Abstract
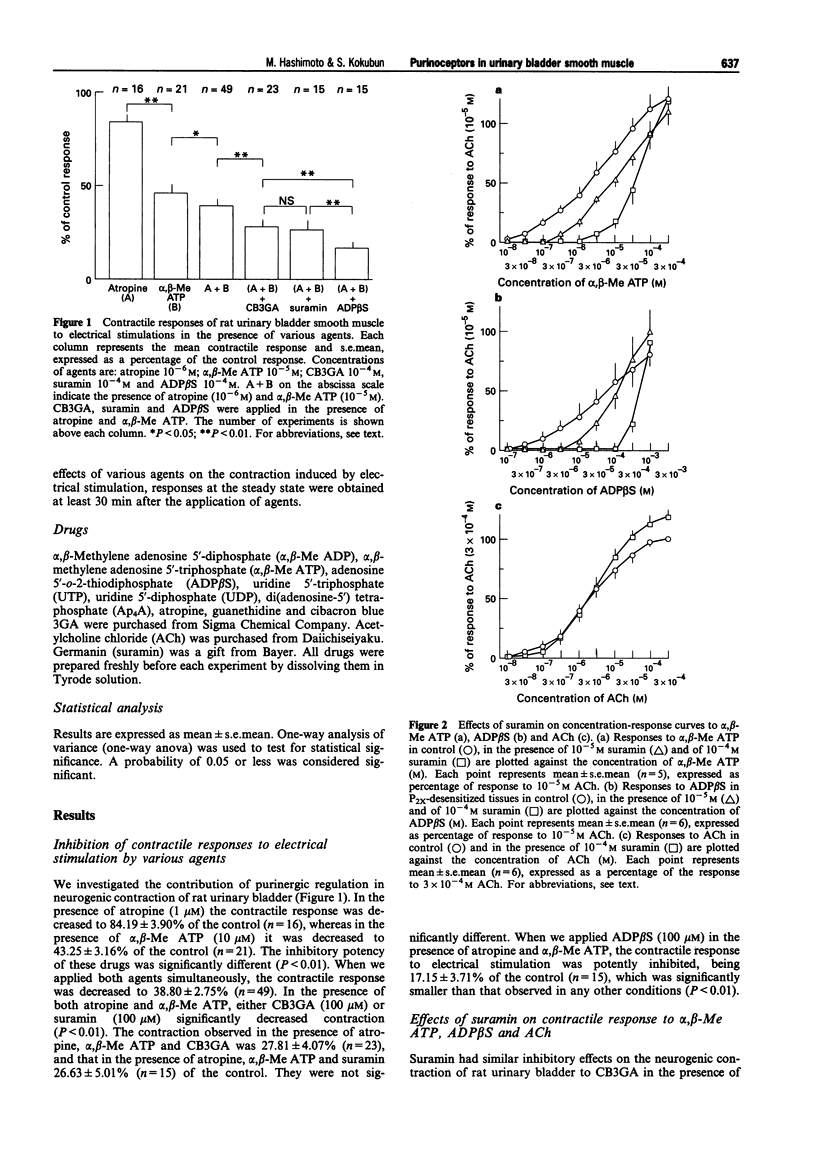
1. The contribution of P2-purinoceptors to neurogenic contraction was investigated in rat urinary bladder smooth muscle by measurement of isotonic tension. 2. Contraction of rat urinary bladder smooth muscle induced by electrical stimulation was decreased to 84.19 +/- 3.90% of the control (n = 16) in the presence of atropine (1 microM), which was further decreased to 38.80 +/- 2.75% of the control (n = 49) in the presence of both atropine and 10 microM alpha, beta-methylene adenosine 5'-triphosphate (alpha, beta-Me ATP). 3. The contractile response induced by electrical stimulation in the presence of atropine and alpha, beta-Me ATP was decreased to 27.81 +/- 4.07% (n = 23) and 26.63 +/- 5.01% (n = 15) of the control, by the addition of 100 microM cibacron blue 3GA and 100 microM suramin, respectively. The application of 100 microM adenosine 5'-o-2-thiodiphosphate (ADP beta S) in the presence of atropine and alpha, beta-Me ATP decreased the contractile response induced by electrical stimulations to 17.15 +/- 3.71% (n = 15) of the control. 4. Pretreatment of muscle strips with 100 microM ADP beta S significantly reduced the response to either 200 microM alpha, beta-methylene adenosine 5'-diphosphate or 200 microM ADP beta S. 5. Uridine 5'-triphosphate (100 microM to 1 mM) concentration-dependently contracted muscle strips, and this contraction was significantly antagonized by desensitization of P2-receptors with alpha, beta-Me ATP (10 microM), and completely antagonized by pretreatment of muscle strips with both alpha, beta-Me ATP and ADP beta S (100 microM).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF
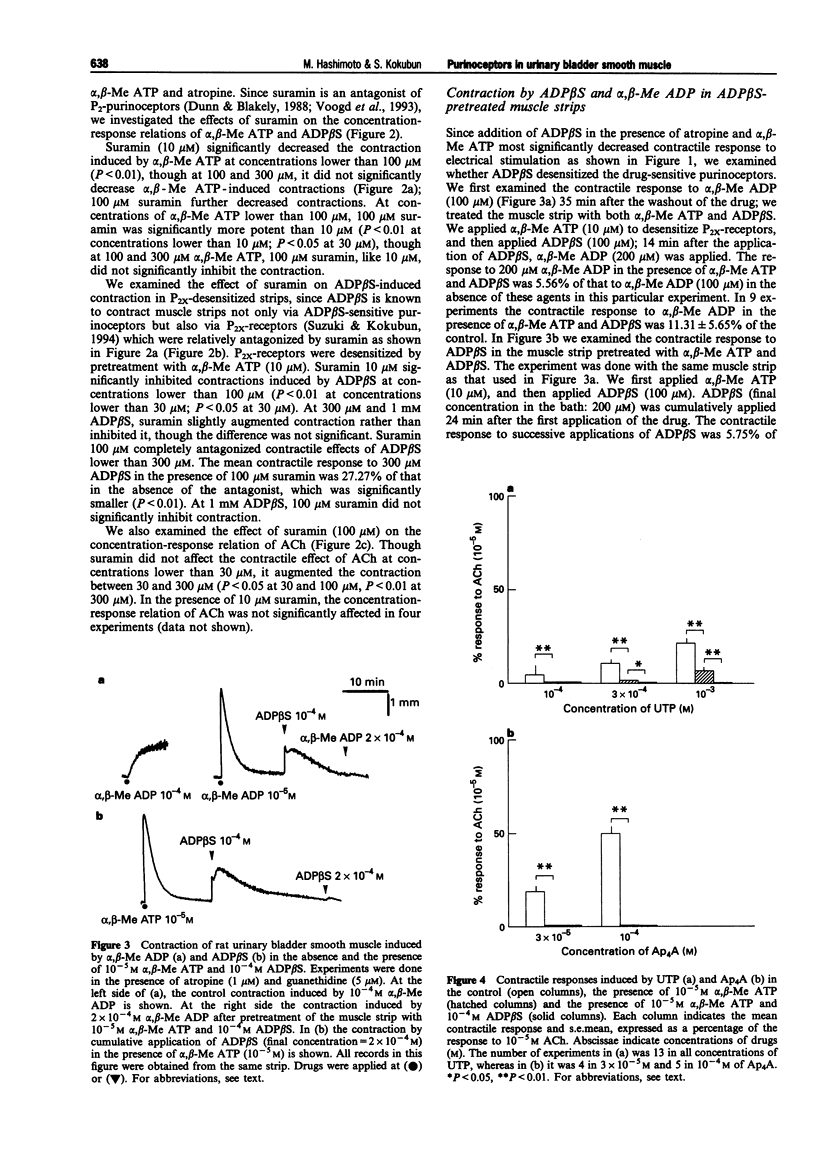


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhat M. B., Mishra S. K., Raviprakash V. Differential susceptibility of cholinergic and noncholinergic neurogenic responses to calcium channel blockers and low Ca2+ medium in rat urinary bladder. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Apr;96(4):837–842. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11892.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boland B., Himpens B., Paques C., Casteels R., Gillis J. M. ATP induced-relaxation in the mouse bladder smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;108(3):749–753. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12872.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Kennedy C. Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptor? Gen Pharmacol. 1985;16(5):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(85)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro E., Pintor J., Miras-Portugal M. T. Ca(2+)-stores mobilization by diadenosine tetraphosphate, Ap4A, through a putative P2Y purinoceptor in adrenal chromaffin cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Aug;106(4):833–837. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14421.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlquist R., Diamant B. Interaction of ATP and calcium on the rat mast cell: effect on histamine release. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1974 May;34(5):368–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1974.tb03533.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn P. M., Blakeley A. G. Suramin: a reversible P2-purinoceptor antagonist in the mouse vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Feb;93(2):243–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11427.