Abstract
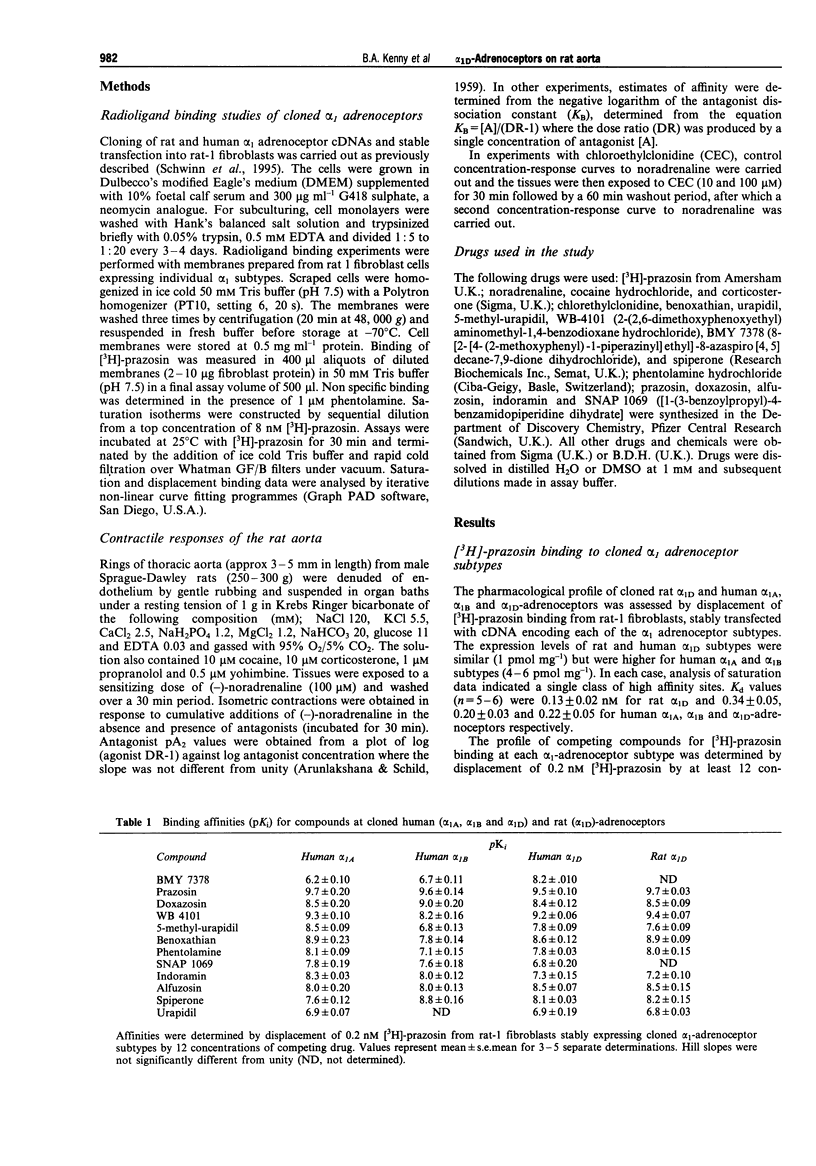
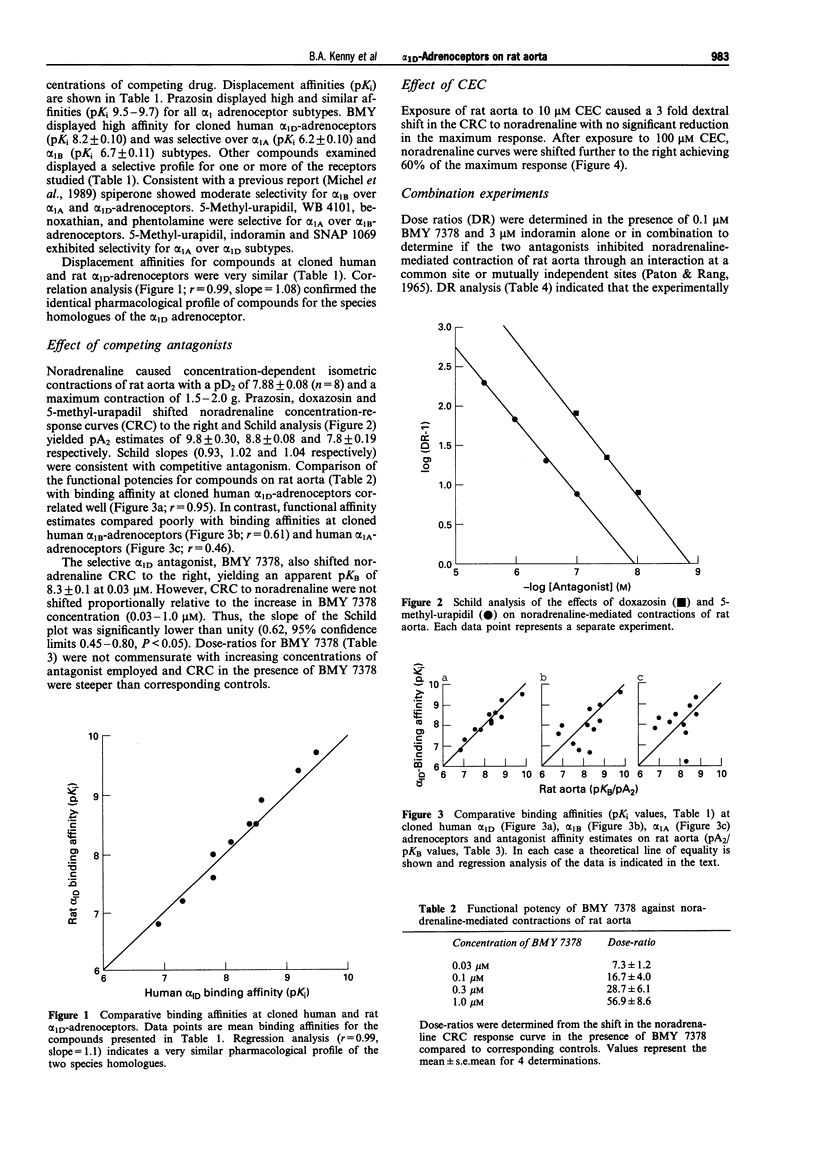
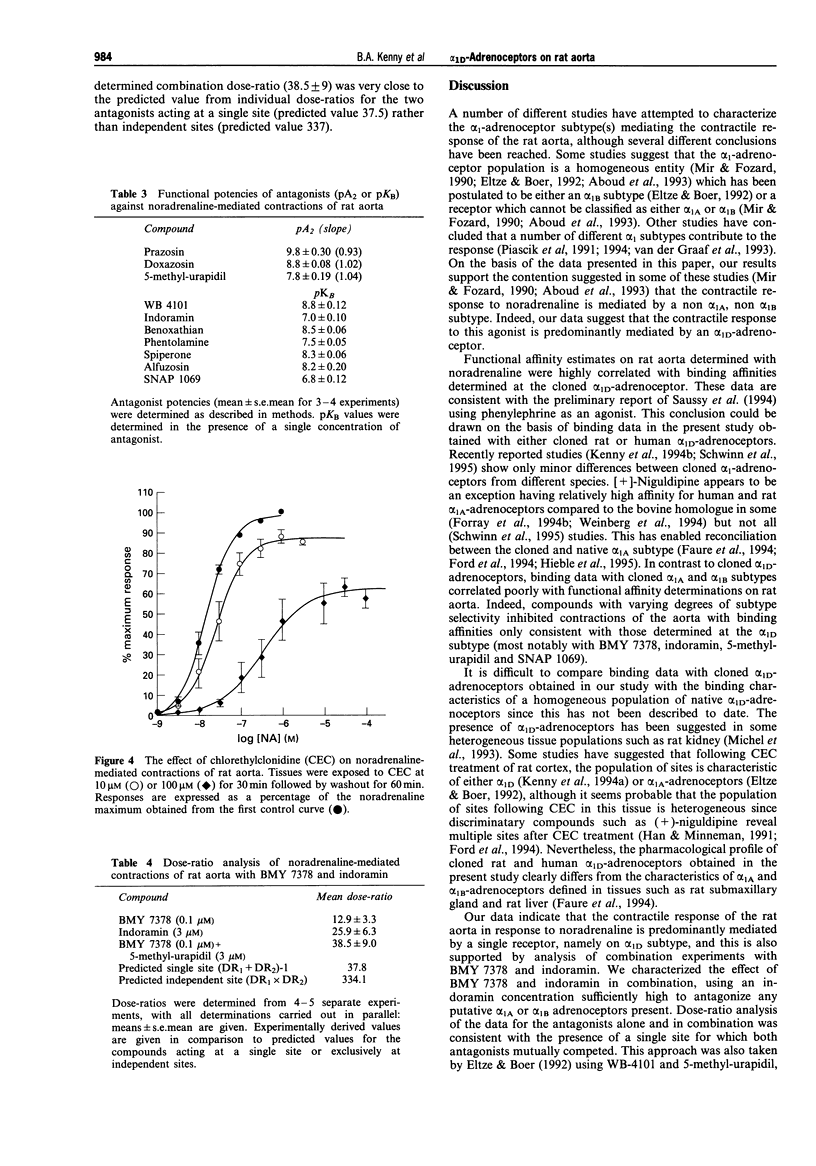
1. The affinities of a number of alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonists were determined by displacement of [3H]-prazosin binding from cloned human alpha 1A-adrenoceptors (previously designated cloned alpha 1c subtype), alpha 1B alpha 1D and rat alpha 1D-adrenoceptors, stably expressed in rat-1 fibroblasts. Functional affinity estimates for these compounds were also determined from noradrenaline-mediated contractions of rat aorta. 2. BMY 7378 displayed high affinity for cloned human alpha 1D-adrenoceptors (pKi = 8.2 +/- 0.10) and was selective over alpha 1A (pKi = 6.2 +/- 0.10) and alpha 1B subtypes (6.7 +/- 0.11). WB 4101, benoxathian and phentolamine displayed high affinity for alpha 1A and alpha 1D adrenoceptors compared to the alpha 1B subtype. Spiperone displayed high affinity and selectivity for alpha 1B adrenoceptors (pKi 8.8 +/- 0.16). 5-Methyl-urapidil was selective for cloned alpha 1A adrenoceptors. 3. Comparative binding affinities (pKi) for compounds at cloned human and rat1D adrenoceptors were almost identical (r = 0.99, slope = 1.08). 4. Prazosin, doxazosin and 5-methyl-urapidil were potent, competitive antagonists of noradrenaline-mediated contractions of rat aorta (pA2 values of 9.8, 8.8 and 7.8 respectively). The selective alpha 1D antagonist BMY 7378 was also a potent antagonist on rat aorta (pKB = 8.3 +/- 0.1) but the interaction of this compound was not consistent with competitive antagonism at a single population of receptors. 5. Functional affinities for compounds determined against noradrenaline-mediated contractions of rat aorta correlated well with binding affinities at cloned alpha 1D-adrenoceptors (r = 0.96), but not with alpha 1A (r = 0.61) or alpha 1B (r = 0.46) subtypes.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARUNLAKSHANA O., SCHILD H. O. Some quantitative uses of drug antagonists. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Mar;14(1):48–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00928.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aboud R., Shafii M., Docherty J. R. Investigation of the subtypes of alpha 1-adrenoceptor mediating contractions of rat aorta, vas deferens and spleen. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 May;109(1):80–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13534.