Abstract
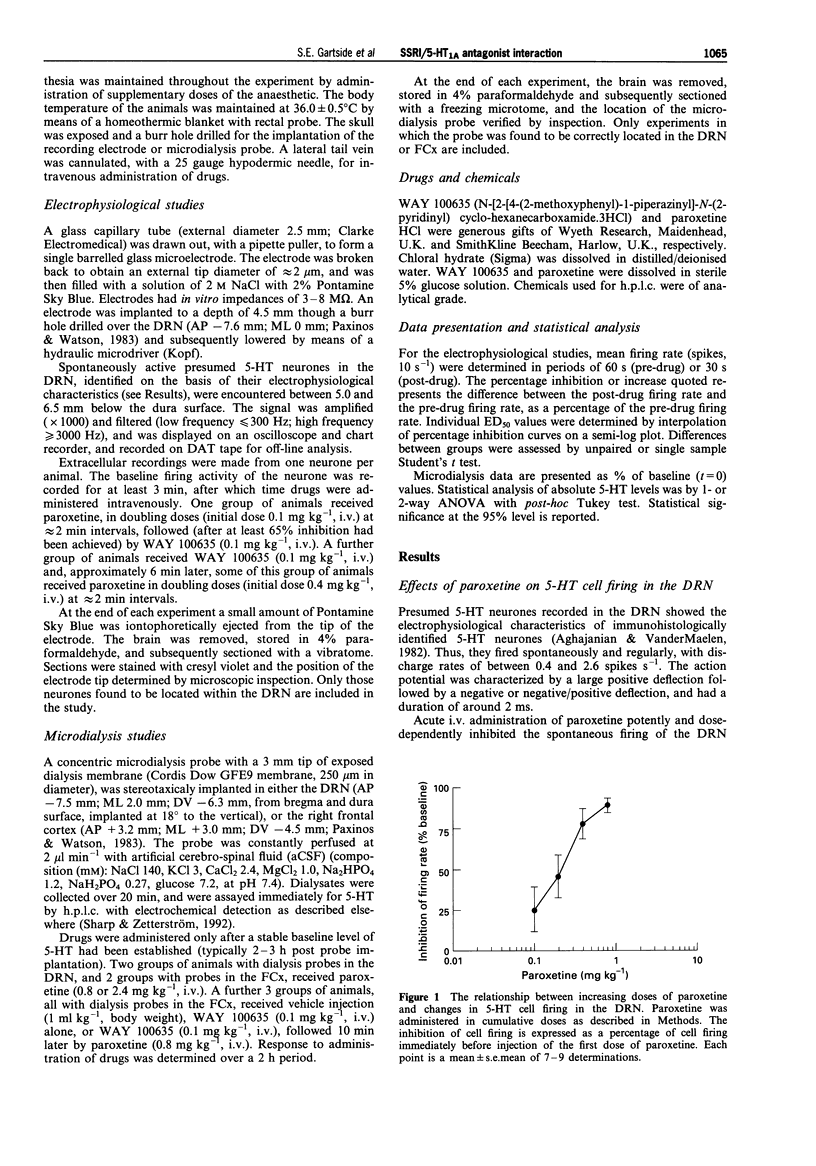
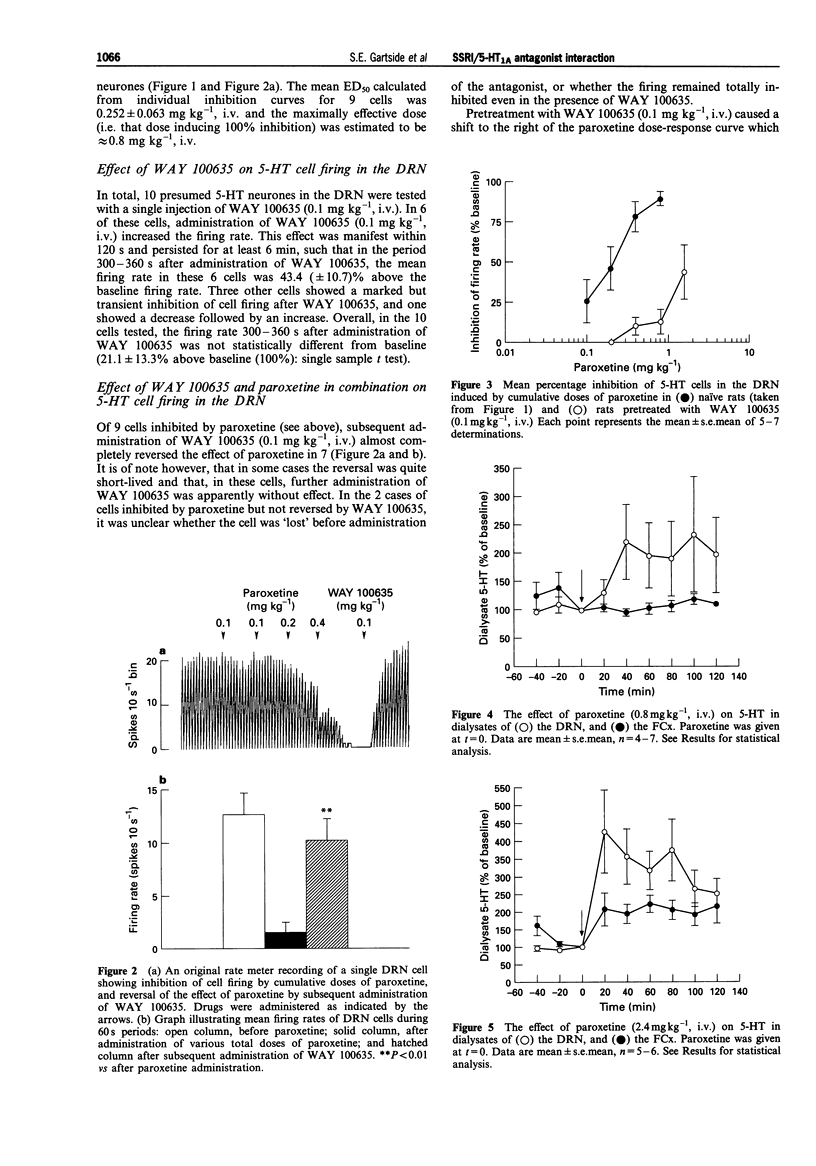
1. The acute inhibitory effect of selective 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) on 5-HT neuronal activity may offset their ability to increase synaptic 5-HT in the forebrain. 2. Here, we determined the effects of the SSRI, paroxetine, and a novel selective 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, WAY 100635, on 5-HT cell firing in the dorsal raphé nucleus (DRN), and on extracellular 5-HT in both the DRN and the frontal cortex (FCx). Extracellular electrophysiological recording and brain microdialysis were used in parallel experiments, in anaesthetized rats. 3. Paroxetine dose-dependently inhibited the firing of 5-HT neurones in the DRN, with a maximally effective dose of approximately 0.8 mg kg-1, i.v. WAY 100635 (0.1 mg kg-1, i.v.) both reversed the inhibitory effect of paroxetine and, when used as a pretreatment, caused a pronounced shift to the right of the paroxetine dose-response curve. 4. Paroxetine (0.8 mg kg-1, i.v.), doubled extracellular 5-HT in the DRN, but did not alter extracellular 5-HT in the FCx. A higher dose of paroxetine (2.4 mg kg-1, i.v.) did increase extracellular 5-HT in the FCx, but to a lesser extent than in the DRN. Whereas 0.8 mg kg-1, i.v. paroxetine alone had no effect on extracellular 5-HT in the FCx, in rats pretreated with WAY 100635 (0.1 mg kg-1), paroxetine (0.8 mg kg-1, i.v.) markedly increased extracellular 5-HT in the FCx.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adell A., Artigas F. Differential effects of clomipramine given locally or systemically on extracellular 5-hydroxytryptamine in raphe nuclei and frontal cortex. An in vivo brain microdialysis study. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;343(3):237–244. doi: 10.1007/BF00251121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aghajanian G. K., Vandermaelen C. P. Intracellular identification of central noradrenergic and serotonergic neurons by a new double labeling procedure. J Neurosci. 1982 Dec;2(12):1786–1792. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-12-01786.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artigas F., Perez V., Alvarez E. Pindolol induces a rapid improvement of depressed patients treated with serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1994 Mar;51(3):248–251. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1994.03950030084009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asberg M., Eriksson B., Mårtensson B., Träskman-Bendz L., Wägner A. Therapeutic effects of serotonin uptake inhibitors in depression. J Clin Psychiatry. 1986 Apr;47 (Suppl):23–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bel N., Artigas F. Fluvoxamine preferentially increases extracellular 5-hydroxytryptamine in the raphe nuclei: an in vivo microdialysis study. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec 8;229(1):101–103. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90292-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blier P., de Montigny C. Current advances and trends in the treatment of depression. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Jul;15(7):220–226. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90315-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carboni E., Di Chiara G. Serotonin release estimated by transcortical dialysis in freely-moving rats. Neuroscience. 1989;32(3):637–645. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaput Y., Blier P., de Montigny C. In vivo electrophysiological evidence for the regulatory role of autoreceptors on serotonergic terminals. J Neurosci. 