Abstract
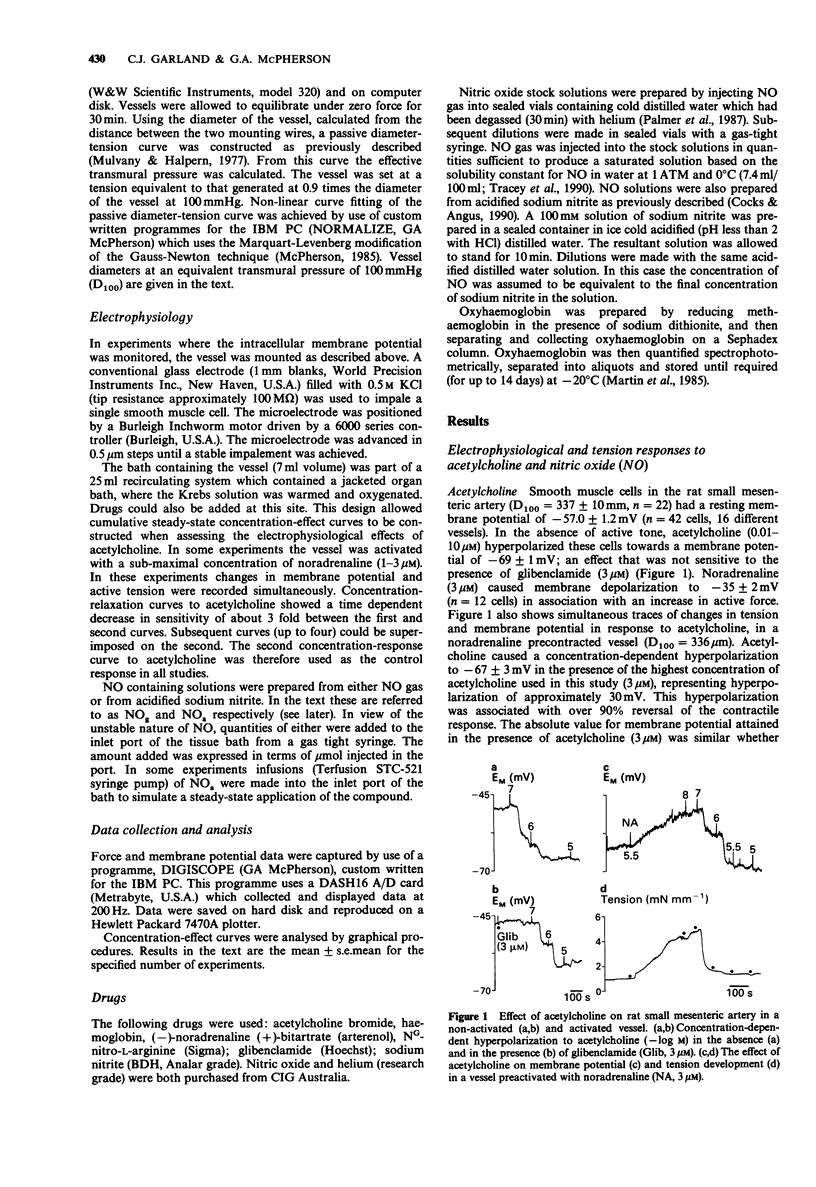
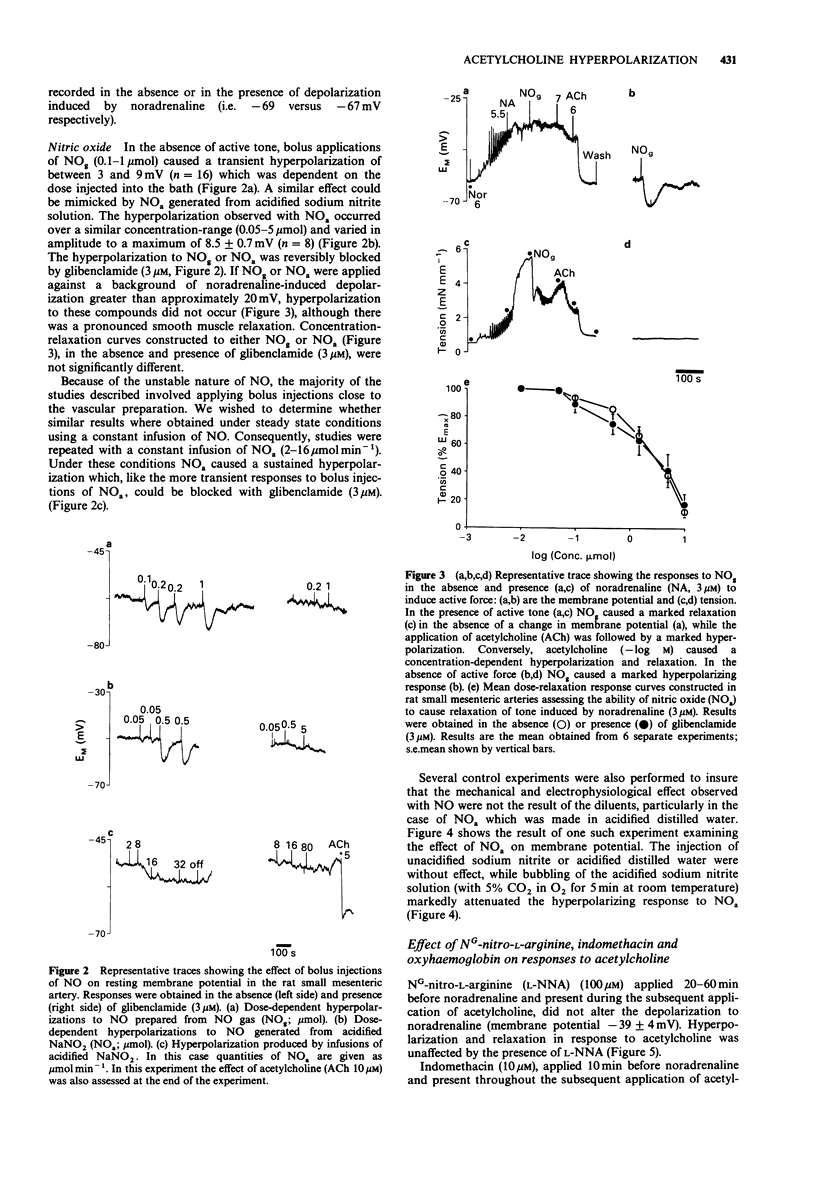
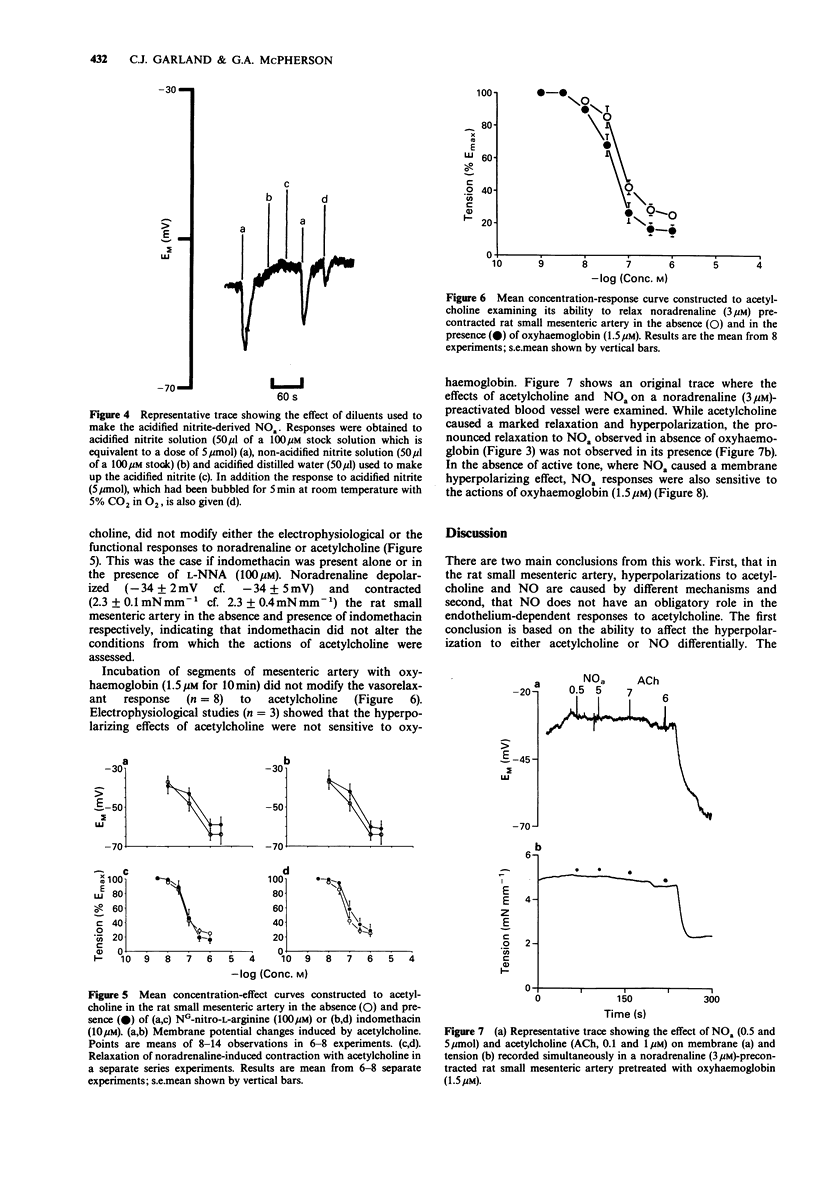
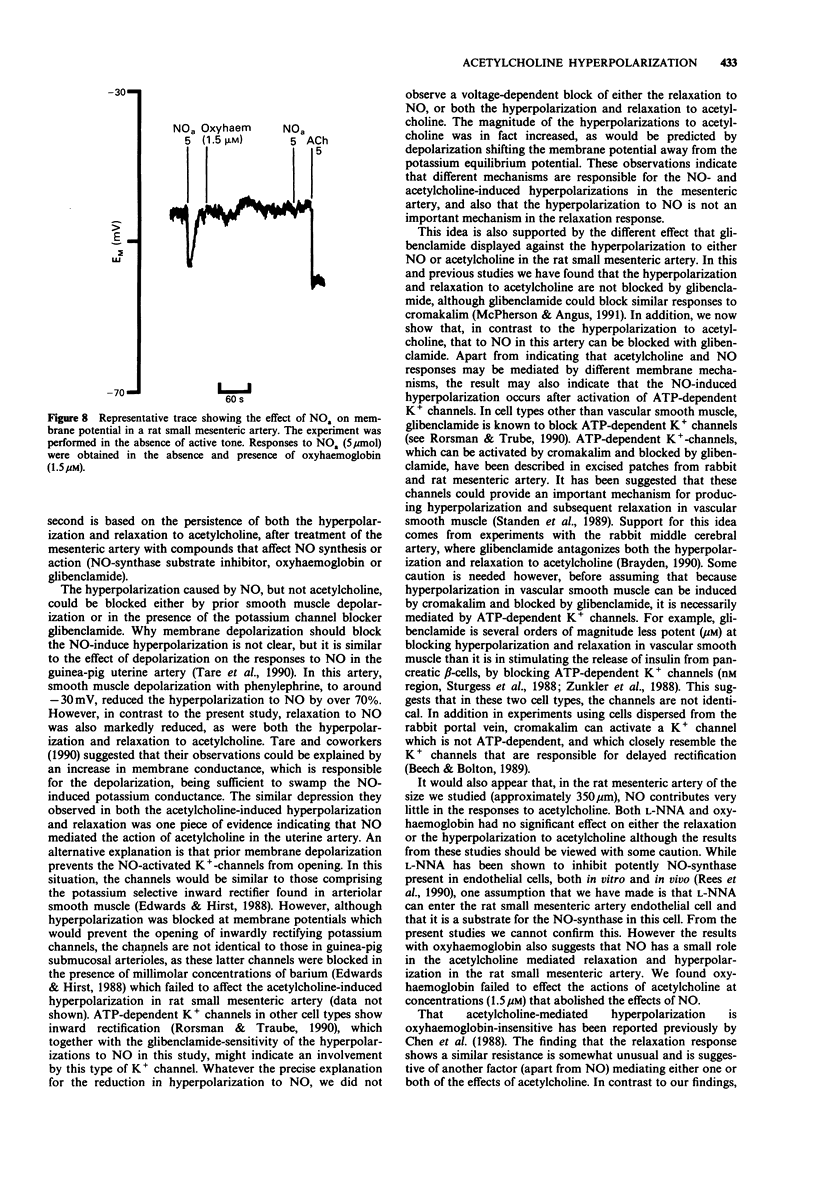
1 Acetylcholine caused a concentration-dependent smooth muscle hyperpolarization and relaxation in rat small mesenteric arteries (diameter at 100 mmHg 250-450 mm) stimulated with noradrenaline (3 microM). 2 Nitric oxide (NO), generated from either NO-gas or from acidified sodium nitrite, also induced smooth muscle hyperpolarization but only in the absence of active force. However, unlike the hyperpolarizations to acetylcholine, those to NO were abolished either by prior smooth muscle depolarization caused by noradrenaline, or by the K+ channel blocker, glibenclamide (3 microM). 3 Hyperpolarization and relaxation to acetylcholine were unaffected by prior exposure of the mesenteric artery to either the cyclo-oxygenase inhibitor, indomethacin (10 microM), or the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, NG-nitro-L-arginine (L-NNA, 100 microM). 4 Haemoglobin (1.5 microM), which binds and inactivates NO, blocked the hyperpolarizing and vasorelaxant response to NO, but did not alter either response to acetylcholine. 5 These data show that, in the rat small mesenteric artery, membrane hyperpolarizations to NO and acetylcholine are mediated by different mechanisms, and that the hyperpolarizations to NO and acetylcholine are mediated by different mechanisms, and that the hyperpolarization induced by NO is not involved in the responses to acetylcholine. In addition, they provide evidence that the acetylcholine responses in this artery, which are endothelium-dependent, are not mediated by the release of NO.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angus J. A., Broughton A., Mulvany M. J. Role of alpha-adrenoceptors in constrictor responses of rat, guinea-pig and rabbit small arteries to neural activation. J Physiol. 1988 Sep;403:495–510. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angus J. A., Cocks T. M. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Pharmacol Ther. 1989;41(1-2):303–352. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(89)90112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beech D. J., Bolton T. B. Properties of the cromakalim-induced potassium conductance in smooth muscle cells isolated from the rabbit portal vein. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):851–864. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14614.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton T. B., Lang R. J., Takewaki T. Mechanisms of action of noradrenaline and carbachol on smooth muscle of guinea-pig anterior mesenteric artery. J Physiol. 1984 Jun;351:549–572. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brayden J. E. Membrane hyperpolarization is a mechanism of endothelium-dependent cerebral vasodilation. Am J Physiol. 1990 Sep;259(3 Pt 2):H668–H673. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.3.H668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busse R., Fichtner H., Lückhoff A., Kohlhardt M. Hyperpolarization and increased free calcium in acetylcholine-stimulated endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1988 Oct;255(4 Pt 2):H965–H969. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.255.4.H965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bény J. L. Endothelial and smooth muscle cells hyperpolarized by bradykinin are not dye coupled. Am J Physiol. 1990 Mar;258(3 Pt 2):H836–H841. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.258.3.H836. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen G., Suzuki H., Weston A. H. Acetylcholine releases endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor and EDRF from rat blood vessels. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;95(4):1165–1174. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11752.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocks T. M., Angus J. A. Comparison of relaxation responses of vascular and non-vascular smooth muscle to endothelium-derived relaxing factor (EDRF), acidified sodium nitrite (NO) and sodium nitroprusside. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Apr;341(4):364–372. doi: 10.1007/BF00180663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards F. R., Hirst G. D. Inward rectification in submucosal arterioles of guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1988 Oct;404:437–454. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1988.sp017298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feletou M., Vanhoutte P. M. Endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization of canine coronary smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Mar;93(3):515–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb10306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furchgott R. F., Carvalho M. H., Khan M. T., Matsunaga K. Evidence for endothelium-dependent vasodilation of resistance vessels by acetylcholine. Blood Vessels. 1987;24(3):145–149. doi: 10.1159/000158689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. H., Busse R., Bassenge E. Endothelium-dependent hyperpolarization of smooth muscle cells in rabbit femoral arteries is not mediated by EDRF (nitric oxide). Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;338(4):438–442. doi: 10.1007/BF00172124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori K., Lorenz R. R., Vanhoutte P. M. Nitric oxide, ACh, and electrical and mechanical properties of canine arterial smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1988 Jul;255(1 Pt 2):H207–H212. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1988.255.1.H207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Villani G. M., Jothianandan D., Furchgott R. F. Selective blockade of endothelium-dependent and glyceryl trinitrate-induced relaxation by hemoglobin and by methylene blue in the rabbit aorta. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Mar;232(3):708–716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A. Analysis of radioligand binding experiments. A collection of computer programs for the IBM PC. J Pharmacol Methods. 1985 Nov;14(3):213–228. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(85)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A., Angus J. A. Evidence that acetylcholine-mediated hyperpolarization of the rat small mesenteric artery does not involve the K+ channel opened by cromakalim. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 May;103(1):1184–1190. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12321.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekata F. The role of hyperpolarization in the relaxation of smooth muscle of monkey coronary artery. J Physiol. 1986 Feb;371:257–265. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp015972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvany M. J., Halpern W. Contractile properties of small arterial resistance vessels in spontaneously hypertensive and normotensive rats. Circ Res. 1977 Jul;41(1):19–26. doi: 10.1161/01.res.41.1.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiye E., Nakao K., Itoh T., Kuriyama H. Factors inducing endothelium-dependent relaxation in the guinea-pig basilar artery as estimated from the actions of haemoglobin. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Mar;96(3):645–655. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11864.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. M., Ferrige A. G., Moncada S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987 Jun 11;327(6122):524–526. doi: 10.1038/327524a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall M. D., Hiley C. R. Detergent and methylene blue affect endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation and pressure/flow relations in rat blood perfused mesenteric arterial bed. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;95(4):1081–1088. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11742.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. D., Palmer R. M., Schulz R., Hodson H. F., Moncada S. Characterization of three inhibitors of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vitro and in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):746–752. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14151.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spagnoli L. G., Villaschi S., Neri L., Palmieri G. Gap junctions in myo-endothelial bridges of rabbit carotid arteries. Experientia. 1982 Jan 15;38(1):124–125. doi: 10.1007/BF01944566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B., Quayle J. M., Davies N. W., Brayden J. E., Huang Y., Nelson M. T. Hyperpolarizing vasodilators activate ATP-sensitive K+ channels in arterial smooth muscle. Science. 