Abstract
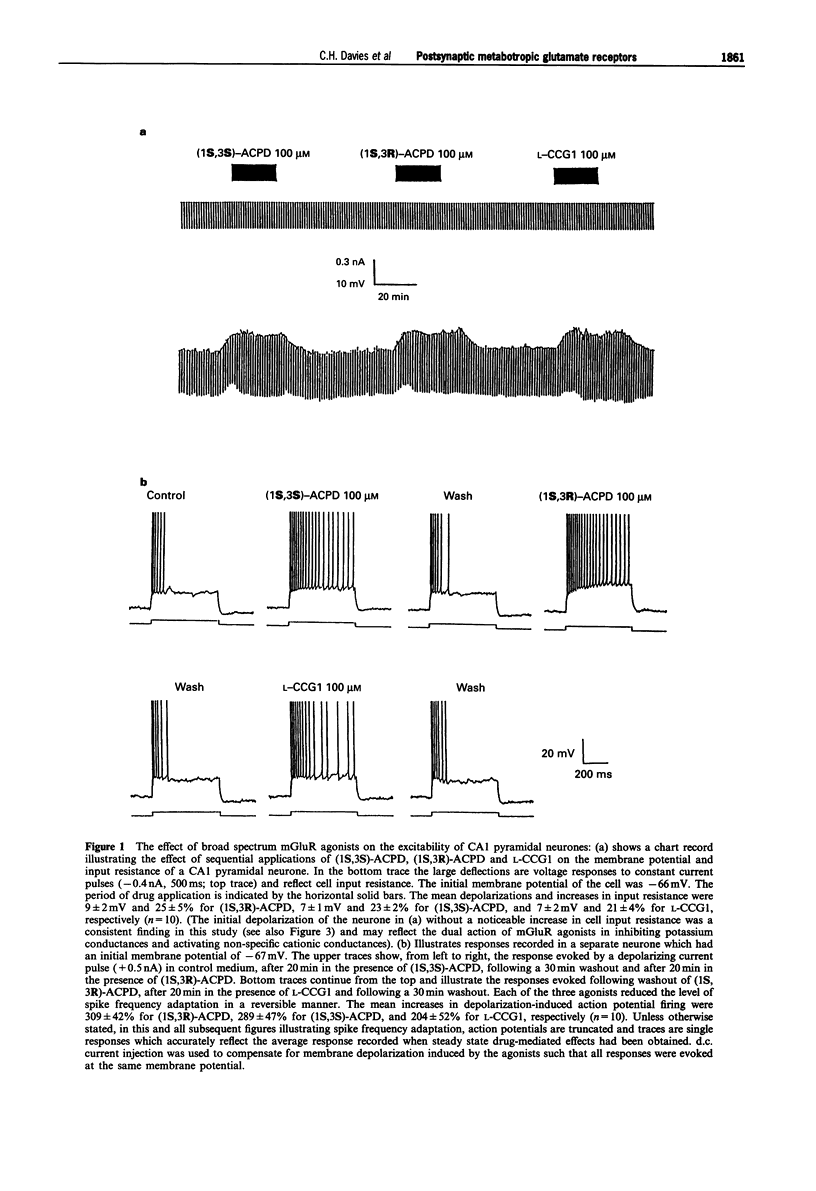
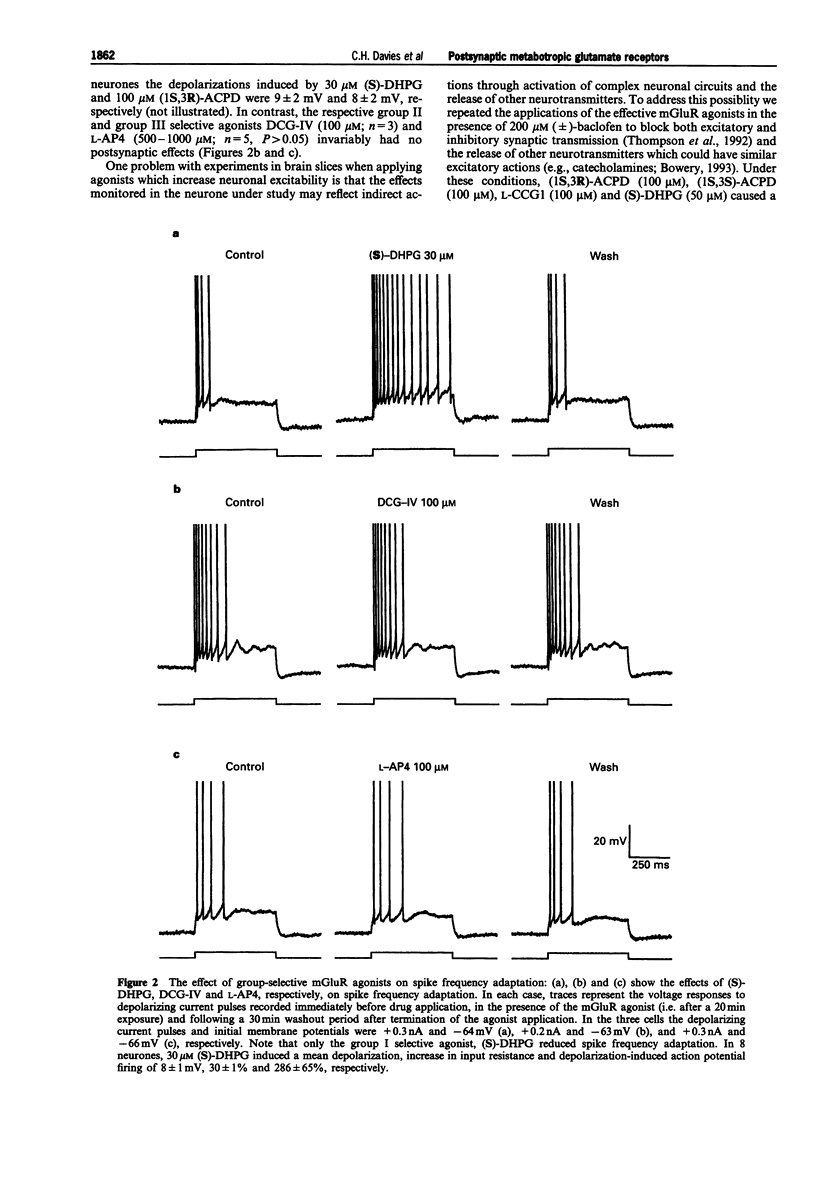
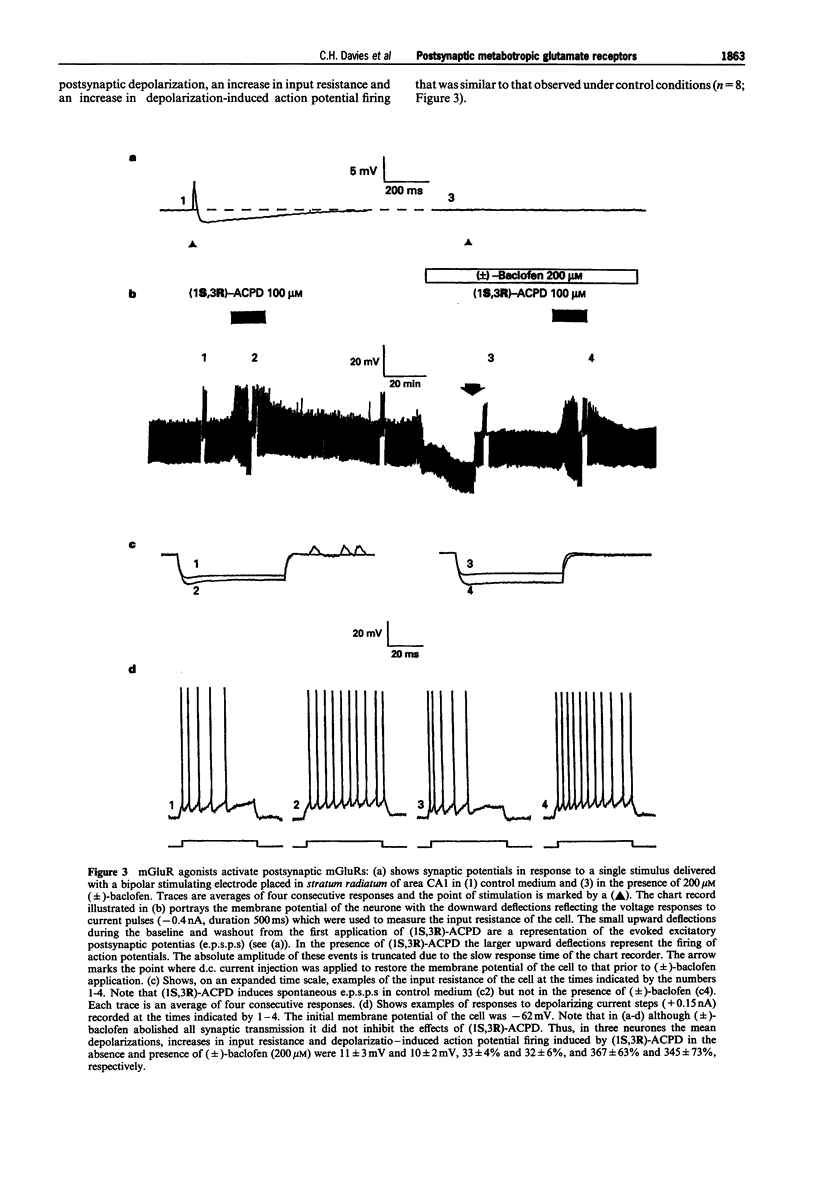
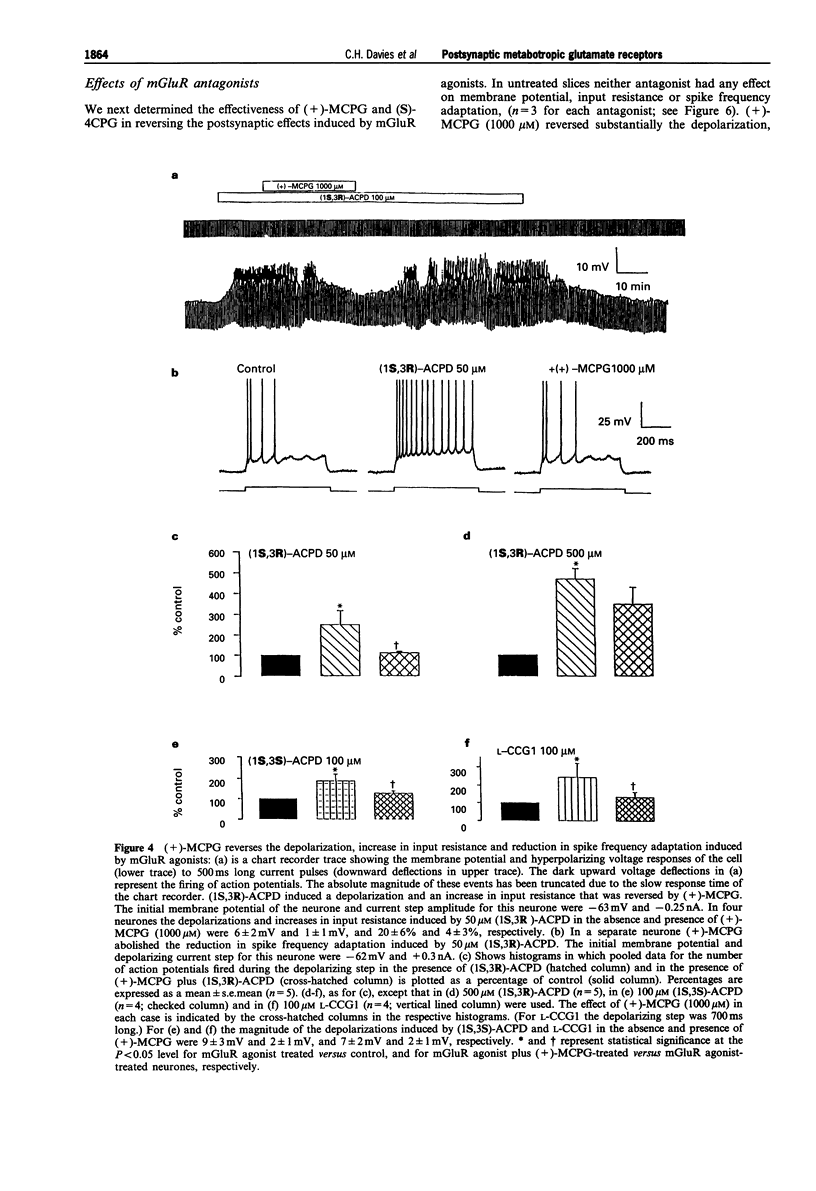
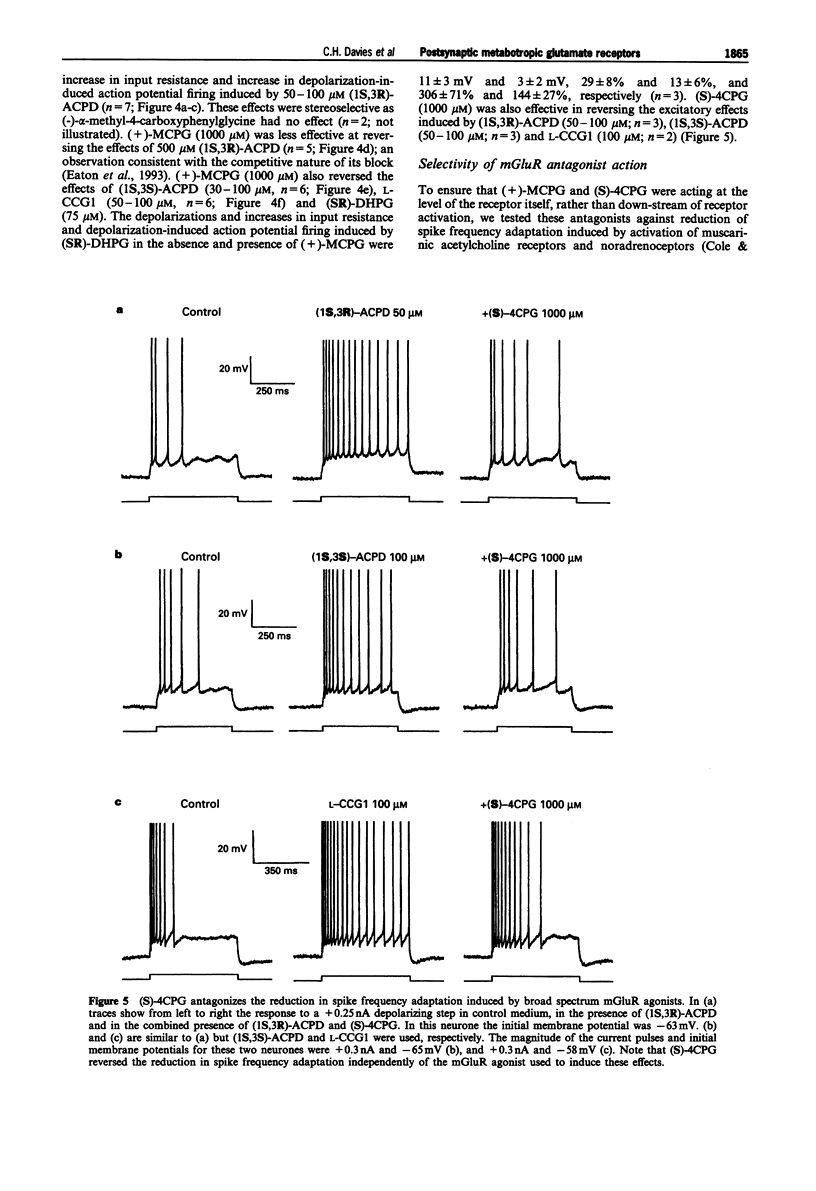
1. Activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurones leads to a depolarization, an increase in input resistance and a reduction in spike frequency adaptation (or accommodation). At least eight subtypes of mGluR have been identified which have been divided into three groups based on their biochemical, structural and pharmacological properties. It is unclear to which group the mGluRs which mediate these excitatory effects in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurones belong. We have attempted to address this question by using intracellular recording to test the effects of a range of mGluR agonists and antagonists, that exhibit different profiles of subtype specificity, on the excitability of CA1 pyramidal neurones in rat hippocampal slices. 2. (2S, 1'S,2'S)-2-(2'-carboxycyclopropyl)glycine (L-CCG1) caused a reduction in spike frequency adaptation and a depolarization (1-10 mV) associated with an increase in input resistance (10-30%) at concentrations (> or = 50 microM) that have been shown to activate mGluRs in groups I, II and III. Similar effects were observed with concentrations (50-100 microM) of (1S,3R)-1-aminocyclopentane-1,3-dicarboxylic acid ((1S,3R)-ACPD) and (1S,3S)-ACPD that exhibit little or no activity at group III mGluRs but which activate groups I and II mGluRs. 3. Inhibition of the release of endogenous neurotransmitters through activation of GABAB receptors, by use of 200 microM (+/-)-baclofen, did not alter the effects of (1S,3R)-ACPD (50-100 microM), (1S,3S)-ACPD (100 microM) or L-CCG1 (100 microM). This suggests that mGluR agonists directly activate CA1 pyramidal neurones. 4. Like these broad spectrum mGluR agonists, the racemic mixture ((SR)-) or resolved (S)-isomer of the selective group I mGluR agonist 3,5-dihydroxyphenylglycine ((SR)-DHPG (50-100 microM) or (S)-DHPG (20-50 microM)) caused a reduction in spike frequency adaptation concomitant with postsynaptic depolarization and an increase in input resistance. In contrast, 2S,1'R,2'R,3'R-2-(2',3'-dicarboxycyclopropyl)glycine (DCG-IV; 100 microM) and (S)-2-amino-4-phosphonobutanoic acid (L-AP4; 100-500 microM), which selectively activate group II mGluRs and group III mGluRs, respectively, had no effect on the passive membrane properties or spike frequency adaptation of CA1 pyramidal neurones. 