1986 Oct;6(10):2796–2801. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-10-02796.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escandon N. A., Zimmermann D. C., McCall R. B. Characterization of the serotonin1A receptor antagonist activity of WAY-100135 and spiperone. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Jan;268(1):441–447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. W. Uptake inhibitors increase extracellular serotonin concentration measured by brain microdialysis. Life Sci. 1994;55(3):163–167. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(94)00876-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartside S. E., Cowen P. J., Hjorth S. Effects of MDL 73005EF on central pre- and postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptor function in the rat in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Dec 4;191(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)94173-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greuel J. M., Glaser T. The putative 5-HT1A receptor antagonists NAN-190 and BMY 7378 are partial agonists in the rat dorsal raphe nucleus in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Feb 11;211(2):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90531-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajós M., Gartside S. E., Sharp T. Inhibition of median and dorsal raphe neurones following administration of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor paroxetine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1995 Jun;351(6):624–629. doi: 10.1007/BF00170162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjorth S., Auerbach S. B. Further evidence for the importance of 5-HT1A autoreceptors in the action of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Aug 1;260(2-3):251–255. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(94)90346-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjorth S. Serotonin 5-HT1A autoreceptor blockade potentiates the ability of the 5-HT reuptake inhibitor citalopram to increase nerve terminal output of 5-HT in vivo: a microdialysis study. J Neurochem. 1993 Feb;60(2):776–779. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Invernizzi R., Belli S., Samanin R. Citalopram's ability to increase the extracellular concentrations of serotonin in the dorsal raphe prevents the drug's effect in the frontal cortex. Brain Res. 1992 Jul 3;584(1-2):322–324. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90914-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolas T., Haj-Dahmane S., Kidd E. J., Langlois X., Lanfumey L., Fattaccini C. M., Vantalon V., Laporte A. M., Adrien J., Gozlan H. Central pre- and postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors in rats treated chronically with a novel antidepressant, cericlamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Mar;268(3):1432–1443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanfumey L., Haj-Dahmane S., Hamon M. Further assessment of the antagonist properties of the novel and selective 5-HT1A receptor ligands (+)-WAY 100 135 and SDZ 216-525. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Nov 2;249(1):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90658-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahata N., Ishimoto H., Mizuno K., Ohizumi Y., Nakanishi H. Dual effects of mastoparan on intracellular free Ca2+ concentrations in human astrocytoma cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 May;112(1):299–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13068.