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B., Eikenberg D. C., Hieble J. P., Langer S. Z., Lefkowitz R. J., Minneman K. P., Molinoff P. B., Ruffolo R. R., Jr, Trendelenburg U. International Union of Pharmacology nomenclature of adrenoceptors. Pharmacol Rev. 1994 Jun;46(2):121–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B. Subtypes of alpha 1- and alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. FASEB J. 1992 Feb 1;6(3):832–839. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.3.1346768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eltze M., Boer R. The adrenoceptor agonist, SDZ NVI 085, discriminates between alpha 1A- and alpha 1B-adrenoceptor subtypes in vas deferens, kidney and aorta of the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec 2;224(2-3):125–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90796-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faure C., Pimoule C., Arbilla S., Langer S. Z., Graham D. Expression of alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes in rat tissues: implications for alpha 1-adrenoceptor classification. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Jul 15;268(2):141–149. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90183-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford A. P., Williams T. J., Blue D. R., Clarke D. E. Alpha 1-adrenoceptor classification: sharpening Occam's razor. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Jun;15(6):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forray C., Bard J. A., Wetzel J. M., Chiu G., Shapiro E., Tang R., Lepor H., Hartig P. R., Weinshank R. L., Branchek T. A. The alpha 1-adrenergic receptor that mediates smooth muscle contraction in human prostate has the pharmacological properties of the cloned human alpha 1c subtype. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Apr;45(4):703–708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C. D., Minneman K. P. Interaction of subtype-selective antagonists with alpha 1-adrenergic receptor binding sites in rat tissues. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;40(4):531–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenny B. A., Naylor A. M., Greengrass P. M., Russell M. J., Friend S. J., Read A. M., Wyllie M. G. Pharmacological properties of the cloned alpha 1A/D-adrenoceptor subtype are consistent with the alpha 1A-adrenoceptor characterized in rat cerebral cortex and vas deferens. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Apr;111(4):1003–1008. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14843.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomasney J. W., Cotecchia S., Lorenz W., Leung W. Y., Schwinn D. A., Yang-Feng T. L., Brownstein M., Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for the alpha 1A-adrenergic receptor. The gene for which is located on human chromosome 5. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6365–6369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. C., Brown C. M., Wilson V. G. Alpha-adrenoceptors: a critical review. Med Res Rev. 1989 Oct-Dec;9(4):407–533. doi: 10.1002/med.2610090403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel A. D., Loury D. N., Whiting R. L. Identification of a single alpha 1-adrenoceptor corresponding to the alpha 1A-subtype in rat submaxillary gland. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):883–889. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14617.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Büscher R., Kerker J., Kraneis H., Erdbrügger W., Brodde O. E. Alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtype affinities of drugs for the treatment of prostatic hypertrophy. Evidence for heterogeneity of chloroethylclonidine-resistant rat renal alpha 1-adrenoceptor. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1993 Oct;348(4):385–395. doi: 10.1007/BF00171338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Insel P. A. Comparison of cloned and pharmacologically defined rat tissue alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1994 Aug;350(2):136–142. doi: 10.1007/BF00241087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minneman K. P. Alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes, inositol phosphates, and sources of cell Ca2+. Pharmacol Rev. 1988 Jun;40(2):87–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu I., Ohmura T., Kigoshi S., Hashimoto S., Oshita M. Pharmacological subclassification of alpha 1-adrenoceptors in vascular smooth muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Jan;99(1):197–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb14678.