Abstract
1. This study was designed to evaluate further the role of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) in regulating susceptibility and/or intensity of audiogenic seizures in genetically epilepsy-prone rats. 2. The effects of sertraline, a highly selective and potent inhibitor of 5-HT uptake, on both the intensity of the audiogenic seizures and the extracellular concentrations of 5-HT in the thalamus were evaluated in severe seizure genetically epilepsy-prone rats. 3. Sertraline (7.5, 15 and 30 mg kg-1, i.p.) produced a dose-dependent reduction in the intensity of the audiogenic seizures. 4. Brain microdialysis studies showed that the same doses of sertraline also caused dose-dependent increases in the extracellular 5-HT concentration in the thalamus of the freely moving rats. 5. The peak anticonvulsant effect correlated temporally with the peak increases in the extracellular 5-HT concentration for this drug. 6. It is concluded that enhancement of 5-hydroxytryptaminergic transmission may contribute to the anticonvulsant effect of sertraline in severe seizure genetically epilepsy-prone rats. 7. The present results coupled with earlier investigations support the hypothesis that 5-HT plays an anticonvulsant role in genetically epilepsy-prone rats.
Full text
PDF

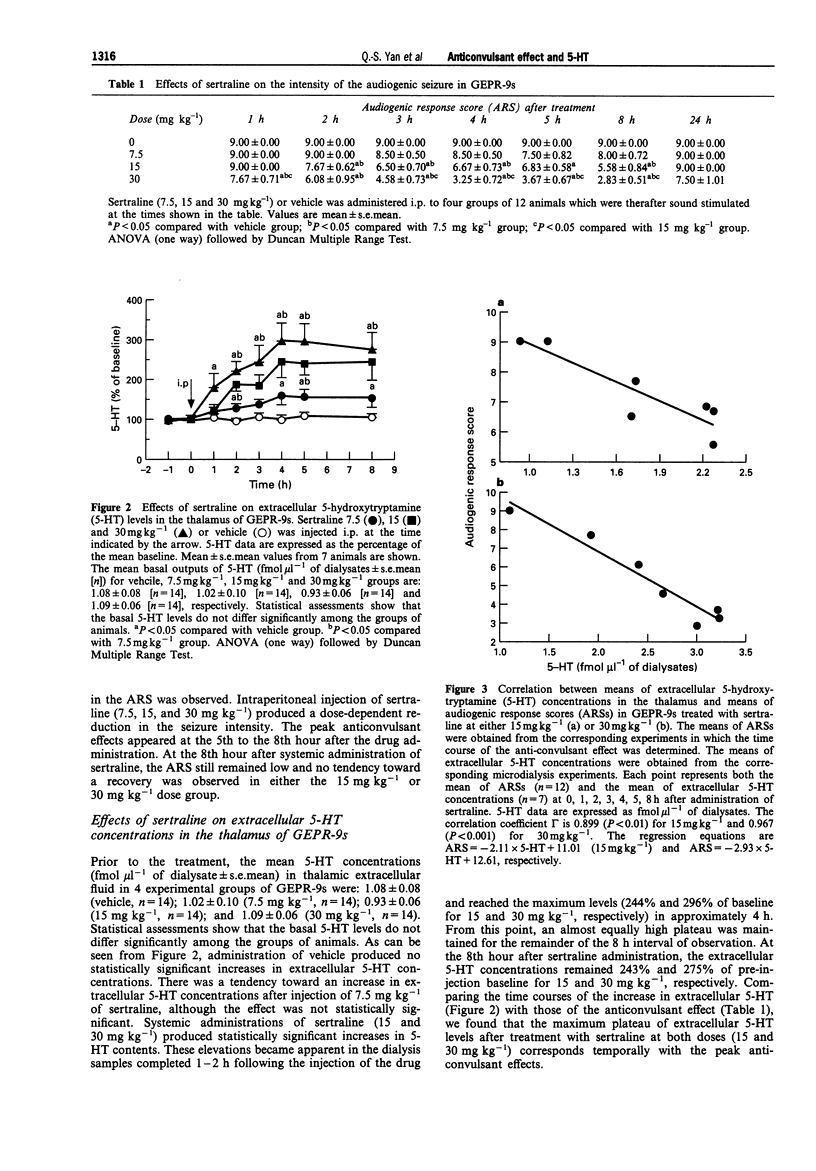
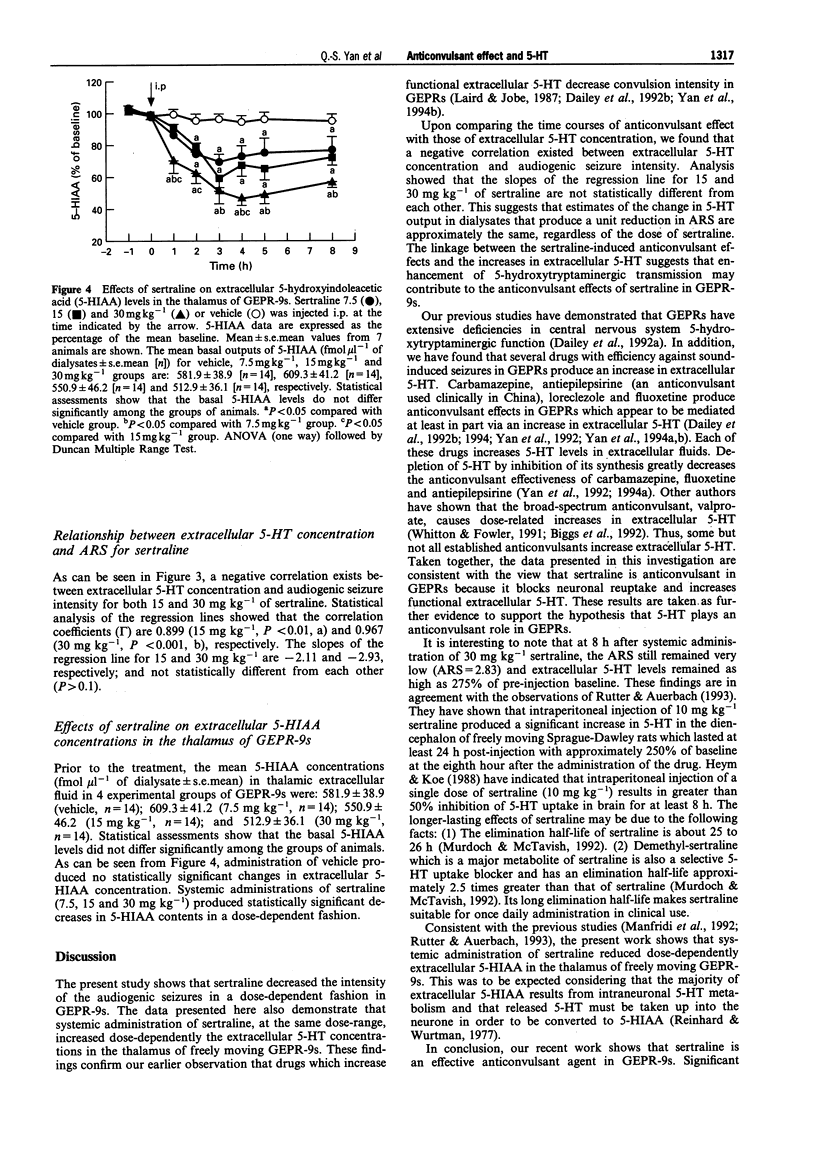

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biggs C. S., Pearce B. R., Fowler L. J., Whitton P. S. Regional effects of sodium valproate on extracellular concentrations of 5-hydroxytryptamine, dopamine, and their metabolites in the rat brain: an in vivo microdialysis study. J Neurochem. 1992 Nov;59(5):1702–1708. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb11001.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey J. W., Jobe P. C. Anticonvulsant drugs and the genetically epilepsy-prone rat. Fed Proc. 1985 Jul;44(10):2640–2644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey J. W., Mishra P. K., Ko K. H., Penny J. E., Jobe P. C. Serotonergic abnormalities in the central nervous system of seizure-naive genetically epilepsy-prone rats. Life Sci. 1992;50(4):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(92)90340-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey J. W., Seo D. O., Yan Q. S., Ko K. H., Jo M., Jobe P. C. The anticonvulsant effect of the broad spectrum anticonvulsant loreclezole may be mediated in part by serotonin in rats: a microdialysis study. Neurosci Lett. 1994 Sep 12;178(2):179–183. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)90754-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey J. W., Yan Q. S., Mishra P. K., Burger R. L., Jobe P. C. Effects of fluoxetine on convulsions and on brain serotonin as detected by microdialysis in genetically epilepsy-prone rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Feb;260(2):533–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heym J., Koe B. K. Pharmacology of sertraline: a review. J Clin Psychiatry. 1988 Aug;49 (Suppl):40–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs B. L., Azmitia E. C. Structure and function of the brain serotonin system. Physiol Rev. 1992 Jan;72(1):165–229. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1992.72.1.