Abstract
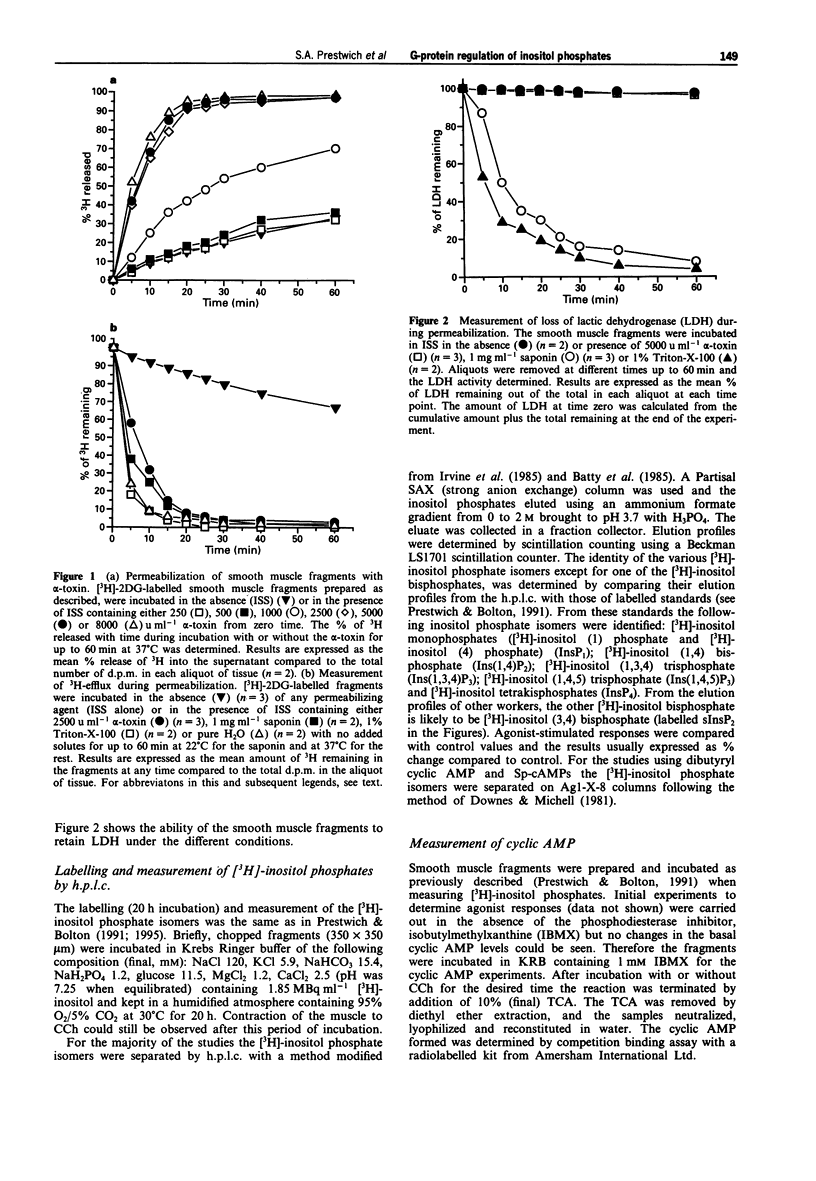
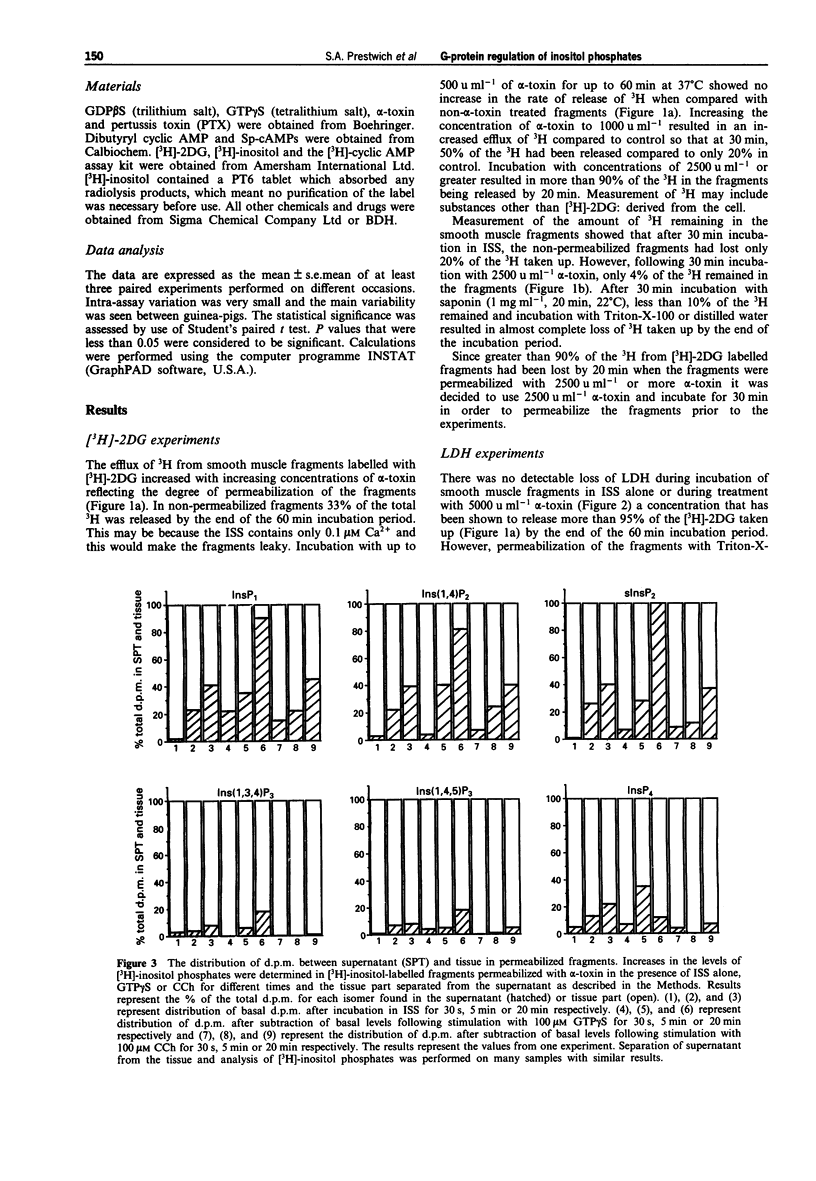
1. Smooth muscle fragments from the longitudinal layer of the small intestine of the guinea-pig were permeabilized with Staphylococcus aureus alpha toxin (alpha-toxin) and used to investigate the role of G-protein activation in the regulation of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (AChR)-stimulated inositol phospholipid hydrolysis. 2. The efficiency of alpha-toxin permeabilization was estimated by the release of [3H]-2-deoxyglucose ([3H]-2DG) after prior loading or lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) enzyme release from the smooth muscle fragments. 3. In alpha-toxin-permeabilized smooth muscle, but not in non-permeabilized muscle, GTP gamma S induced time- and concentration-dependent increases in labelled inositol phosphates. Carbachol (CCh) increased labelled inositol phosphates in both permeabilized and non-permeabilized muscle, although the increases were greater in non-permeabilized smooth muscle. The response to 100 microM CCh was severely reduced by 0.5 microM atropine. 4. In permeabilized muscle the effects of GTP gamma S or CCh on inositol phosphate levels were reduced by treatment with pertussis toxin (PTX) and completely inhibited by GDP beta S. 5. GTP gamma S caused a concentration-dependent inhibition of the CCh-induced increases in the levels of labelled inositol phosphates. Dibutyryl cyclic AMP or Sp-cAMPs (adenosine-3',5'-cyclic phosphorothiolate-Sp) reduced the effects of CCh on inositol phosphate levels. 6. The results suggest that muscarinic AChR activation induces inositol phospholipid hydrolysis via more than one G-protein in this smooth muscle and that several mechanisms may contribute to the modulation of both stimulatory and inhibitory responses observed.
