Abstract
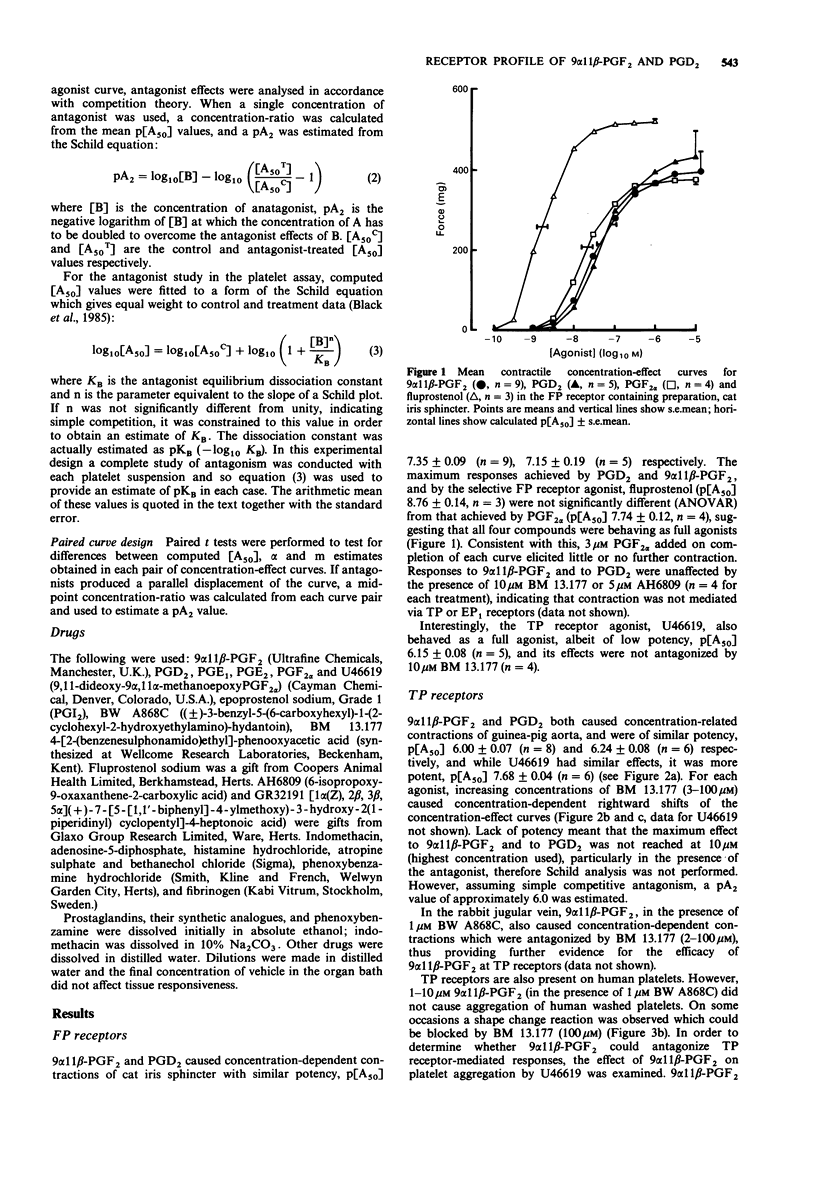
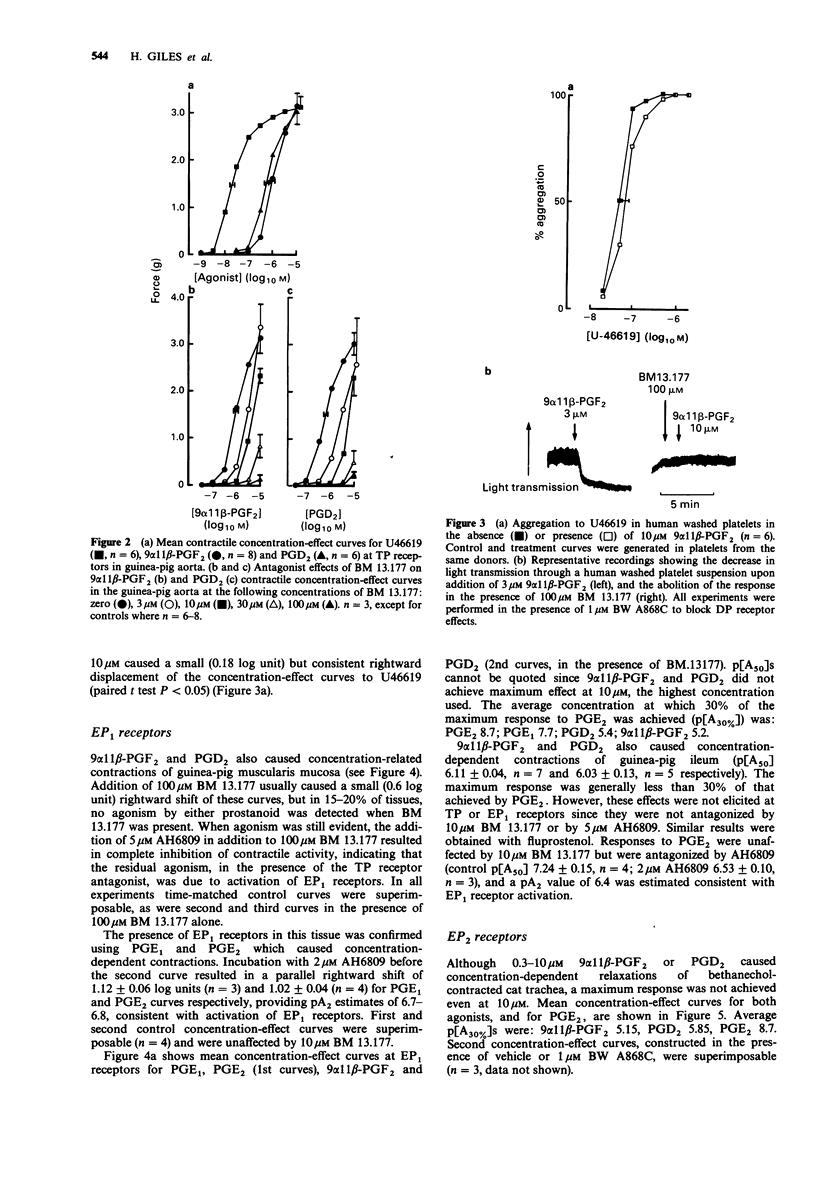
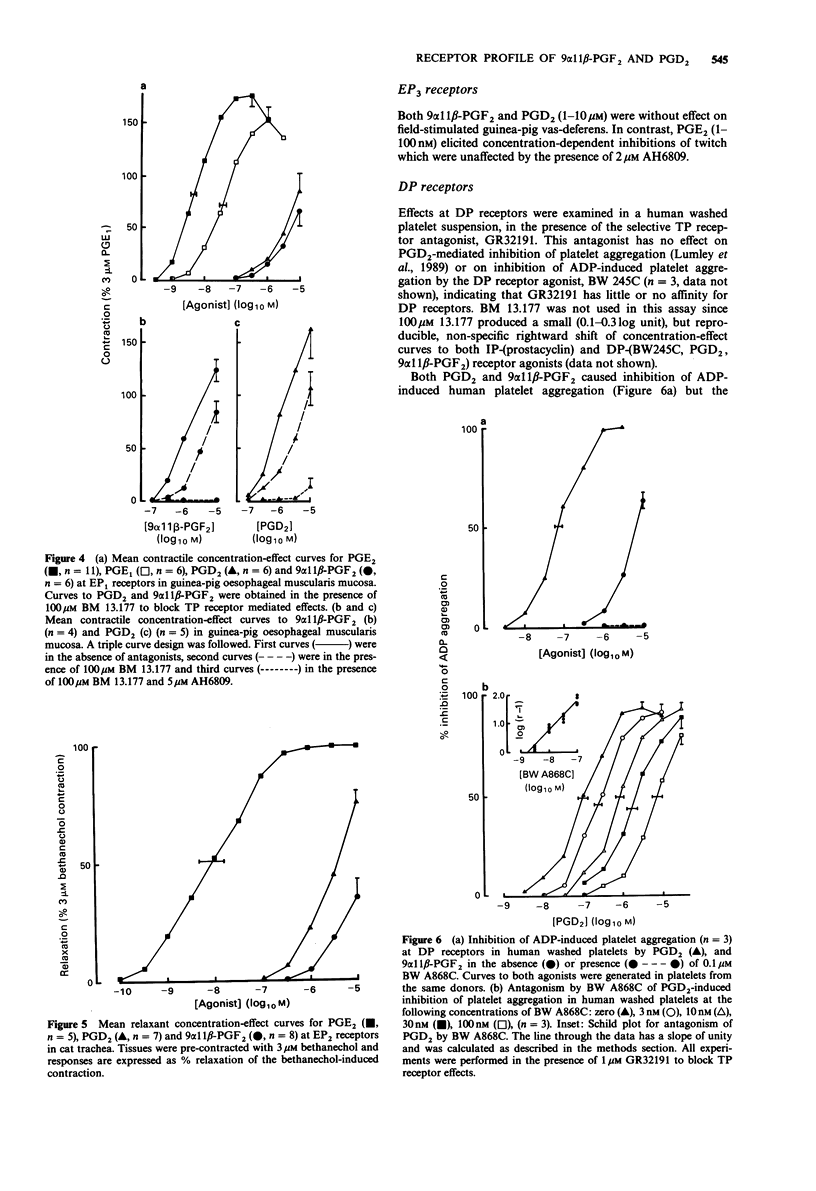
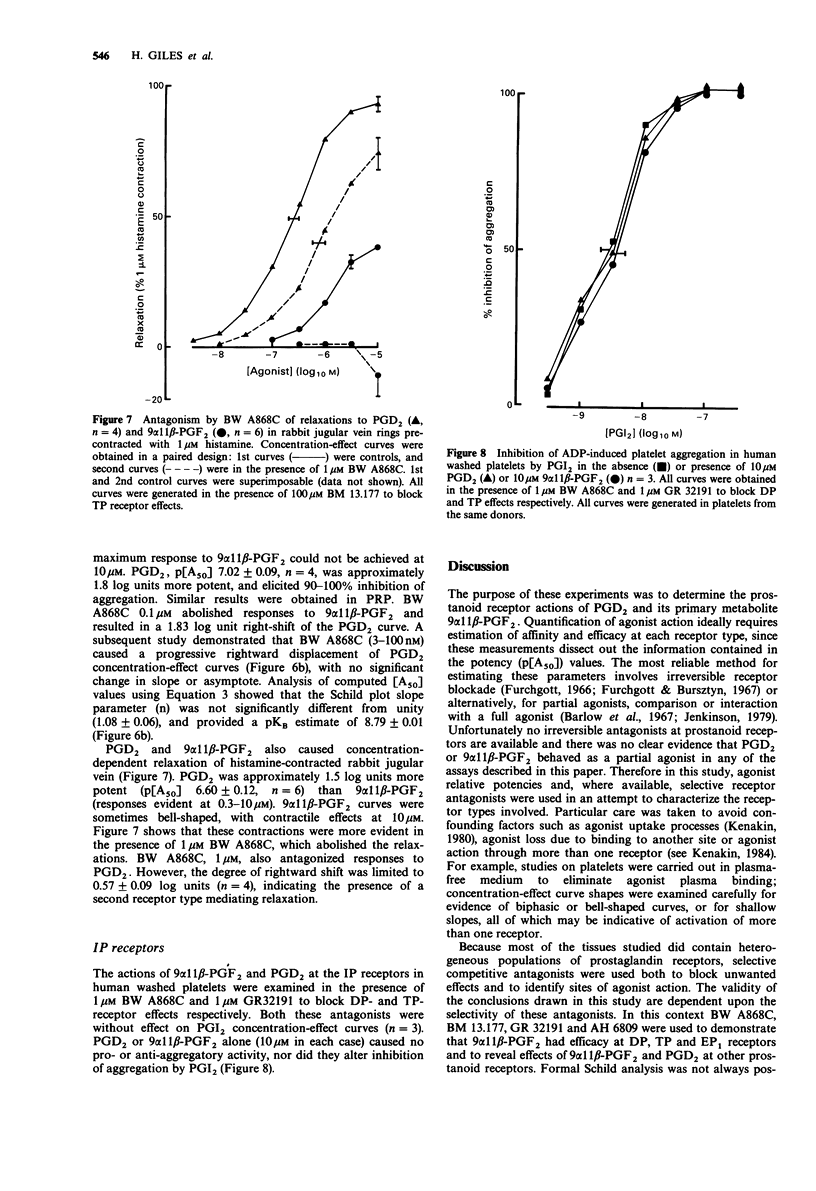
1. The aim of this study was to determine the receptor profile of 9 alpha 11 beta-prostaglandin F2 (PGF2) and compare it with that of its parent, prostaglandin D2 (PGD2). The experiments were designed to overcome the problems associated with the presence of multiple prostanoid receptor sub-types in most tissues; the lack of selective antagonists for each receptor means that conclusions regarding efficacy at FP and EP2 receptors must remain provisional. 2. At DP receptors in human platelets and rabbit jugular vein, PGD2 was a full agonist, p[A50] 7.02 +/- 0.09 and 6.60 +/- 0.12 respectively. 9 alpha 11 beta-PGF2 was approximately 30-60 fold less potent than PGD2. 3. 9 alpha 11 beta-PGF2 was a full agonist in the FP receptor containing preparation, cat iris sphincter (p [A50] 7.35 +/- 0.09) comparable in potency to PGD2 (p[A50] 7.15 +/- 0.19). Likewise the two prostanoids showed similar potency at the TP receptor in guinea-pig aorta (9 alpha 11 beta-PGF2 p[A50] 6.00 +/- 0.07; PGD2 6.24 +/- 0.08). 4. 9 alpha 11 beta-PGF2 and PGD2 had efficacy but low potency at EP1 receptors (guinea-pig oesophageal muscularis mucosa) and demonstrated 2000-3000 fold lower potency than PGE2 (p[A50] 8.35 +/- 0.09). Similarly, in the EP2 receptor-containing preparation, cat trachea, 9 alpha 11 beta-PGF2 was 3500 fold less potent and PGD2 700 fold less potent than PGE2 (p[A50] 8.06 +/- 0.26).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barlow R. B., Scott N. C., Stephenson R. P. The affinity and efficacy of onium salts on the frog rectus abdominis. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1967 Sep;31(1):188–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1967.tb01989.