Abstract
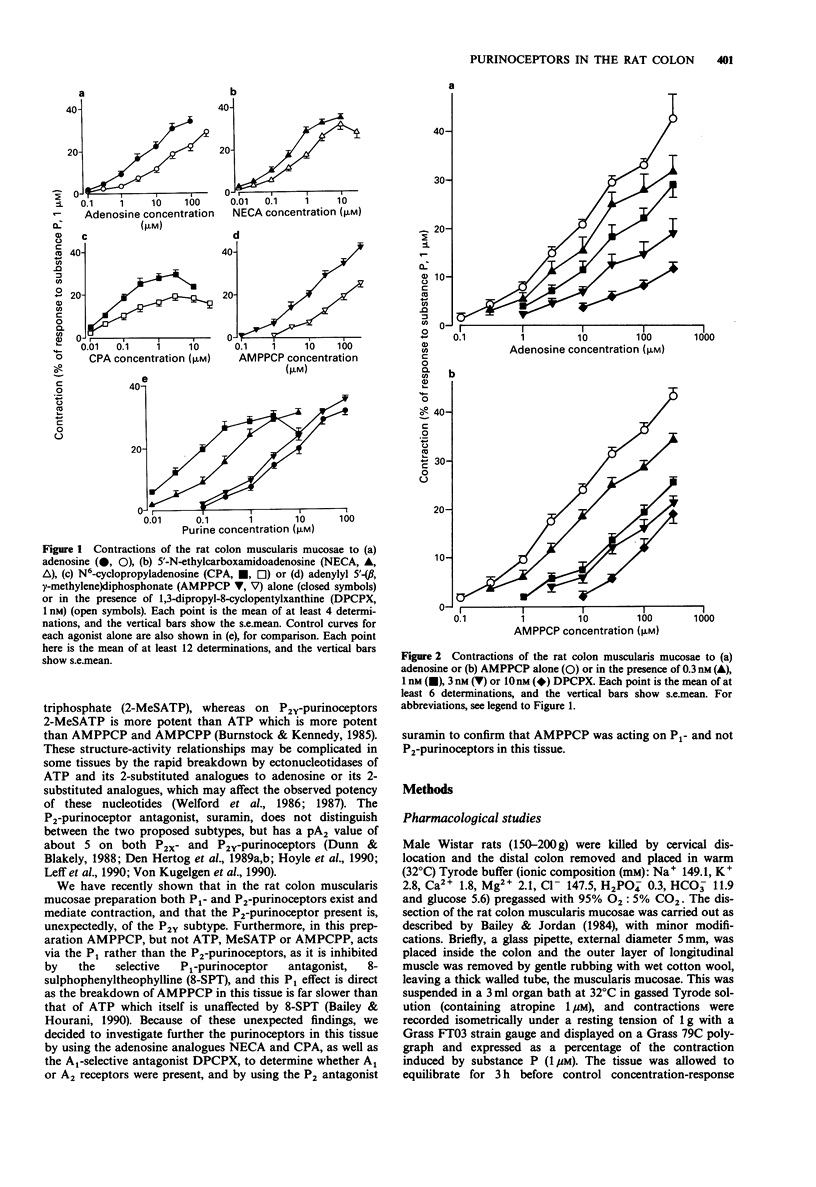
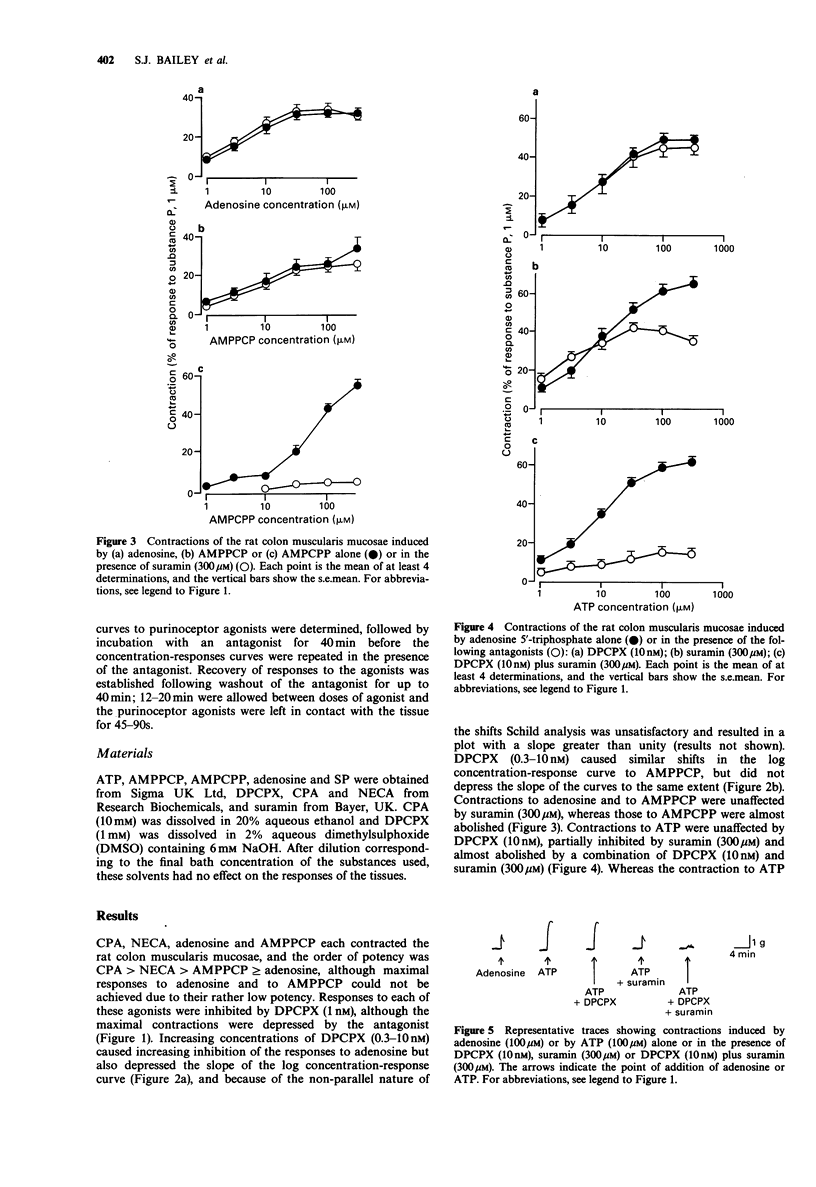
1. Previous studies had shown that adenosine and adenine nucleotides including adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) caused contraction of the rat colon muscularis mucosae via P1 and P2Y-purinoceptors respectively, and that the stable ATP analogue adenylyl 5'-(beta,gama- methylene)diphosphonate (AMPPCP) had an unexpected direct action on the P1-purinoceptors. The P1-purinoceptors have now therefore been further characterized by use of the adenosine analogues 5'-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine (NECA) and N6-cyclopropyladenosine (CPA) and the antagonist 1,3-dipropyl-8-cyclopentylxanthine (DPCPX), which is selective for the A1 subtype. The P2-purinoceptor antagonist suramin was also used, to investigate the selectivity of the P2 agonists. 2. The order of potency of P1 agonists for contraction was CPA greater than NECA greater than AMPPCP greater than or equal to adenosine, and DPCPX (1 nM) caused greater than two fold shifts to the right of the log concentration-response curves for each of these agonists, although the shifts were not always parallel and Schild analysis of the inhibition of the effect of adenosine resulted in a plot with a slope greater than unity. These results indicate that the P1-purinoceptor mediating contraction is of the A1 subtype, as has been found in other tissues in which adenosine causes contraction. 3. The P2-purinoceptor antagonist suramin (300 microM) had no effect on the responses to adenosine or to AMPPCP, but abolished contractions induced by the related stable ATP analogue adenosine 5'-(alpha,beta-methylene)triphosphonate (AMPCPP).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey S. J., Hourani S. M. A study of the purinoceptors mediating contraction in the rat colon. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):753–756. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14087.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey S. J., Jordan C. C. A study of [D-Pro2, D-Phe7, D-Trp9]-substance P and [D-Trp7,9]-substance P as tachykinin partial agonists in the rat colon. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Jun;82(2):441–451. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb10779.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruns R. F. Adenosine receptors. Roles and pharmacology. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;603:211–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb37674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Kennedy C. Is there a basis for distinguishing two types of P2-purinoceptor? Gen Pharmacol. 1985;16(5):433–440. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(85)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G. Overview. Purinergic mechanisms. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;603:1–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb37657.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis M. G., Jacobson K. A., Tomkins D. M. Apparent affinity of some 8-phenyl-substituted xanthines at adenosine receptors in guinea-pig aorta and atria. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep;92(1):69–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb11297.