Full text
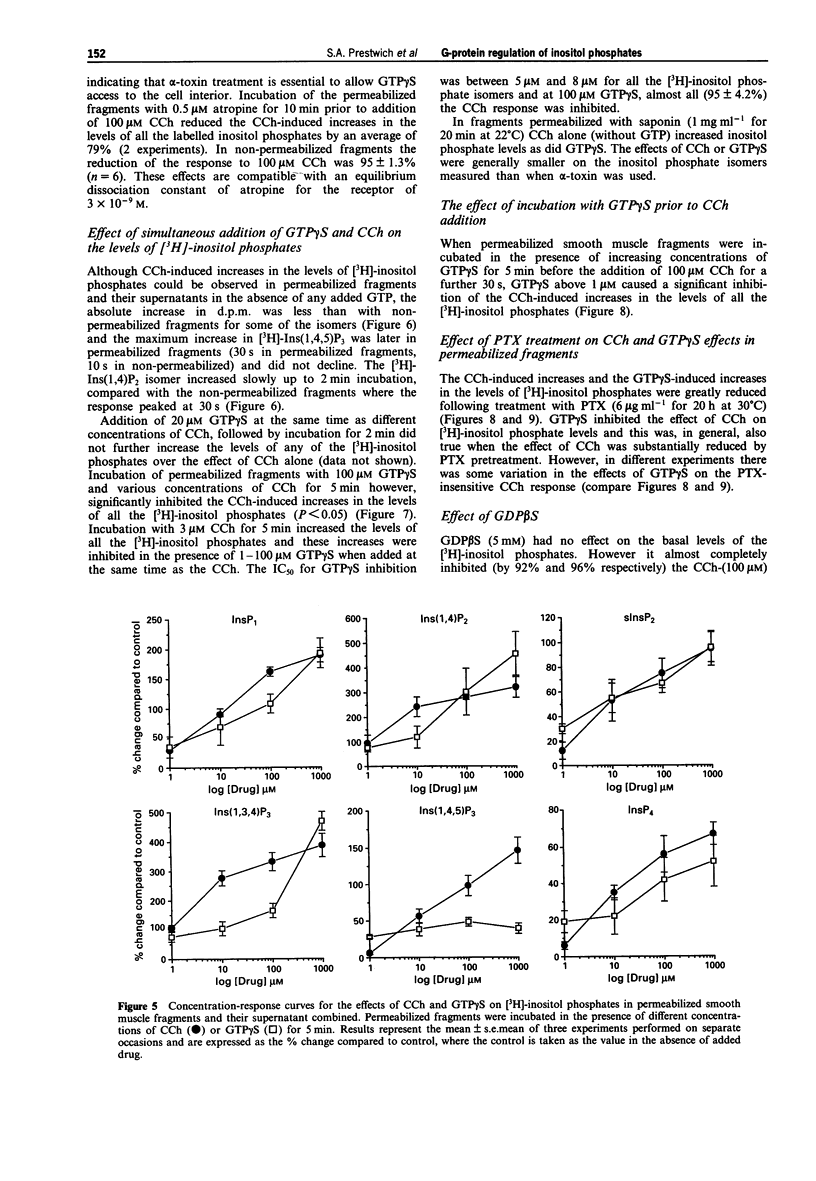
PDF

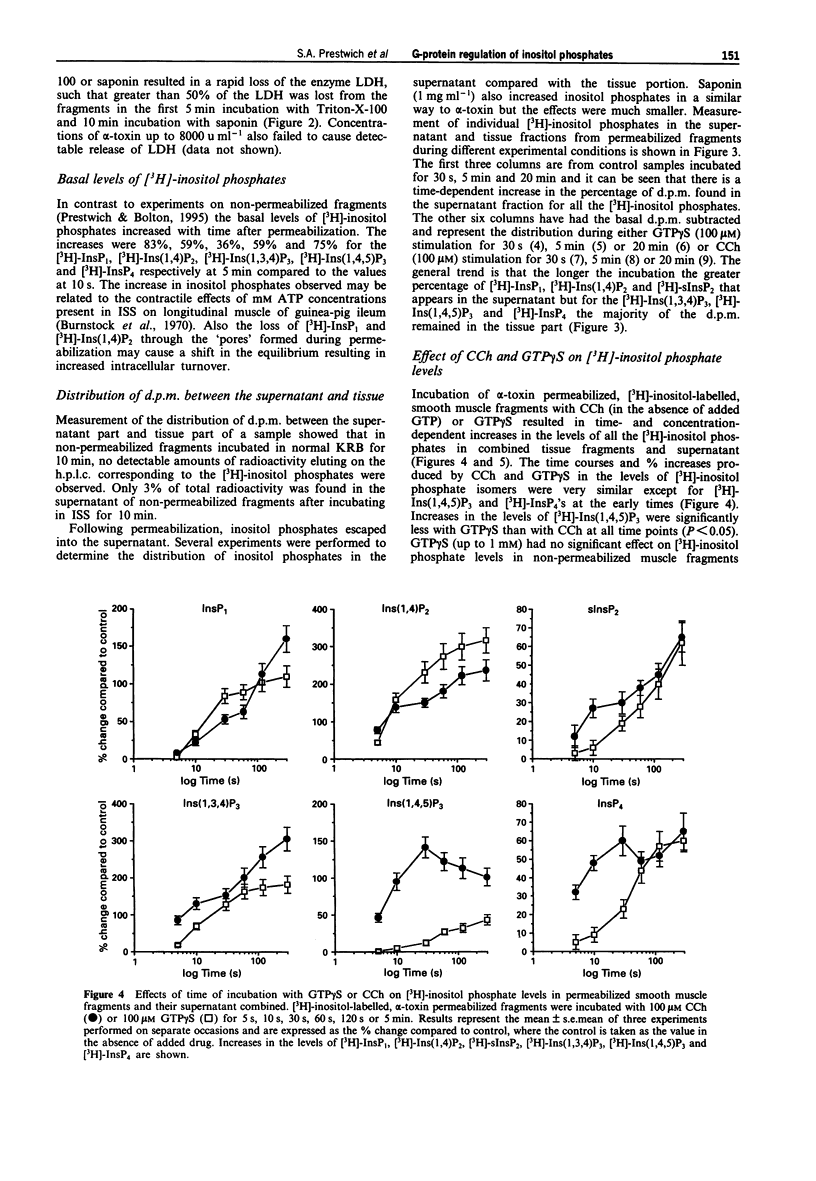
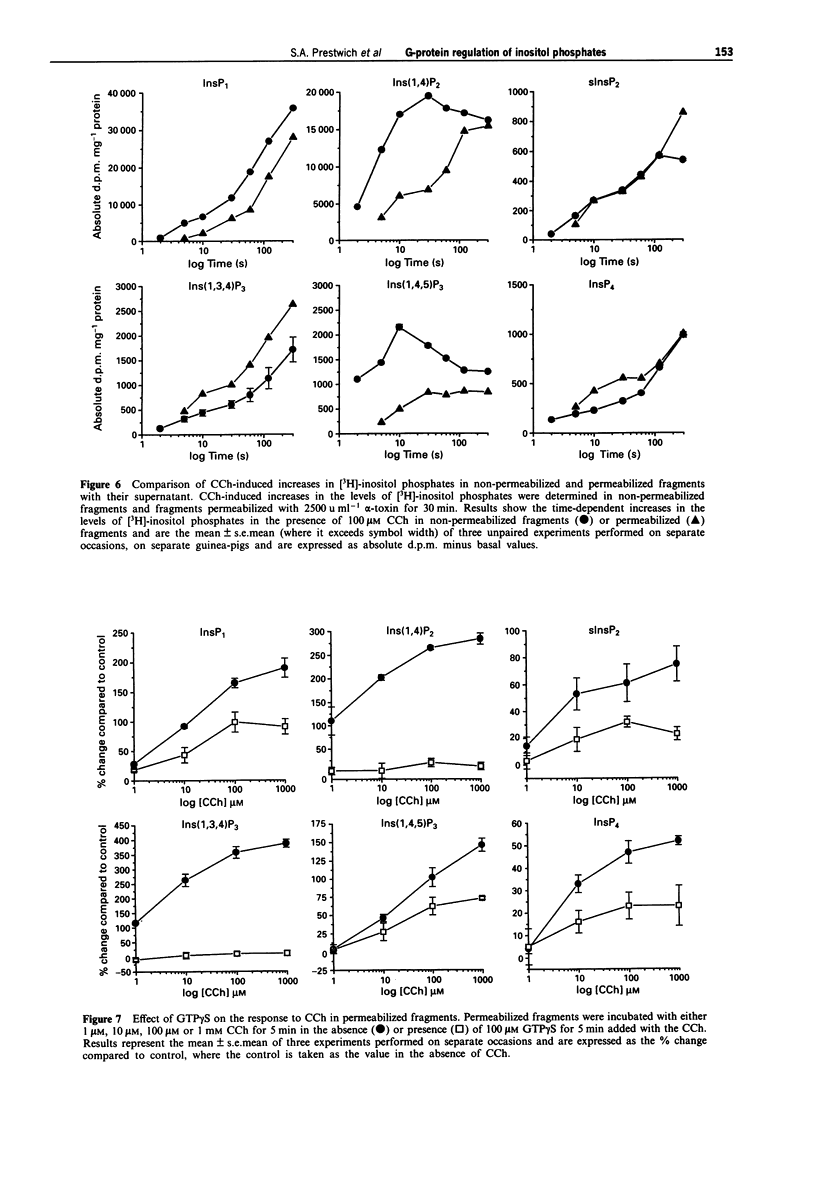
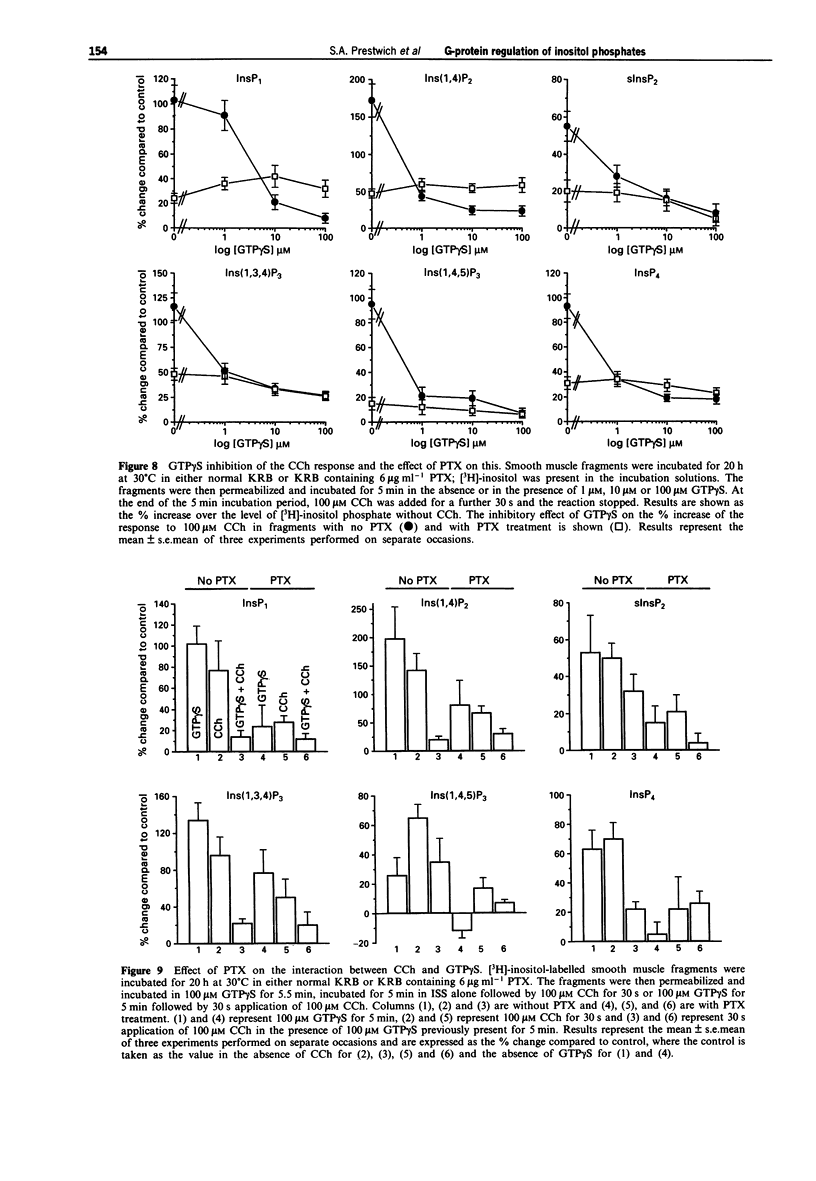



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashkenazi A., Peralta E. G., Winslow J. W., Ramachandran J., Capon D. J. Functionally distinct G proteins selectively couple different receptors to PI hydrolysis in the same cell. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):487–493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90251-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barocelli E., Chiavarini M., Ballabeni V., Bordi F., Impicciatore M. Interaction of selective compounds with muscarinic receptors at dispersed intestinal smooth muscle cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;108(2):393–397. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12815.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batty I. R., Nahorski S. R., Irvine R. F. Rapid formation of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate following muscarinic receptor stimulation of rat cerebral cortical slices. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):211–215. doi: 10.1042/bj2320211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Best L., Bolton T. B. Depolarisation of guinea-pig visceral smooth muscle causes hydrolysis of inositol phospholipids. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 May;333(1):78–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00569664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Damage to mammalian cells by proteins that form transmembrane pores. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1987;107:147–223. doi: 10.1007/BFb0027646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bizzarri C., Di Girolamo M., D'Orazio M. C., Corda D. Evidence that a guanine nucleotide-binding protein linked to a muscarinic receptor inhibits directly phospholipase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4889–4893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnstock G., Campbell G., Satchell D., Smythe A. Evidence that adenosine triphosphate or a related nucleotide is the transmitter substance released by non-adrenergic inhibitory nerves in the gut. Br J Pharmacol. 1970 Dec;40(4):668–688. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1970.tb10646.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey P. J., Gilman A. G. G protein involvement in receptor-effector coupling. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2577–2580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo M. G., Vicentini L. M. Differential mechanisms of inositol phosphate generation at the receptors for bombesin and platelet-derived growth factor. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 1;262(2):665–668. doi: 10.1042/bj2620665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Role of guanine nucleotide binding protein in the activation of polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):534–536. doi: 10.1038/314534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Michell R. H. The polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase of erythrocyte membranes. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 15;198(1):133–140. doi: 10.1042/bj1980133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fermum R., Kosche D., Möritz K. U. Membrane-associated signal transduction modulates contractile responses to Ca2+ in saponin-skinned coronary smooth muscle. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 Feb;343(2):209–216. doi: 10.1007/BF00168612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Füssle R., Bhakdi S., Sziegoleit A., Tranum-Jensen J., Kranz T., Wellensiek H. J. On the mechanism of membrane damage by Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):83–94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutowski S., Smrcka A., Nowak L., Wu D. G., Simon M., Sternweis P. C. Antibodies to the alpha q subfamily of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein alpha subunits attenuate activation of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate hydrolysis by hormones. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20519–20524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohman R. J. Aggregation of IgE receptors induces degranulation in rat basophilic leukemia cells permeabilized with alpha-toxin from Staphylococcus aureus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1624–1628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honkanen R. E., Abdel-Latif A. A. Muscarinic-agonist and guanine nucleotide stimulation of myo-inositol trisphosphate formation in membranes isolated from bovine iris sphincter smooth muscle: effects of short-term cholinergic desensitization. Membr Biochem. 1989;8(1):39–59. doi: 10.3109/09687688909025825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Anggård E. E., Letcher A. J., Downes C. P. Metabolism of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 15;229(2):505–511. doi: 10.1042/bj2290505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T., Kuriyama H., Suzuki H. Differences and similarities in the noradrenaline- and caffeine-induced mechanical responses in the rabbit mesenteric artery. J Physiol. 1983 Apr;337:609–629. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jafferji S. S., Michell R. H. Muscarinic cholinergic stimulation of phosphatidylinositol turnover in the longitudinal smooth muscle of guinea-pig ileum. Biochem J. 1976 Mar 15;154(3):653–657. doi: 10.1042/bj1540653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Gilman A. G., Watanabe Y., Bauer S., Jakobs K. H. Protein kinase C phosphorylates the inhibitory guanine-nucleotide-binding regulatory component and apparently suppresses its function in hormonal inhibition of adenylate cyclase. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):431–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A., Wu D., Simon M. I. Subunits beta gamma of heterotrimeric G protein activate beta 2 isoform of phospholipase C. Nature. 1992 Dec 17;360(6405):686–689. doi: 10.1038/360686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitazawa T., Gaylinn B. D., Denney G. H., Somlyo A. P. G-protein-mediated Ca2+ sensitization of smooth muscle contraction through myosin light chain phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1708–1715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight D. E., Scrutton M. C. Gaining access to the cytosol: the technique and some applications of electropermeabilization. Biochem J. 1986 Mar 15;234(3):497–506. doi: 10.1042/bj2340497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. B., Shin S. H., Hepler J. R., Gilman A. G., Rhee S. G. Activation of phospholipase C-beta 2 mutants by G protein alpha q and beta gamma subunits. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25952–25957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litosch I., Wallis C., Fain J. N. 5-Hydroxytryptamine stimulates inositol phosphate production in a cell-free system from blowfly salivary glands. Evidence for a role of GTP in coupling receptor activation to phosphoinositide breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5464–5471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logothetis D. E., Kim D. H., Northup J. K., Neer E. J., Clapham D. E. Specificity of action of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein subunits on the cardiac muscarinic K+ channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5814–5818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Carroll R. C., Cox A. C. Characterization of multiple forms of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C purified from human platelets. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):139–145. doi: 10.1042/bj2370139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel A. D., Whiting R. L. The binding of [3H]4-diphenylacetoxy-N-methylpiperidine methiodide to longitudinal ileal smooth muscle muscarinic receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Feb 6;176(2):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90528-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura J., Khalil R. A., Drenth J. P., van Breemen C. Evidence for increased myofilament Ca2+ sensitivity in norepinephrine-activated vascular smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jul;259(1 Pt 2):H2–H8. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.259.1.H2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura J., Kolber M., van Breemen C. Norepinephrine and GTP-gamma-S increase myofilament Ca2+ sensitivity in alpha-toxin permeabilized arterial smooth muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 15;157(2):677–683. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80303-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obara K., Yamada T. Some properties of chemically skinned single smooth muscle cells. Jpn J Physiol. 1984;34(6):1089–1104. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.34.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M. Mechanisms of the ability of insulin to activate the glucose-transport system in rat adipocytes. Biochem J. 1978 Apr 15;172(1):137–145. doi: 10.1042/bj1720137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono T., Mita M., Suga O., Hashimoto T., Oishi K., Uchida M. K. Receptor-coupled shortening of alpha-toxin-permeabilized single smooth muscle cells from the guinea-pig stomach. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Jul;106(3):539–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14371.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otero A. D. Transphosphorylation and G protein activation. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 May 1;39(9):1399–1404. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90420-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacaud P., Bolton T. B. Relation between muscarinic receptor cationic current and internal calcium in guinea-pig jejunal smooth muscle cells. J Physiol. 1991 Sep;441:477–499. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park D., Jhon D. Y., Lee C. W., Lee K. H., Rhee S. G. Activation of phospholipase C isozymes by G protein beta gamma subunits. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):4573–4576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prestwich S. A., Bolton T. B. G-protein involvement in muscarinic receptor-stimulation of inositol phosphates in longitudinal smooth muscle from the small intestine of the guinea-pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 Jan;114(1):119–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb14915.