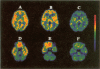
Abstract
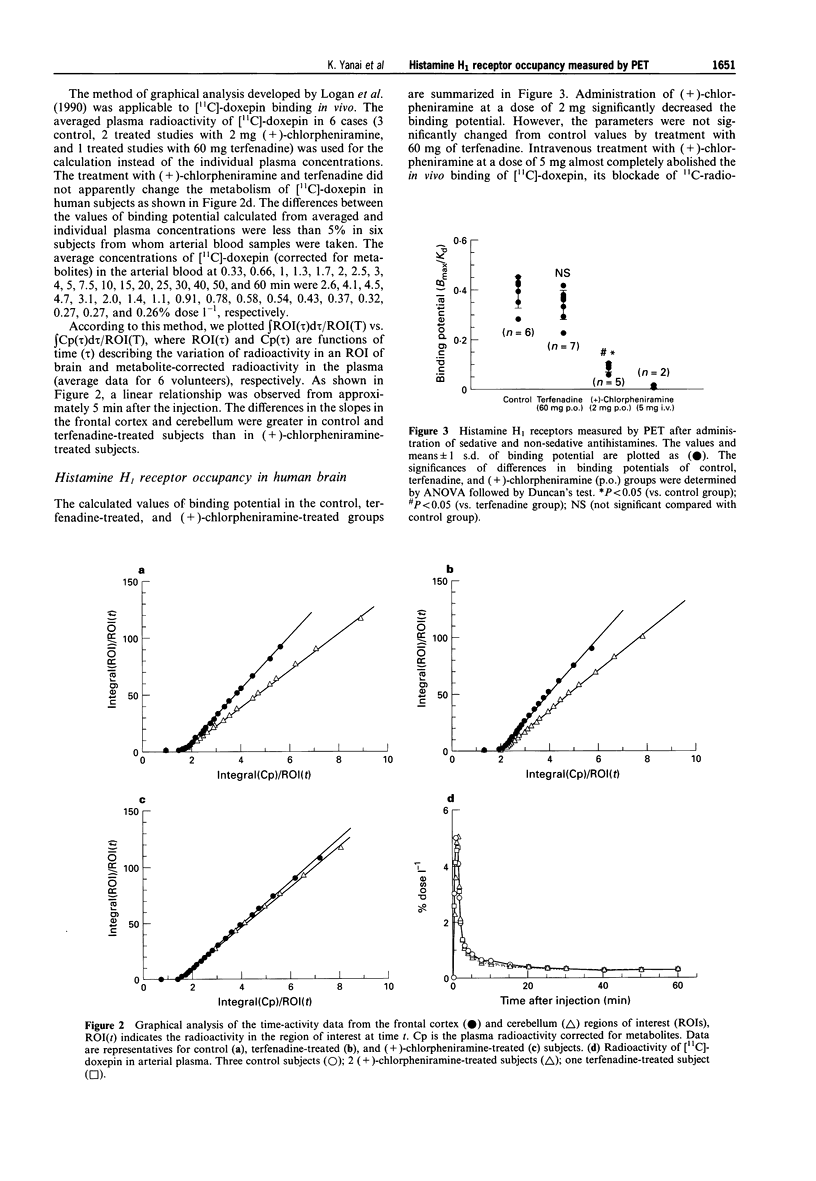
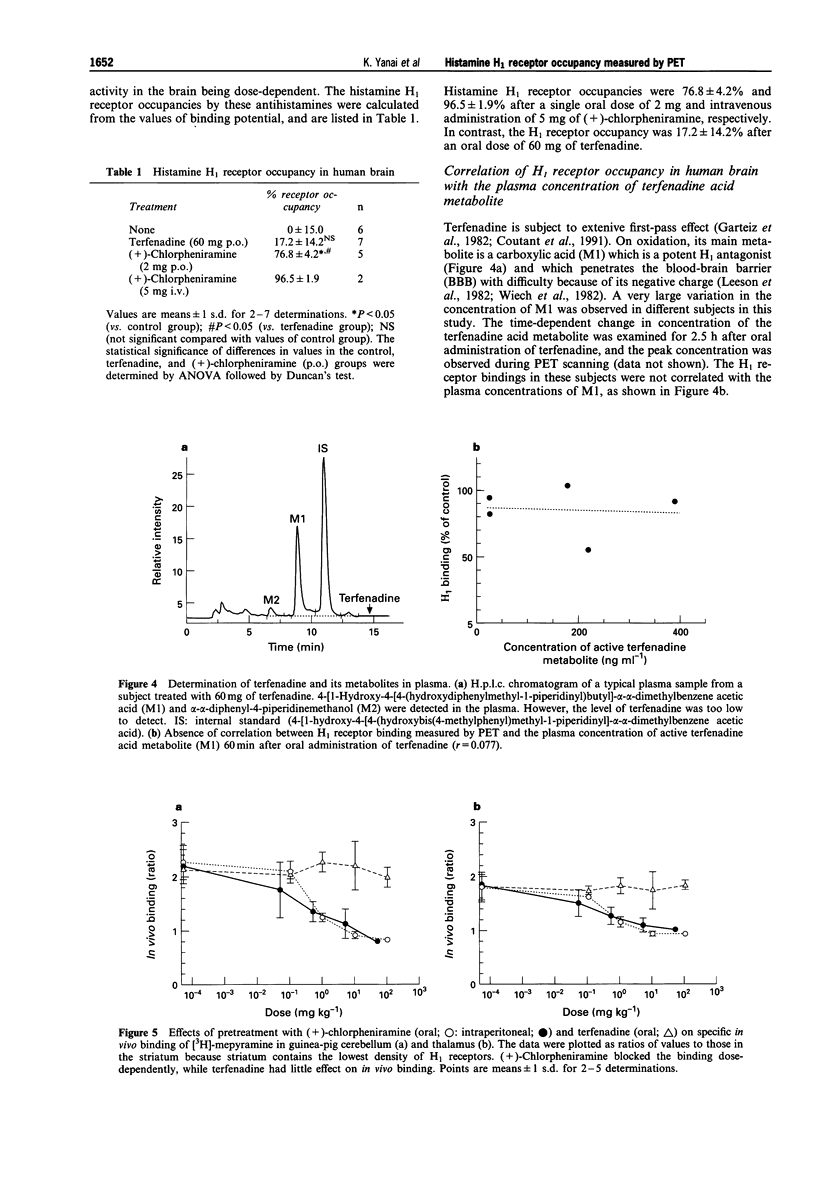
1. Histamine H1 receptor occupancy in the human brain was measured in 20 healthy young men by positron emission tomography (PET) using [11C]-doxepin. 2. (+)-Chlorpheniramine, a selective and classical antihistamine, occupied 76.8 +/- 4.2% of the averaged values of available histamine H1 receptors in the frontal cortex after its administration in a single oral dose of 2 mg. Intravenous administration of 5 mg (+)-chlorpheniramine almost completely abolished the binding of [11C]-doxepin to H1 receptors (H1 receptor occupancy: 98.2 +/- 1.2%). 3. Terfenadine, a nonsedative antihistamine, occupied 17.2 +/- 14.2% of the available H1 receptors in the human frontal cortex after its administration in a single oral dose of 60 mg. 4. There was no correlation between H1 receptor occupancy by terfenadine and the plasma concentration of the active acid metabolite of terfenadine in each subject. 5. PET data on human brain were essentially compatible with those on H1 receptor occupancy in guinea-pig brain determined by in vivo binding techniques, although for the same H1 receptor occupancy the dose was less in human subjects than in guinea-pigs. 6. The PET studies demonstrated the usefulness of measuring H1 receptor occupancy with classical and second-generation antihistamines in human brain to estimate their unwanted side effects such as sedation and drowsiness quantitatively.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhatti J. Z., Hindmarch I. The effects of terfenadine with and without alcohol on an aspect of car driving performance. Clin Exp Allergy. 1989 Nov;19(6):609–611. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1989.tb02754.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brouillet E., Chavoix C., Bottlaender M., Khalili-Varasteh M., Hantraye P., Fournier D., Dodd R. H., Mazière M. In vivo bidirectional modulatory effect of benzodiazepine receptor ligands on GABAergic transmission evaluated by positron emission tomography in non-human primates. Brain Res. 1991 Aug 23;557(1-2):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90131-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang R. S., Tran V. T., Snyder S. H. Heterogeneity of histamine H1-receptors: species variations in [3H]mepyramine binding of brain membranes. J Neurochem. 1979 Jun;32(6):1653–1663. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb02276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavoix C., Brouillet E., Kunimoto M., De la Sayette V., Khalili-Varasteh M., Hantraye P., Dodd R. H., Guibert B., Prenant C., Naquet R. Relationships between benzodiazepine receptors, impairment of GABAergic transmission and convulsant activity of beta-CCM: a PET study in the baboon Papio papio. Epilepsy Res. 1991 Jan-Feb;8(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0920-1211(91)90030-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cimbura