Abstract
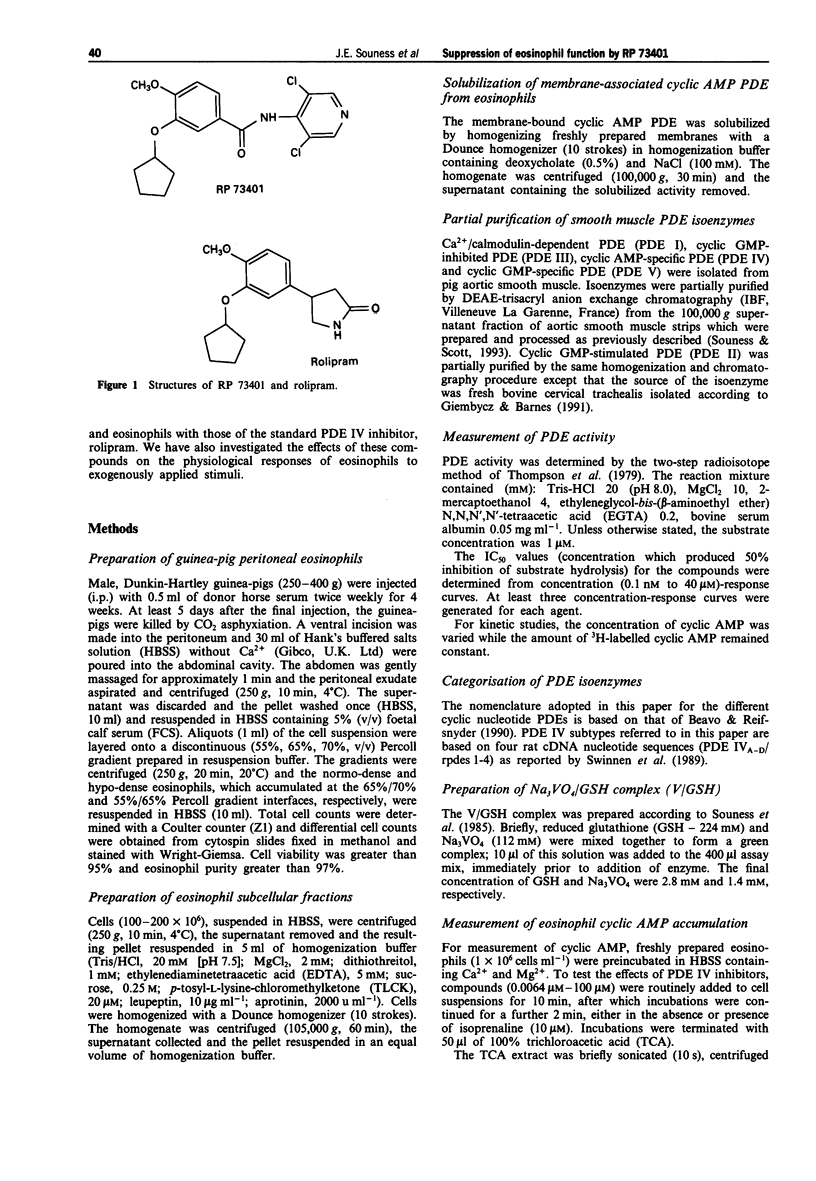
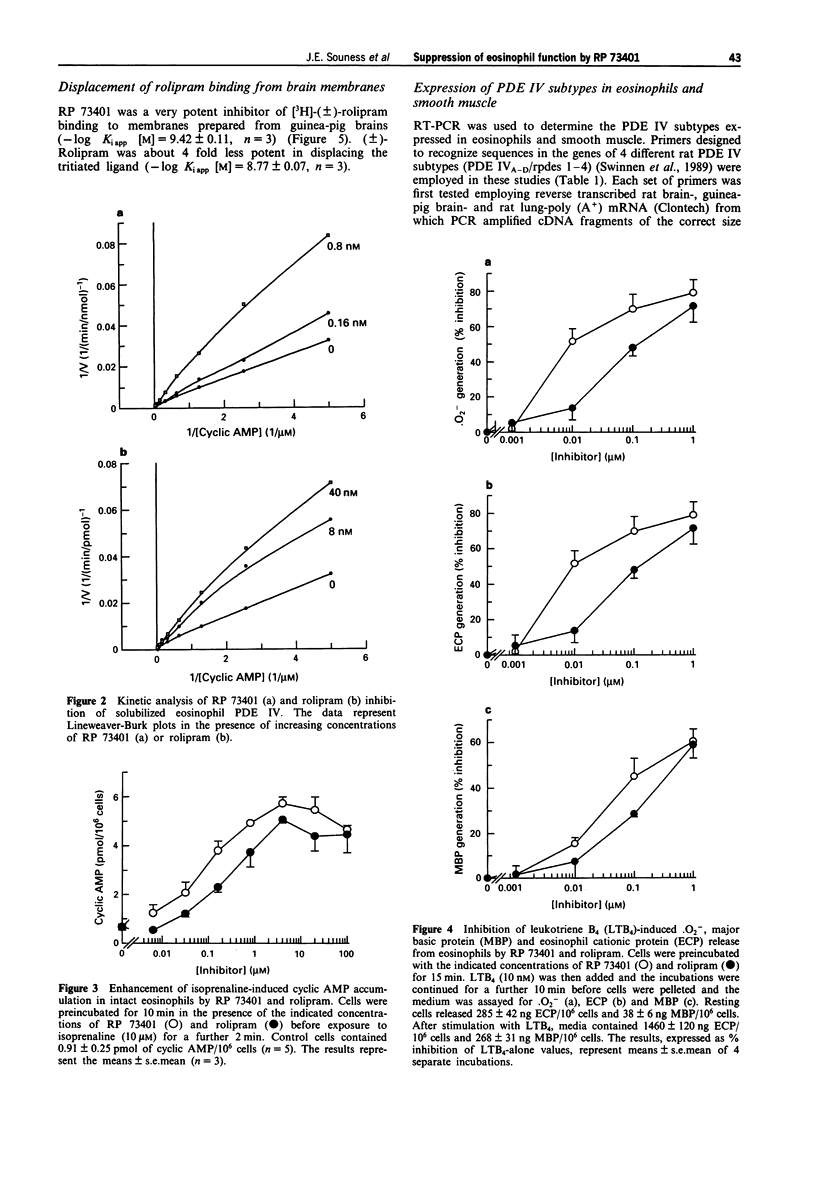
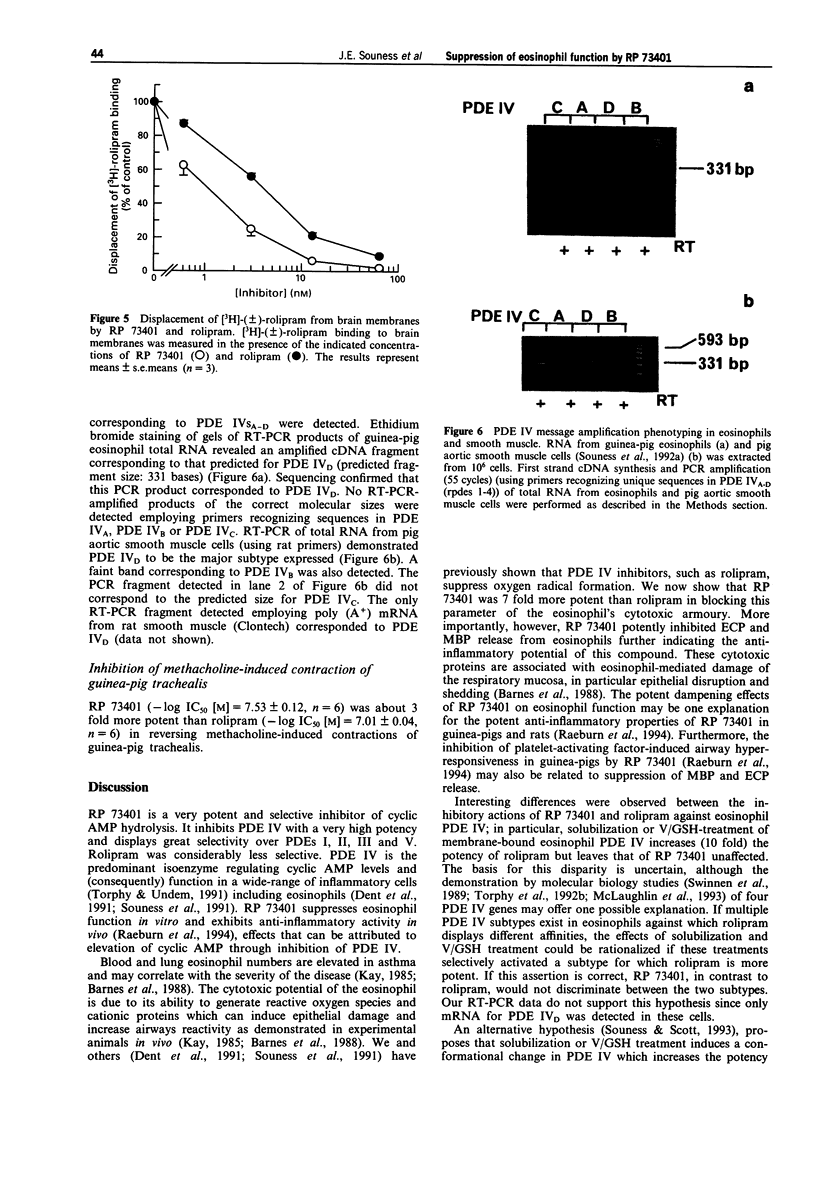
1. We have investigated the inhibitory potency of RP 73401, a novel, highly selective and potent inhibitor of cyclic AMP-specific phosphodiesterase (PDE IV), against partially-purified PDE isoenzymes from smooth muscle and the particulate PDE IV from guinea-pig eosinophils. The inhibitory effects of RP 73401 on the generation of superoxide (.O2-), major basic protein (MBP) and eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) from guinea-pig eosinophils have also been studied. 2. RP 73401 potently inhibited partially-purified cyclic AMP-specific phosphodiesterase (PDE IV) from pig aortic smooth muscle (IC50 = 1.2 nM); it was similarly potent against the particulate PDE IV from guinea-pig peritoneal eosinophils (IC50 = 0.7 nM). It displayed at least a 19000 fold selectivity for PDE IV compared to its potencies against other PDE isoenzymes. Rolipram was approximately 2600 fold less potent than RP 73401 against pig aortic smooth muscle PDE IV (IC50 = 3162 nM) and about 250 times less potent against eosinophil PDE IV (IC50 = 186 nM). 3. Solubilization of the eosinophil particulate PDE IV increased the potency of rolipram 10 fold but did not markedly affect the potency of RP 73401. A similar (10 fold) increase in the PDE IV inhibitory potency of rolipram, but not RP 73401, was observed when eosinophil membranes were exposed to vanadate/glutathione complex (V/GSH). 4. Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), using primer pairs designed against specific sequences in four distinct rat PDE IV subtype cDNA clones (PDE IVA-D), showed only mRNA for PDE IVD in guinea-pig eosinophils. PDE IVD was also the predominant subtype expressed in pig aortic smooth muscle cells.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashton M. J., Cook D. C., Fenton G., Karlsson J. A., Palfreyman M. N., Raeburn D., Ratcliffe A. J., Souness J. E., Thurairatnam S., Vicker N. Selective type IV phosphodiesterase inhibitors as antiasthmatic agents. The syntheses and biological activities of 3-(cyclopentyloxy)-4-methoxybenzamides and analogues. J Med Chem. 1994 May 27;37(11):1696–1703. doi: 10.1021/jm00037a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes P. J., Chung K. F., Page C. P. Inflammatory mediators and asthma. Pharmacol Rev. 1988 Mar;40(1):49–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavo J. A., Reifsnyder D. H. Primary sequence of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isozymes and the design of selective inhibitors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Apr;11(4):150–155. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90066-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies G. E., Evans D. P. Studies with two new phosphodiesterase inhibitors (ICI 58, 301 and ICI 63, 197) on anaphylaxis in guinea pigs, mice and rats. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1973;45(3):467–478. doi: 10.1159/000231064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dent G., Giembycz M. A., Rabe K. F., Barnes P. J. Inhibition of eosinophil cyclic nucleotide PDE activity and opsonised zymosan-stimulated respiratory burst by 'type IV'-selective PDE inhibitors. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;103(2):1339–1346. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb09790.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein P. M., Hachisu R. Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase in normal and leukemic human lymphocytes and lymphoblasts. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;16:303–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fonteh A. N., Winkler J. D., Torphy T. J., Heravi J., Undem B. J., Chilton F. H. Influence of isoproterenol and phosphodiesterase inhibitors on platelet-activating factor biosynthesis in the human neutrophil. J Immunol. 1993 Jul 1;151(1):339–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giembycz M. A., Barnes P. J. Selective inhibition of a high affinity type IV cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase in bovine trachealis by AH 21-132. Relevance to the spasmolytic and anti-spasmogenic actions of AH 21-132 in the intact tissue. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 15;42(3):663–677. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90330-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giembycz M. A. Could isoenzyme-selective phosphodiesterase inhibitors render bronchodilator therapy redundant in the treatment of bronchial asthma? Biochem Pharmacol. 1992 May 28;43(10):2041–2051. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(92)90160-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J., Loegering D. A., Maldonado J. E. Identification of a major basic protein in guinea pig eosinophil granules. J Exp Med. 1973 Jun 1;137(6):1459–1471. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.6.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. L., Connell M. J., Ferguson E. W., Wallace A. M., Gordon R. J., Pagani E. D., Silver P. J. Role of low Km cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase inhibition in tracheal relaxation and bronchodilation in the guinea pig. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Oct;251(1):199–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt T. C., Summers J. A., Campos M. G., Rimmer S. J., Sturton G., Palfai S., Church M. K. Monoclonal antibodies specific for guinea pig eosinophil major basic protein: their use in an ELISA, immunocytochemistry and flow cytometry. Clin Exp Allergy. 1993 May;23(5):425–434. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1993.tb00349.