Abstract
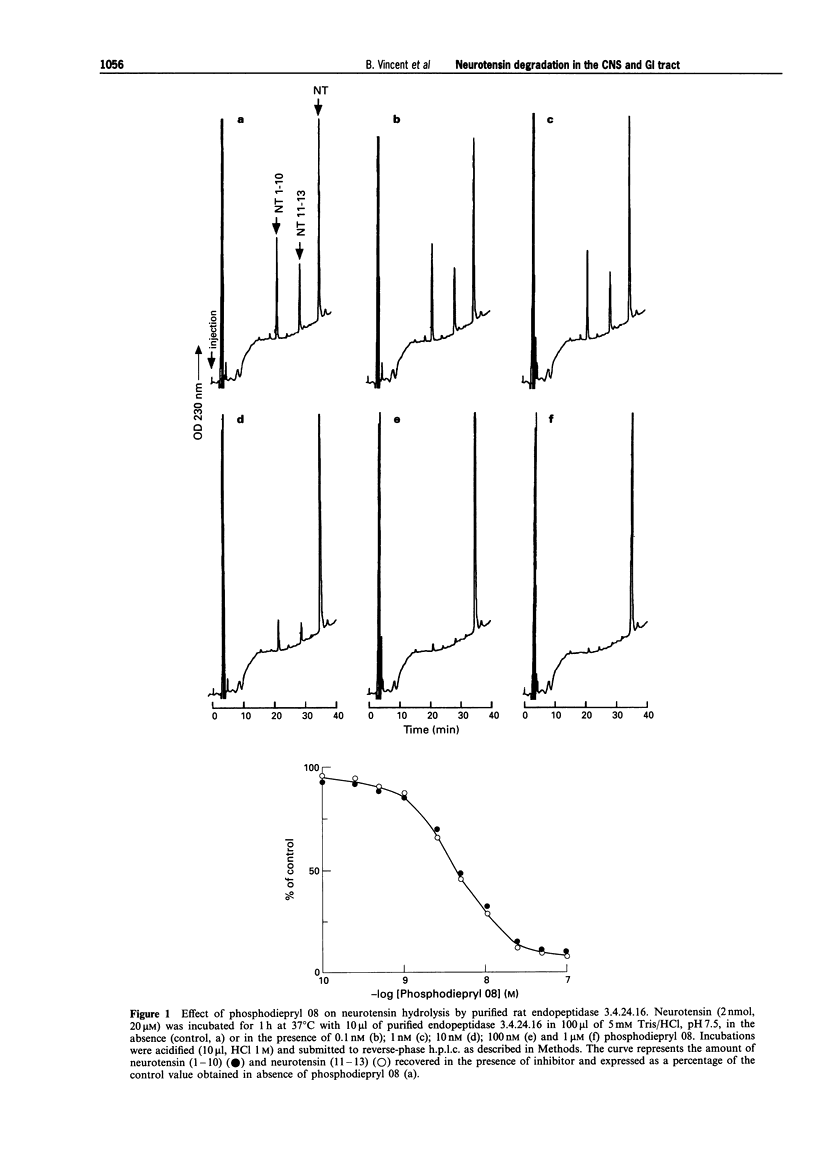
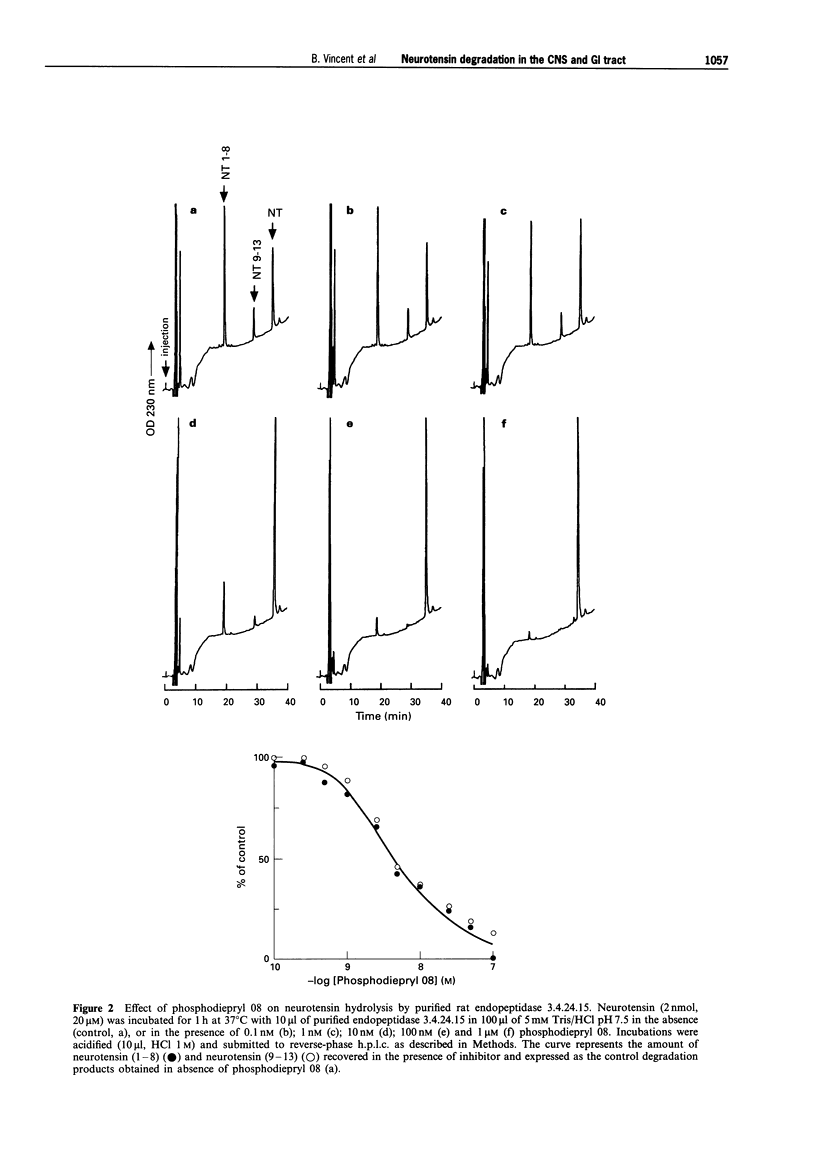
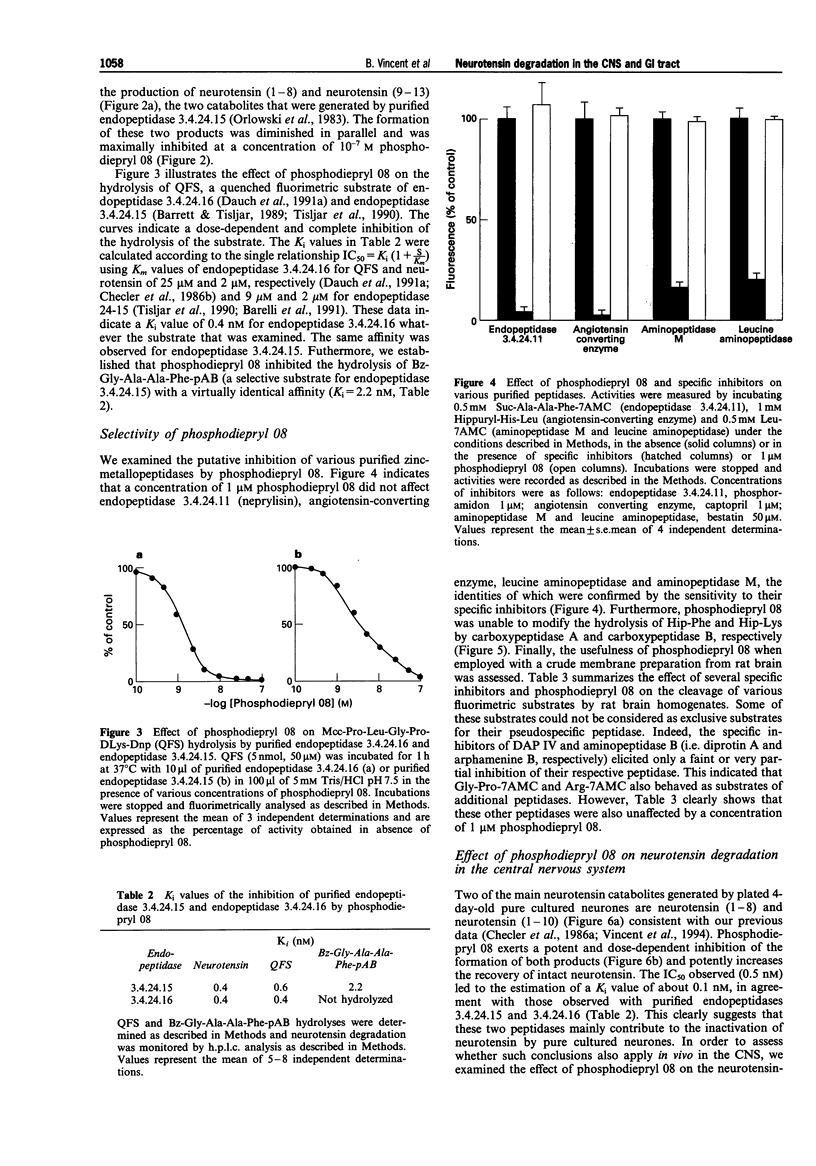
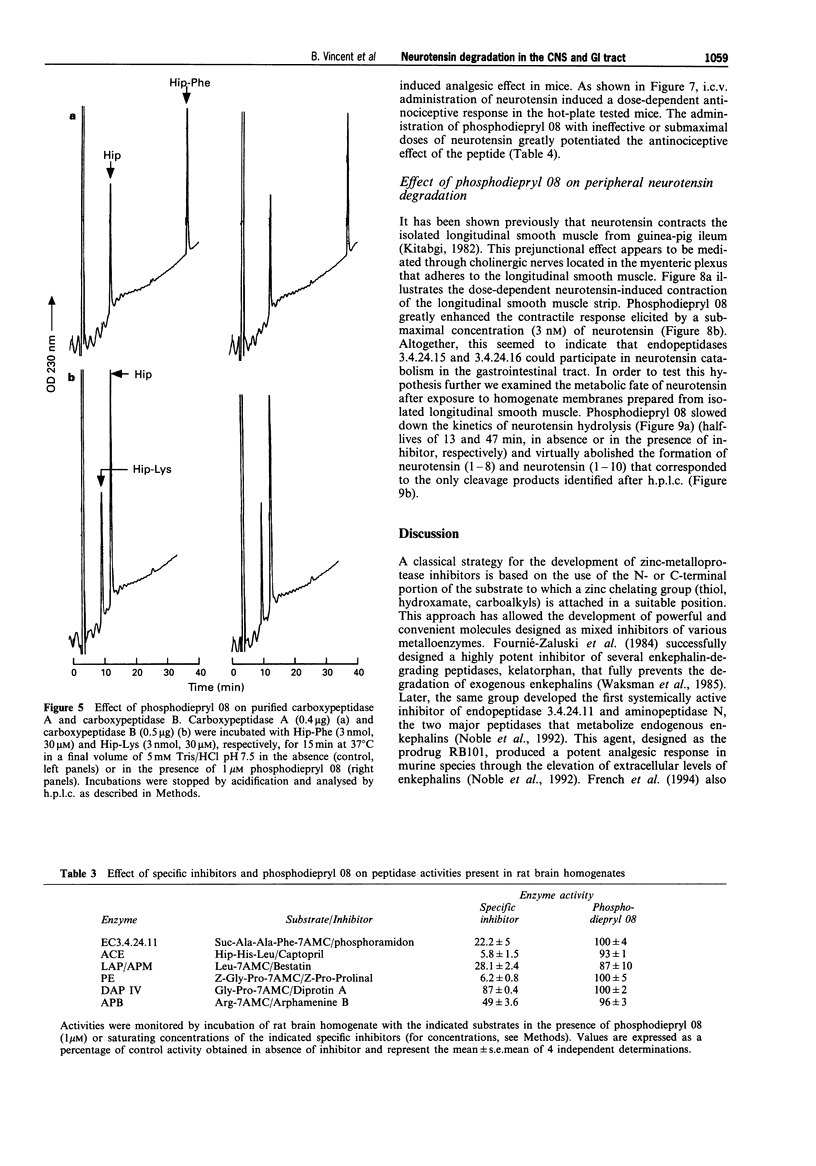
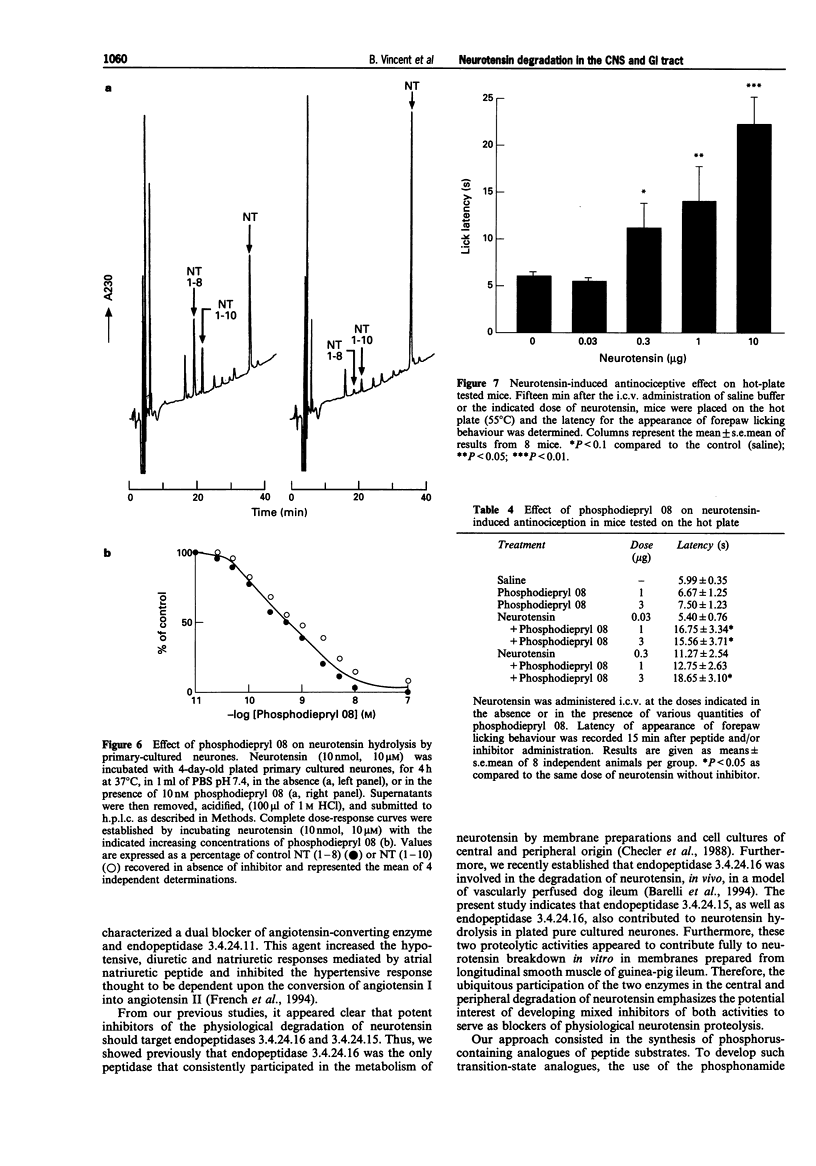
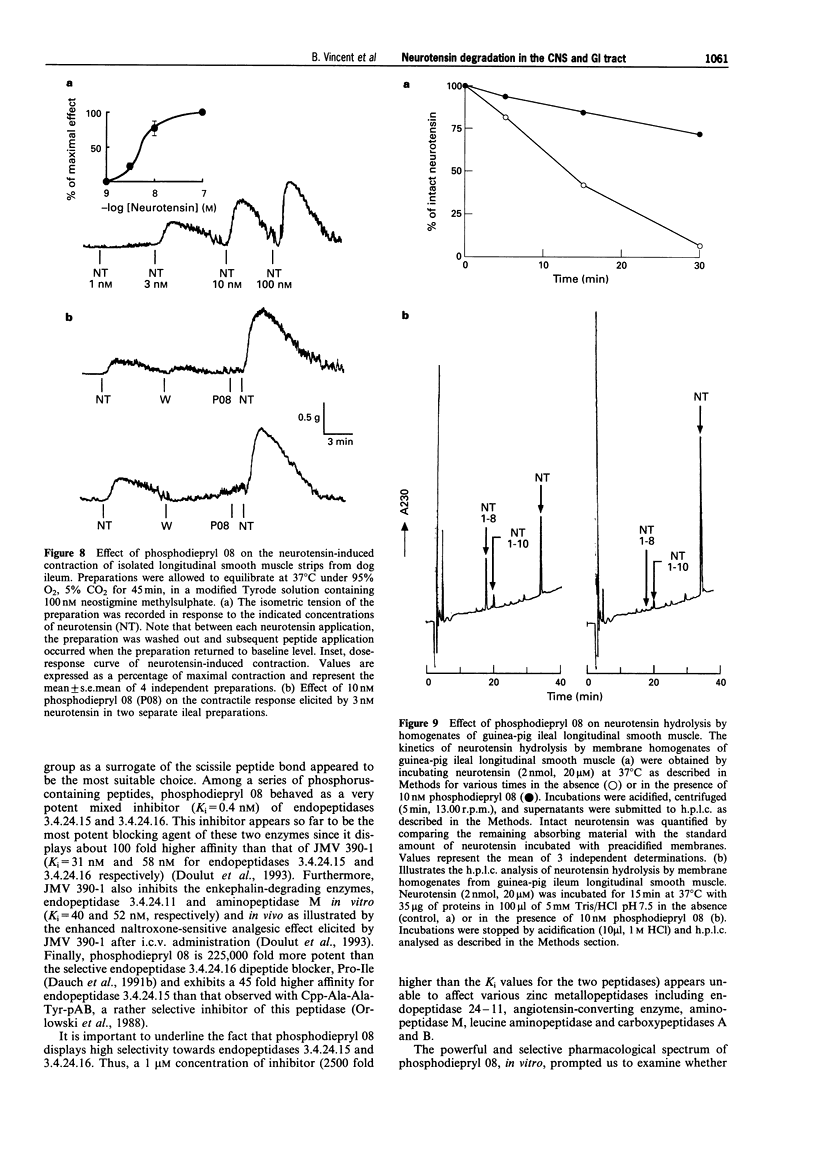
1. We have examined several phosphorus-containing peptides as potential mixed inhibitors of two neurotensin-degrading zinc metallopeptidases, endopeptidase 3.4.24.15 and endopeptidase 3.4.24.16. 2. Among a series of 13 phosphonamide peptides, N-(2-(2-naphtyl)ethylphosphonyl-glycyl-prolyl-norleucine (phosphodiepryl 08) was found to inhibit potently the hydrolysis of neurotensin by purified endopeptidase 3.4.24.15 and 3.4.24.16 with an identical Ki value of 0.4 nM. 3. Phosphodiepryl 08 displayed a strong selectivity towards the two peptidases since it failed to inhibit several other zinc-containing peptidases such as endopeptidase 3.4.24.11, angiotensin-converting enzyme, aminopeptidase M, leucine aminopeptidase and carboxypeptidases A and B. 4. The protective effect of phosphodiepryl 08 on neurotensin degradation was examined in vitro and in vivo in central and peripheral bioassays. 5. Phosphodiepryl 08 virtually abolished neurotensin degradation by 4-day-old plated pure cultured neurones from mouse embryos and greatly potentiated neurotensin-induced antinociception in the mouse hot plate test. 6. In the periphery, phosphodiepryl 08 inhibited neurotensin degradation by membranes prepared from isolated longitudinal smooth muscle of guinea-pig ileum and greatly potentiated the neurotensin-induced contraction of the same longitudinal smooth muscle preparation. 