1989 Jul 14;245(4914):177–180. doi: 10.1126/science.2501869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgess N. C., Kozlowski R. Z., Carrington C. A., Hales C. N., Ashford M. L. Effects of sulphonylureas and diazoxide on insulin secretion and nucleotide-sensitive channels in an insulin-secreting cell line. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;95(1):83–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb16551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tare M., Parkington H. C., Coleman H. A., Neild T. O., Dusting G. J. Hyperpolarization and relaxation of arterial smooth muscle caused by nitric oxide derived from the endothelium. Nature. 1990 Jul 5;346(6279):69–71. doi: 10.1038/346069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taugner R., Kirchheim H., Forssmann W. G. Myoendothelial contacts in glomerular arterioles and in renal interlobular arteries of rat, mouse and Tupaia belangeri. Cell Tissue Res. 1984;235(2):319–325. doi: 10.1007/BF00217856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. G., Weston A. H. Endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor: a new endogenous inhibitor from the vascular endothelium. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1988 Aug;9(8):272–274. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(88)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey W. R., Linden J., Peach M. J., Johns R. A. Comparison of spectrophotometric and biological assays for nitric oxide (NO) and endothelium-derived relaxing factor (EDRF): nonspecificity of the diazotization reaction for NO and failure to detect EDRF. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Mar;252(3):922–928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zünkler B. J., Lenzen S., Männer K., Panten U., Trube G. Concentration-dependent effects of tolbutamide, meglitinide, glipizide, glibenclamide and diazoxide on ATP-regulated K+ currents in pancreatic B-cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1988 Feb;337(2):225–230. doi: 10.1007/BF00169252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