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedan J. S., Dagirmanjian J. P., Attfield M. D., Chideckel E. W. Evidence that the P2x purinoceptor of the smooth muscle of the guinea pig vas deferens is an ATP4- receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Oct;255(1):46–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredholm B. B., Abbracchio M. P., Burnstock G., Daly J. W., Harden T. K., Jacobson K. A., Leff P., Williams M. Nomenclature and classification of purinoceptors. Pharmacol Rev. 1994 Jun;46(2):143–156. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L. Extracellular ATP: effects, sources and fate. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):309–319. doi: 10.1042/bj2330309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilderman R. H., Martin M., Zimmerman J. K., Pivorun E. B. Identification of a unique membrane receptor for adenosine 5',5"'-P1,P4-tetraphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 15;266(11):6915–6918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hisayama T., Shinkai M., Takayanagi I., Toyoda T. Mechanism of action of nicotine in isolated urinary bladder of guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;95(2):465–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11667.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacovou J. W., Hill S. J., Birmingham A. T. Agonist-induced contraction and accumulation of inositol phosphates in the guinea-pig detrusor: evidence that muscarinic and purinergic receptors raise intracellular calcium by different mechanisms. J Urol. 1990 Sep;144(3):775–779. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)39590-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasakov L., Burnstock G. The use of the slowly degradable analog, alpha, beta-methylene ATP, to produce desensitisation of the P2-purinoceptor: effect on non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic responses of the guinea-pig urinary bladder. Eur J Pharmacol. 1982 Dec 24;86(2):291–294. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(82)90330-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls J., Hourani S. M., Kitchen I. Characterization of P1-purinoceptors on rat duodenum and urinary bladder. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;105(3):639–642. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09032.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor S. E., Dainty I. A., Leff P. Further subclassification of ATP receptors based on agonist studies. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Apr;12(4):137–141. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90530-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg T. H., Silverstein S. C. Extracellular ATP4- promotes cation fluxes in the J774 mouse macrophage cell line. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3118–3122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Kokubun S. Subtypes of purinoceptors in rat and dog urinary bladder smooth muscles. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 May;112(1):117–122. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13039.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voogd T. E., Vansterkenburg E. L., Wilting J., Janssen L. H. Recent research on the biological activity of suramin. Pharmacol Rev. 1993 Jun;45(2):177–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



