Abstract
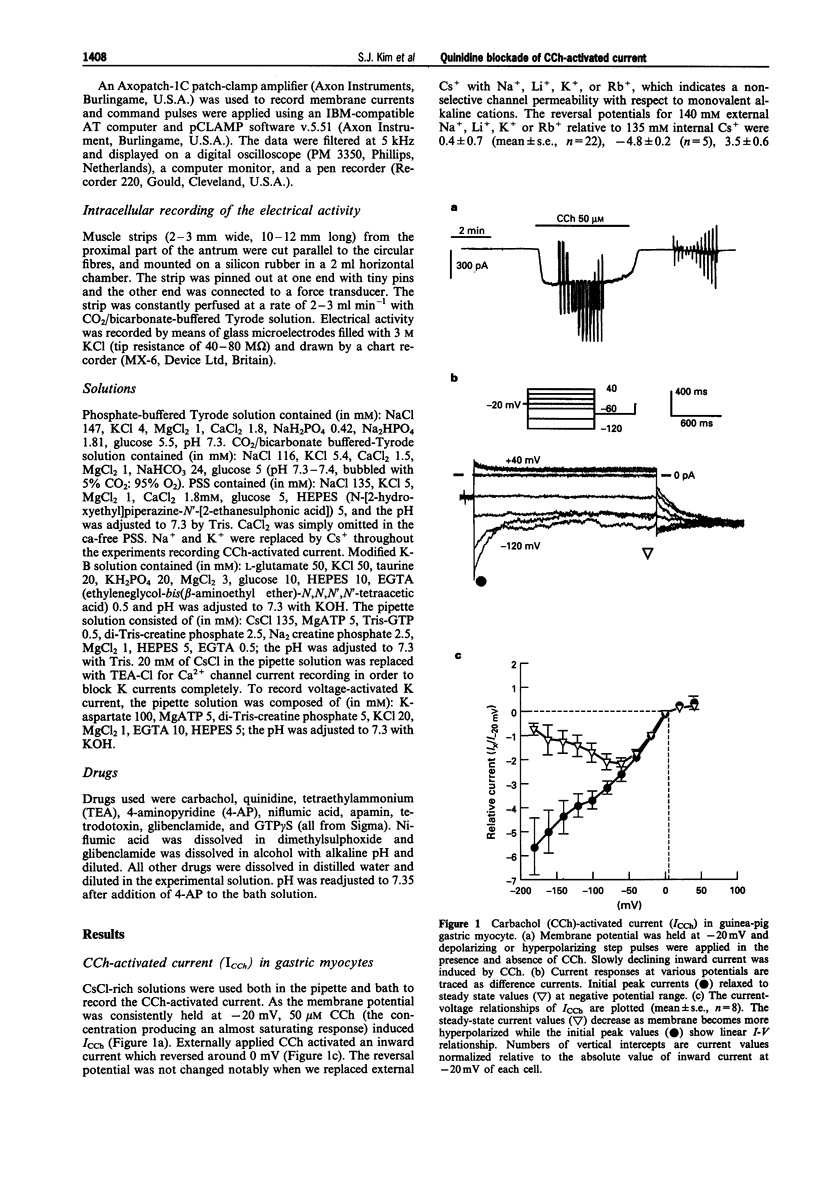
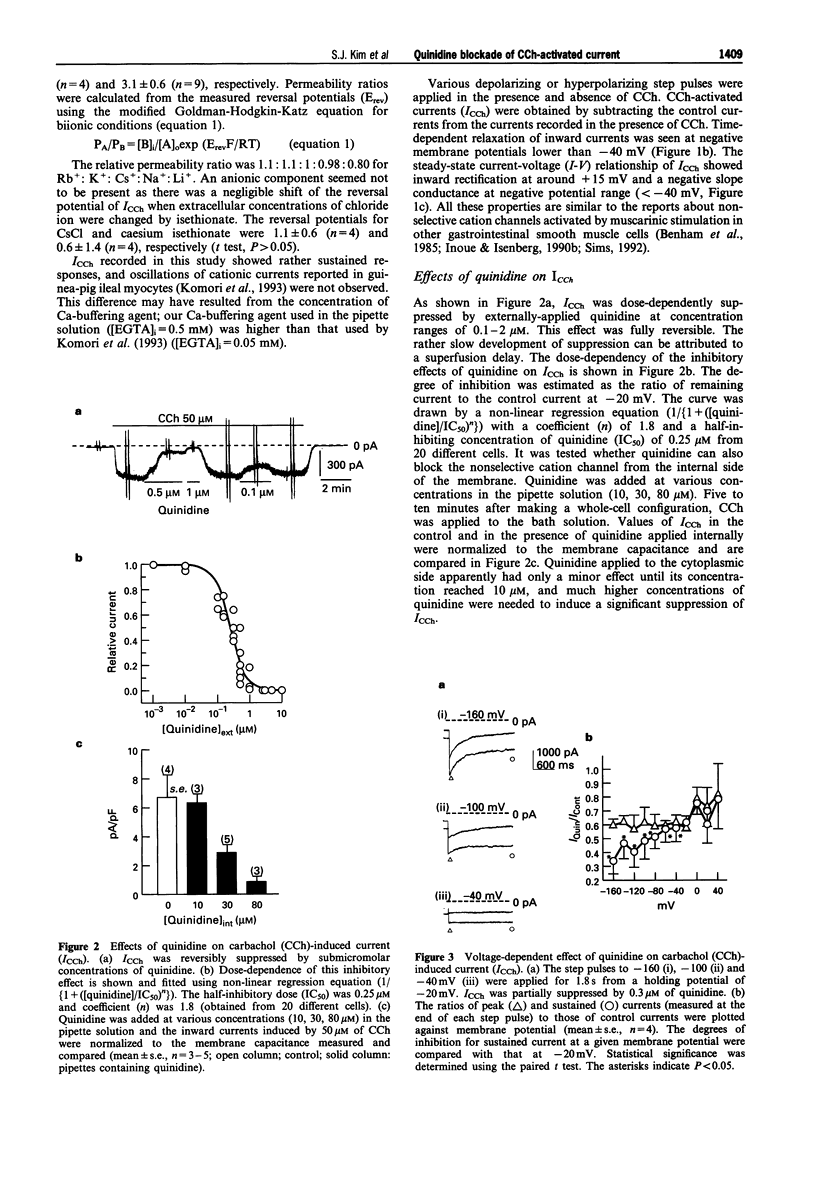
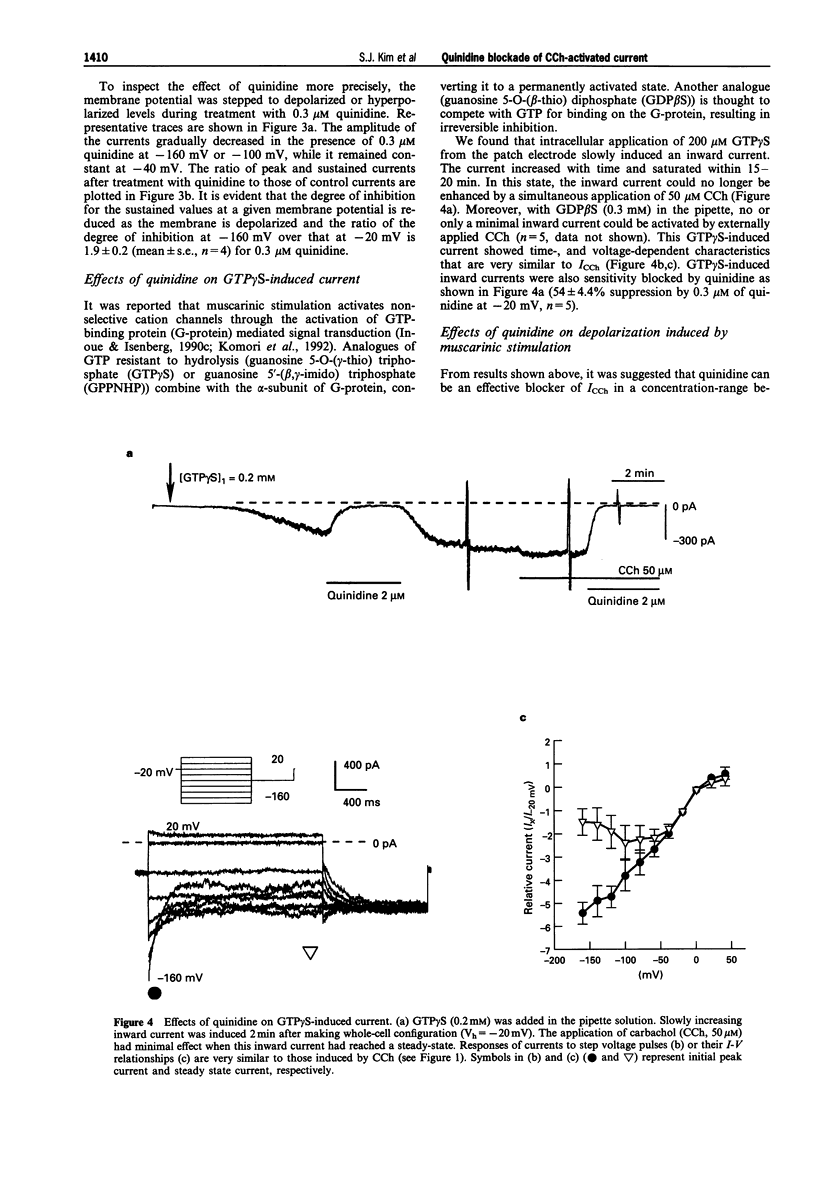
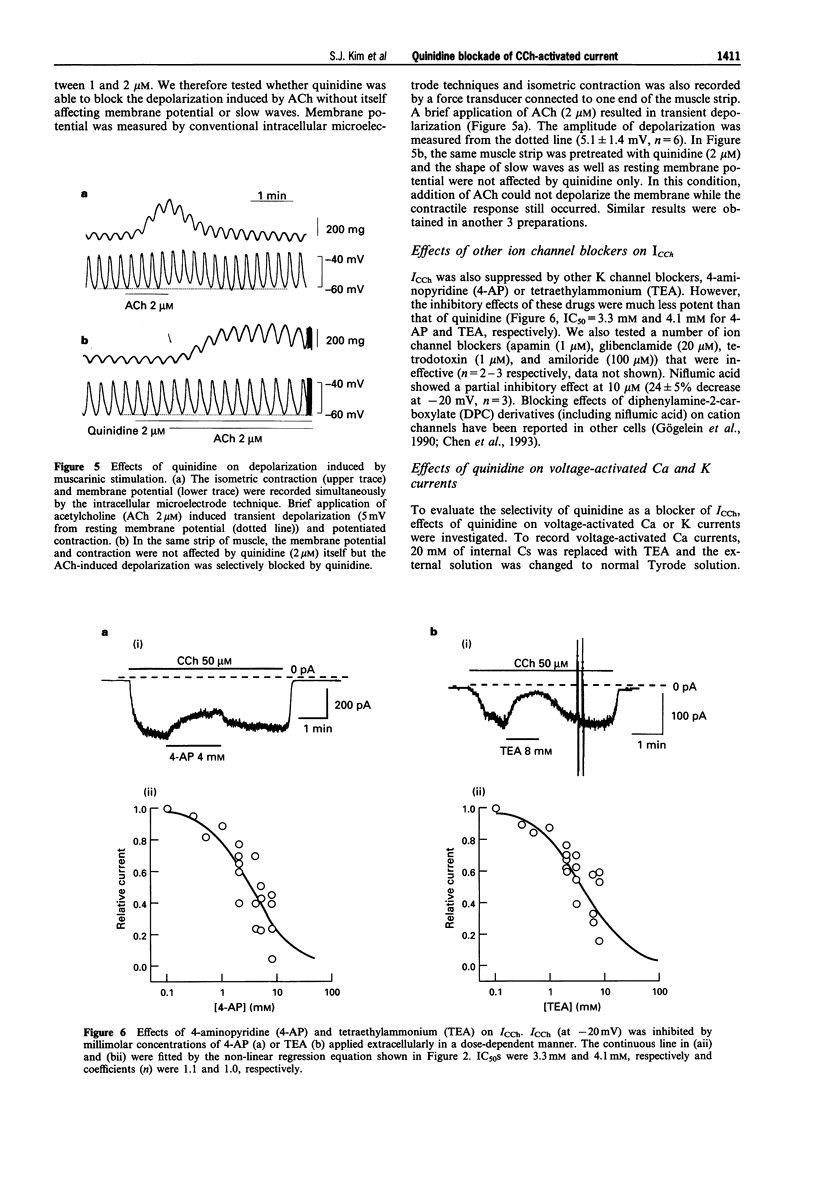
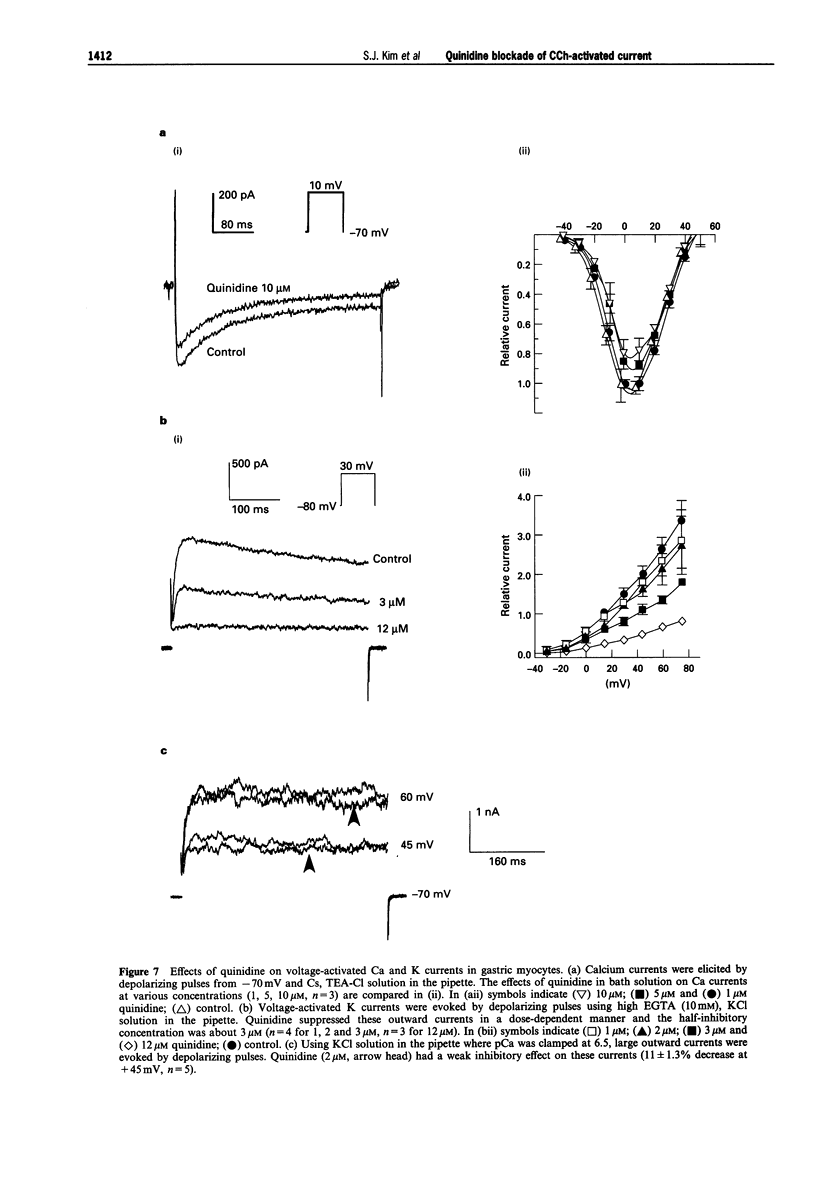
1. In guinea-pig gastric myocytes isolated from the antral circular layer, stimulation of muscarinic receptors by carbachol (CCh) induces a cationic current (ICCh) which is known as the main mechanism of depolarization induced by muscarinic stimulation. 2. We tested the effects of a number of ion channel blockers on ICCh and focused upon quinidine which was a highly potent blocker. Externally applied quinidine suppressed ICCh (IC50 = 0.25 microM) in a reversible and voltage-dependent manner. Applied internally, quinidine was about 100 times less potent than when applied externally. Persistent activation of G-protein by GTP gamma S also induced a cationic current similar to ICCh and this current was also blocked by quinidine. 4-Aminopyridine and tetraethylammonium also suppressed ICCh in a dose-dependent manner (IC50 = 3.3 mM and 4.1 mM, respectively). 3. Pretreatment with quinidine (2 microM) selectively blocked the acetylcholine (ACh)-induced depolarization which was recorded in the multicellular tissues by a conventional intracellular microelectrode technique. 4. Voltage-dependent K-currents were also suppressed by quinidine but in a higher concentration range (IC50 = 3 microM). Quinidine, 10 microM, decreased the amplitude of the voltage-dependent Ca current to only a small extent (15% decrease at 0 mV). Quinidine, 2 microM, also suppressed only a minute proportion of the Ca-activated K current (11.1% decrease at 45 mV). 