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobe P. C., Picchioni A. L., Chin L. Role of brain norepinephrine in audiogenic seizure in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Jan;184(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koe B. K., Weissman A., Welch W. M., Browne R. G. Sertraline, 1S,4S-N-methyl-4-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-naphthylamine, a new uptake inhibitor with selectivity for serotonin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Sep;226(3):686–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manfridi A., Clavenna A., De Simoni M. G. Serotonin uptake inhibition: in vivo effect of sertraline in rats. Neurosci Lett. 1992 May 11;139(1):69–72. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(92)90860-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mishra P. K., Dailey J. W., Reigel C. E., Tomsic M. L., Jobe P. C. Sex-specific distinctions in audiogenic convulsions exhibited by severe seizure genetically epilepsy-prone rats (GEPR-9s). Epilepsy Res. 1988 Sep-Oct;2(5):309–316. doi: 10.1016/0920-1211(88)90039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murdoch D., McTavish D. Sertraline. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties, and therapeutic potential in depression and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Drugs. 1992 Oct;44(4):604–624. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199244040-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhard J. F., Jr, Wurtman R. J. Relation between brain 5-HIAA levels and the release of serotonin into brain synapses. Life Sci. 1977 Dec 15;21(12):1741–1746. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(77)90153-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter J. J., Auerbach S. B. Acute uptake inhibition increases extracellular serotonin in the rat forebrain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Jun;265(3):1319–1324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitton P. S., Fowler L. J. The effect of valproic acid on 5-hydroxytryptamine and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid concentration in hippocampal dialysates in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 23;200(1):167–169. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90681-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan Q. S., Jobe P. C., Cheong J. H., Ko K. H., Dailey J. W. Role of serotonin in the anticonvulsant effect of fluoxetine in genetically epilepsy-prone rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1994 Aug;350(2):149–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00241089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan Q. S., Jobe P. C., Dailey J. W. Evidence that a serotonergic mechanism is involved in the anticonvulsant effect of fluoxetine in genetically epilepsy-prone rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Jan 24;252(1):105–112. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(94)90581-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan Q. S., Mishra P. K., Burger R. L., Bettendorf A. F., Jobe P. C., Dailey J. W. Evidence that carbamazepine and antiepilepsirine may produce a component of their anticonvulsant effects by activating serotonergic neurons in genetically epilepsy-prone rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 May;261(2):652–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



