Abstract
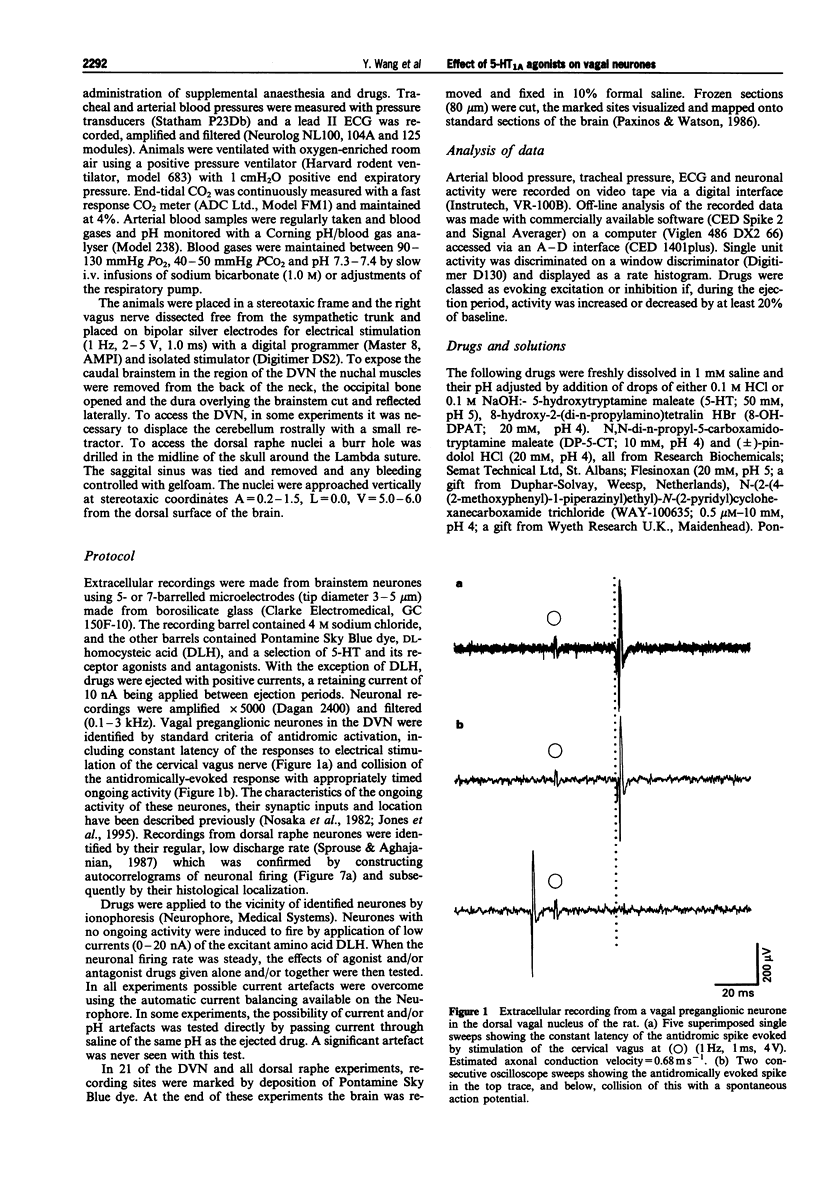
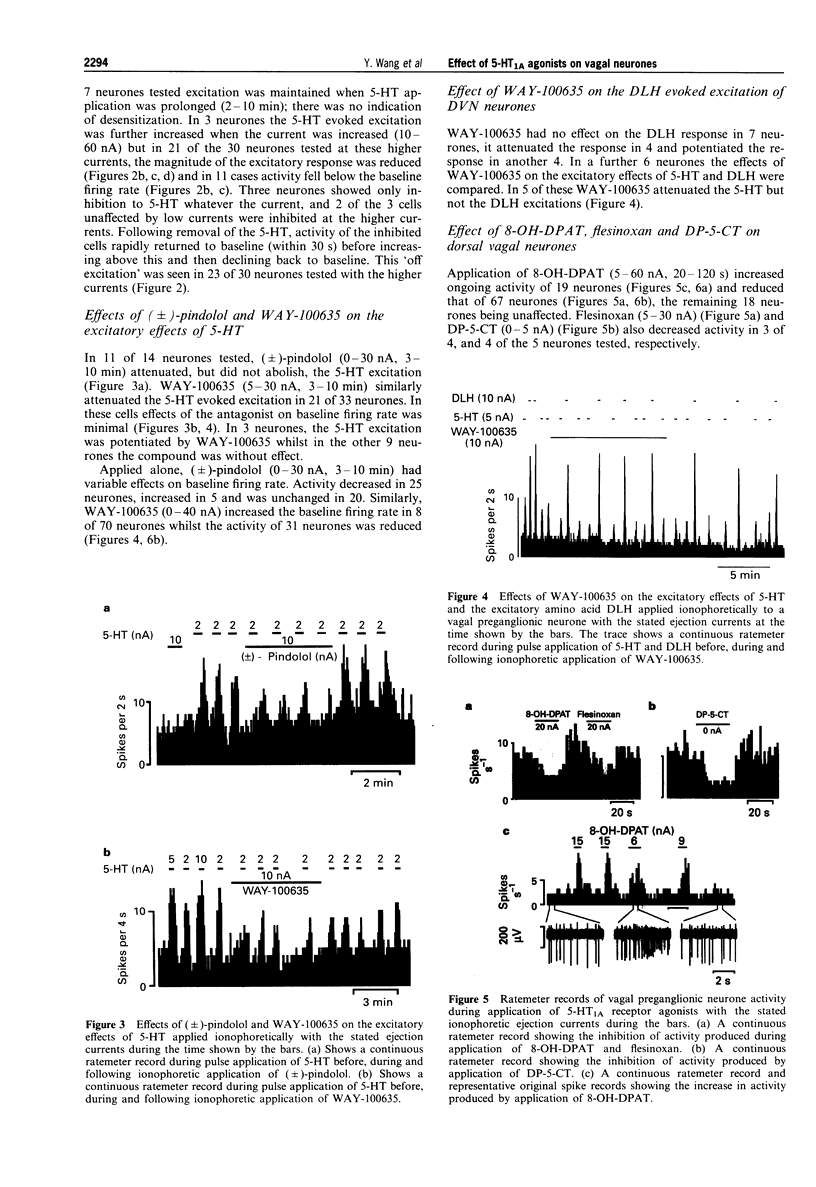
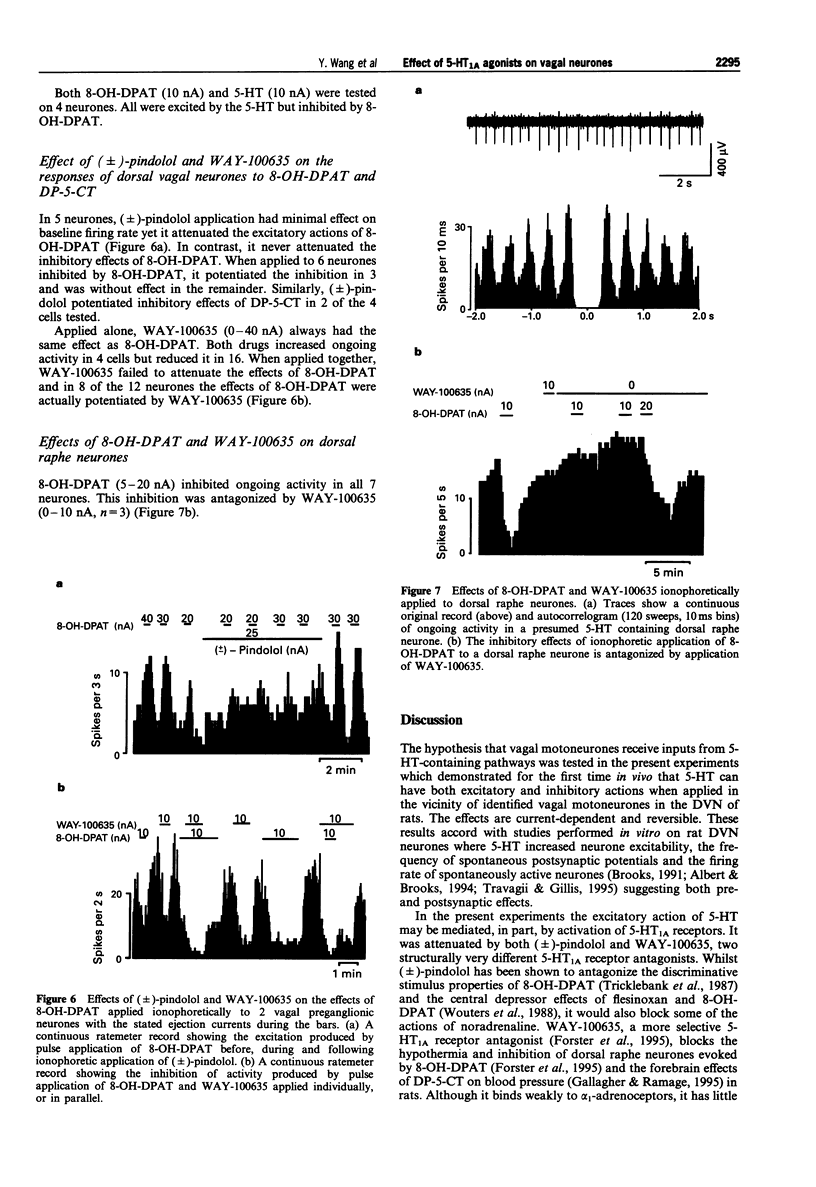
1. Effects of ionophoretic administration of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) and selective 5-HT1A receptor agonists and antagonists on identified dorsal vagal preganglionic and dorsal raphe neurones were studied in pentobarbitone sodium or chloral hydrate-anaesthetized rats, respectively. 2. Extracellular recordings were made from 176 preganglionic neurones in the dorsal vagal nucleus (DVN). Application of 5-HT at low currents (< or = 10 nA) increased the activity of these neurones. However, at increased currents (10-60 nA), it had a predominantly depressant effect. Application of selective 5-HT1A receptor antagonists, (+/-)-pindolol or WAY-100635, attenuated the excitatory responses evoked by 5-HT. 3. Ionophoresis of the 5-HT1A receptor agonist, 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin (8-OH-DPAT) (5-30 nA) increased the firing rate of 19 and decreased that of 67 of the 104 vagal neurones tested. Other 5-HT1A receptor agonists, flesinoxan and N,N-di-n-propyl-5-carboxamidotryptamine (DP-5-CT) also had predominantly depressant effects. 4. (+/-)-Pindolol attenuated excitations but not inhibitions evoked by 8-OH-DPAT. Surprisingly, WAY-100635 and 8-OH-DPAT produced the same effect on these neurones and when applied together, WAY-100635 failed to attenuate the 8-OH-DPAT responses. 5. Dorsal raphe neurones were identified by their low, regular firing rate and their subsequent histological localization. 8-OH-DPAT reversibly reduced the activity in all 7 neurones tested and this was antagonized by WAY-100635 in all 3 neurones tested. 6. In conclusion, 5-HT applied to vagal preganglionic neurones evokes excitatory and inhibitory responses. The excitatory, but not the inhibitory responses may be mediated, at least in part, by activation of 5-HT1A receptors.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bogle R. G., Pires J. G., Ramage A. G. Evidence that central 5-HT1A-receptors play a role in the von Bezold-Jarisch reflex in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug;100(4):757–760. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charléty P. J., Chergui K., Akaoka H., Saunier C. F., Buda M., Aston-Jones G., Chouvet G. Serotonin differentially modulates responses mediated by specific excitatory amino acid receptors in the rat locus coeruleus. Eur J Neurosci. 1993 Aug 1;5(8):1024–1028. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1993.tb00954.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor H. E., Higgins G. A. Cardiovascular effects of 5-HT1A receptor agonists injected into the dorsal raphe nucleus of conscious rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Jun 21;182(1):63–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90493-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton D. W. The cardiovascular effects of centrally administered 5-hydroxytryptamine in the conscious normotensive and hypertensive rat. J Auton Pharmacol. 