Abstract
1. The interaction between chloroethylclonidine (CEC) and noradrenaline (NA) has been examined at alpha-adrenoceptors mediating contractions of rat aorta. 2. In rat aorta, the competitive antagonist prazosin, over the concentration-range 0.01-10 microM, produced concentration-dependent shifts in the contractile potency of NA, so that there was no component of the NA contraction resistant to prazosin. 3. The irreversible alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonists, phenoxybenzamine (PBZ) (1-10 microM) and benextramine (10 microM) produced shifts in potency of NA and reduced the maximum response in a concentration-dependent manner. 4. The irreversible alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist, CEC (100 microM), produced a non-parallel shift in the NA concentration-response curve so that low concentrations of NA produced relatively small contractions but relatively high concentrations produced further contractions, so that the maximum response was not significantly reduced. 5. The combination of CEC pretreatment and subsequent prazosin (0.1 microM) produced a parallel shift in the potency of NA. However, prazosin (10 microM) failed to produce any further effect on the response to high concentrations of NA following CEC pretreatment. Hence, a component of the contraction to NA in the presence of CEC was resistant to subsequent prazosin. Likewise, this component was resistant to a combination of prazosin (10 microM) and yohimbine (10 microM). 6. Receptor protection experiments were carried out in which tissues were exposed to NA (100 microM), yohimbine (10 microM) or prazosin (0.1 microM) prior to and during exposure to CEC. Receptor protection with NA, yohimbine or prazosin (0.1 microM), followed by washout prevented the shift in potency of NA produced by CEC. 7. Further experiments examined the effects of prazosin (10 microM) on responses to NA following receptor protection with NA (100 microM), yohimbine (10 microM), prazosin (10 microM), or xylazine (100 microM).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF

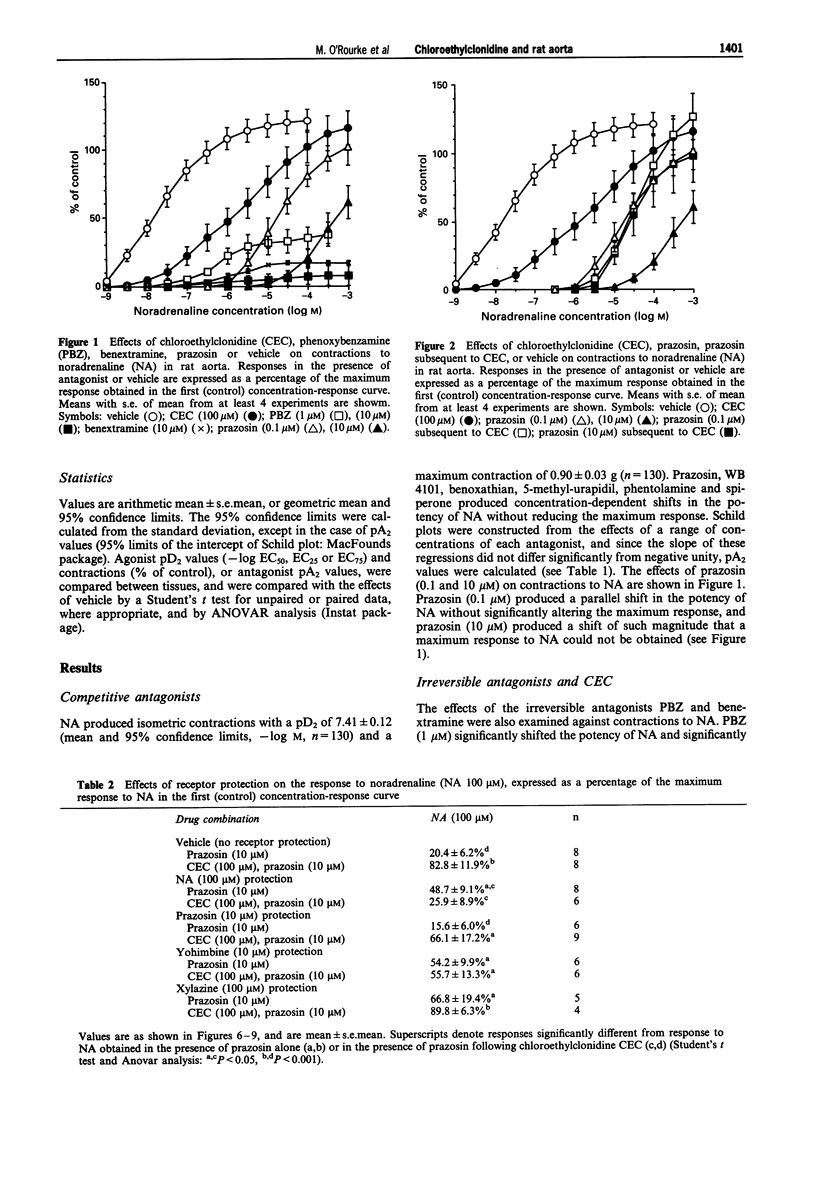


Selected References
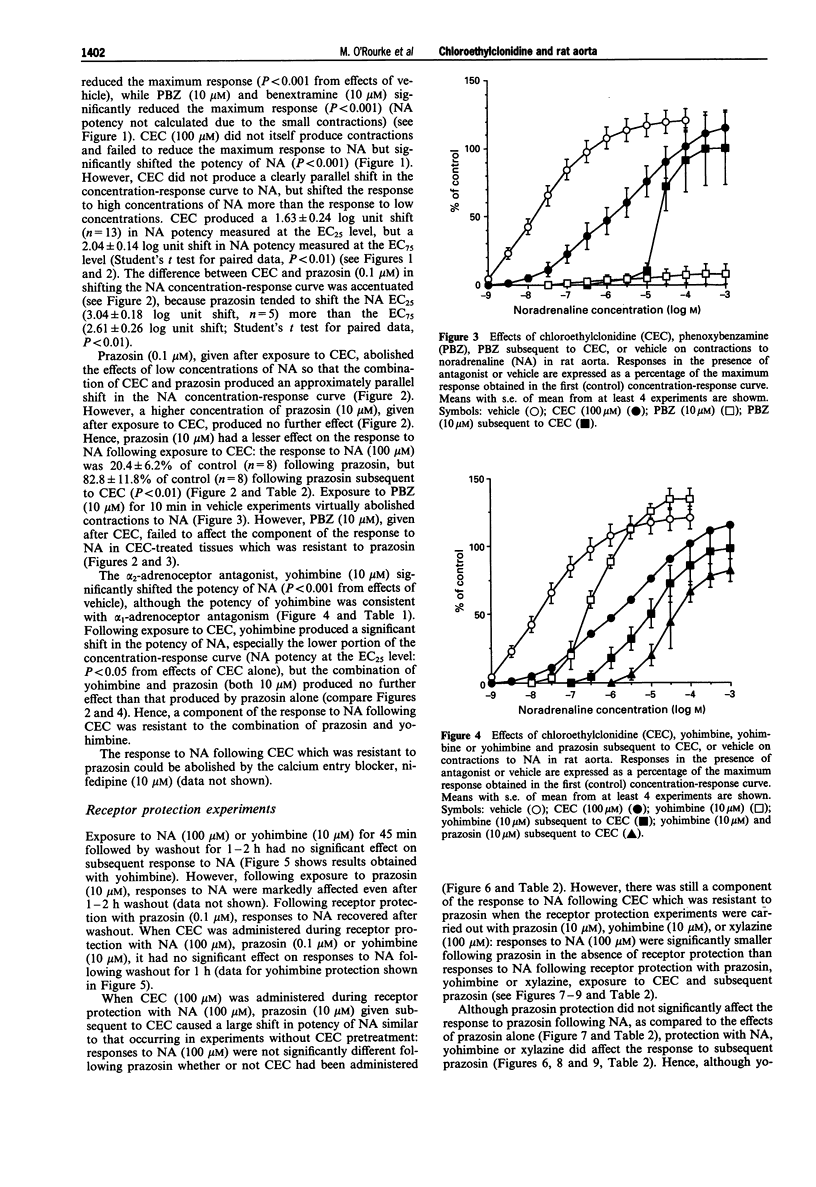
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
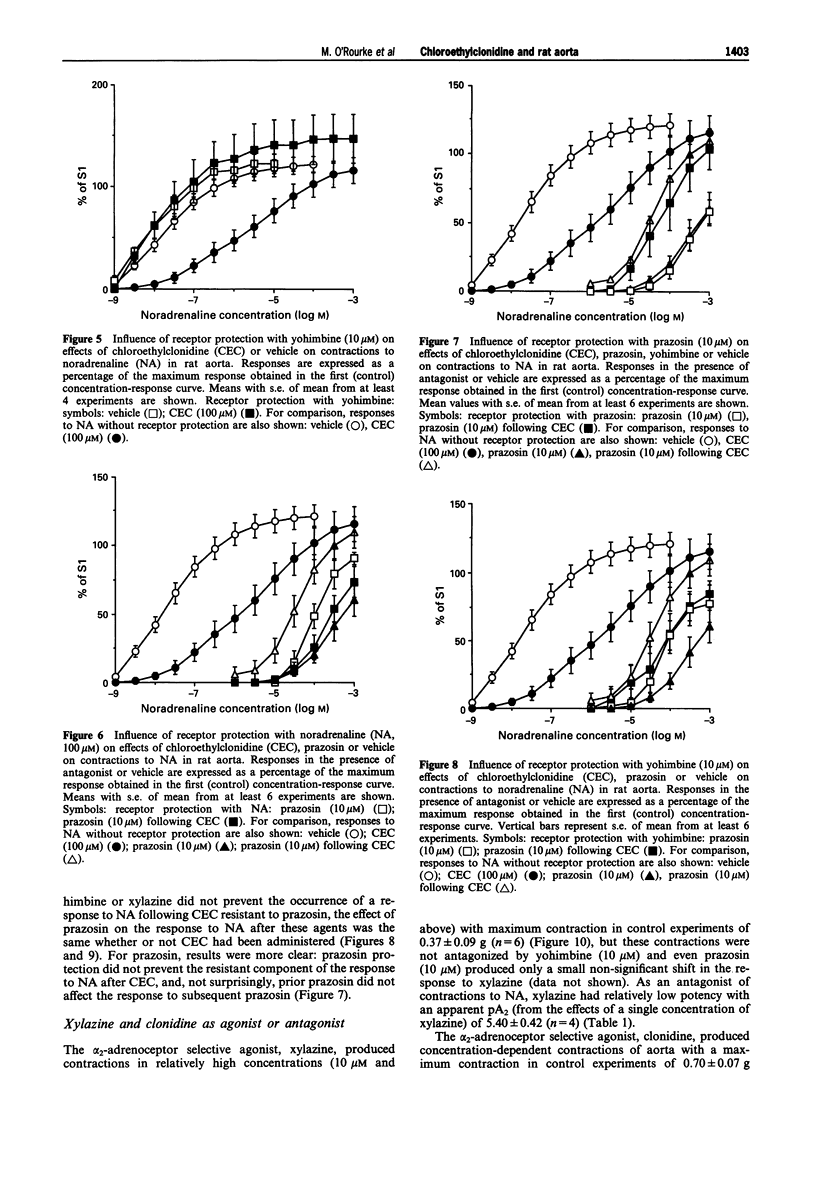
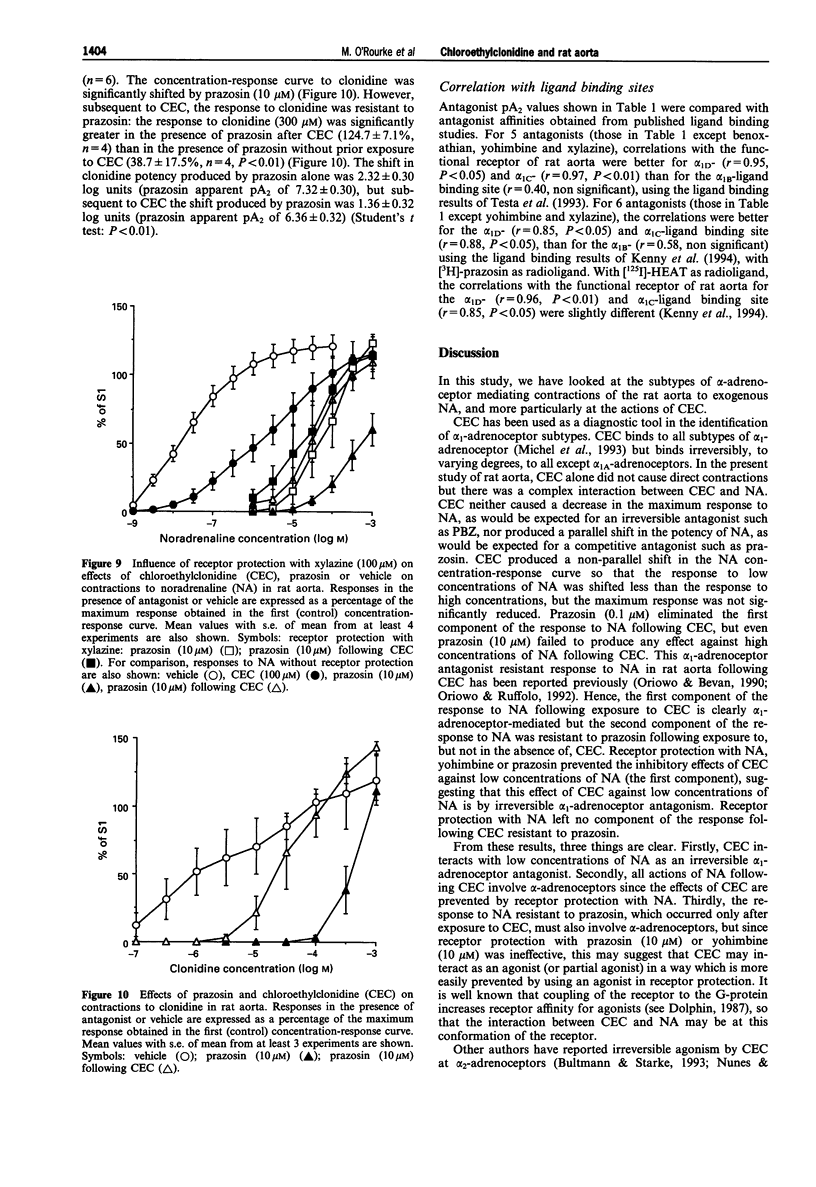
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aboud R., Shafii M., Docherty J. R. Investigation of the subtypes of alpha 1-adrenoceptor mediating contractions of rat aorta, vas deferens and spleen. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 May;109(1):80–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13534.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bültmann R., Starke K. Chloroethylclonidine: an irreversible agonist at prejunctional alpha 2-adrenoceptors in rat vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Feb;108(2):336–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb12806.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotecchia S., Schwinn D. A., Randall R. R., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G., Kobilka B. K. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for the hamster alpha 1-adrenergic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7159–7163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. R., Hyland L. No evidence for differences between pre- and post-junctional alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 Oct;86(2):335–339. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08901.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty J. R. The pharmacology of alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenoceptors: evidence for and against a further subdivision. Pharmacol Ther. 1989;44(2):241–284. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(89)90067-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross G., Hanft G., Rugevics C. 5-Methyl-urapidil discriminates between subtypes of the alpha 1-adrenoceptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 7;151(2):333–335. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90819-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C., Abel P. W., Minneman K. P. Alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes linked to different mechanisms for increasing intracellular Ca2+ in smooth muscle. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):333–335. doi: 10.1038/329333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C., Li J., Minneman K. P. Subtypes of alpha 1-adrenoceptors in rat blood vessels. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov 6;190(1-2):97–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94116-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanft G., Gross G. Subclassification of alpha 1-adrenoceptor recognition sites by urapidil derivatives and other selective antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;97(3):691–700. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12005.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny B. A., Naylor A. M., Greengrass P. M., Russell M. J., Friend S. J., Read A. M., Wyllie M. G. Pharmacological properties of the cloned alpha 1A/D-adrenoceptor subtype are consistent with the alpha 1A-adrenoceptor characterized in rat cerebral cortex and vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Apr;111(4):1003–1008. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14843.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomasney J. W., Cotecchia S., Lorenz W., Leung W. Y., Schwinn D. A., Yang-Feng T. L., Brownstein M., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for the alpha 1A-adrenergic receptor. The gene for which is located on human chromosome 5. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6365–6369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Kerker J., Branchek T. A., Forray C. Selective irreversible binding of chloroethylclonidine at alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenoceptor subtypes. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;44(6):1165–1170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow A. L., Creese I. Characterization of alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes in rat brain: a reevaluation of [3H]WB4104 and [3H]prazosin binding. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;29(4):321–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu I., Kigoshi S., Ohmura T. Subtypes of alpha 1-adrenoceptors involved in noradrenaline-induced contractions of rat thoracic aorta and dog carotid artery. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;57(4):535–544. doi: 10.1254/jjp.57.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunes J. P., Guimarães S. Chloroethylclonidine irreversibly activates postjunctional alpha 2-adrenoceptors in the dog saphenous vein. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1993 Sep;348(3):264–268. doi: 10.1007/BF00169154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oriowo M. A., Bevan J. A. Chloroethylclonidine unmasks a non-alpha-adrenoceptor noradrenaline binding site in the rat aorta. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Mar 20;178(2):243–246. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90482-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oriowo M. A., Ruffolo R. R., Jr Heterogeneity of postjunctional alpha 1-adrenoceptors in mammalian aortae: subclassification based on chlorethylclonidine, WB 4101 and nifedipine. J Vasc Res. 1992 Jan-Feb;29(1):33–40. doi: 10.1159/000158929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez D. M., Piascik M. T., Graham R. M. Solution-phase library screening for the identification of rare clones: isolation of an alpha 1D-adrenergic receptor cDNA. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;40(6):876–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piascik M. T., Sparks M. S., Pruitt T. A., Soltis E. E. Evidence for a complex interaction between the subtypes of the alpha 1-adrenoceptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 9;199(3):279–289. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90491-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ping P., Faber J. E. Characterization of alpha-adrenoceptor gene expression in arterial and venous smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1993 Nov;265(5 Pt 2):H1501–H1509. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1993.265.5.H1501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rokosh D. G., Bailey B. A., Stewart A. F., Karns L. R., Long C. S., Simpson P. C. Distribution of alpha 1C-adrenergic receptor mRNA in adult rat tissues by RNase protection assay and comparison with alpha 1B and alpha 1D. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 May 16;200(3):1177–1184. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwinn D. A., Lomasney J. W., Lorenz W., Szklut P. J., Fremeau R. T., Jr, Yang-Feng T. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Cotecchia S. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for a novel alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtype. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8183–8189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K., Docherty J. R. Are the prejunctional alpha 2-adrenoceptors of the rat vas deferens and submandibular gland of the alpha 2A- or alpha 2D-subtype? Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Aug 25;219(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90297-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Testa R., Guarneri L., Ibba M., Strada G., Poggesi E., Taddei C., Simonazzi I., Leonardi A. Characterization of alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes in prostate and prostatic urethra of rat, rabbit, dog and man. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Nov 16;249(3):307–315. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90527-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian W. N., Gupta S., Deth R. C. Species differences in chlorethylclonidine antagonism at vascular alpha-1 adrenergic receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 May;253(2):877–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voigt M. M., Kispert J., Chin H. M. Sequence of a rat brain cDNA encoding an alpha-1B adrenergic receptor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):1053–1053. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.1053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