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beasley C. R., Robinson C., Featherstone R. L., Varley J. G., Hardy C. C., Church M. K., Holgate S. T. 9 alpha,11 beta-prostaglandin F2, a novel metabolite of prostaglandin D2 is a potent contractile agonist of human and guinea pig airways. J Clin Invest. 1987 Mar;79(3):978–983. doi: 10.1172/JCI112909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett A., Sanger G. J. The effects of prostaglandin D2 on the circular muscle of guinea-pig isolated ileum and colon [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Jun;63(2):357P–358P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black J. W., Leff P., Shankley N. P. Further analysis of anomalous pKB values for histamine H2-receptor antagonists on the mouse isolated stomach assay. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Nov;86(3):581–587. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08934.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman R. A., Humphrey P. P., Kennedy I., Levy G. P., Lumley P. U-46619, a selective thromboxane A2-like agonist? [proceedings]. Br J Pharmacol. 1980 Jan;68(1):127P–128P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman R. A., Sheldrick R. L. Prostanoid-induced contraction of human bronchial smooth muscle is mediated by TP-receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Mar;96(3):688–692. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11869.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dukes M., Russell W., Walpole A. L. Potent luteolytic agents related to prostaglandin F2alpha. Nature. 1974 Jul 26;250(464):330–331. doi: 10.1038/250330a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglen R. M., Whiting R. L. Characterization of the prostanoid receptor profile of enprostil and isomers in smooth muscle and platelets in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;98(4):1335–1343. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12682.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglen R. M., Whiting R. L. The action of prostanoid receptor agonists and antagonists on smooth muscle and platelets. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;94(2):591–601. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11565.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles H., Leff P., Bolofo M. L., Kelly M. G., Robertson A. D. The classification of prostaglandin DP-receptors in platelets and vasculature using BW A868C, a novel, selective and potent competitive antagonist. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Feb;96(2):291–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11816.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giles H., Leff P. The biology and pharmacology of PGD2. Prostaglandins. 1988 Feb;35(2):277–300. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(88)90093-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. L., Peesapati V., Wilson N. H. Antagonism of the thromboxane-sensitive contractile systems of the rabbit aorta, dog saphenous vein and guinea-pig trachea. Br J Pharmacol. 1982 Jul;76(3):423–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1982.tb09236.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keery R. J., Lumley P. AH6809, a prostaglandin DP-receptor blocking drug on human platelets. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul;94(3):745–754. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11584.