1986 Mar;6(1):67–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1986.tb00632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davie M., Wilkinson L. S., Roberts M. H. Evidence for excitatory 5-HT2-receptors on rat brainstem neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;94(2):483–491. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11551.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M., Wilkinson L. S., Roberts M. H. Evidence for depressant 5-HT1-like receptors on rat brainstem neurones. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;94(2):492–499. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11552.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreteler G. H., Wouters W., Saxena P. R. Comparison of the cardiovascular effects of the 5-HT1A receptor agonist flesinoxan with that of 8-OH-DPAT in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 May 16;180(2-3):339–349. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90319-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton S. A., Salt T. E. Modulatory effects of serotonin on excitatory amino acid responses and sensory synaptic transmission in the ventrobasal thalamus. Neuroscience. 1989;33(2):285–292. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90208-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gradin K., Pettersson A., Hedner T., Persson B. Acute administration of 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin (8-OH-DPAT), a selective 5-HT-receptor agonist, causes a biphasic blood pressure response and a bradycardia in the normotensive Sprague-Dawley rat and in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. J Neural Transm. 1985;62(3-4):305–319. doi: 10.1007/BF01252244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izzo P. N., Deuchars J., Spyer K. M. Localization of cardiac vagal preganglionic motoneurones in the rat: immunocytochemical evidence of synaptic inputs containing 5-hydroxytryptamine. J Comp Neurol. 1993 Jan 22;327(4):572–583. doi: 10.1002/cne.903270408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkman P. M., Kelly J. S. Ionic mechanisms mediating 5-hydroxytryptamine- and noradrenaline-evoked depolarization of adult rat facial motoneurones. J Physiol. 1992 Oct;456:473–490. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. I., Coote J. H. The influence of 5-hydroxytryptamine agonists and antagonists on identified sympathetic preganglionic neurones in the rat, in vivo. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Apr;99(4):667–672. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb12987.