Abstract
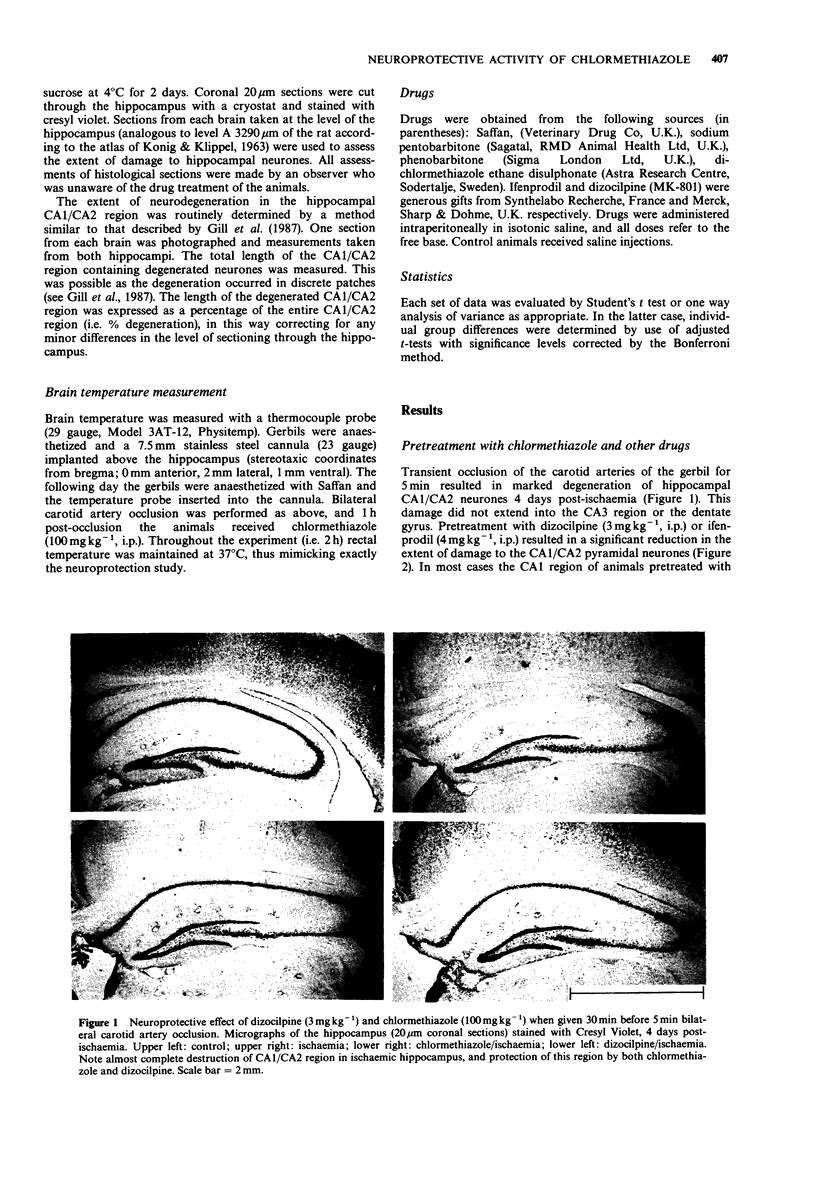
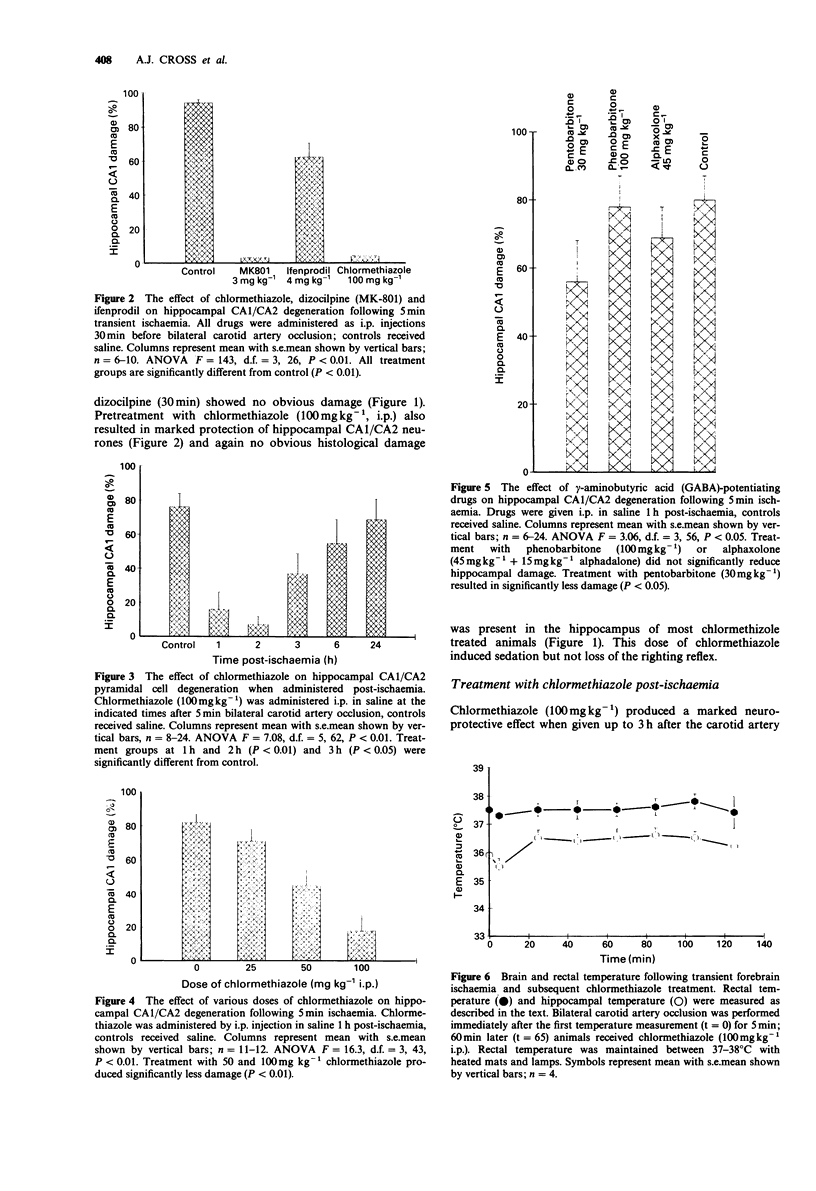
1. The effect of chlormethiazole, and other drugs which potentiate gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) function on delayed neuronal death in the hippocampus has been examined in the gerbil. 2. Chlormethiazole (100 mg kg-1, i.p.) and two other drugs previously reported to be neuroprotective (dizocilpine, 3 mg kg-1, i.p. and ifenprodil, 4 mg kg-1, i.p.) were all found to prevent neurodegeneration of CA1/CA2 neurones in the hippocampus when given 30 min before a 5 min episode of bilateral carotid artery occlusion. 3. Chlormethiazole (100 mg kg-1) was neuroprotective when given up to 3 h, after the ischaemic episode. 4. Given 1 h after the cartoid artery occlusion, chlormethiazole produced significant protection against hippocampal neurodegeneration at a dose of 50 mg kg-1, but not at 25 mg kg-1. 5. Phenobarbitone (100 mg kg-1, i.p.) and Saffan (alphaxalone, 45 mg kg-1 plus alphadalone, 15 mg kg-1, i.p.) were not protective when given 1 h after the ischaemic episode while pentobarbitone (30 mg kg-1, i.p.) had a modest protective effect. 6. Evidence is presented to show that neither the operating procedure nor the chlormethiazole administration lowered rectal or cerebral temperature. 7. The data suggest that chlormethiazole may be a useful treatment in the prevention of neurodegeneration following stroke or cardiac arrest.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addae J. I., Stone T. W. Effects of anticonvulsants on responses to excitatory amino acids applied topically to rat cerebral cortex. Gen Pharmacol. 1988;19(3):455–462. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(88)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alps B. J., Calder C., Hass W. K., Wilson A. D. Comparative protective effects of nicardipine, flunarizine, lidoflazine and nimodipine against ischaemic injury in the hippocampus of the Mongolian gerbil. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Apr;93(4):877–883. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11475.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste H., Drejer J., Schousboe A., Diemer N. H. Elevation of the extracellular concentrations of glutamate and aspartate in rat hippocampus during transient cerebral ischemia monitored by intracerebral microdialysis. J Neurochem. 1984 Nov;43(5):1369–1374. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb05396.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G., Hudson A. L., Price G. W. GABAA and GABAB receptor site distribution in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience. 1987 Feb;20(2):365–383. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90098-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. W., Levy D. E., Kublik M., Harrow J., Plum F., Brierley J. B. Selective chromatolysis of neurons in the gerbil brain: a possible consequence of "epileptic" activity produced by common carotid artery occlusion. Ann Neurol. 