7. Our study indicates that phosphodiepryl 08 behaves as a potent and selective mixed inhibitor of endopeptidase 3.4.24.15 and 3.4.24.16 and can be used as a powerful agent to prevent neurotensin degradation, in vitro and in vivo, in central and peripheral assays.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barelli H., Fox-Threlkeld J. E., Dive V., Daniel E. E., Vincent J. P., Checler F. Role of endopeptidase 3.4.24.16 in the catabolism of neurotensin, in vivo, in the vascularly perfused dog ileum. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 May;112(1):127–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13041.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barelli H., Vincent J. P., Checler F. Peripheral inactivation of neurotensin. Isolation and characterization of a metallopeptidase from rat ileum. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 15;175(3):481–489. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14220.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Tisljar U. The activities of 'Pz-peptidase' and 'endopeptidase 24.15' are due to a single enzyme. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 1;261(3):1047–1050. doi: 10.1042/bj2611047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett P. A., Marlowe C. K. Possible role for water dissociation in the slow binding of phosphorus-containing transition-state-analogue inhibitors of thermolysin. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 29;26(26):8553–8561. doi: 10.1021/bi00400a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabry J., Checler F., Vincent J. P., Mazella J. Colocalization of neurotensin receptors and of the neurotensin-degrading enzyme endopeptidase 24-16 in primary cultures of neurons. J Neurosci. 