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oriowo M. A., Ruffolo R. R., Jr Heterogeneity of postjunctional alpha 1-adrenoceptors in mammalian aortae: subclassification based on chlorethylclonidine, WB 4101 and nifedipine. J Vasc Res. 1992 Jan-Feb;29(1):33–40. doi: 10.1159/000158929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D., RANG H. P. THE UPTAKE OF ATROPINE AND RELATED DRUGS BY INTESTINAL SMOOTH MUSCLE OF THE GUINEA-PIG IN RELATION TO ACETYLCHOLINE RECEPTORS. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1965 Aug 24;163:1–44. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1965.0058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez D. M., Piascik M. T., Graham R. M. Solution-phase library screening for the identification of rare clones: isolation of an alpha 1D-adrenergic receptor cDNA. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;40(6):876–883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piascik M. T., Smith M. S., Soltis E. E., Perez D. M. Identification of the mRNA for the novel alpha 1D-adrenoceptor and two other alpha 1-adrenoceptors in vascular smooth muscle. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Jul;46(1):30–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piascik M. T., Sparks M. S., Pruitt T. A., Soltis E. E. Evidence for a complex interaction between the subtypes of the alpha 1-adrenoceptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jul 9;199(3):279–289. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90491-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffolo R. R., Jr, Nichols A. J., Stadel J. M., Hieble J. P. Structure and function of alpha-adrenoceptors. Pharmacol Rev. 1991 Dec;43(4):475–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwinn D. A., Johnston G. I., Page S. O., Mosley M. J., Wilson K. H., Worman N. P., Campbell S., Fidock M. D., Furness L. M., Parry-Smith D. J. Cloning and pharmacological characterization of human alpha-1 adrenergic receptors: sequence corrections and direct comparison with other species homologues. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Jan;272(1):134–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg D. H., Trivedi P., Tan C. P., Mitra S., Perkins-Barrow A., Borkowski D., Strader C. D., Bayne M. Cloning, expression and characterization of human alpha adrenergic receptors alpha 1a, alpha 1b and alpha 1c. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Jun 30;201(3):1296–1304. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



