Abstract
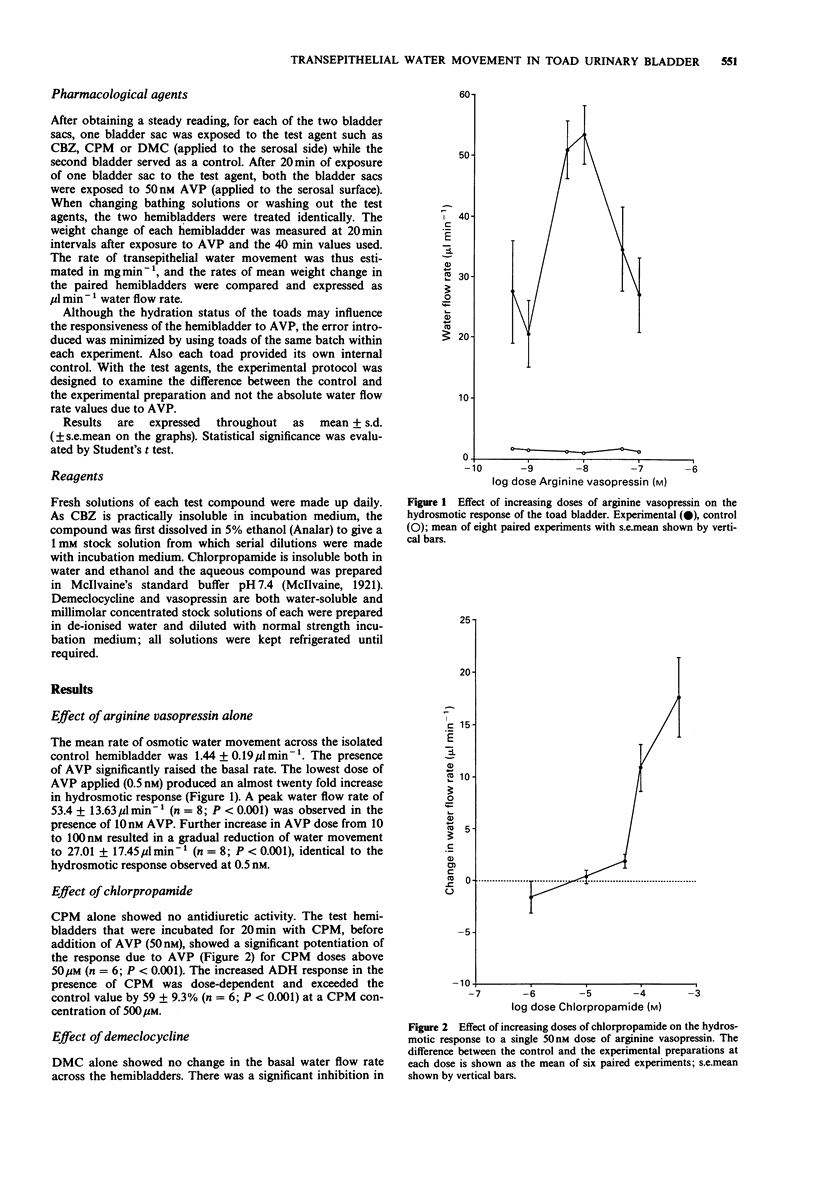
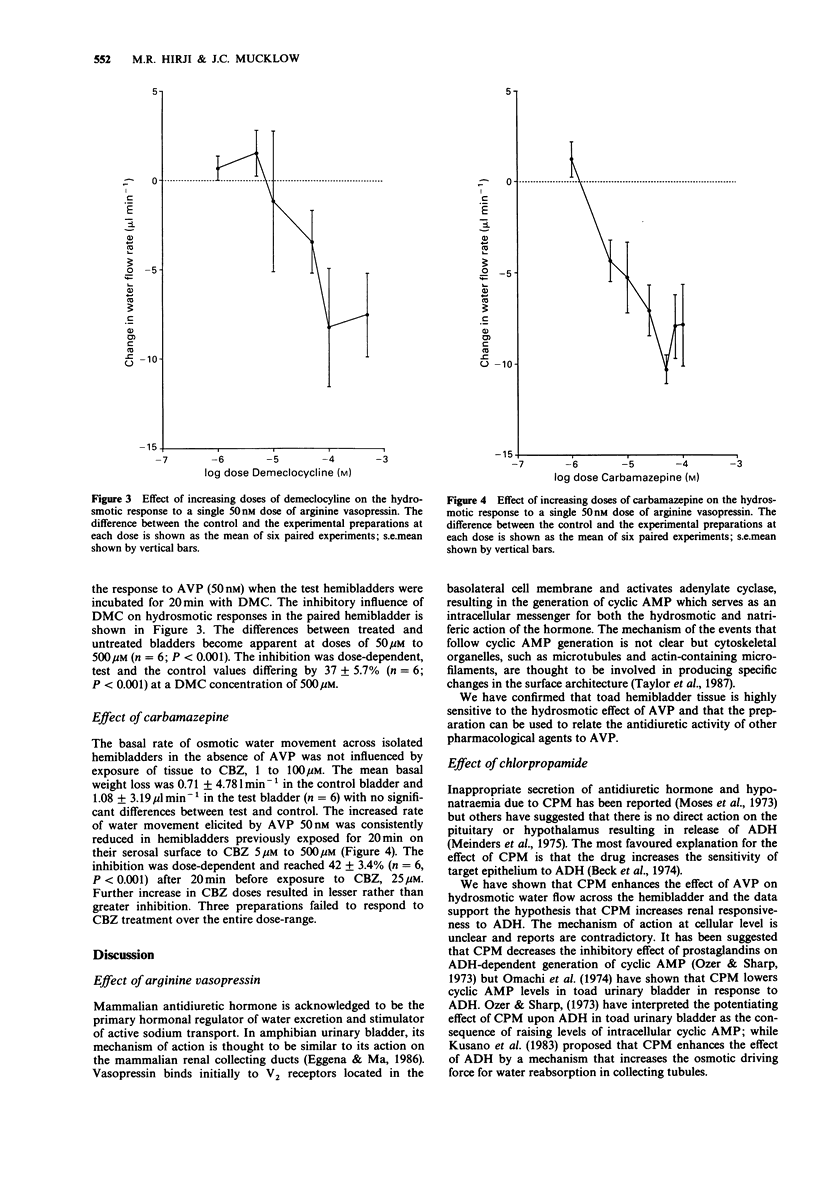
1. Osmotic water movement across toad isolated hemibladders was measured by a gravimetric method. 2. The influence of carbamazepine, chlorpropamide and demeclocycline on the antidiuretic hormone (ADH)-induced water flow rate was examined. 3. No antidiuretic activity due to carbamazepine alone was observed but a slight inhibition due to ADH-induced water flow was observed in the presence of carbamazepine over a selected dose-range. This was unexpected and is inconsistent with data from in vivo studies in man. 4. Chlorpropamide potentiated ADH-induced water flow, in keeping with the hypothesis that chlorpropamide sensitizes the renal tubules to ADH-induced water flow. 5. Demeclocycline inhibited ADH-induced water flow. The mechanism of action remains unclear.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BENTLEY P. J. The effects of neurohypophysial extracts on the water transfer across the wall of the isolated urinary bladder of the toad Bufo marinus. J Endocrinol. 1958 Sep;17(3):201–209. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0170201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck N., Kim K. S., Davis B. B. Effect of chlorpropamide on cyclic AMP in rat renal medulla. Endocrinology. 1974 Sep;95(3):771–775. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-3-771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley P. J. The physiology of the urinary bladder of amphibia. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1966 May;41(2):275–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1966.tb01494.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunhofer J., Zicha L. Eröffnet Tegretal neue Therapiemöglichkeiten bei bestimmten neurologischen und endokrinen Krankheitsbildern? Eine klinische elektroenzephalographische und dünnschichtchromatographische Studie. Med Welt. 1966 Sep 3;(36):1875–1880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggena P., Ma C. L. Downregulation of vasopressin receptors in toad bladder. Am J Physiol. 1986 Mar;250(3 Pt 1):C453–C459. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.3.C453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman H. A., Singer I. Comparative effects of tetracyclines on water flow across toad urinary bladders. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1974 Aug;190(2):358–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanefeld F., Levsen I., Stefan H. Zur Wirkung von Carbamazepin auf die neurosektretorischen Kerne der Ratte. Z Gesamte Exp Med. 1970;153(1):95–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura T., Matsui K., Sato T., Yoshinaga K. Mechanism of carbamazepine (Tegretol)-induced antidiuresis: evidence for release of antidiuretic hormone and impaired excretion of a water load. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Mar;38(3):356–362. doi: 10.1210/jcem-38-3-356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusano E., Braun-Werness J. L., Vick D. J., Keller M. J., Dousa T. P. Chlorpropamide action on renal concentrating mechanism in rats with hypothalamic diabetes insipidus. J Clin Invest. 1983 Oct;72(4):1298–1313. doi: 10.1172/JCI111086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEAF A., ANDERSON J., PAGE L. B. Active sodium transport by the isolated toad bladder. J Gen Physiol. 1958 Mar 20;41(4):657–668. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.4.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahr M. B. Hyponatremia during carbamazepine therapy. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1985 Jun;37(6):693–696. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1985.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinders A. E., Cejka V., Robertson G. L. The antidiuretic action of carbamazepine in man. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1974 Oct;47(4):289–299. doi: 10.1042/cs0470289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinders A. E., van Leeuwen A. M., Borst J. G., Cejka V. Paradoxical diuresis after vasopressin administration to patients with neurohypophyseal diabetes insipidus treated with chlorpropamide, carbamazepine or clofibrate. Clin Sci Mol Med. 1975 Oct;49(4):283–290. doi: 10.1042/cs0490283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. M., Numann P., Miller M. Mechanism of chlorpropamide-induced antidiuresis in man: evidence for release of ADH and enhancement of peripheral action. Metabolism. 