1990 Dec;10(12):3916–3921. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-12-03916.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Checler F., Barelli H., Dauch P., Dive V., Vincent B., Vincent J. P. Neurolysin: purification and assays. Methods Enzymol. 1995;248:593–614. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(95)48038-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Checler F., Barelli H., Kitabgi P., Vincent J. P. Neurotensin metabolism in various tissues of central and peripheral origins: ubiquitous involvement of a novel neurotensin degrading metalloendopeptidase. Biochimie. 1988 Jan;70(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90161-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Checler F., Emson P. C., Vincent J. P., Kitabgi P. Inactivation of neurotensin by rat brain synaptic membranes. Cleavage at the Pro10-Tyr11 bond by endopeptidase 24.11 (enkephalinase) and a peptidase different from proline-endopeptidase. J Neurochem. 1984 Nov;43(5):1295–1301. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb05386.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Checler F., Mazella J., Kitabgi P., Vincent J. P. High-affinity receptor sites and rapid proteolytic inactivation of neurotensin in primary cultured neurons. J Neurochem. 1986 Dec;47(6):1742–1748. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb13083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Checler F., Vincent J. P., Kitabgi P. Degradation of neurotensin by rat brain synaptic membranes: involvement of a thermolysin-like metalloendopeptidase (enkephalinase), angiotensin-converting enzyme, and other unidentified peptidases. J Neurochem. 1983 Aug;41(2):375–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb04753.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Checler F., Vincent J. P., Kitabgi P. Inactivation of neurotensin by rat brain synaptic membranes partly occurs through cleavage at the Arg8-Arg9 peptide bond by a metalloendopeptidase. J Neurochem. 1985 Nov;45(5):1509–1513. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07220.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Checler F., Vincent J. P., Kitabgi P. Purification and characterization of a novel neurotensin-degrading peptidase from rat brain synaptic membranes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11274–11281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dauch P., Barelli H., Vincent J. P., Checler F. Fluorimetric assay of the neurotensin-degrading metalloendopeptidase, endopeptidase 24.16. Biochem J. 1991 Dec 1;280(Pt 2):421–426. doi: 10.1042/bj2800421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dauch P., Vincent J. P., Checler F. Specific inhibition of endopeptidase 24.16 by dipeptides. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Dec 5;202(2):269–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dive V., Yiotakis A., Nicolaou A., Toma F. Inhibition of Clostridium histolyticum collagenases by phosphonamide peptide inhibitors. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Aug 17;191(3):685–693. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doulut S., Dubuc I., Rodriguez M., Vecchini F., Fulcrand H., Barelli H., Checler F., Bourdel E., Aumelas A., Lallement J. C. Synthesis and analgesic effects of N-[3-[(hydroxyamino) carbonyl]-1-oxo-2(R)-benzylpropyl]-L-isoleucyl-L-leucine, a new potent inhibitor of multiple neurotensin/neuromedin N degrading enzymes. J Med Chem. 1993 May 14;36(10):1369–1379. doi: 10.1021/jm00062a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDDY N. B., LEIMBACH D. Synthetic analgesics. II. Dithienylbutenyl- and dithienylbutylamines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1953 Mar;107(3):385–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournie-Zaluski M. C., Chaillet P., Bouboutou R., Coulaud A., Cherot P., Waksman G., Costentin J., Roques B. P. Analgesic effects of kelatorphan, a new highly potent inhibitor of multiple enkephalin degrading enzymes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Jul 20;102(3-4):525–528. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90575-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French J. F., Flynn G. A., Giroux E. L., Mehdi S., Anderson B., Beach D. C., Koehl J. R., Dage R. C. Characterization of a dual inhibitor of angiotensin I-converting enzyme and neutral endopeptidase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Jan;268(1):180–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabgi P. Effects of neurotensin on intestinal smooth muscle: application to the study of structure-activity relationships. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;400:37–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb31559.