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hearn E., Molliver M. E. Organization of raphe-cortical projections in rat: a quantitative retrograde study. Brain Res Bull. 1984 Dec;13(6):709–726. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(84)90232-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter J. J., Auerbach S. B. Acute uptake inhibition increases extracellular serotonin in the rat forebrain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Jun;265(3):1319–1324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatzberg A. F., Dessain E., O'Neil P., Katz D. L., Cole J. O. Recent studies on selective serotonergic antidepressants: trazodone, fluoxetine, and fluvoxamine. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 1987 Dec;7(6 Suppl):44S–49S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp T., Bramwell S. R., Hjorth S., Grahame-Smith D. G. Pharmacological characterization of 8-OH-DPAT-induced inhibition of rat hippocampal 5-HT release in vivo as measured by microdialysis. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Nov;98(3):989–997. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb14630.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp T., Hjorth S. Application of brain microdialysis to study the pharmacology of the 5-HT1A autoreceptor. J Neurosci Methods. 1990 Sep;34(1-3):83–90. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(90)90045-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheard M. H., Zolovick A., Aghajanian G. K. Rophe neurons: effect of tricyclic antidepressant drugs. Brain Res. 1972 Aug 25;43(2):690–694. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90432-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sotelo Constantino, Cholley Béatrice, El Mestikawy Salah, Gozlan Henri, Hamon Michel. Direct Immunohistochemical Evidence of the Existence of 5-HT1A Autoreceptors on Serotoninergic Neurons in the Midbrain Raphe Nuclei. Eur J Neurosci. 1990;2(12):1144–1154. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1990.tb00026.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprouse J. S., Aghajanian G. K. Electrophysiological responses of serotoninergic dorsal raphe neurons to 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B agonists. Synapse. 1987;1(1):3–9. doi: 10.1002/syn.890010103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starkey S. J., Skingle M. 5-HT1D as well as 5-HT1A autoreceptors modulate 5-HT release in the guinea-pig dorsal raphé nucleus. Neuropharmacology. 1994 Mar-Apr;33(3-4):393–402. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)90069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungerstedt U. Stereotaxic mapping of the monoamine pathways in the rat brain. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1971;367:1–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-201x.1971.tb10998.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verge D., Daval G., Patey A., Gozlan H., el Mestikawy S., Hamon M. Presynaptic 5-HT autoreceptors on serotonergic cell bodies and/or dendrites but not terminals are of the 5-HT1A subtype. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Jul 31;113(3):463–464. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90099-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh N. J., Shankley N. P., Black J. W. Comparative analysis of the vagal stimulation of gastric acid secretion in rodent isolated stomach preparations. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 May;112(1):93–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13035.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