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis M. G., Stoggall S. M., Martin F. M. Apparent affinity of 1,3-dipropyl-8-cyclopentylxanthine for adenosine A1 and A2 receptors in isolated tissues from guinea-pigs. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug;97(4):1274–1278. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12589.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusack N. J., Hourani S. M. Subtypes of P2-purinoceptors. Studies using analogues of ATP. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;603:172–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb37671.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Den Hertog A., Van den Akker J., Nelemans A. Suramin and the inhibitory junction potential in taenia caeci of the guinea-pig. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec 7;173(2-3):207–209. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90522-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn P. M., Blakeley A. G. Suramin: a reversible P2-purinoceptor antagonist in the mouse vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Feb;93(2):243–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11427.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. G., Canning B. J., Wilkins D. E. Adenosine receptor-mediated contraction and relaxation of guinea-pig isolated tracheal smooth muscle: effects of adenosine antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Oct;95(2):371–378. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11655.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. L. Extracellular ATP: effects, sources and fate. Biochem J. 1986 Jan 15;233(2):309–319. doi: 10.1042/bj2330309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hourani S. M., Bailey S. J., Nicholls J., Kitchen I. Direct effects of adenylyl 5'-(beta,gamma-methylene)diphosphonate, a stable ATP analogue, on relaxant P1-purinoceptors in smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;104(3):685–690. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyle C. H., Knight G. E., Burnstock G. Suramin antagonizes responses to P2-purinoceptor agonists and purinergic nerve stimulation in the guinea-pig urinary bladder and taenia coli. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Mar;99(3):617–621. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12979.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenakin T. P., Pike N. B. An in vitro analysis of purine-mediated renal vasoconstriction in rat isolated kidney. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Feb;90(2):373–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb08967.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy C. P1- and P2-purinoceptor subtypes--an update. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1990 Jan-Feb;303:30–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff P., Wood B. E., O'Connor S. E. Suramin is a slowly-equilibrating but competitive antagonist at P2x-receptors in the rabbit isolated ear artery. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):645–649. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14134.