5. The mGluR antagonists (+)-alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine ((+)-MCPG; 1000 microM) and (S)-4-carboxyphenylglycine ((S)-4CPG; 1000 microM), which block groups I and II mGluRs and group I mGluRs, respectively, had no effect on membrane potential, input resistance or spike frequency adaptation per se.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abe T., Sugihara H., Nawa H., Shigemoto R., Mizuno N., Nakanishi S. Molecular characterization of a novel metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR5 coupled to inositol phosphate/Ca2+ signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13361–13368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aiba A., Chen C., Herrup K., Rosenmund C., Stevens C. F., Tonegawa S. Reduced hippocampal long-term potentiation and context-specific deficit in associative learning in mGluR1 mutant mice. Cell. 1994 Oct 21;79(2):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90204-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aramori I., Nakanishi S. Signal transduction and pharmacological characteristics of a metabotropic glutamate receptor, mGluR1, in transfected CHO cells. Neuron. 1992 Apr;8(4):757–765. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90096-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashir Z. I., Bortolotto Z. A., Davies C. H., Berretta N., Irving A. J., Seal A. J., Henley J. M., Jane D. E., Watkins J. C., Collingridge G. L. Induction of LTP in the hippocampus needs synaptic activation of glutamate metabotropic receptors. Nature. 1993 May 27;363(6427):347–350. doi: 10.1038/363347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baskys A., Malenka R. C. Agonists at metabotropic glutamate receptors presynaptically inhibit EPSCs in neonatal rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1991 Dec;444:687–701. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birse E. F., Eaton S. A., Jane D. E., Jones P. L., Porter R. H., Pook P. C., Sunter D. C., Udvarhelyi P. M., Wharton B., Roberts P. J. Phenylglycine derivatives as new pharmacological tools for investigating the role of metabotropic glutamate receptors in the central nervous system. Neuroscience. 1993 Feb;52(3):481–488. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90400-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowery N. G. GABAB receptor pharmacology. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1993;33:109–147. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.33.040193.000545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartmell J., Curtis A. R., Kemp J. A., Kendall D. A., Alexander S. P. Subtypes of metabotropic excitatory amino acid receptor distinguished by stereoisomers of the rigid glutamate analogue, 1-aminocyclopentane-1,3-dicarboxylate. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Apr 16;153(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90088-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavanni P., Pinnola V., Mugnaini M., Trist D., Van Amsterdam F. T., Ferraguti F. Pharmacological analysis of carboxyphenylglycines at metabotropic glutamate receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Sep 15;269(1):9–15. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charpak S., Gähwiler B. H., Do K. Q., Knöpfel T. Potassium conductances in hippocampal neurons blocked by excitatory amino-acid transmitters. Nature. 1990 Oct 25;347(6295):765–767. doi: 10.1038/347765a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinestra P., Aniksztejn L., Diabira D., Ben-Ari Y. (RS)-alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine neither prevents induction of LTP nor antagonizes metabotropic glutamate receptors in CA1 hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1993 Dec;70(6):2684–2689. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.70.6.2684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole A. E., Nicoll R. A. Acetylcholine mediates a slow synaptic potential in hippocampal pyramidal cells. Science. 1983 Sep 23;221(4617):1299–1301. doi: 10.1126/science.6612345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conquet F., Bashir Z. I., Davies C. H., Daniel H., Ferraguti F., Bordi F., Franz-Bacon K., Reggiani A., Matarese V., Condé F. Motor deficit and impairment of synaptic plasticity in mice lacking mGluR1. Nature. 1994 Nov 17;372(6503):237–243. doi: 10.1038/372237a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crépel V., Aniksztejn L., Ben-Ari Y., Hammond C. Glutamate metabotropic receptors increase a Ca(2+)-activated nonspecific cationic current in CA1 hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1994 Oct;72(4):1561–1569. doi: 10.1152/jn.1994.72.4.1561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies C. H., Davies S. N., Collingridge G. L. Paired-pulse depression of monosynaptic GABA-mediated inhibitory postsynaptic responses in rat hippocampus. J Physiol. 1990 May;424:513–531. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai M. A., Conn P. J. Excitatory effects of ACPD receptor activation in the hippocampus are mediated by direct effects on pyramidal cells and blockade of synaptic inhibition. J Neurophysiol. 