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble F., Soleilhac J. M., Soroca-Lucas E., Turcaud S., Fournie-Zaluski M. C., Roques B. P. Inhibition of the enkephalin-metabolizing enzymes by the first systemically active mixed inhibitor prodrug RB 101 induces potent analgesic responses in mice and rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1992 Apr;261(1):181–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M., Michaud C., Chu T. G. A soluble metalloendopeptidase from rat brain. Purification of the enzyme and determination of specificity with synthetic and natural peptides. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Sep 1;135(1):81–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlowski M., Michaud C., Molineaux C. J. Substrate-related potent inhibitors of brain metalloendopeptidase. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 26;27(2):597–602. doi: 10.1021/bi00402a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton W. D., Zar M. A. The origin of acetylcholine released from guinea-pig intestine and longitudinal muscle strips. J Physiol. 1968 Jan;194(1):13–33. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierotti A., Dong K. W., Glucksman M. J., Orlowski M., Roberts J. L. Molecular cloning and primary structure of rat testes metalloendopeptidase EC 3.4.24.15. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 13;29(45):10323–10329. doi: 10.1021/bi00497a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt C., Peyroux J., Noble F., Fournié-Zaluski M. C., Roques B. P. Analgesic responses elicited by endogenous enkephalins (protected by mixed peptidase inhibitors) in a variety of morphine-sensitive noxious tests. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Jan 10;192(2):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90050-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisljar U., Knight C. G., Barrett A. J. An alternative quenched fluorescence substrate for Pz-peptidase. Anal Biochem. 1990 Apr;186(1):112–115. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90582-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent B., Vincent J. P., Checler F. Neurotensin and neuromedin N undergo distinct catabolic processes in murine astrocytes and primary cultured neurons. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Apr 1;221(1):297–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18741.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman G., Bouboutou R., Chaillet P., Devin J., Coulaud A., Hamel E., Besselievre R., Costentin J., Fournie-Zaluski M. C., Roques B. P. Kelatorphan: a full inhibitor of enkephalin degrading enzymes. Biochemical and pharmacological properties, regional distribution of enkephalinase in rat brain by use of a tritiated derivative. Neuropeptides. 1985 Feb;5(4-6):529–532. doi: 10.1016/0143-4179(85)90071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yiotakis A., Lecoq A., Nicolaou A., Labadie J., Dive V. Phosphinic peptide analogues as potent inhibitors of Corynebacterium rathayii bacterial collagenase. Biochem J. 1994 Oct 1;303(Pt 1):323–327. doi: 10.1042/bj3030323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