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prestwich S. A., Bolton T. B. Measurement of picomole amounts of any inositol phosphate isomer separable by h.p.l.c. by means of a bioluminescence assay. Biochem J. 1991 Mar 15;274(Pt 3):663–672. doi: 10.1042/bj2740663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Gilman A. G. Biochemical properties of hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:533–564. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. H., Lee S. Y., Lee K. Y., Rhee S. G. Catalytic properties of inositol trisphosphate kinase: activation by Ca2+ and calmodulin. FASEB J. 1987 Nov;1(5):388–393. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.1.5.2824270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smellie F. W., Davis C. W., Daly J. W., Wells J. N. Alkylxanthines: inhibition of adenosine-elicited accumulation of cyclic AMP in brain slices and of brain phosphodiesterase activity. Life Sci. 1979 Jun 25;24(26):2475–2482. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(79)90458-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Lane B. C., Kusaka I., Verghese M. W., Snyderman R. Chemoattractant receptor-induced hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in human polymorphonuclear leukocyte membranes. Requirement for a guanine nucleotide regulatory protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):5875–5878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. V., Bond M., Somlyo A. P., Scarpa A. Inositol trisphosphate-induced calcium release and contraction in vascular smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5231–5235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. Aluminum: a requirement for activation of the regulatory component of adenylate cyclase by fluoride. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4888–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Smrcka A. V. Regulation of phospholipase C by G proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Dec;17(12):502–506. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90340-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhing R. J., Prpic V., Jiang H., Exton J. H. Hormone-stimulated polyphosphoinositide breakdown in rat liver plasma membranes. Roles of guanine nucleotides and calcium. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2140–2146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Geet C., Deckmyn H., Kienast J., Wittevrongel C., Vermylen J. Guanine nucleotide-dependent inhibition of phospholipase C in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):7920–7926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods N. M., Cuthbertson K. S., Cobbold P. H. Phorbol-ester-induced alterations of free calcium ion transients in single rat hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1987 Sep 15;246(3):619–623. doi: 10.1042/bj2460619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