1991 Jul;66(1):40–52. doi: 10.1152/jn.1991.66.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desai M. A., Smith T. S., Conn P. J. Multiple metabotropic glutamate receptors regulate hippocampal function. Synapse. 1992 Nov;12(3):206–213. doi: 10.1002/syn.890120305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton S. A., Jane D. E., Jones P. L., Porter R. H., Pook P. C., Sunter D. C., Udvarhelyi P. M., Roberts P. J., Salt T. E., Watkins J. C. Competitive antagonism at metabotropic glutamate receptors by (S)-4-carboxyphenylglycine and (RS)-alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Jan 15;244(2):195–197. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(93)90028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fotuhi M., Standaert D. G., Testa C. M., Penney J. B., Jr, Young A. B. Differential expression of metabotropic glutamate receptors in the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex of the rat. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1994 Feb;21(3-4):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(94)90259-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genazzani A. A., Casabona G., L'Episcopo M. R., Condorelli D. F., Dell'Albani P., Shinozaki H., Nicoletti F. Characterization of metabotropic glutamate receptors negatively linked to adenylyl cyclase in brain slices. Brain Res. 1993 Sep 17;622(1-2):132–138. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90811-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber U., Lüthi A., Gähwiler B. H. Inhibition of a slow synaptic response by a metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonist in hippocampal CA3 pyramidal cells. Proc Biol Sci. 1993 Nov 22;254(1340):169–172. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1993.0142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaum S. R., Sunter D. C., Udvarhelyi P. M., Watkins J. C., Miller R. J. The actions of phenylglycine derived metabotropic glutamate receptor antagonists on multiple (1S,3R)-ACPD responses in the rat nucleus of the tractus solitarius. Neuropharmacology. 1993 Dec;32(12):1419–1425. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(93)90039-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guérineau N. C., Gähwiler B. H., Gerber U. Reduction of resting K+ current by metabotropic glutamate and muscarinic receptors in rat CA3 cells: mediation by G-proteins. J Physiol. 1994 Jan 1;474(1):27–33. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp019999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. W., Stevens D. R., Cotman C. W. Hippocampal cells primed with quisqualate are depolarized by AP4 and AP6, ligands for a putative glutamate uptake site. Brain Res. 1987 Aug 25;418(2):361–365. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90104-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Momiyama A., Takahashi T., Ohishi H., Ogawa-Meguro R., Shigemoto R., Mizuno N., Nakanishi S. Role of a metabotropic glutamate receptor in synaptic modulation in the accessory olfactory bulb. Nature. 1993 Dec 16;366(6456):687–690. doi: 10.1038/366687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Sekiyama N., Nakanishi S., Jane D. E., Sunter D. C., Birse E. F., Udvarhelyi P. M., Watkins J. C. Analysis of agonist and antagonist activities of phenylglycine derivatives for different cloned metabotropic glutamate receptor subtypes. J Neurosci. 1994 May;14(5 Pt 2):3370–3377. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-05-03370.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Tanabe Y., Aramori I., Masu M., Shimamoto K., Ohfune Y., Nakanishi S. Agonist analysis of 2-(carboxycyclopropyl)glycine isomers for cloned metabotropic glutamate receptor subtypes expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;107(2):539–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb12780.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu G. Y., Storm J. F. 2-Amino-3-phosphonopropionate fails to block postsynaptic effects of metabotropic glutamate receptors in rat hippocampal neurones. Acta Physiol Scand. 1992 Jun;145(2):187–191. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1992.tb09354.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida M., Saitoh T., Shimamoto K., Ohfune Y., Shinozaki H. A novel metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist: marked depression of monosynaptic excitation in the newborn rat isolated spinal cord. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Aug;109(4):1169–1177. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13745.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito I., Kohda A., Tanabe S., Hirose E., Hayashi M., Mitsunaga S., Sugiyama H. 3,5-Dihydroxyphenyl-glycine: a potent agonist of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Neuroreport. 1992 Nov;3(11):1013–1016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jane D. E., Jones P. L., Pook P. C., Salt T. E., Sunter D. C., Watkins J. C. Stereospecific antagonism by (+)-alpha-methyl-4-carboxyphenylglycine (MCPG) of (1S,3R)-ACPD-induced effects in neonatal rat motoneurones and rat thalamic neurones. Neuropharmacology. 