5. From these experiments, it is concluded that some organic agents known as K channel blockers are able to block the CCh-activated cation channel in a non-specific manner and among them, quinidine can be used as an effective blocker for ICCh in guinea-pig gastric myocytes.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benham C. D., Bolton T. B., Lang R. J. Acetylcholine activates an inward current in single mammalian smooth muscle cells. Nature. 1985 Jul 25;316(6026):345–347. doi: 10.1038/316345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Claret M., Jenkinson D. H. Effects of quinine and apamin on the calcium-dependent potassium permeability of mammalian hepatocytes and red cells. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:67–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S., Inoue R., Ito Y. Pharmacological characterization of muscarinic receptor-activated cation channels in guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;109(3):793–801. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13644.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabiato A., Fabiato F. Calculator programs for computing the composition of the solutions containing multiple metals and ligands used for experiments in skinned muscle cells. J Physiol (Paris) 1979;75(5):463–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gögelein H., Capek K. Quinine inhibits chloride and nonselective cation channels in isolated rat distal colon cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 24;1027(2):191–198. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gögelein H., Dahlem D., Englert H. C., Lang H. J. Flufenamic acid, mefenamic acid and niflumic acid inhibit single nonselective cation channels in the rat exocrine pancreas. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jul 30;268(1):79–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80977-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraoka M., Sawada K., Kawano S. Effects of quinidine on plateau currents of guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1986 Oct;18(10):1097–1106. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2828(86)80296-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaizumi Y., Giles W. R. Quinidine-induced inhibition of transient outward current in cardiac muscle. Am J Physiol. 1987 Sep;253(3 Pt 2):H704–H708. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.253.3.H704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue R. Effect of external Cd2+ and other divalent cations on carbachol-activated non-selective cation channels in guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1991 Oct;442:447–463. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue R., Isenberg G. Acetylcholine activates nonselective cation channels in guinea pig ileum through a G protein. Am J Physiol. 1990 Jun;258(6 Pt 1):C1173–C1178. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.6.C1173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue R., Isenberg G. Effect of membrane potential on acetylcholine-induced inward current in guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1990 May;424:57–71. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue R., Isenberg G. Intracellular calcium ions modulate acetylcholine-induced inward current in guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1990 May;424:73–92. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue R., Kitamura K., Kuriyama H. Acetylcholine activates single sodium channels in smooth muscle cells. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Sep;410(1-2):69–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00581898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg G., Klockner U. Calcium tolerant ventricular myocytes prepared by preincubation in a "KB medium". Pflugers Arch. 1982 Oct;395(1):6–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00584963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori S., Kawai M., Pacaud P., Ohashi H., Bolton T. B. Oscillations of receptor-operated cationic current and internal calcium in single guinea-pig ileal smooth muscle cells. Pflugers Arch. 1993 Sep;424(5-6):431–438. doi: 10.1007/BF00374905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komori S., Kawai M., Takewaki T., Ohashi H. GTP-binding protein involvement in membrane currents evoked by carbachol and histamine in guinea-pig ileal muscle. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:105–126. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. K., Bayguinov O., Sanders K. M. Role of nonselective cation current in muscarinic responses of canine colonic muscle. Am J Physiol. 1993 Dec;265(6 Pt 1):C1463–C1471. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.6.C1463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. S., Hume J. R., Giles W., Brown A. M. Sodium current depression by lidocaine and quinidine in isolated ventricular cells. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):325–327. doi: 10.1038/291325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao K., Inoue R., Yamanaka K., Kitamura K. Actions of quinidine and apamin on after-hyperpolarization of the spike in circular smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig ileum. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Dec;334(4):508–513. doi: 10.1007/BF00569394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura M., Huan R. M., Habuchi Y., Tsuji Y., Nakanishi T., Watanabe Y. Membrane actions of quinidine sulfate in the rabbit atrioventricular node studied by voltage clamp method. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 Feb;244(2):780–788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims S. M. Cholinergic activation of a non-selective cation current in canine gastric smooth muscle is associated with contraction. J Physiol. 1992 Apr;449:377–398. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgess N. C., Hales C. N., Ashford M. L. Calcium and ATP regulate the activity of a non-selective cation channel in a rat insulinoma cell line. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Aug;409(6):607–615. doi: 10.1007/BF00584661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogalis F., Sanders K. M. Cholinergic stimulation activates a non-selective cation current in canine pyloric circular muscle cells. J Physiol. 1990 Oct;429:223–236. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong B. S. Quinidine blockade of calcium-activated potassium channels in dissociated gastric smooth muscle cells. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Aug;414(4):416–422. doi: 10.1007/BF00585051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



