 40-7592 and CGP 28014; 10 and 30 mg kg-1, i.p.) in male rats given levodopa (L-DOPA, 50 mg kg-1, i.p.) and carbidopa ((-)-L-alpha-methyl dopa, 50 mg kg-1, i.p.). In some studies pretreatment with pargyline (80 mg kg-1, i.p.) was used to block the function of monoamine oxidase (MAO). 2. Decreases of hypothalamic and striatal 3-O-methyl-dopa (3-OMD) levels were used as measures of the inhibition of peripheral COMT. The inhibition of brain COMT activity was estimated by decreases of hypothalamic and striatal homovanillic acid (HVA) and 3-methoxytyramine (3-MT; after pargyline) levels. 3. The three COMT inhibitors studied had different individual characteristics. OR-611 was primarily a peripherally acting COMT inhibitor, decreasing 3-OMD levels in the striatum (to 31-52%) and in the hypothalamus (to 16-27%) both in the control and pargyline-treated animals at 1 and 3 h. It did not have any effect on brain HVA and 3-MT. 3. Ro 40-7592 was a broad spectrum COMT inhibitor decreasing striatal and hypothalamic 3-OMD (always to less than 30%), HVA (to less than 50%) and 3-MT levels (to less than 23%) significantly both at 1 and 3 h. It was more potent than OR-611. 4. CGP 28014 functioned as a weak COMT inhibitor in the periphery inhibiting 3-OMD formation only at 3 h. In contrast, it was fairly potent in decreasing the brain HVA and 3-MT levels at 1 h (to 37-22% and 42-35% in the striatum, and to 57-33% and 64-35% in the hypothalamus, respectively) but not at 3 h. Since CGP 28014, unlike OR-611 and Ro 40-7592, did not generally increase the brain DOPA, dopamine or DOPAC levels, it was not a typical COMT inhibitor.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldessarini R. J. Inhibition of catechol-O-methyl transferase by L-dopa and decarboxylase inhibitors. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1972 Jan;24(1):78–80. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1972.tb08873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedarbaum J. M. Clinical pharmacokinetics of anti-parkinsonian drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1987 Sep;13(3):141–178. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198713030-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etemadzadeh E., Koskinen L., Kaakkola S. Computerized rotometer apparatus for recording circling behavior. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 1989 Jun;11(6):399–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glowinski J., Iversen L. L. Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain. I. The disposition of [3H]norepinephrine, [3H]dopamine and [3H]dopa in various regions of the brain. J Neurochem. 1966 Aug;13(8):655–669. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb09873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato T., Dong B., Ishii K., Kinemuchi H. Brain dialysis: in vivo metabolism of dopamine and serotonin by monoamine oxidase A but not B in the striatum of unrestrained rats. J Neurochem. 1986 Apr;46(4):1277–1282. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb00650.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopin I. J. Catecholamine metabolism: basic aspects and clinical significance. Pharmacol Rev. 1985 Dec;37(4):333–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Männistö P. T., Kaakkola S. New selective COMT inhibitors: useful adjuncts for Parkinson's disease? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Feb;10(2):54–56. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Männistö P. T., Kaakkola S., Nissinen E., Linden I. B., Pohto P. Properties of novel effective and highly selective inhibitors of catechol-O-methyltransferase. Life Sci. 1988;43(18):1465–1471. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(88)90258-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Männistö P. T., Kaakkola S. Rationale for selective COMT inhibitors as adjuncts in the drug treatment of Parkinson's disease. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990 May;66(5):317–323. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1990.tb00756.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Männistö P. T., Tuomainen P. Effect of high single doses of levodopa and carbidopa on brain dopamine and its metabolites: modulation by selective inhibitors of monoamine oxidase and/or catechol-O-methyltransferase in the male rat. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;344(4):412–418. doi: 10.1007/BF00172580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Männistö P. T., Tuomainen P., Toivonen M., Törnwall M., Kaakkola S. Effect of acute levodopa on brain catecholamines after selective MAO and COMT inhibition in male rats. J Neural Transm Park Dis Dement Sect. 1990;2(1):31–43. doi: 10.1007/BF02251244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissinen E., Lindén I. B., Schultz E., Kaakkola S., Männistö P. T., Pohto P. Inhibition of catechol-O-methyltransferase activity by two novel disubstituted catechols in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Aug 24;153(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90614-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oreland L., Arai Y., Stenström A. The effect of deprenyl (selegiline) on intra- and extraneuronal dopamine oxidation. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1983;95:81–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1983.tb01518.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trendelenburg U. The uptake and metabolism of 3H-catecholamines in rat cerebral cortex slices. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Mar;339(3):293–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00173580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J., Vitali P., Palfreyman M. G., Zraika M., Huot S. Simultaneous determination of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine, 5-hydroxytryptophan, dopamine, 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenylalanine, norepinephrine, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, homovanillic acid, serotonin, and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in rat cerebrospinal fluid and brain by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. J Neurochem. 1982 May;38(5):1241–1254. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb07897.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmeier P. C., Baumann P. A., Feldtrauer J. J., Hauser K., Bittiger H., Bischoff S., von Sprecher G. CGP 28014, a new inhibitor of cerebral catechol-O-methylation with a non-catechol structure. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Sep;342(3):305–311. doi: 10.1007/BF00169442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldmeier P. C., De Herdt P., Maitre L. Effects of the COMT inhibitor, CGP 28014, on plasma homovanillic acid and O-methylation of exogenous L-dopa in the rat. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1990;32:381–386. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-9113-2_52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zürcher G., Colzi A., Da Prada M. Ro 40-7592: inhibition of COMT in rat brain and extracerebral tissues. J Neural Transm Suppl. 1990;32:375–380. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-9113-2_51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