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. I., Sermasi E., Coote J. H. Excitatory and indirect inhibitory actions of 5-hydroxytryptamine on sympathetic preganglionic neurones in the neonate rat spinal cord in vitro. Brain Res. 1993 May 7;610(2):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91410-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall R. B., Clement M. E. Identification of serotonergic and sympathetic neurons in medullary raphe nuclei. Brain Res. 1989 Jan 16;477(1-2):172–182. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91405-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedergaard S., Engberg I., Flatman J. A. Serotonin facilitates NMDA responses of cat neocortical neurones. Acta Physiol Scand. 1986 Oct;128(2):323–325. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1986.tb07983.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nosaka S., Yasunaga K., Tamai S. Vagal cardiac preganglionic neurons: distribution, cell types, and reflex discharges. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jul;243(1):R92–R98. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1982.243.1.R92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pazos A., Palacios J. M. Quantitative autoradiographic mapping of serotonin receptors in the rat brain. I. Serotonin-1 receptors. Brain Res. 1985 Nov 4;346(2):205–230. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90856-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering A. E., Spanswick D., Logan S. D. 5-Hydoxytryptamine evokes depolarizations and membrane potential oscillations in rat sympathetic preganglionic neurones. J Physiol. 1994 Oct 1;480(Pt 1):109–121. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramage A. G., Fozard J. R. Evidence that the putative 5-HT1A receptor agonists, 8-OH-DPAT and ipsapirone, have a central hypotensive action that differs from that of clonidine in anaesthetised cats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun 19;138(2):179–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90431-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramage A. G., Wouters W., Bevan P. Evidence that the novel antihypertensive agent, flesinoxan, causes differential sympathoinhibition and also increases vagal tone by a central action. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Jul 14;151(3):373–379. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90533-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoeffter P., Hoyer D. Centrally acting hypotensive agents with affinity for 5-HT1A binding sites inhibit forskolin-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity in calf hippocampus. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Nov;95(3):975–985. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11728.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepheard S. L., Jordan D., Ramage A. G. Comparison of the effects of IVth ventricular administration of some tryptamine analogues with those of 8-OH-DPAT on autonomic outflow in the anaesthetized cat. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Feb;111(2):616–624. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14781.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporton S. C., Shepheard S. L., Jordan D., Ramage A. G. Microinjections of 5-HT1A agonists into the dorsal motor vagal nucleus produce a bradycardia in the atenolol-pretreated anaesthetized rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;104(2):466–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12452.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprouse J. S., Aghajanian G. K. Electrophysiological responses of serotoninergic dorsal raphe neurons to 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B agonists. Synapse. 1987;1(1):3–9. doi: 10.1002/syn.890010103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprouse J. S., Aghajanian G. K. Responses of hippocampal pyramidal cells to putative serotonin 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B agonists: a comparative study with dorsal raphe neurons. Neuropharmacology. 1988 Jul;27(7):707–715. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(88)90079-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbusch H. W. Distribution of serotonin-immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the rat-cell bodies and terminals. Neuroscience. 1981;6(4):557–618. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90146-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thor K. B., Blitz-Siebert A., Helke C. J. Autoradiographic localization of 5HT1 binding sites in autonomic areas of the rat dorsomedial medulla oblongata. Synapse. 1992 Mar;10(3):217–227. doi: 10.1002/syn.890100305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travagli R. A., Gillis R. A. Effects of 5-HT alone and its interaction with TRH on neurons in rat dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus. Am J Physiol. 1995 Feb;268(2 Pt 1):G292–G299. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1995.268.2.G292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tricklebank M. D., Neill J., Kidd E. J., Fozard J. R. Mediation of the discriminative stimulus properties of 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino) tetralin (8-OH-DPAT) by the putative 5-HT1A receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jan 6;133(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90204-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. H., Lovick T. A. Inhibitory serotonergic effects on rostral ventrolateral medullary neurons. Pflugers Arch. 1992 Nov;422(2):93–97. doi: 10.1007/BF00370407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wouters W., Tulp M. T., Bevan P. Flesinoxan lowers blood pressure and heart rate in cats via 5-HT1A receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 May 10;149(3):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90651-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


