Abstract
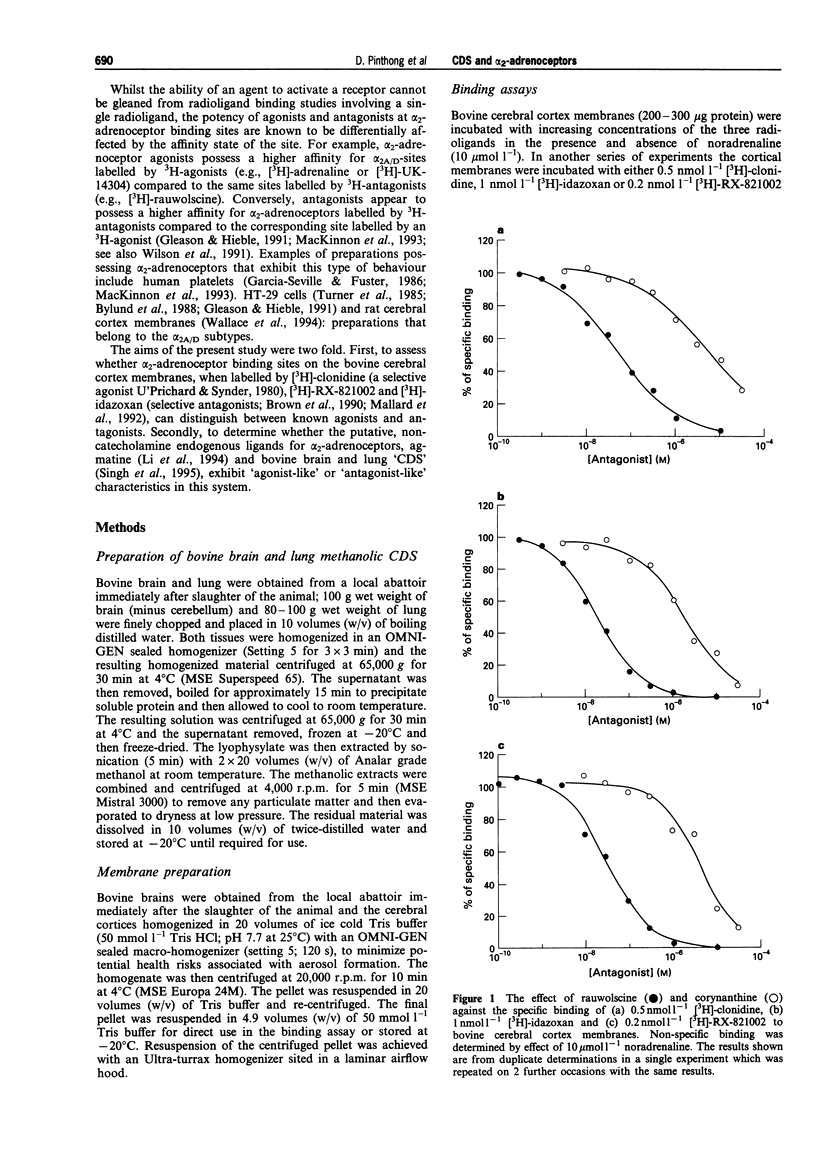
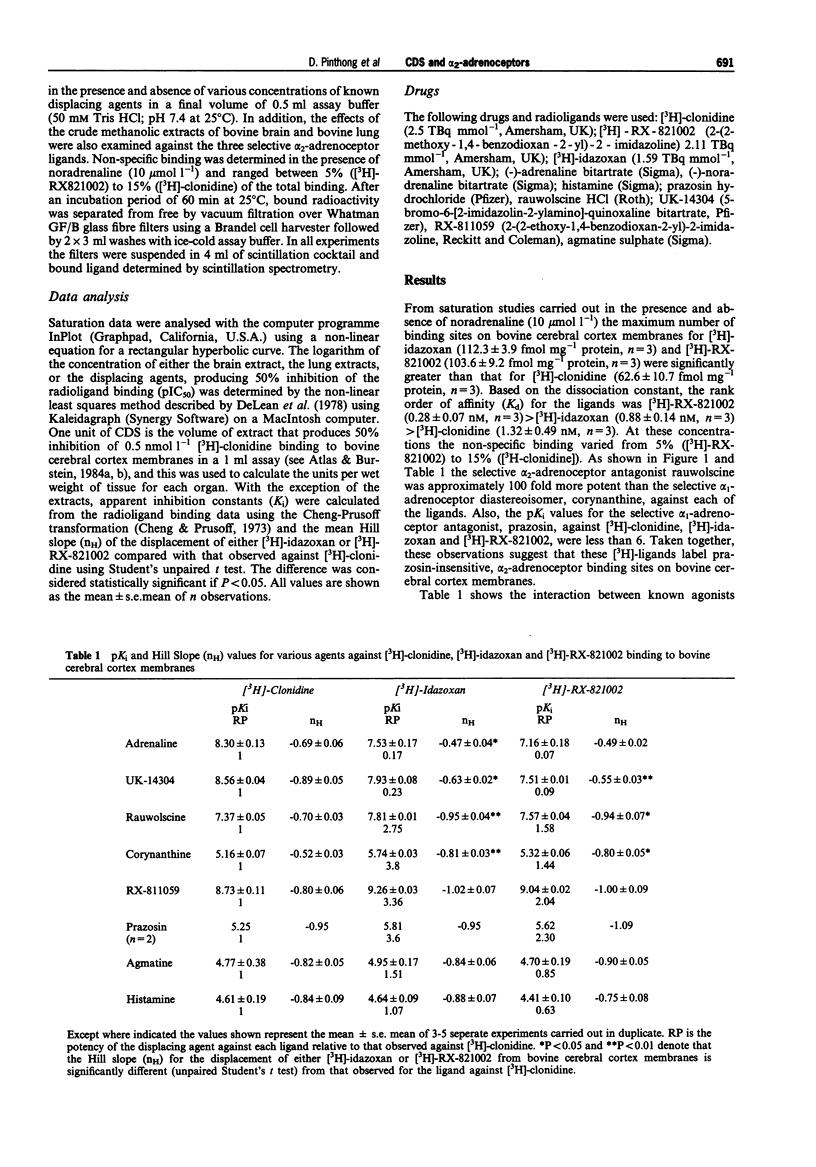
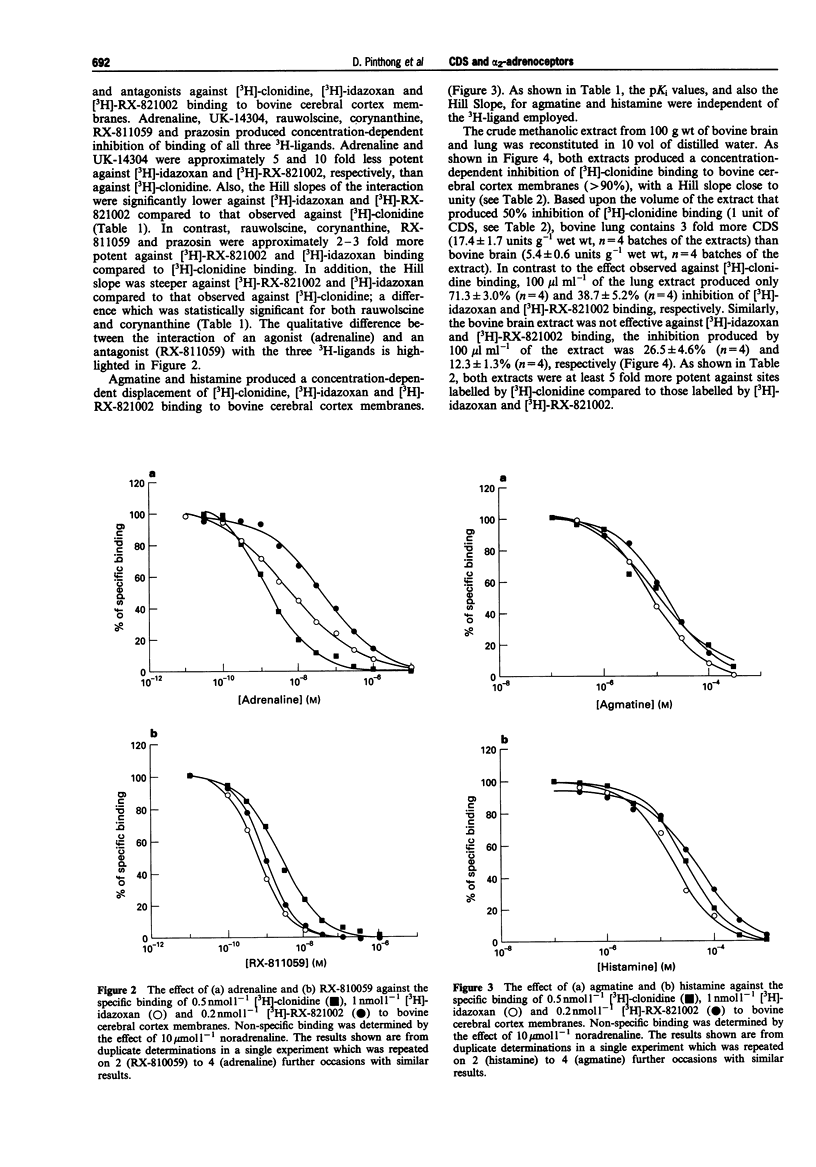
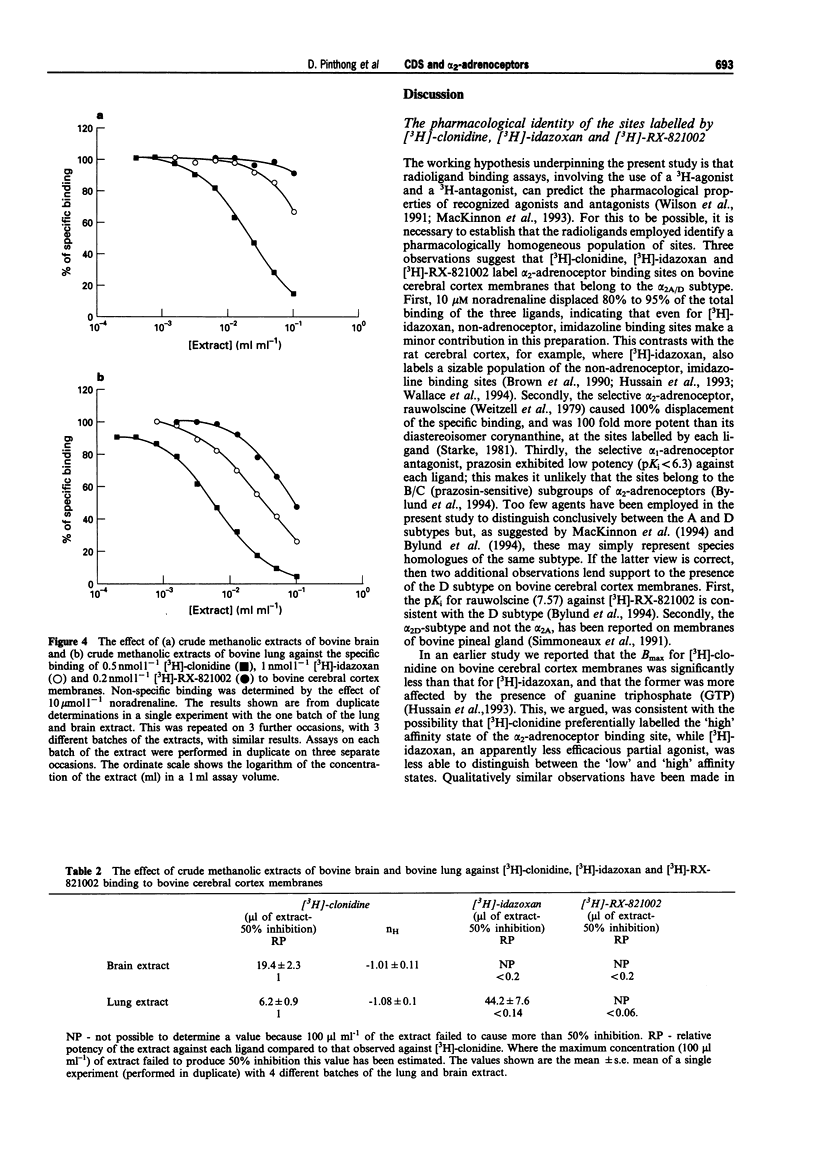
1. In the present study we have evaluated whether alpha 2-adrenoceptor binding sites on bovine cerebral cortex membranes labelled by [3H]-clonidine, [3H]-idazoxan and [3H]-RX-821002 can distinguish between known agonists and antagonists. This model has then been used to compare the binding profiles of the putative non-catecholamine, clonidine-displacing substance (CDS), agmatine and crude methanolic extracts of bovine lung and brain. 2. Saturation studies carried out in the presence and absence of noradrenaline, 10 mumol 1(-1), revealed that the maximum number of binding sites on bovine cerebral cortex membranes for [3H]-idazoxan and [3H]-RX-821002 were approximately 60-80% greater than those for [3H]-clonidine (62.6 fmol mg-1 protein). Rauwolscine, the selective alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonist, was approximately 100 fold more potent against each of the ligands than the selective alpha 1-adrenoceptor diastereoisomer, corynanthine. Also, the pKi value for the selective alpha 1-adrenoceptor prazosin against each ligand was less than 6. 3. Adrenaline, UK-14034, rauwolscine, corynanthine, RX-811059 and prazosin produced concentration-dependent inhibition of binding of all three 3H-ligands. The agonists, adrenaline and UK-14304, were approximately 5 and 10 fold less potent against [3H]-idazoxan and [3H]-RX-821002, respectively, than against [3H]-clonidine. In marked contrast, the antagonists, rauwolscine, corynanthine, RX-811059 and prazosin exhibited a different profile, being approximately 2-3 fold more potent against sites labelled by [3H]-RX-821002 and [3H]-idazoxan compared to sites labelled by [3H]-clonidine.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atlas D., Burstein Y. Isolation and partial purification of a clonidine-displacing endogenous brain substance. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Oct 15;144(2):287–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08462.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atlas D., Burstein Y. Isolation of an endogenous clonidine-displacing substance from rat brain. FEBS Lett. 1984 May 21;170(2):387–390. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81350-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atlas D. Clonidine-displacing substance (CDS) and its putative imidazoline receptor. New leads for further divergence of alpha 2-adrenergic receptor activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Jun 1;41(11):1541–1549. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90152-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. M., MacKinnon A. C., McGrath J. C., Spedding M., Kilpatrick A. T. Alpha 2-adrenoceptor subtypes and imidazoline-like binding sites in the rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Apr;99(4):803–809. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb13010.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B., Eikenberg D. C., Hieble J. P., Langer S. Z., Lefkowitz R. J., Minneman K. P., Molinoff P. B., Ruffolo R. R., Jr, Trendelenburg U. International Union of Pharmacology nomenclature of adrenoceptors. Pharmacol Rev. 1994 Jun;46(2):121–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B., Ray-Prenger C., Murphy T. J. Alpha-2A and alpha-2B adrenergic receptor subtypes: antagonist binding in tissues and cell lines containing only one subtype. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 May;245(2):600–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLean A., Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Simultaneous analysis of families of sigmoidal curves: application to bioassay, radioligand assay, and physiological dose-response curves. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E97–102. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamant S., Atlas D. An endogenous brain substance, CDS (clonidine-displacing-substance), inhibits the twitch response of rat vas deferens. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 14;134(1):184–190. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90545-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamant S., Eldor A., Atlas D. A low molecular weight brain substance interacts, similarly to clonidine, with alpha 2-adrenoceptors of human platelets. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Dec 15;144(3):247–255. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90377-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernsberger P., Meeley M. P., Reis D. J. An endogenous substance with clonidine-like properties: selective binding to imidazole sites in the ventrolateral medulla. Brain Res. 1988 Feb 16;441(1-2):309–318. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91409-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Sevilla J. A., Fuster M. J. Labelling of human platelet alpha 2-adrenoceptors with the full agonist [3H](-)adrenaline. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 May 13;124(1-2):31–41. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90121-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleason M. M., Hieble J. P. Ability of SK&F 104078 and SK&F 104856 to identify alpha-2 adrenoceptor subtypes in NCB20 cells and guinea pig lung. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Dec;259(3):1124–1132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain J. F., Kendall D. A., Wilson V. G. Species-selective binding of [3H]-idazoxan to alpha 2-adrenoceptors and non-adrenoceptor, imidazoline binding sites in the central nervous system. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;109(3):831–837. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13650.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G., Regunathan S., Barrow C. J., Eshraghi J., Cooper R., Reis D. J. Agmatine: an endogenous clonidine-displacing substance in the brain. Science. 