Abstract
1. The cardiovascular effects of bilateral injection into the hypothalamic paraventricular nuclei of selective mu-, delta-, and kappa-opioid receptor agonists were investigated in conscious, unrestrained Wistar Kyoto rats, chronically instrumented with pulsed Doppler flow probes for measurement of regional haemodynamics. 2. The selective mu-agonist [D-Ala2,MePhe4,Gly5ol]enkephalin (DAMGO), injected bilaterally into the hypothalamic paraventricular nuclei (0.01-1.0 nmol), caused increases in blood pressure, tachycardias, vasoconstriction in renal and superior mesenteric vascular beds and substantial vasodilatation in the hindquarter vascular bed. 3. The administration of increasing doses (0.01-5.0 nmol) of the selective delta-agonist [D-Phe2,5]enkephalin (DPDPE) or the selective kappa-agonist, U50488H into the paraventricular nuclei (PVN) had no significant effect on blood pressure, heart rate, or regional haemodynamics. 4. Together, the present results are further evidence of a role for opioid peptides, especially acting at mu-receptors in the PVN, in the central regulation of the cardiovascular system, whereas a role for opioid peptides, acting at delta- and kappa-receptors in the PVN, seems less obvious from the present results.
Full text
PDF

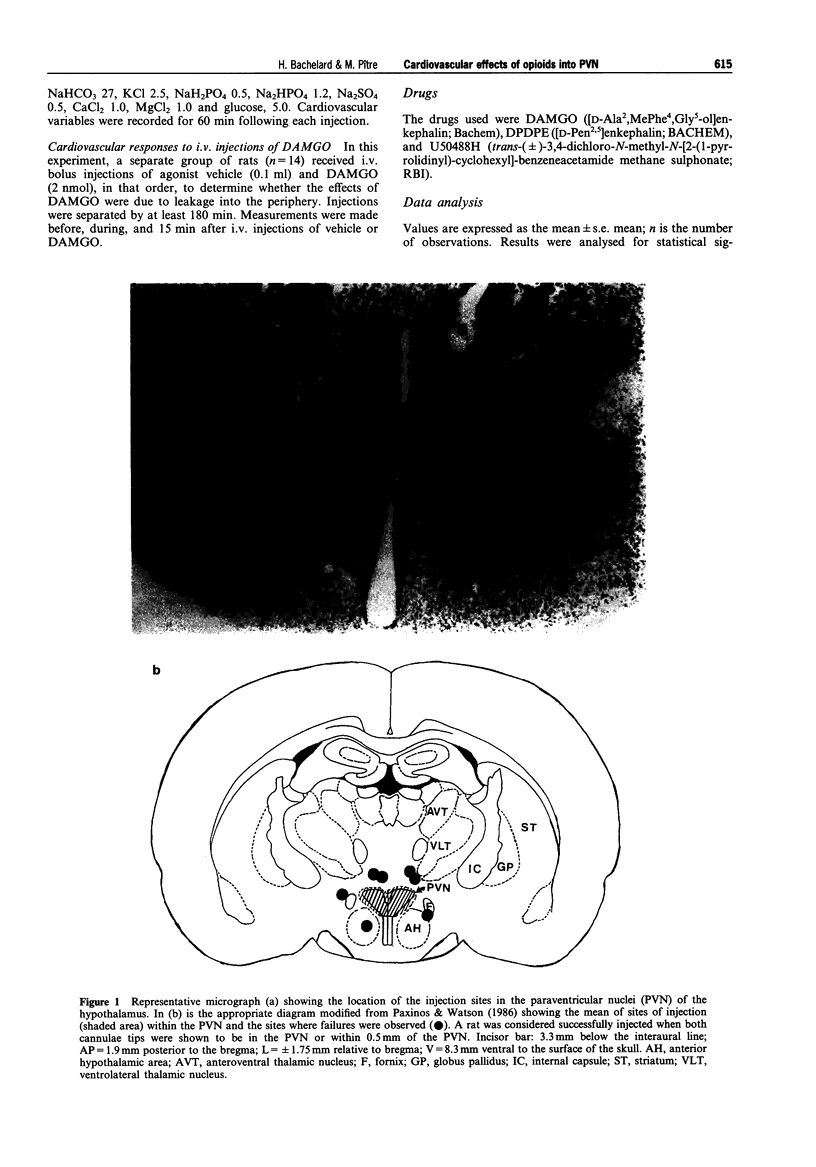
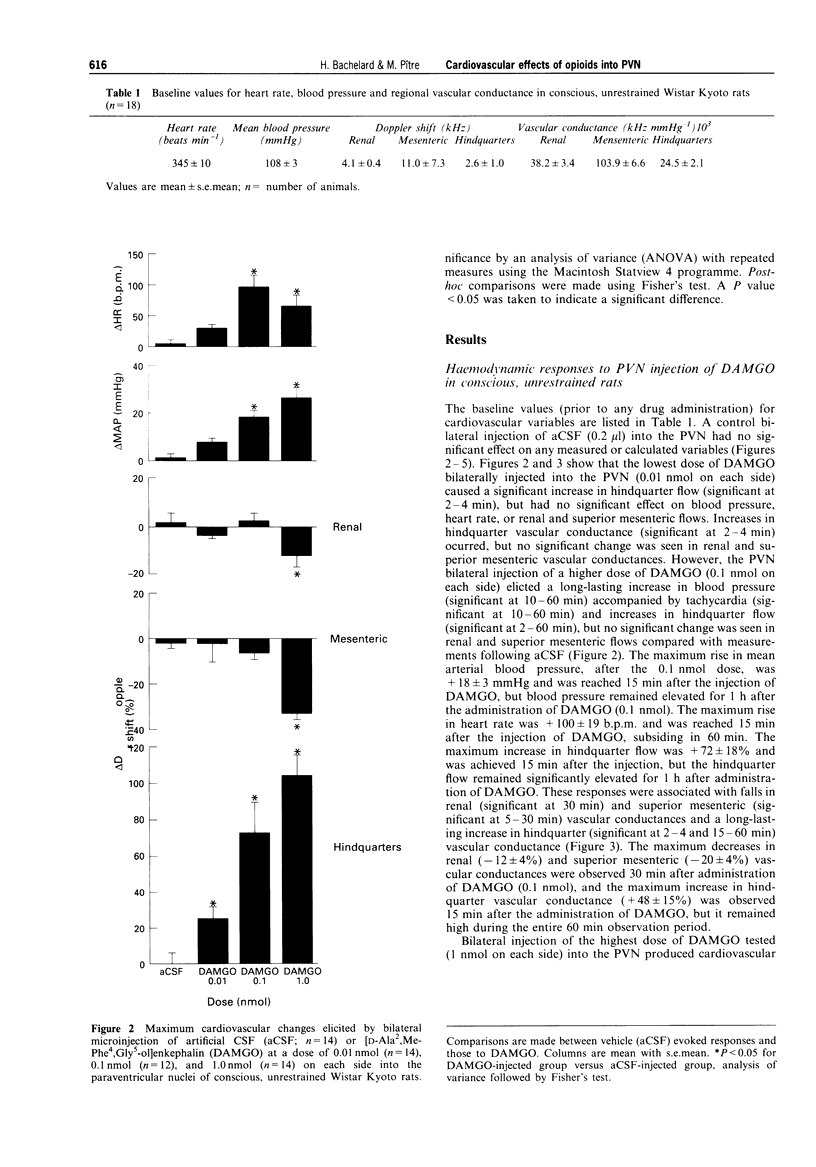
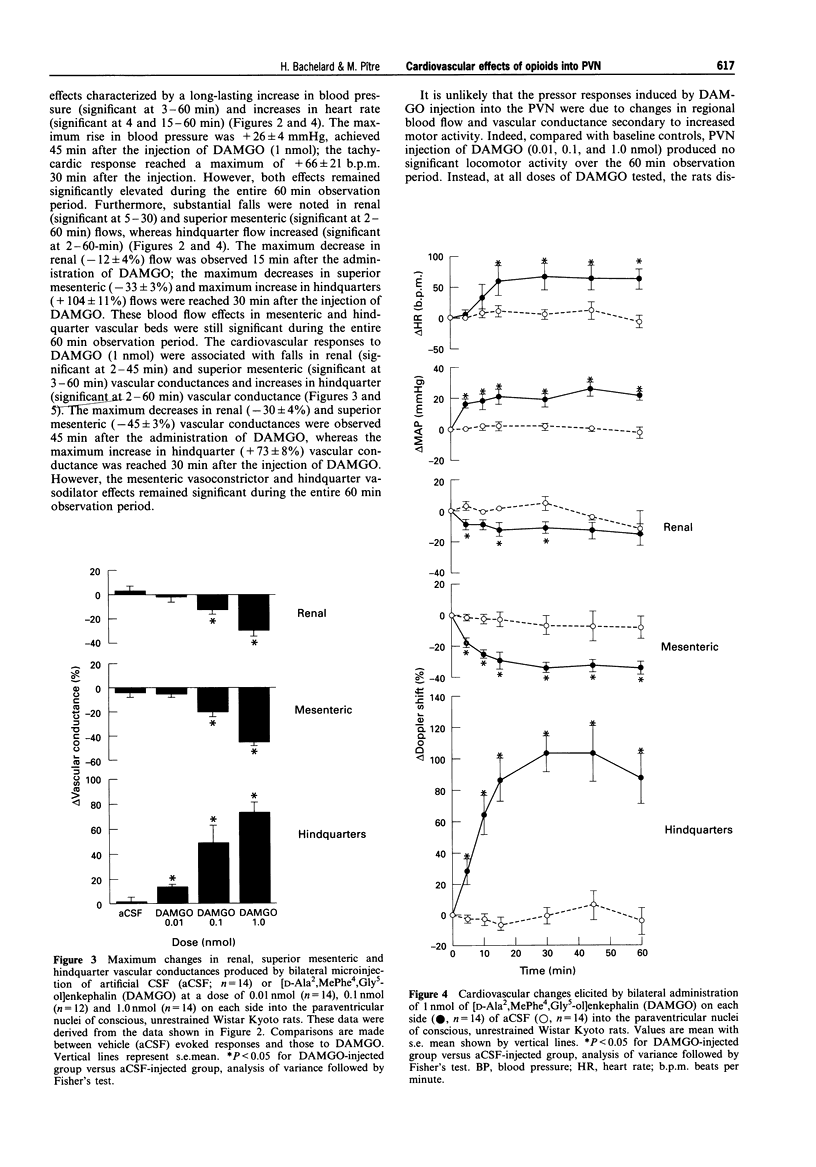
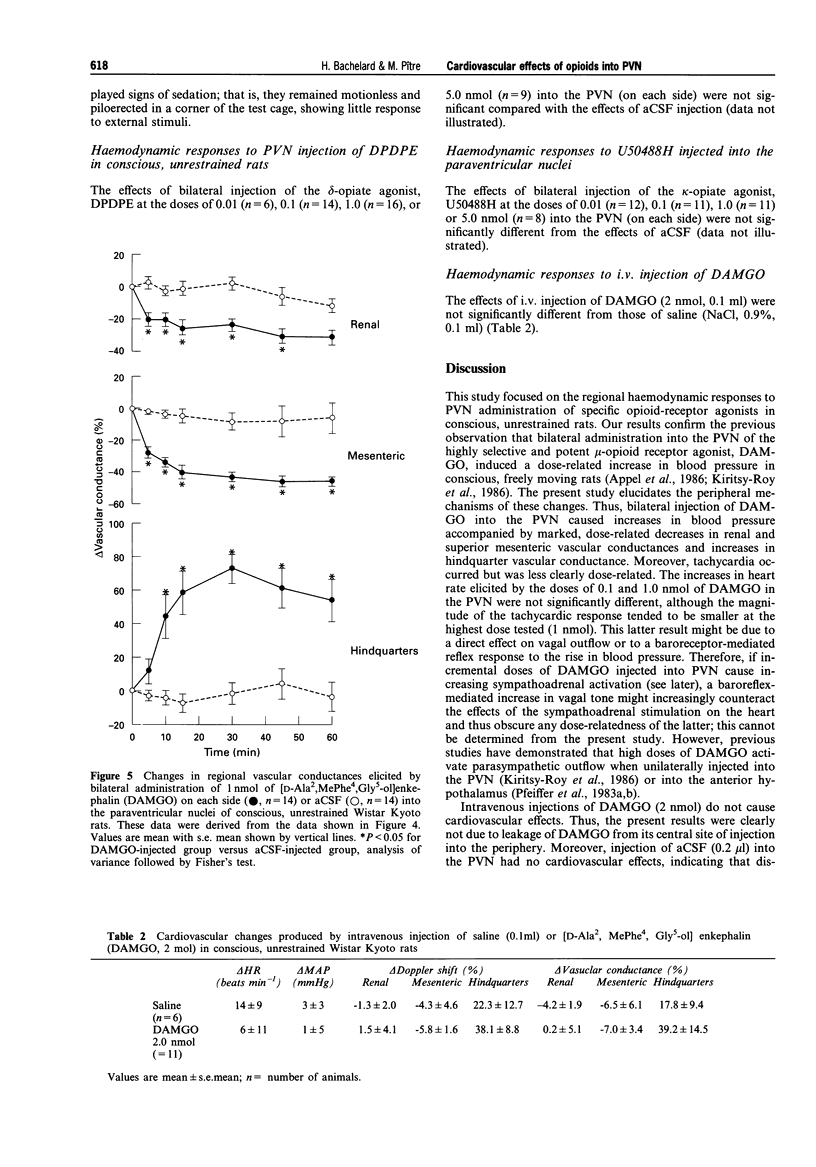



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Appel N. M., Kiritsy-Roy J. A., van Loon G. R. Mu receptors at discrete hypothalamic and brainstem sites mediate opioid peptide-induced increases in central sympathetic outflow. Brain Res. 1986 Jul 16;378(1):8–20. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90281-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atweh S. F., Kuhar M. J. Autoradiographic localization of opiate receptors in rat brain. I. Spinal cord and lower medulla. Brain Res. 1977 Mar 18;124(1):53–67. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90863-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachelard H., Gardiner S. M., Kemp P. A., Bennett T. Regional haemodynamic effects of carbachol injected into the hypothalamic paraventricular nuclei of conscious, unrestrained rats. Neuropharmacology. 1994 Jun;33(6):769–788. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)90117-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachelard H., Harland D., Gardiner S. M., Kemp P. A., Bennett T. Regional haemodynamic effects of noradrenaline injected into the hypothalamic paraventricular nuclei of conscious, unrestrained rats: possible mechanisms of action. Neuroscience. 1992;47(4):941–957. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90042-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caverson M. M., Ciriello J., Calaresu F. R. Cardiovascular afferent inputs to neurons in the ventrolateral medulla projecting directly to the central autonomic area of the thoracic cord in the cat. Brain Res. 1983 Sep 12;274(2):354–358. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90718-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciriello J., Calaresu F. R. Role of paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei in central cardiovascular regulation in the cat. Am J Physiol. 1980 Jul;239(1):R137–R142. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1980.239.1.R137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desjardins G. C., Brawer J. R., Beaudet A. Distribution of mu, delta, and kappa opioid receptors in the hypothalamus of the rat. Brain Res. 1990 Dec 17;536(1-2):114–123. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drolet G., Morilak D. A., Chalmers J. Endogenous opioids tonically inhibit the depressor neurones in the caudal ventrolateral medulla of rabbits: mediation through delta- and kappa-receptors. Neuropharmacology. 1991 Apr;30(4):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(91)90064-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallon J. H., Leslie F. M. Distribution of dynorphin and enkephalin peptides in the rat brain. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Jul 15;249(3):293–336. doi: 10.1002/cne.902490302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerstein G., Siren A. L. The opioid peptides. A role in hypertension? Hypertension. 1987 Jun;9(6):561–565. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.9.6.561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuerstein G. The opioid system and central cardiovascular control: analysis of controversies. Peptides. 1985;6 (Suppl 2):51–56. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(85)90134-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner S. M., Bennett T. Regional hemodynamic responses to adrenoceptor antagonism in conscious rats. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 2):H813–H824. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.255.4.H813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner S. M., Compton A. M., Bennett T., Hartley C. J. Can pulsed Doppler technique measure changes in aortic blood flow in conscious rats? Am J Physiol. 1990 Aug;259(2 Pt 2):H448–H456. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.2.H448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glatt C. E., Kenner J. R., Long J. B., Holaday J. W. Cardiovascular effects of dynorphin A (1-13) in conscious rats and its modulation of morphine bradycardia over time. Peptides. 1987 Nov-Dec;8(6):1089–1092. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(87)90141-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., James I. F. Site-directed alkylation of multiple opioid receptors. II. Pharmacological selectivity. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 May;25(3):343–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Naidu A. Multiple opioid receptors: ligand selectivity profiles and binding site signatures. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Aug;36(2):265–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. R., Snyder S. H., Kuhar M. J., Young W. S., 3rd Differentiation of delta and mu opiate receptor localizations by light microscopic autoradiography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6239–6243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon F. J. Central opioid receptors and baroreflex control of sympathetic and cardiovascular function. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 May;237(2):428–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulya K., Pelton J. T., Hruby V. J., Yamamura H. I. Cyclic somatostatin octapeptide analogues with high affinity and selectivity toward mu opioid receptors. Life Sci. 1986 Jun 16;38(24):2221–2229. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(86)90574-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handa B. K., Land A. C., Lord J. A., Morgan B. A., Rance M. J., Smith C. F. Analogues of beta-LPH61-64 possessing selective agonist activity at mu-opiate receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Apr 9;70(4):531–540. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90364-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassen A. H., Feuerstein G., Faden A. I. Differential cardiovascular effects mediated by mu and kappa opiate receptors in hindbrain nuclei. Peptides. 1983 Sep-Oct;4(5):621–625. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(83)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haywood J. R., Shaffer R. A., Fastenow C., Fink G. D., Brody M. J. Regional blood flow measurement with pulsed Doppler flowmeter in conscious rat. Am J Physiol. 1981 Aug;241(2):H273–H278. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1981.241.2.H273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holaday J. W. Cardiovascular effects of endogenous opiate systems. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1983;23:541–594. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.23.040183.002545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James I. F., Goldstein A. Site-directed alkylation of multiple opioid receptors. I. Binding selectivity. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 May;25(3):337–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin C. B., Rockhold R. W. Effects of paraventricular hypothalamic microinfusions of kainic acid on cardiovascular and renal excretory function in conscious rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Dec;251(3):969–975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin C. B., Rockhold R. W. Sympathoadrenal control by paraventricular hypothalamic beta-endorphin in hypertension. Hypertension. 1991 Oct;18(4):503–515. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.18.4.503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannan H., Hayashida Y., Yamashita H. Increase in sympathetic outflow by paraventricular nucleus stimulation in awake rats. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 2):R1325–R1330. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1989.256.6.R1325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kannan H., Yamashita H. Connections of neurons in the region of the nucleus tractus solitarius with the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus: their possible involvement in neural control of the cardiovascular system in rats. Brain Res. 1985 Mar 11;329(1-2):205–212. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90526-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiritsy-Roy J. A., Appel N. M., Bobbitt F. G., Van Loon G. R. Effects of mu-opioid receptor stimulation in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus on basal and stress-induced catecholamine secretion and cardiovascular responses. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Dec;239(3):814–822. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luiten P. G., ter Horst G. J., Karst H., Steffens A. B. The course of paraventricular hypothalamic efferents to autonomic structures in medulla and spinal cord. Brain Res. 1985 Mar 11;329(1-2):374–378. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90554-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansour A., Khachaturian H., Lewis M. E., Akil H., Watson S. J. Anatomy of CNS opioid receptors. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Jul;11(7):308–314. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marson L., Kiritsy-Roy J. A., Van Loon G. R. mu-Opioid peptide modulation of cardiovascular and sympathoadrenal responses to stress. Am J Physiol. 1989 Oct;257(4 Pt 2):R901–R908. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1989.257.4.R901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. S., Haywood J. R. Sympathetic nervous system activation by glutamate injections into the paraventricular nucleus. Brain Res. 1992 Apr 17;577(2):261–267. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90282-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. S., Segura T., Haywood J. R. Cardiovascular responses to bicuculline in the paraventricular nucleus of the rat. Hypertension. 1991 Jul;18(1):48–55. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.18.1.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. R. Pharmacology of opioids. Pharmacol Rev. 1983 Dec;35(4):283–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura K., Abe I., Tominaga M., Tsuchihashi T., Kobayashi K., Fujishima M. Differential modulation by mu- and delta-opioids on baroreceptor reflex in conscious rabbits. Hypertension. 1992 Jun;19(6 Pt 2):648–652. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.19.6.648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May C. N., Dashwood M. R., Whitehead C. J., Mathias C. J. Differential cardiovascular and respiratory responses to central administration of selective opioid agonists in conscious rabbits: correlation with receptor distribution. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):903–913. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14620.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morilak D. A., Drolet G., Chalmers J. Tonic opioid inhibition of the pressor region of the rostral ventrolateral medulla of rabbits is mediated by delta receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Aug;254(2):671–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosberg H. I., Hurst R., Hruby V. J., Gee K., Yamamura H. I., Galligan J. J., Burks T. F. Bis-penicillamine enkephalins possess highly improved specificity toward delta opioid receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5871–5874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulder A. H., Wardeh G., Hogenboom F., Frankhuyzen A. L. Selectivity of various opioid peptides towards delta-, kappa; and mu-opioid receptors mediating presynaptic inhibition of neurotransmitter release in the brain. Neuropeptides. 1989 Aug-Sep;14(2):99–104. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(89)90065-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson S. J., Robson L. E., Kosterlitz H. W. Classification of opioid receptors. Br Med Bull. 1983 Jan;39(1):31–36. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer A., Feuerstein G., Faden A., Kopin I. J. Evidence for an involvement of mu-, but not delta- or kappa-opiate receptors in sympathetically and parasympathetically mediated cardiovascular responses to opiates upon anterior hypothalamic injection. Life Sci. 1982 Sep 20;31(12-13):1279–1282. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90361-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer A., Feuerstein G., Kopin I. J., Faden A. I. Cardiovascular and respiratory effects of mu-, delta- and kappa-opiate agonists microinjected into the anterior hypothalamic brain area of awake rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jun;225(3):735–741. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer A., Feuerstein G., Zerbe R. L., Faden A. I., Kopin I. J. Mu-receptors mediate opioid cardiovascular effects at anterior hypothalamic sites through sympatho-adrenomedullary and parasympathetic pathways. Endocrinology. 1983 Sep;113(3):929–938. doi: 10.1210/endo-113-3-929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisine T., Bell G. I. Molecular biology of opioid receptors. Trends Neurosci. 1993 Dec;16(12):506–510. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90194-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochford J., Godin C., Henry J. L. Intrathecal administration of dynorphin A and its fragments increase heart rate and arterial pressure in the urethane anesthetized rat: mediation by a nonopioid mechanism. Brain Res. 1991 Nov 22;565(1):67–77. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91737-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawchenko P. E., Swanson L. W. Immunohistochemical identification of neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus that project to the medulla or to the spinal cord in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Mar 1;205(3):260–272. doi: 10.1002/cne.902050306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirén A. L., Feuerstein G. Hypothalamic opioid mu-receptors regulate discrete hemodynamic functions in the conscious rat. Neuropharmacology. 1991 Feb;30(2):143–152. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(91)90197-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirén A. L., Paakkari P., Goldstein D. S., Feuerstein G. Mechanisms of central hemodynamic and sympathetic regulation by mu opioid receptors: effects of dermorphin in the conscious rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Feb;248(2):596–604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strack A. M., Sawyer W. B., Hughes J. H., Platt K. B., Loewy A. D. A general pattern of CNS innervation of the sympathetic outflow demonstrated by transneuronal pseudorabies viral infections. Brain Res. 1989 Jul 3;491(1):156–162. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90098-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strack A. M., Sawyer W. B., Platt K. B., Loewy A. D. CNS cell groups regulating the sympathetic outflow to adrenal gland as revealed by transneuronal cell body labeling with pseudorabies virus. Brain Res. 1989 Jul 10;491(2):274–296. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson L. W., Sawchenko P. E. Hypothalamic integration: organization of the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1983;6:269–324. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.06.030183.001413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonvoigtlander P. F., Lahti R. A., Ludens J. H. U-50,488: a selective and structurally novel non-Mu (kappa) opioid agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Jan;224(1):7–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wamsley J. K. Opioid receptors: autoradiography. Pharmacol Rev. 1983 Mar;35(1):69–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. E., Angus J. A., Korner P. I. Vascular amplifier properties in renovascular hypertension in conscious rabbits. Hindquarter responses to constrictor and dilator stimuli. Hypertension. 1987 Feb;9(2):122–131. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.9.2.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita H., Inenaga K., Koizumi K. Possible projections from regions of paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei to the spinal cord: electrophysiological studies. Brain Res. 1984 Apr 2;296(2):373–378. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