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung E., Jacobson K. A., Green R. D. Analysis of agonist-antagonist interactions at A1 adenosine receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Jul;38(1):72–83. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson R. A., Pearson J. D. Cardiovascular purinoceptors. Physiol Rev. 1990 Jul;70(3):761–845. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1990.70.3.761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. A., Sebastião A. M. Adenosine receptors and calcium: basis for proposing a third (A3) adenosine receptor. Prog Neurobiol. 1986;26(3):179–209. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(86)90015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. A., Buxton I. L., Westfall D. P. Pharmacological classification of receptors for adenyl purines in guinea pig myometrium. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Dec;247(3):1059–1063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoggall S. M., Shaw J. S. The coexistence of adenosine A1 and A2 receptors in guinea-pig aorta. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 13;190(3):329–335. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94197-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W. Purine receptors in the rat anococcygeus muscle. J Physiol. 1983 Feb;335:591–608. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone T. W. Receptors for adenosine and adenine nucleotides. Gen Pharmacol. 1991;22(1):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0306-3623(91)90305-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welford L. A., Cusack N. J., Hourani S. M. ATP analogues and the guinea-pig taenia coli: a comparison of the structure-activity relationships of ectonucleotidases with those of the P2-purinoceptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Oct 7;129(3):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90431-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welford L. A., Cusack N. J., Hourani S. M. The structure-activity relationships of ectonucleotidases and of excitatory P2-purinoceptors: evidence that dephosphorylation of ATP analogues reduces pharmacological potency. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Sep 2;141(1):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90418-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White T. D. Role of adenine compounds in autonomic neurotransmission. Pharmacol Ther. 1988;38(2):129–168. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(88)90095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- den Hertog A., Nelemans A., Van den Akker J. The inhibitory action of suramin on the P2-purinoceptor response in smooth muscle cells of guinea-pig taenia caeci. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug 3;166(3):531–534. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90370-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Kügelgen I., Bültmann R., Starke K. Interaction of adenine nucleotides, UTP and suramin in mouse vas deferens: suramin-sensitive and suramin-insensitive components in the contractile effect of ATP. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;342(2):198–205. doi: 10.1007/BF00166965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



