Abstract
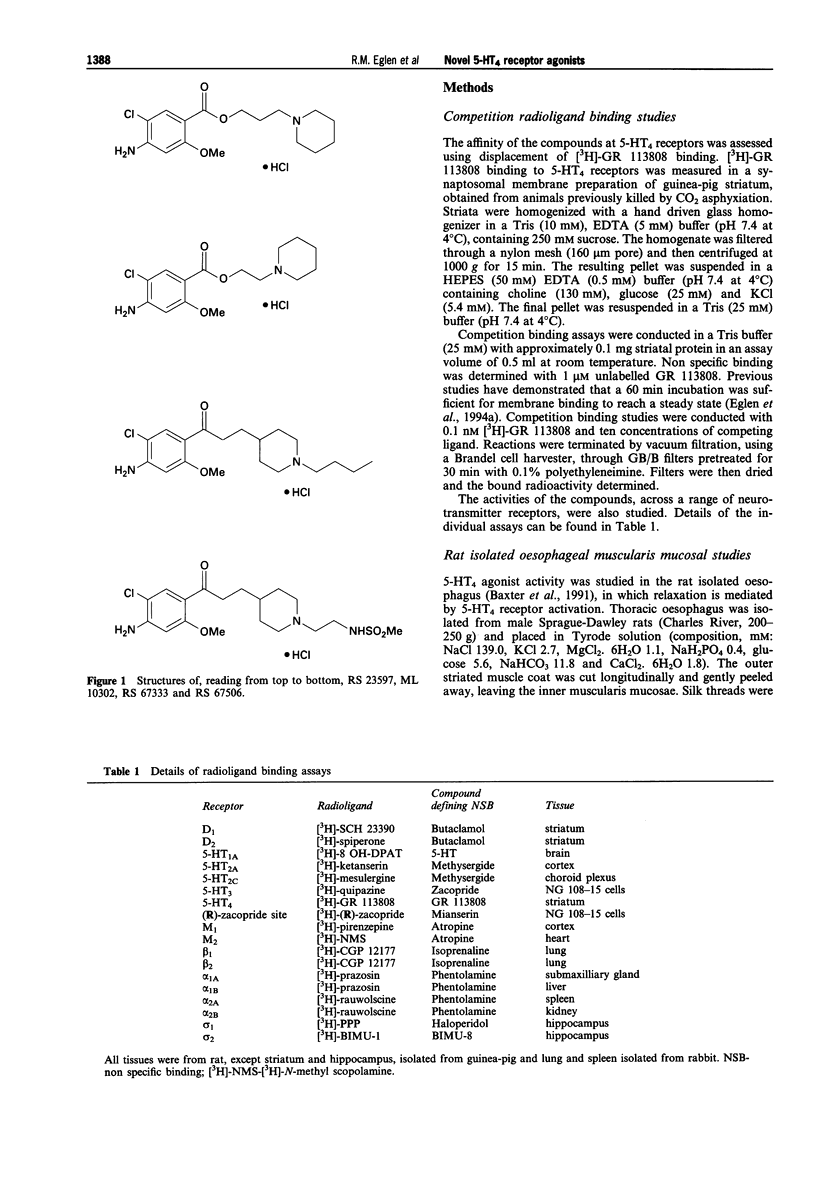
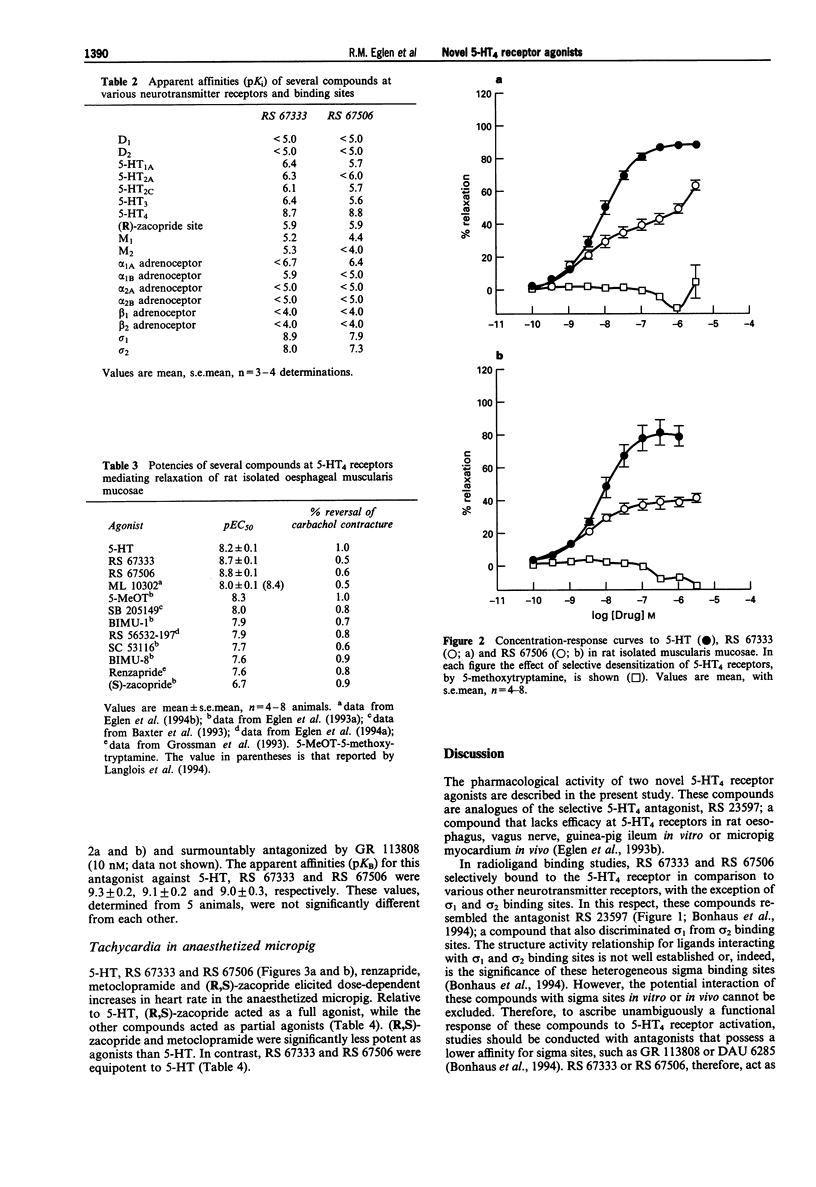
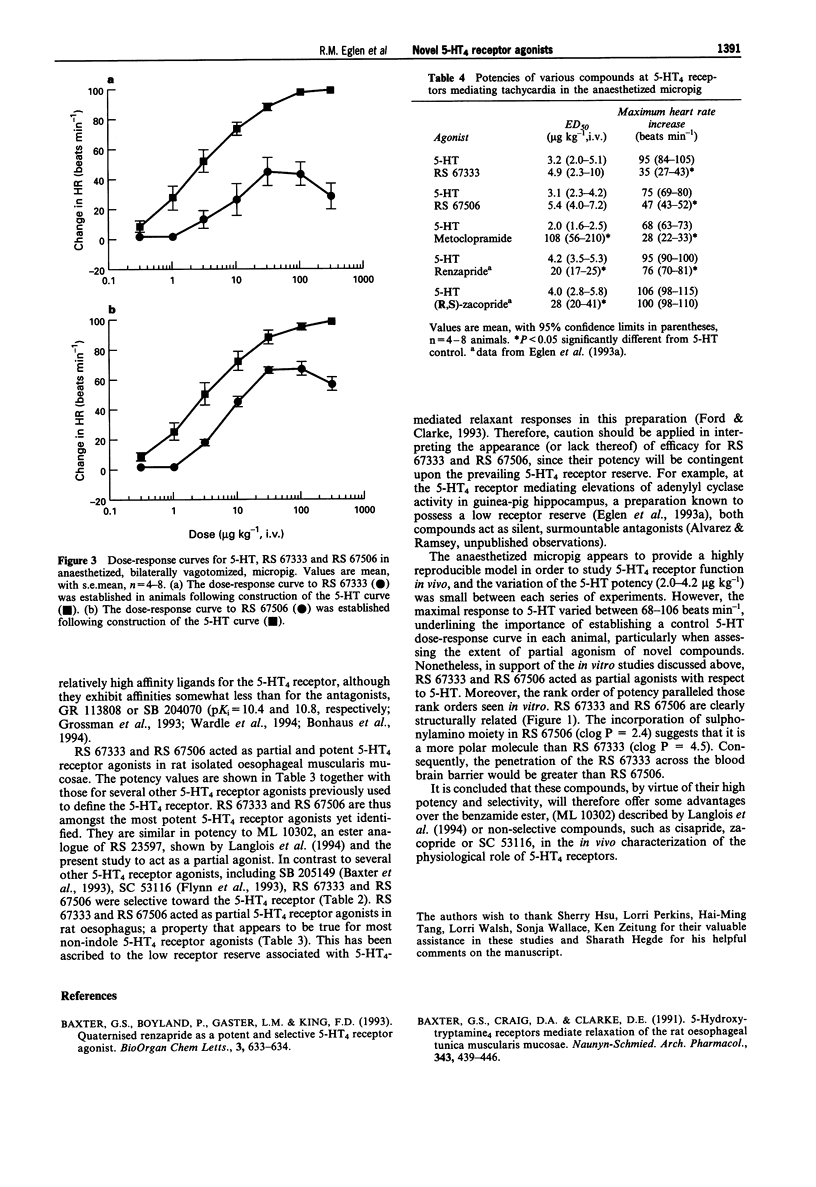
1. The pharmacology of two novel 5-HT4 receptor agonists, RS 67333 (1-(4-amino-5-chloro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-3-[1(n-butyl)-4-piperidinyl]-1- propanone HCl) and RS 67506 (1-(4-amino-5-chloro-2-methoxy-phenyl)-3-[1-(2-methyl sulphonylamino)ethyl-4-piperidinyl]-1-propanone HCl) have been assessed in vitro and in vivo. 2. RS 67333 and RS 67506 exhibited affinities (pKi = 8.7 and 8.8, respectively) for the 5-HT4 binding sites, labelled with [3H]-GR 113808, in guinea-pig striatum. The Hill coefficients from these displacement curves were not significantly different from unity. The compounds exhibited lower affinities (< 6.0) at several other receptors including 5-HT1A, 5-HT1D, 5-HT2A, 5-HT2C, dopamine D1, D2 and muscarinic M1-M3 receptors. However, RS 67333 and RS 67506 did exhibit affinities for the sigma 1 (pKi = 8.9 and 7.9, respectively) and sigma 2 (pKi = 8.0 and 7.3, respectively) binding sites. 3. At the 5-HT4 receptor mediating relaxation of the carbachol-precontracted oesophagus, RS 67333 and RS 67506 acted as potent (pEC50 8.4 and 8.6, respectively), partial agonists (intrinsic activities, with respect to 5-HT were 0.5 and 0.6, respectively) with respect to 5-HT. Relaxant responses to RS 67333 or RS 67506 were surmountably antagonized by GR 11308 (10 nM), with apparent affinities (pKB) of 9.1 and 9.0, respectively. RS 67333 and RS 67506 induced dose-dependent increases in heart rate of the anaesthetized micropig (ED50 4.9 and 5.4 micrograms kg-1, i.v.), with maximal increases of 35 and 47 beats min-1, respectively.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baxter G. S., Craig D. A., Clarke D. E. 5-Hydroxytryptamine4 receptors mediate relaxation of the rat oesophageal tunica muscularis mucosae. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 May;343(5):439–446. doi: 10.1007/BF00169544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonhaus D. W., Loury D. N., Jakeman L. B., Hsu S. A., To Z. P., Leung E., Zeitung K. D., Eglen R. M., Wong E. H. [3H]RS-23597-190, a potent 5-hydroxytryptamine4 antagonist labels sigma-1 but not sigma-2 binding sites in guinea pig brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Oct;271(1):484–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumuis A., Sebben M., Monferini E., Nicola M., Turconi M., Ladinsky H., Bockaert J. Azabicycloalkyl benzimidazolone derivatives as a novel class of potent agonists at the 5-HT4 receptor positively coupled to adenylate cyclase in brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;343(3):245–251. doi: 10.1007/BF00251122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglen R. M., Alvarez R., Johnson L. G., Leung E., Wong E. H. The action of SDZ 205,557 at 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT3 and 5-HT4) receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;108(2):376–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12812.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglen R. M., Bley K., Bonhaus D. W., Clark R. D., Hegde S. S., Johnson L. G., Leung E., Wong E. H. RS 23597-190: a potent and selective 5-HT4 receptor antagonist. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Sep;110(1):119–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13780.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglen R. M., Bonhaus D. W., Clark R. D., Johnson L. G., Lee C. H., Leung E., Smith W. L., Wong E. H., Whiting R. L. (R) and (S) RS 56532: mixed 5-HT3 and 5-HT4 receptor ligands with opposing enantiomeric selectivity. Neuropharmacology. 1994 Mar-Apr;33(3-4):515–526. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eglen R. M., Perkins L. A., Walsh L. K., Whiting R. L. Agonist action of indole derivatives at 5-HT1-like, 5-HT3, and 5HT4 receptors in vitro. J Auton Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;12(5):321–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1992.tb00381.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn D. L., Zabrowski D. L., Becker D. P., Nosal R., Villamil C. I., Gullikson G. W., Moummi C., Yang D. C. SC-53116: the first selective agonist at the newly identified serotonin 5-HT4 receptor subtype. J Med Chem. 1992 Apr 17;35(8):1486–1489. doi: 10.1021/jm00086a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford A. P., Clarke D. E. The 5-HT4 receptor. Med Res Rev. 1993 Nov;13(6):633–662. doi: 10.1002/med.2610130603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale J. D., Grossman C. J., Whitehead J. W., Oxford A. W., Bunce K. T., Humphrey P. P. GR113808: a novel, selective antagonist with high affinity at the 5-HT4 receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jan;111(1):332–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14064.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman C. J., Kilpatrick G. J., Bunce K. T. Development of a radioligand binding assay for 5-HT4 receptors in guinea-pig and rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;109(3):618–624. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13617.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung E., Michelson S., Villarubia C., Perkins L. A., Eglen R. M. Analysis of concentration-response relationships by seemingly unrelated nonlinear regression (SUNR) technique. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 1992 Dec;28(4):209–216. doi: 10.1016/1056-8719(92)90006-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. B., Waud D. R. Pharmacological estimation of drug-receptor dissociation constants. Statistical evaluation. I. Agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Apr;177(1):1–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romanelli