1979 Feb;5(2):127–138. doi: 10.1002/ana.410050206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busto R., Dietrich W. D., Globus M. Y., Valdés I., Scheinberg P., Ginsberg M. D. Small differences in intraischemic brain temperature critically determine the extent of ischemic neuronal injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1987 Dec;7(6):729–738. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1987.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen J. H., Andreasen F., Kristoffersen M. B. Comparison of the anaesthetic and haemodynamic effects of chlormethiazole and thiopentone. Br J Anaesth. 1983 May;55(5):391–397. doi: 10.1093/bja/55.5.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crockard A., Iannotti F., Hunstock A. T., Smith R. D., Harris R. J., Symon L. Cerebral blood flow and edema following carotid occlusion in the gerbil. Stroke. 1980 Sep-Oct;11(5):494–498. doi: 10.1161/01.str.11.5.494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. J., Stirling J. M., Robinson T. N., Bowen D. M., Francis P. T., Green A. R. The modulation by chlormethiazole of the GABAA-receptor complex in rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;98(1):284–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb16893.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLeo J., Schubert P., Kreutzberg G. W. Propentofylline (HWA 285) protects hippocampal neurons of Mongolian gerbils against ischemic damage in the presence of an adenosine antagonist. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Feb 3;84(3):307–311. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90526-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis A., Pulsinelli W. The response of GABAergic and cholinergic neurons to transient cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 1982 Jul 15;243(2):271–278. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90250-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryd Johansen F., Balslev Jørgensen M., Diemer N. H. Resistance of hippocampal CA-1 interneurons to 20 min of transient cerebral ischemia in the rat. Acta Neuropathol. 1983;61(2):135–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00697393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill R., Foster A. C., Woodruff G. N. MK-801 is neuroprotective in gerbils when administered during the post-ischaemic period. Neuroscience. 1988 Jun;25(3):847–855. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90040-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill R., Foster A. C., Woodruff G. N. Systemic administration of MK-801 protects against ischemia-induced hippocampal neurodegeneration in the gerbil. J Neurosci. 1987 Oct;7(10):3343–3349. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-10-03343.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Globus M. Y., Busto R., Dietrich W. D., Martinez E., Valdes I., Ginsberg M. D. Effect of ischemia on the in vivo release of striatal dopamine, glutamate, and gamma-aminobutyric acid studied by intracerebral microdialysis. J Neurochem. 1988 Nov;51(5):1455–1464. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotti B., Duverger D., Bertin J., Carter C., Dupont R., Frost J., Gaudilliere B., MacKenzie E. T., Rousseau J., Scatton B. Ifenprodil and SL 82.0715 as cerebral anti-ischemic agents. I. Evidence for efficacy in models of focal cerebral ischemia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Dec;247(3):1211–1221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A. R., Murray T. K. A simple intravenous infusion method in rodents for determining the potency of anticonvulsants acting through GABAergic mechanisms. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;41(12):879–880. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1989.tb06395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi R., Zoli M., Agnati L. F., Ferraguti F., Fuxe K., Toffano G., Zini I. Effects of transient forebrain ischemia on peptidergic neurons and astroglial cells: evidence for recovery of peptide immunoreactivities in neocortex and striatum but not hippocampal formation. Exp Brain Res. 1990;82(1):123–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00230844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagberg H., Lehmann A., Sandberg M., Nyström B., Jacobson I., Hamberger A. Ischemia-induced shift of inhibitory and excitatory amino acids from intra- to extracellular compartments. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1985 Sep;5(3):413–419. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1985.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison N. L., Simmonds M. A. Two distinct interactions of barbiturates and chlormethiazole with the GABAA receptor complex in rat cuneate nucleus in vitro. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Oct;80(2):387–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb10045.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermans C., Fransen J. F., Wauquier A. Survival and neurological outcome of the Mongolian gerbil with or without bilateral carotid ligation after treatment with ether, thiopental or etomidate. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1983 Jun;263(2):314–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen F. F., Zimmer J., Diemer N. H. Early loss of somatostatin neurons in dentate hilus after cerebral ischemia in the rat precedes CA-1 pyramidal cell loss. Acta Neuropathol. 1987;73(2):110–114. doi: 10.1007/BF00693775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirino T. Delayed neuronal death in the gerbil hippocampus following ischemia. Brain Res. 1982 May 6;239(1):57–69. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90833-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirino T., Tamura A., Sano K. A reversible type of neuronal injury following ischemia in the gerbil hippocampus. Stroke. 1986 May-Jun;17(3):455–459. doi: 10.1161/01.str.17.3.455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightfoote W. E., 2nd, Molinari G. F., Chase T. N. Modification of cerebral ischemic damage by anesthetics. Stroke. 