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay A. B. Eosinophils as effector cells in immunity and hypersensitivity disorders. Clin Exp Immunol. 1985 Oct;62(1):1–12. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin M. M., Cieslinski L. B., Burman M., Torphy T. J., Livi G. P. A low-Km, rolipram-sensitive, cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase from human brain. Cloning and expression of cDNA, biochemical characterization of recombinant protein, and tissue distribution of mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6470–6476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peachell P. T., Undem B. J., Schleimer R. P., MacGlashan D. W., Jr, Lichtenstein L. M., Cieslinski L. B., Torphy T. J. Preliminary identification and role of phosphodiesterase isozymes in human basophils. J Immunol. 1992 Apr 15;148(8):2503–2510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raeburn D., Karlsson J. A. Effects of isoenzyme-selective inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase on microvascular leak in guinea pig airways in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Dec;267(3):1147–1152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raeburn D., Souness J. E., Tomkinson A., Karlsson J. A. Isozyme-selective cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase inhibitors: biochemistry, pharmacology and therapeutic potential in asthma. Prog Drug Res. 1993;40:9–32. doi: 10.1007/978-3-0348-7147-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raeburn D., Underwood S. L., Lewis S. A., Woodman V. R., Battram C. H., Tomkinson A., Sharma S., Jordan R., Souness J. E., Webber S. E. Anti-inflammatory and bronchodilator properties of RP 73401, a novel and selective phosphodiesterase type IV inhibitor. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Dec;113(4):1423–1431. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17156.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robicsek S. A., Blanchard D. K., Djeu J. Y., Krzanowski J. J., Szentivanyi A., Polson J. B. Multiple high-affinity cAMP-phosphodiesterases in human T-lymphocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 25;42(4):869–877. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90047-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schade F. U., Schudt C. The specific type III and IV phosphodiesterase inhibitor zardaverine suppresses formation of tumor necrosis factor by macrophages. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Jan 5;230(1):9–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90403-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H. H., Schmiechen R., Brezinski M., Seidler J. Stereospecific binding of the antidepressant rolipram to brain protein structures. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Aug 7;127(1-2):105–115. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90210-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semmler J., Wachtel H., Endres S. The specific type IV phosphodiesterase inhibitor rolipram suppresses tumor necrosis factor-alpha production by human mononuclear cells. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1993 Apr;15(3):409–413. doi: 10.1016/0192-0561(93)90052-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sette C., Vicini E., Conti M. The ratPDE3/IVd phosphodiesterase gene codes for multiple proteins differentially activated by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 15;269(28):18271–18274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shakur Y., Pryde J. G., Houslay M. D. Engineered deletion of the unique N-terminal domain of the cyclic AMP-specific phosphodiesterase RD1 prevents plasma membrane association and the attainment of enhanced thermostability without altering its sensitivity to inhibition by rolipram. Biochem J. 1993 Jun 15;292(Pt 3):677–686. doi: 10.1042/bj2920677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souness J. E., Carter C. M., Diocee B. K., Hassall G. A., Wood L. J., Turner N. C. Characterization of guinea-pig eosinophil phosphodiesterase activity. Assessment of its involvement in regulating superoxide generation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 25;42(4):937–945. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90056-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souness J. E., Hassall G. A., Parrott D. P. Inhibition of pig aortic smooth muscle cell DNA synthesis by selective type III and type IV cyclic AMP phosphodiesterase inhibitors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1992 Sep 1;44(5):857–866. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(92)90116-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souness J. E., Maslen C., Scott L. C. Effects of solubilization and vanadate/glutathione complex on inhibitor potencies against eosinophil cyclic AMP-specific phosphodiesterase. FEBS Lett. 1992 May 11;302(2):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80435-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souness J. E., Scott L. C. Stereospecificity of rolipram actions on eosinophil cyclic AMP-specific phosphodiesterase. Biochem J. 1993 Apr 15;291(Pt 2):389–395. doi: 10.1042/bj2910389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souness J. E., Thompson W. J., Strada S. J. Adipocyte cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase activation by vanadate. J Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphor Res. 1985;10(4):383–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souness J. E., Villamil M. E., Scott L. C., Tomkinson A., Giembycz M. A., Raeburn D. Possible role of cyclic AMP phosphodiesterases in the actions of ibudilast on eosinophil thromboxane generation and airways smooth muscle tone. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Apr;111(4):1081–1088. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14855.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swinnen J. V., Joseph D. R., Conti M. Molecular cloning of rat homologues of the Drosophila melanogaster dunce cAMP phosphodiesterase: evidence for a family of genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5325–5329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. J., Terasaki W. L., Epstein P. M., Strada S. J. Assay of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase and resolution of multiple molecular forms of the enzyme. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:69–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torphy T. J., Cieslinski L. B. Characterization and selective inhibition of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase isozymes in canine tracheal smooth muscle. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Feb;37(2):206–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torphy T. J., Livi G. P., Balcarek J. M., White J. R., Chilton F. H., Undem B. J. Therapeutic potential of isozyme-selective phosphodiesterase inhibitors in the treatment of asthma. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1992;25:289–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torphy T. J., Stadel J. M., Burman M., Cieslinski L. B., McLaughlin M. M., White J. R., Livi G. P. Coexpression of human cAMP-specific phosphodiesterase activity and high affinity rolipram binding in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1798–1804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torphy T. J., Undem B. J. Phosphodiesterase inhibitors: new opportunities for the treatment of asthma. Thorax. 1991 Jul;46(7):512–523. doi: 10.1136/thx.46.7.512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underwood D. C., Osborn R. R., Novak L. B., Matthews J. K., Newsholme S. J., Undem B. J., Hand J. M., Torphy T. J. Inhibition of antigen-induced bronchoconstriction and eosinophil infiltration in the guinea pig by the cyclic AMP-specific phosphodiesterase inhibitor, rolipram. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Jul;266(1):306–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassom D. L., Loegering D. A., Gleich G. J. Measurement of guinea pig eosinophil major basic protein by radioimmunoassay. Mol Immunol. 1979 Sep;16(9):711–719. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90012-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. D., Kuipers P. J., Kobylarz-Singer D., Devall L. J., Klinkefus B. A., Weishaar R. E. Differential inhibition of human neutrophil functions. Role of cyclic AMP-specific, cyclic GMP-insensitive phosphodiesterase. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Aug 15;40(4):699–707. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90304-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