1973 Jan;22(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90029-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omachi R. S., Robbie D. E., Handler J. S., Orloff J. Effects of ADH and other agents on cyclic AMP accumulation in toad bladder epithelium. Am J Physiol. 1974 May;226(5):1152–1157. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.226.5.1152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozer A., Sharp G. W. Modulation of adenyl cyclase action in toad bladder by chlorpropamide: antagonism to prostaglandin E. Eur J Pharmacol. 1973 Jun;22(3):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(73)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer I., Rotenberg D. Demeclocycline-induced nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. In-vivo and in-vitro studies. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Nov;79(5):679–683. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-5-679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith N. J., Espir M. L., Baylis P. H. Raised plasma arginine vasopressin concentration in carbamazepine-induced water intoxication. Br Med J. 1977 Sep 24;2(6090):804–804. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6090.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens W. P., Coe J. Y., Baylis P. H. Plasma arginine vasopressin concentrations and antidiuretic action of carbamazepine. Br Med J. 1978 Jun 3;1(6125):1445–1447. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6125.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens W. P., Espir M. L., Tattersall R. B., Quinn N. P., Gladwell S. R., Galbraith A. W., Reynolds E. H. Water intoxication due to carbamazepine. Br Med J. 1977 Mar 19;1(6063):754–755. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6063.754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A., Eich E., Pearl M., Brem A. S., Peeper E. Q. Cytosolic calcium and the action of vasopressin in toad urinary bladder. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jun;252(6 Pt 2):F1028–F1041. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1987.252.6.F1028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wales J. K. Treatment of diabetes insipidus with carbamazepine. Lancet. 1975 Nov 15;2(7942):948–951. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90361-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