1977 Sep-Oct;8(5):627–628. doi: 10.1161/01.str.8.5.627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldrum B. Protection against ischaemic neuronal damage by drugs acting on excitatory neurotransmission. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev. 1990 Spring;2(1):27–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moody E. J., Skolnick P. Chlormethiazole: neurochemical actions at the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor complex. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 May 2;164(1):153–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogren S. O. Chlormethiazole--mode of action. Acta Psychiatr Scand Suppl. 1986;329:13–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olney J. W., Labruyere J., Price M. T. Pathological changes induced in cerebrocortical neurons by phencyclidine and related drugs. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1360–1362. doi: 10.1126/science.2660263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheardown M. J., Nielsen E. O., Hansen A. J., Jacobsen P., Honoré T. 2,3-Dihydroxy-6-nitro-7-sulfamoyl-benzo(F)quinoxaline: a neuroprotectant for cerebral ischemia. Science. 1990 Feb 2;247(4942):571–574. doi: 10.1126/science.2154034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds M. A., Turner J. P. Potentiators of responses to activation of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABAA) receptors. Neuropharmacology. 1987 Jul;26(7B):923–930. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(87)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. P., Griffiths T., Evans M. C., Swan J. H., Meldrum B. S. Calcium overload in selectively vulnerable neurons of the hippocampus during and after ischemia: an electron microscopy study in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1984 Sep;4(3):350–361. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1984.52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternau L. L., Lust W. D., Ricci A. J., Ratcheson R. Role for gamma-aminobutyric acid in selective vulnerability in gerbils. Stroke. 1989 Feb;20(2):281–287. doi: 10.1161/01.str.20.2.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taft W. C., Clifton G. L., Blair R. E., DeLorenzo R. J. Phenytoin protects against ischemia-produced neuronal cell death. Brain Res. 1989 Mar 27;483(1):143–148. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tricklebank M. D., Singh L., Oles R. J., Preston C., Iversen S. D. The behavioural effects of MK-801: a comparison with antagonists acting non-competitively and competitively at the NMDA receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug 11;167(1):127–135. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90754-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincens M., Enjalbert A., Lloyd K. G., Paillard J. J., Thuret F., Kordon C., Lechat P. Evidence that clomethiazole interacts with the macromolecular GABA A-receptor complex in the central nervous system and in the anterior pituitary gland. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1989 Apr;339(4):397–402. doi: 10.1007/BF00736053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