1993 Jul;32(7):725–727. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(93)90088-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen P., Suzdak P. D., Thomsen C. Expression pattern and pharmacology of the rat type IV metabotropic glutamate receptor. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Jun 11;155(2):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90697-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison D. V., Nicoll R. A. Noradrenaline blocks accommodation of pyramidal cell discharge in the hippocampus. Nature. 1982 Oct 14;299(5884):636–638. doi: 10.1038/299636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzoni O. J., Weisskopf M. G., Nicoll R. A. MCPG antagonizes metabotropic glutamate receptors but not long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci. 1994 Jun 1;6(6):1050–1054. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1994.tb00599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuinness N., Anwyl R., Rowan M. Trans-ACPD enhances long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 May 17;197(2-3):231–232. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90529-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa Y., Saitoh K., Ishihara T., Ishida M., Shinozaki H. (2S,3S,4S) alpha-(carboxycyclopropyl)glycine is a novel agonist of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug 2;184(1):205–206. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90686-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: synaptic transmission, modulation, and plasticity. Neuron. 1994 Nov;13(5):1031–1037. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S. Molecular diversity of glutamate receptors and implications for brain function. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):597–603. doi: 10.1126/science.1329206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer E., Monaghan D. T., Cotman C. W. Trans-ACPD, a selective agonist of the phosphoinositide-coupled excitatory amino acid receptor. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug 3;166(3):585–587. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pin J. P., Duvoisin R. The metabotropic glutamate receptors: structure and functions. Neuropharmacology. 1995 Jan;34(1):1–26. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)00129-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoepp D. D., Goldsworthy J., Johnson B. G., Salhoff C. R., Baker S. R. 3,5-dihydroxyphenylglycine is a highly selective agonist for phosphoinositide-linked metabotropic glutamate receptors in the rat hippocampus. J Neurochem. 