Abstract
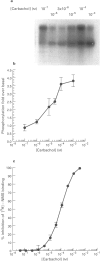
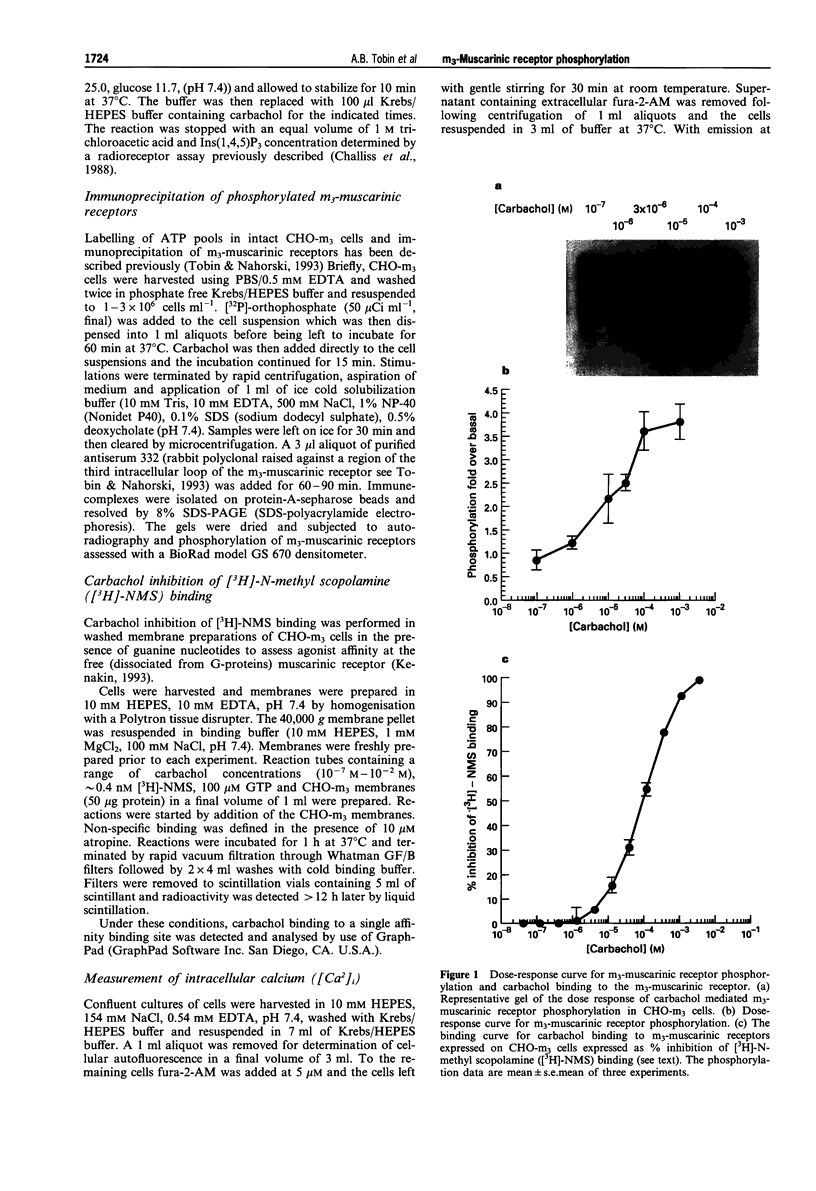
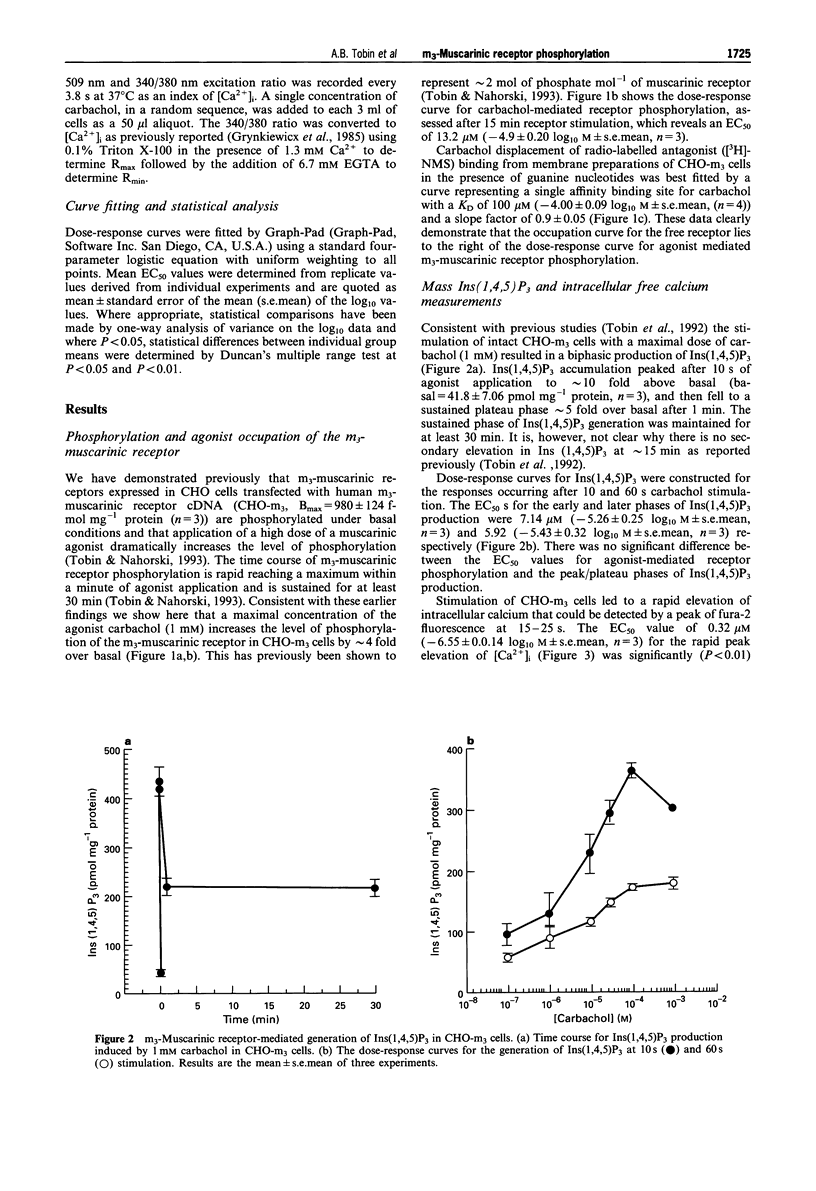
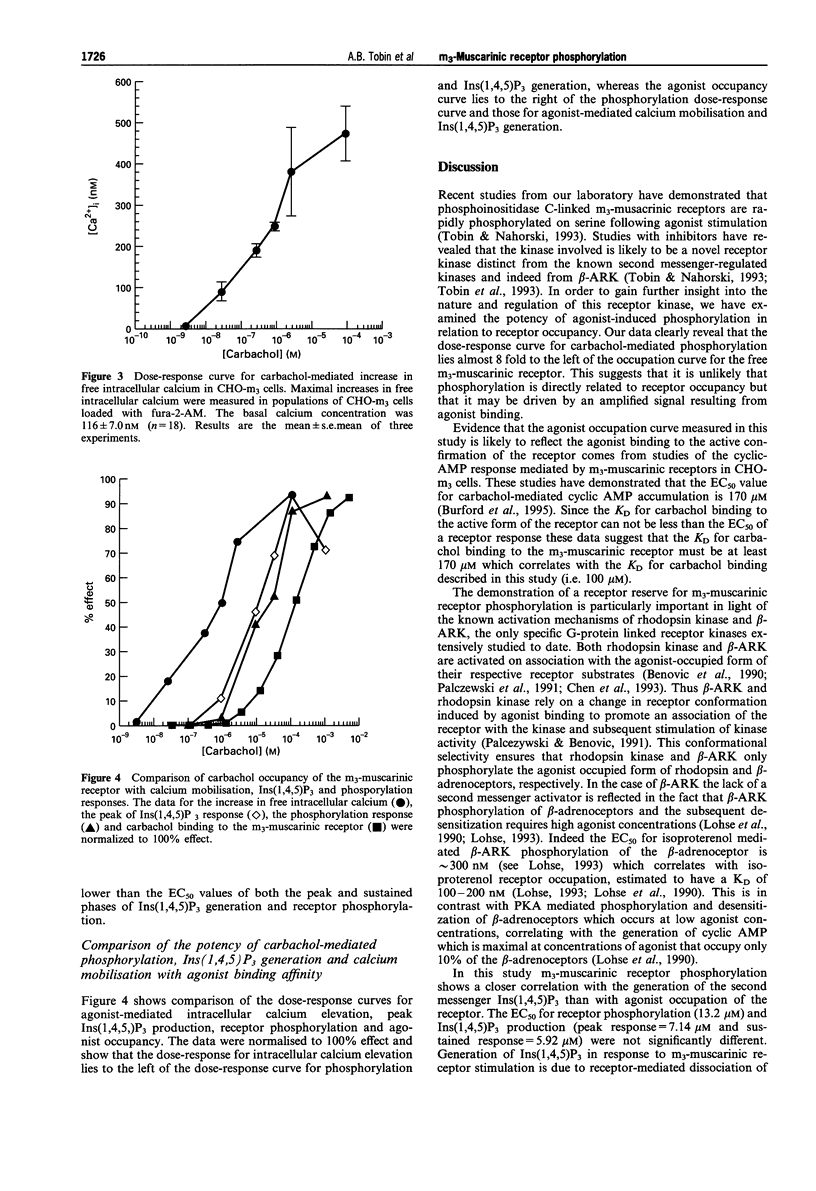
1. Phosphoinositidase C-linked m3-muscarinic receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells (CHO-m3 cells) are phosphorylated on serine following agonist stimulation. 2. m3-Muscarinic receptor phosphorylation is concentration-dependent requiring a carbachol concentration of 13.2 microM for half maximal stimulation. 3. The phosphorylation concentration-response curve lies to the left of the curve for carbachol binding to muscarinic receptors (KD = 100 microM) in membranes from CHO-m3 cells. In contrast, receptor phosphorylation closely correlates with receptor-mediated phosphoinositidase C activation (EC50 for inositol 1,4,5 trisphosphate accumulation during the peak and plateau phases were 7.14 microM and 5.92 microM respectively) but not with rapid agonist-mediated calcium elevation (EC50 = 0.32 microM) measured in fura-2-AM loaded cells. 4. These data suggest a dissociation of receptor phosphorylation from agonist occupation. Such an apparent 'receptor reserve' for m3-muscarinic receptor phosphorylation may be indicative of a mechanism that is dependent on a small amplification of the receptor signal, though probably dissociated from the calcium signal.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benovic J. L., Onorato J., Lohse M. J., Dohlman H. G., Staniszewski C., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Synthetic peptides of the hamster beta 2-adrenoceptor as substrates and inhibitors of the beta-adrenoceptor kinase. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1990;30 (Suppl 1):3S–12S. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1990.tb05462.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benovic J. L., Regan J. W., Matsui H., Mayor F., Jr, Cotecchia S., Leeb-Lundberg L. M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Agonist-dependent phosphorylation of the alpha 2-adrenergic receptor by the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17251–17253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caulfield M. P. Muscarinic receptors--characterization, coupling and function. Pharmacol Ther. 1993 Jun;58(3):319–379. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(93)90027-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challiss R. A., Batty I. H., Nahorski S. R. Mass measurements of inositol(1,4,5)trisphosphate in rat cerebral cortex slices using a radioreceptor assay: effects of neurotransmitters and depolarization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 15;157(2):684–691. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80304-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. Y., Dion S. B., Kim C. M., Benovic J. L. Beta-adrenergic receptor kinase. Agonist-dependent receptor binding promotes kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):7825–7831. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S. K., Slowiejko D. M., McEwen E. L. A rapid attenuation of muscarinic agonist stimulated phosphoinositide hydrolysis precedes receptor sequestration in human SH-SY-5Y neuroblastoma cells. Neurochem Res. 1994 May;19(5):549–554. doi: 10.1007/BF00971329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. M., Dion S. B., Benovic J. L. Mechanism of beta-adrenergic receptor kinase activation by G proteins. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):15412–15418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwatra M. M., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Hosey M. M. Phosphorylation of chick heart muscarinic cholinergic receptors by the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase. Biochemistry. 1989 May 30;28(11):4543–4547. doi: 10.1021/bi00437a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwatra M. M., Schwinn D. A., Schreurs J., Blank J. L., Kim C. M., Benovic J. L., Krause J. E., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. The substance P receptor, which couples to Gq/11, is a substrate of beta-adrenergic receptor kinase 1 and 2. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9161–9164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazareno S., Farries T., Birdsall N. J. Pharmacological characterization of guanine nucleotide exchange reactions in membranes from CHO cells stably transfected with human muscarinic receptors m1-m4. Life Sci. 1993;52(5-6):449–456. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(93)90301-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Multiple pathways of rapid beta 2-adrenergic receptor desensitization. Delineation with specific inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3202–3211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohse M. J. Molecular mechanisms of membrane receptor desensitization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Nov 7;1179(2):171–188. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(93)90139-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palczewski K., Benovic J. L. G-protein-coupled receptor kinases. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Oct;16(10):387–391. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90157-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palczewski K., Buczyłko J., Kaplan M. W., Polans A. S., Crabb J. W. Mechanism of rhodopsin kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):12949–12955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitcher J. A., Inglese J., Higgins J. B., Arriza J. L., Casey P. J., Kim C., Benovic J. L., Kwatra M. M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Role of beta gamma subunits of G proteins in targeting the beta-adrenergic receptor kinase to membrane-bound receptors. Science. 1992 Aug 28;257(5074):1264–1267. doi: 10.1126/science.1325672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Choi K. D. Regulation of inositol phospholipid-specific phospholipase C isozymes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12393–12396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin A. B., Keys B., Nahorski S. R. Phosphorylation of a phosphoinositidase C-linked muscarinic receptor by a novel kinase distinct from beta-adrenergic receptor kinase. FEBS Lett. 1993 Dec 13;335(3):353–357. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80418-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin A. B., Lambert D. G., Nahorski S. R. Rapid desensitization of muscarinic m3 receptor-stimulated polyphosphoinositide responses. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;42(6):1042–1048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobin A. B., Nahorski S. R. Rapid agonist-mediated phosphorylation of m3-muscarinic receptors revealed by immunoprecipitation. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9817–9823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wojcikiewicz R. J., Tobin A. B., Nahorski S. R. Desensitization of cell signalling mediated by phosphoinositidase C. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1993 Jul;14(7):279–285. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(93)90131-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wojcikiewicz R. J., Tobin A. B., Nahorski S. R. Muscarinic receptor-mediated inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate formation in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells is regulated acutely by cytosolic Ca2+ and by rapid desensitization. J Neurochem. 1994 Jul;63(1):177–185. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.63010177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]