M. N., Ghelardini C., Dei S., Matucci R., Mori F., Scapecchi S., Teodori E., Bartolini A., Galli A., Giotti A. Synthesis and biological activity of a series of aryl tropanyl esters and amides chemically related to 1H-indole-3-carboxylic acid endo 8-methyl-8-azabicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-yl ester. Development of a 5-HT4 agonist endowed with potent antinociceptive activity. Arzneimittelforschung. 1993 Aug;43(8):913–918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonini M., Messori E., Franceschetti G. P., Rizzi C. A., Castoldi A. F., Coccini T., Candura S. M. Characterization of the 5-HT receptor potentiating neuromuscular cholinergic transmission in strips of human isolated detrusor muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Sep;113(1):1–2. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb16163.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villalón C. M., den Boer M. O., Heiligers J. P., Saxena P. R. Mediation of 5-hydroxytryptamine-induced tachycardia in the pig by the putative 5-HT4 receptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):665–667. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14073.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardle K. A., Ellis E. S., Baxter G. S., Kennett G. A., Gaster L. M., Sanger G. J. The effects of SB 204070, a highly potent and selective 5-HT4 receptor antagonist, on guinea-pig distal colon. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jul;112(3):789–794. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13148.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiseman L. R., Faulds D. Cisapride. An updated review of its pharmacology and therapeutic efficacy as a prokinetic agent in gastrointestinal motility disorders. Drugs. 1994 Jan;47(1):116–152. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199447010-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