1994 Aug;63(2):769–772. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.63020769.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoepp D. D. The biochemical pharmacology of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Biochem Soc Trans. 1993 Feb;21(1):97–102. doi: 10.1042/bst0210097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigemoto R., Nomura S., Ohishi H., Sugihara H., Nakanishi S., Mizuno N. Immunohistochemical localization of a metabotropic glutamate receptor, mGluR5, in the rat brain. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Nov 26;163(1):53–57. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90227-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratton K. R., Worley P. F., Baraban J. M. Excitation of hippocampal neurons by stimulation of glutamate Qp receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec 7;173(2-3):235–237. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90529-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe Y., Masu M., Ishii T., Shigemoto R., Nakanishi S. A family of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):169–179. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90118-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe Y., Nomura A., Masu M., Shigemoto R., Mizuno N., Nakanishi S. Signal transduction, pharmacological properties, and expression patterns of two rat metabotropic glutamate receptors, mGluR3 and mGluR4. J Neurosci. 1993 Apr;13(4):1372–1378. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-04-01372.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. M., Gähwiler B. H. Comparison of the actions of baclofen at pre- and postsynaptic receptors in the rat hippocampus in vitro. J Physiol. 1992;451:329–345. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen C., Boel E., Suzdak P. D. Actions of phenylglycine analogs at subtypes of the metabotropic glutamate receptor family. Eur J Pharmacol. 1994 Mar 15;267(1):77–84. doi: 10.1016/0922-4106(94)90227-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J., Collingridge G. Phenylglycine derivatives as antagonists of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Sep;15(9):333–342. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittemore E. R., Cotman C. W. Agonists selective for phosphoinositide-coupled receptors sensitize neurons to depolarization by L-2-amino-4-phosphonobutanoic acid (L-AP4). Brain Res. 1991 Aug 2;555(2):215–219. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90344-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