1994 Feb 18;263(5149):966–969. doi: 10.1126/science.7906055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon A. C., Spedding M., Brown C. M. Alpha 2-adrenoceptors: more subtypes but fewer functional differences. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Apr;15(4):119–123. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90048-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon A. C., Spedding M., Brown C. M. Sodium modulation of 3H-agonist and 3H-antagonist binding to alpha 2-adrenoceptor subtypes. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jun;109(2):371–378. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13579.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallard N. J., Hudson A. L., Nutt D. J. Characterization and autoradiographical localization of non-adrenoceptor idazoxan binding sites in the rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Aug;106(4):1019–1027. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14450.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parini A., Coupry I., Graham R. M., Uzielli I., Atlas D., Lanier S. M. Characterization of an imidazoline/guanidinium receptive site distinct from the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 15;264(20):11874–11878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinthong D., Wright I. K., Hanmer C., Millns P., Mason R., Kendall D. A., Wilson V. G. Agmatine recognizes alpha 2-adrenoceptor binding sites but neither activates nor inhibits alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1995 Jan;351(1):10–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00169058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonneaux V., Ebadi M., Bylund D. B. Identification and characterization of alpha 2D-adrenergic receptors in bovine pineal gland. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Aug;40(2):235–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh G., Hussain J. F., MacKinnon A., Brown C. M., Kendall D. A., Wilson V. G. Evidence for the presence of a non-catecholamine, clonidine-displacing substance in crude, methanolic extracts of bovine brain and lung. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1995 Jan;351(1):17–26. doi: 10.1007/BF00169059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starke K. Alpha-adrenoceptor subclassification. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1981;88:199–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner J. T., Ray-Prenger C., Bylund D. B. Alpha 2-adrenergic receptors in the human cell line, HT29. Characterization with the full agonist radioligand [3H]UK-14,304 and inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Nov;28(5):422–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- U'Prichard D. C., Snyder S. H. Interactions of divalent cations and guanine nucleotides at alpha 2-noradrenergic receptor binding sites in bovine brain mechanisms. J Neurochem. 1980 Feb;34(2):385–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb06608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace D. R., Muskardin D. T., Zahniser N. R. Pharmacological characterization of [3H]idazoxan, [3H]RX821002 and p-[125I]iodoclonidine binding to alpha 2-adrenoceptors in rat cerebral cortical membranes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Jun 2;258(1-2):67–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(94)90058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weitzell R., Tanaka T., Starke K. Pre- and postsynaptic effects of yohimbine stereoisomers on noradrenergic transmission in the pulmonary artery of the rabbit. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1979 Aug;308(2):127–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00499054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson V. G., Brown C. M., McGrath J. C. Are there more than two types of alpha-adrenoceptors involved in physiological responses? Exp Physiol. 1991 May;76(3):317–346. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1991.sp003501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