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenakin T. P. Errors in the measurement of agonist potency-ratios produced by uptake processes: a general model applied to beta-adrenoceptor agonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1980;71(2):407–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1980.tb10953.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenakin T. P. The classification of drugs and drug receptors in isolated tissues. Pharmacol Rev. 1984 Sep;36(3):165–222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy I., Coleman R. A., Humphrey P. P., Levy G. P., Lumley P. Studies on the characterisation of prostanoid receptors: a proposed classification. Prostaglandins. 1982 Nov;24(5):667–689. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(82)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy I., Coleman R. A., Humphrey P. P., Lumley P. Studies on the characterization of prostanoid receptors. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Leukot Res. 1983;11:327–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence R. A., Jones R. L., Wilson N. H. Relaxant potencies of prostaglandin E analogues on rabbit jugular vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;98 (Suppl):796P–796P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liston T. E., Roberts L. J., 2nd Transformation of prostaglandin D2 to 9 alpha, 11 beta-(15S)-trihydroxyprosta-(5Z,13E)-dien-1-oic acid (9 alpha, 11 beta-prostaglandin F2): a unique biologically active prostaglandin produced enzymatically in vivo in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6030–6034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumley P., White B. P., Humphrey P. P. GR32191, a highly potent and specific thromboxane A2 receptor blocking drug on platelets and vascular and airways smooth muscle in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;97(3):783–794. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12017.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugliese G., Spokas E. G., Marcinkiewicz E., Wong P. Y. Hepatic transformation of prostaglandin D2 to a new prostanoid, 9 alpha,11 beta-prostaglandin F2, that inhibits platelet aggregation and constricts blood vessels. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14621–14625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts L. J., 2nd, Seibert K., Liston T. E., Tantengco M. V., Robertson R. M. PGD2 is transformed by human coronary arteries to 9 alpha, 11 beta-PGF2, which contracts human coronary artery rings. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Leukot Res. 1987;17A:427–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer A. I., Cooper B., O'Hara D., Handin R. I. Identification of platelet receptors for prostaglandin I2 and D2. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2914–2917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seibert K., Sheller J. R., Roberts L. J., 2nd (5Z,13E)-(15S)-9 alpha,11 beta,15-trihydroxyprosta-5,13-dien-1-oic acid (9 alpha,11 beta-prostaglandin F2): formation and metabolism by human lung and contractile effects on human bronchial smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):256–260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegl A. M., Smith J. B., Silver M. J., Nicolaou K. C., Ahern D. Selective binding site for [3H]prostacyclin on platelets. J Clin Invest. 1979 Feb;63(2):215–220. doi: 10.1172/JCI109292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stier C. T., Jr, Roberts L. J., 2nd, Wong P. Y. Renal response to 9 alpha, 11 beta-prostaglandin F2 in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Nov;243(2):487–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