G., Lucas D. M., Bennett R. C., Warren R. A., Simpson H. M. Incidence and toxicological aspects of drugs detected in 484 fatally injured drivers and pedestrians in Ontario. J Forensic Sci. 1982 Oct;27(4):855–867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutant J. E., Westmark P. A., Nardella P. A., Walter S. M., Okerholm R. A. Determination of terfenadine and terfenadine acid metabolite in plasma using solid-phase extraction and high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J Chromatogr. 1991 Sep 18;570(1):139–148. doi: 10.1016/0378-4347(91)80208-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cusack B., Nelson A., Richelson E. Binding of antidepressants to human brain receptors: focus on newer generation compounds. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1994 May;114(4):559–565. doi: 10.1007/BF02244985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley D., Tran V. T., Snyder S. H. Histamine H1-receptors labeled in vivo: antidepressant and antihistamine interactions. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Jun 13;64(2-3):177–181. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90043-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farde L., Nordström A. L., Wiesel F. A., Pauli S., Halldin C., Sedvall G. Positron emission tomographic analysis of central D1 and D2 dopamine receptor occupancy in patients treated with classical neuroleptics and clozapine. Relation to extrapyramidal side effects. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1992 Jul;49(7):538–544. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1992.01820070032005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garteiz D. A., Hook R. H., Walker B. J., Okerholm R. A. Pharmacokinetics and biotransformation studies of terfenadine in man. Arzneimittelforschung. 1982;32(9A):1185–1190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill S. J., Emson P. C., Young J. M. The binding of [3H]mepyramine to histamine H1 receptors in guinea-pig brain. J Neurochem. 1978 Oct;31(4):997–1004. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb00139.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizuka H., Sawada Y., Ito K., Sugiyama Y., Suzuki H., Iga T., Hanano M. Nonlinear relationship between benzodiazepine receptor occupancy and glucose metabolic response in the conscious mouse brain in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Oct;251(1):362–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones A. K., Friston K. J., Qi L. Y., Harris M., Cunningham V. J., Jones T., Feinman C., Frackowiak R. S. Sites of action of morphine in the brain. Lancet. 1991 Sep 28;338(8770):825–825. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90717-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanba S., Richelson E. Histamine H1 receptors in human brain labelled with [3H]doxepin. Brain Res. 1984 Jun 18;304(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90856-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. C., Wagner H. N., Jr, Tanada S., Frost J. J., Bice A. N., Dannals R. F. Duration of occupancy of opiate receptors by naltrexone. J Nucl Med. 1988 Jul;29(7):1207–1211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeson G. A., Chan K. Y., Knapp W. C., Biedenbach S. A., Wright G. J., Okerholm R. A. Metabolic disposition of terfenadine in laboratory animals. Arzneimittelforschung. 1982;32(9A):1173–1178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan J., Fowler J. S., Volkow N. D., Wolf A. P., Dewey S. L., Schlyer D. J., MacGregor R. R., Hitzemann R., Bendriem B., Gatley S. J. Graphical analysis of reversible radioligand binding from time-activity measurements applied to [N-11C-methyl]-(-)-cocaine PET studies in human subjects. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1990 Sep;10(5):740–747. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1990.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson A. N. Antihistamines and sedation. Lancet. 1983 Jul 23;2(8343):211–212. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90185-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson A. N., Pascoe P. A., Turner C., Ganellin C. R., Greengrass P. M., Casy A. F., Mercer A. D. Sedation and histamine H1-receptor antagonism: studies in man with the enantiomers of chlorpheniramine and dimethindene. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Sep;104(1):270–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12418.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordström A. L., Farde L., Wiesel F. A., Forslund K., Pauli S., Halldin C., Uppfeldt G. Central D2-dopamine receptor occupancy in relation to antipsychotic drug effects: a double-blind PET study of schizophrenic patients. Biol Psychiatry. 1993 Feb 15;33(4):227–235. doi: 10.1016/0006-3223(93)90288-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quach T. T., Duchemin A. M., Rose C., Schwartz J. C. In vivo occupation of cerebral histamine H1-receptors evaluated with 3H-mepyramine may predict sedative properties of psychotropic drugs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1979 Dec 20;60(4):391–392. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(79)90250-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quach T. T., Duchemin A. M., Rose C., Schwartz J. C. Labeling of histamine H1-receptors in the brain of the living mouse. Neurosci Lett. 1980 Apr;17(1-2):49–54. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(80)90060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose C., Quach T. T., Llorens C., Schwartz J. C. Relationship between occupation of cerebral H1-receptors and sedative properties of antihistamines. Assessment in the case of terfenadine. Arzneimittelforschung. 1982;32(9A):1171–1173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinotoh H., Iyo M., Yamada T., Inoue O., Suzuki K., Itoh T., Fukuda H., Yamasaki T., Tateno Y., Hirayama K. Detection of benzodiazepine receptor occupancy in the human brain by positron emission tomography. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1989;99(2):202–207. doi: 10.1007/BF00442808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons F. E., Simons K. J. The pharmacology and use of H1-receptor-antagonist drugs. N Engl J Med. 1994 Jun 9;330(23):1663–1670. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199406093302307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran V. T., Lebovitz R., Toll L., Snyder S. H. [3H]doxepin interactions with histamine H1-receptors and other sites in guinea pig and rat brain homogenates. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Apr 9;70(4):501–509. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90361-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villemagne V. L., Dannals R. F., Sánchez-Roa P. M., Ravert H. T., Vazquez S., Wilson A. A., Natarajan T. K., Wong D. F., Yanai K., Wagner H. N., Jr Imaging histamine H1 receptors in the living human brain with carbon-11-pyrilamine. J Nucl Med. 1991 Feb;32(2):308–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villemagne V. L., Frost J. J., Dannals R. F., Lever J. R., Tanada S., Natarajan T. K., Wilson A. A., Ravert H. T., Wagner H. N., Jr Comparison of [11C]diprenorphine and [11C]carfentanil in vivo binding to opiate receptors in man using a dual detector system. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 May 12;257(1-2):195–197. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(94)90712-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiech N. L., Martin J. S. Absence of an effect of terfenadine on guinea pig brain histamine H1-receptors in vivo determined by receptor binding techniques. Arzneimittelforschung. 1982;32(9A):1167–1170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanai K., Watanabe T., Meguro K., Yokoyama H., Sato I., Sasano H., Itoh M., Iwata R., Takahashi T., Ido T. Age-dependent decrease in histamine H1 receptor in human brains revealed by PET. Neuroreport. 1992 May;3(5):433–436. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199205000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanai K., Watanabe T., Yokoyama H., Hatazawa J., Iwata R., Ishiwata K., Meguro K., Itoh M., Takahashi T., Ido T. Mapping of histamine H1 receptors in the human brain using [11C]pyrilamine and positron emission tomography. J Neurochem. 1992 Jul;59(1):128–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb08883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanai K., Yagi N., Watanabe T., Itoh M., Ishiwata K., Ido T., Matsuzawa T. Specific binding of [3H]pyrilamine to histamine H1 receptors in guinea pig brain in vivo: determination of binding parameters by a kinetic four-compartment model. J Neurochem. 1990 Aug;55(2):409–420. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb04152.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]