Abstract
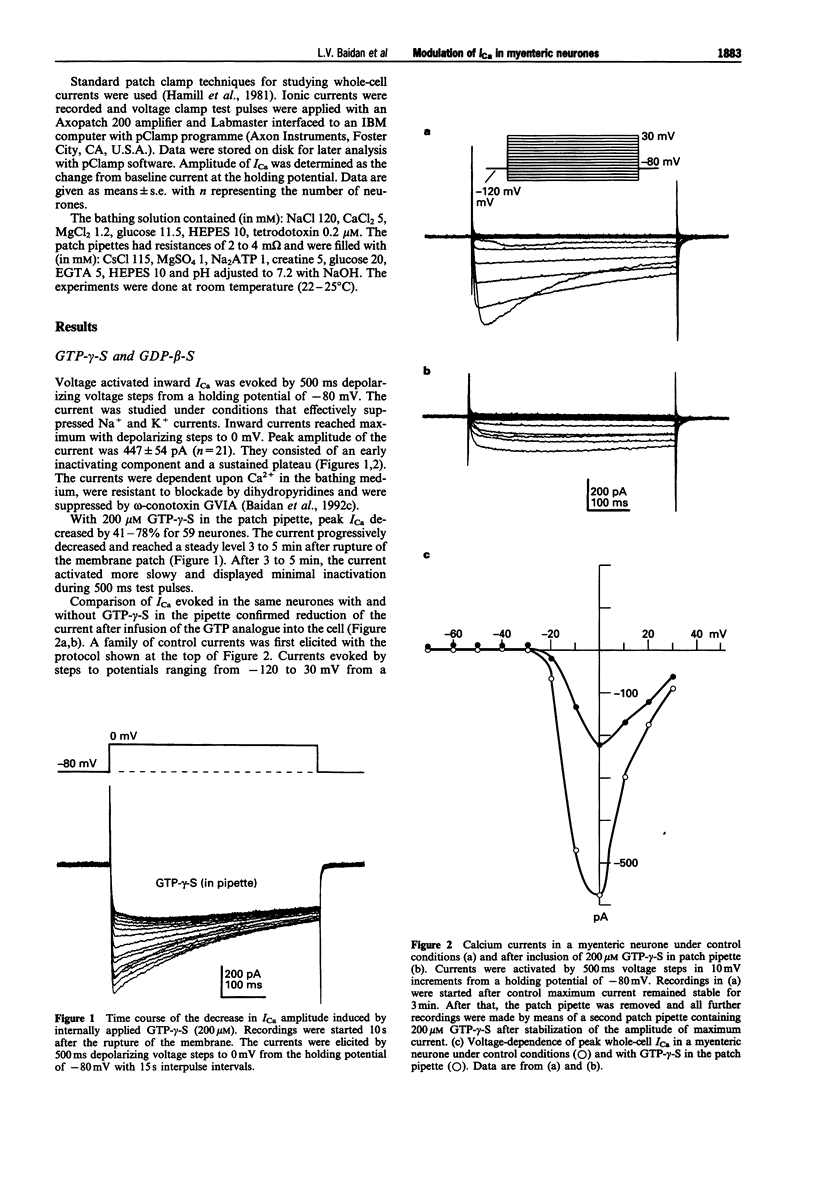
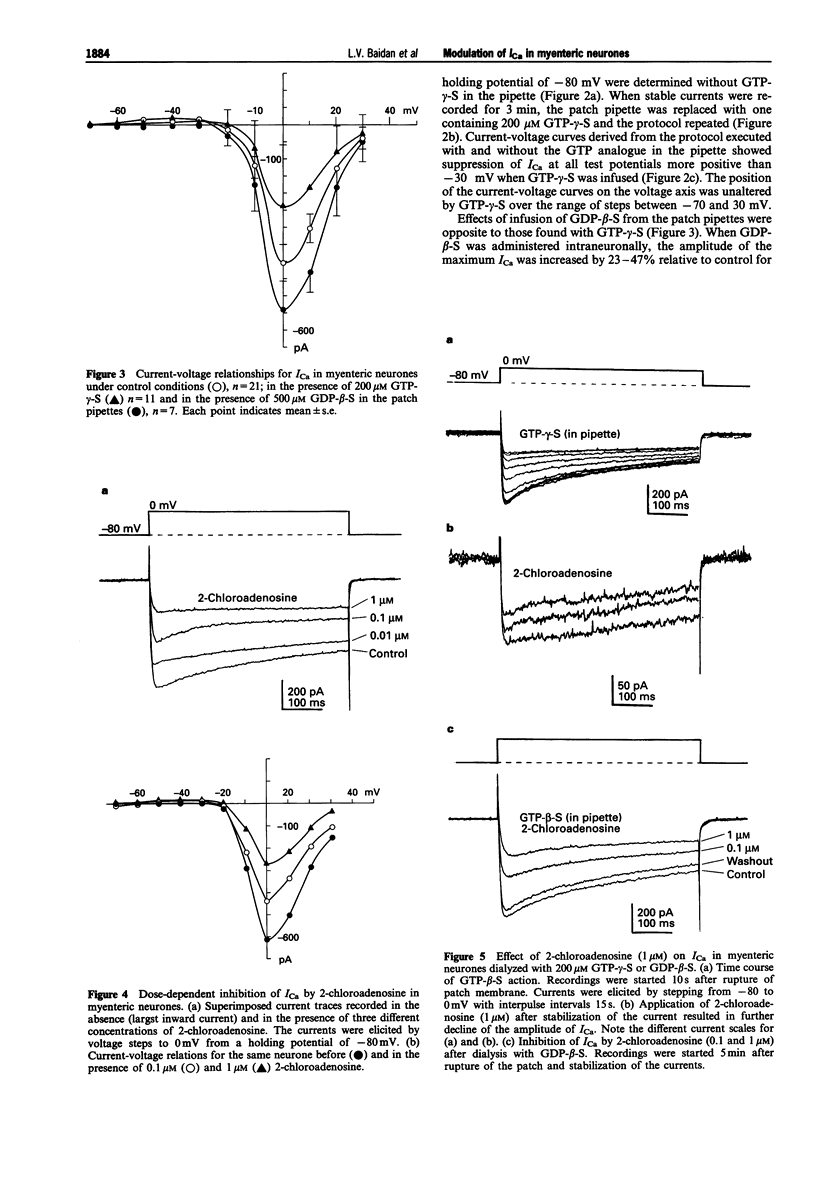
1. Whole-cell patch clamp methods were used to analyse voltage-dependent calcium currents in cultured myenteric neurones enzymatically isolated from adult guinea-pig small intestine. 2. Activation of G-proteins by intracellular administration of GTP-gamma-S (100-200 microM in pipette) decreased the amplitude of high voltage activated Ca2+ current (ICa) by more than 50%. Residual ICa was activated more slowly and was non-inactivating during 500 ms test pulses when GTP-gamma-S was included in the pipette solution. 3. Inclusion of 500 microM GDP-beta-S in the patch pipettes increased the amplitude of ICa by over 30% without altering the voltage-dependency. 4. Extracellular application of 2-chloroadenosine suppressed ICa dose-dependently by reducing both transient and sustained components of the current. 5. Pretreatment of the neurones with cholera toxin or forskolin did not alter the actions of GTP-gamma-S or GDP-beta-S or 2-chloroadenosine. 6. The results suggest that high threshold calcium channels in myenteric neurones are influenced by G-proteins and that the inhibitory action of 2-chloroadenosine on ICa involves G-protein coupling of the adenosine receptors to the Ca2+ channel.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baidan L. V., Zholos A. V., Shuba M. F., Wood J. D. Patch-clamp recording in myenteric neurons of guinea pig small intestine. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jun;262(6 Pt 1):G1074–G1078. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1992.262.6.G1074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barajas-Lopez C., Surprenant A., North R. A. Adenosine A1 and A2 receptors mediate presynaptic inhibition and postsynaptic excitation in guinea pig submucosal neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Aug;258(2):490–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. R., Kerr R., Khurana G. Adenosine modulation of calcium currents in postganglionic neurones of avian cultured ciliary ganglia. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 May;106(1):25–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14287.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bley K. R., Tsien R. W. Inhibition of Ca2+ and K+ channels in sympathetic neurons by neuropeptides and other ganglionic transmitters. Neuron. 1990 Mar;4(3):379–391. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90050-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christofi F. L., Tack J., Wood J. D. Suppression of nicotinic synaptic transmission by adenosine in myenteric ganglia of the guinea-pig gastric antrum. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 May 27;216(1):17–22. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90203-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christofi F. L., Wood J. D. Presynaptic inhibition by adenosine A1 receptors on guinea pig small intestinal myenteric neurons. Gastroenterology. 1993 May;104(5):1420–1429. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(93)90351-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C. Ca2+ channel currents in rat sensory neurones: interaction between guanine nucleotides, cyclic AMP and Ca2+ channel ligands. J Physiol. 1991 Jan;432:23–43. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C., Forda S. R., Scott R. H. Calcium-dependent currents in cultured rat dorsal root ganglion neurones are inhibited by an adenosine analogue. J Physiol. 1986 Apr;373:47–61. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C. G protein modulation of calcium currents in neurons. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:243–255. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grafe P., Mayer C. J., Wood J. D. Synaptic modulation of calcium-dependent potassium conductance in myenteric neurones in the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1980 Aug;305:235–248. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray R., Johnston D. Noradrenaline and beta-adrenoceptor agonists increase activity of voltage-dependent calcium channels in hippocampal neurons. Nature. 1987 Jun 18;327(6123):620–622. doi: 10.1038/327620a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross R. A., Macdonald R. L., Ryan-Jastrow T. 2-Chloroadenosine reduces the N calcium current of cultured mouse sensory neurones in a pertussis toxin-sensitive manner. J Physiol. 1989 Apr;411:585–595. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Johnson S. M., van Helden D. F. The calcium current in a myenteric neurone of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:297–314. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. D., Johnson S. M., van Helden D. F. The slow calcium-dependent potassium current in a myenteric neurone of the guinea-pig ileum. J Physiol. 1985 Apr;361:315–337. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai H., Aosaki T. Modulation of Ca-channel current by an adenosine analog mediated by a GTP-binding protein in chick sensory neurons. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Jun;414(2):145–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00580956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londos C., Wolff J. Two distinct adenosine-sensitive sites on adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5482–5486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemeth P. R., Palmer J. M., Wood J. D., Zafirov D. H. Effects of forskolin on electrical behaviour of myenteric neurones in guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol. 1986 Jul;376:439–450. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North R. A. The calcium-dependent slow after-hyperpolarization in myenteric plexus neurones with tetrodotoxin-resistant action potentials. Br J Pharmacol. 1973 Dec;49(4):709–711. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1973.tb08550.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohya Y., Sperelakis N. Involvement of a GTP-binding protein in stimulating action of angiotensin II on calcium channels in vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 1991 Mar;68(3):763–771. doi: 10.1161/01.res.68.3.763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. M., Wood J. D., Zafirov D. H. Elevation of adenosine 3',5'-phosphate mimics slow synaptic excitation in myenteric neurones of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1986 Jul;376:451–460. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. M., Wood J. D., Zafirov D. H. Purinergic inhibition in the small intestinal myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:357–369. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro J. A., Sebastião A. M. Adenosine receptors and calcium: basis for proposing a third (A3) adenosine receptor. Prog Neurobiol. 1986;26(3):179–209. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(86)90015-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz K. P., Miller R. J. Analysis of adenosine actions on Ca2+ currents and synaptic transmission in cultured rat hippocampal pyramidal neurones. J Physiol. 1991 Apr;435:373–393. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. H., Pearson H. A., Dolphin A. C. Aspects of vertebrate neuronal voltage-activated calcium currents and their regulation. Prog Neurobiol. 1991;36(6):485–520. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(91)90014-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surprenant A., Shen K. Z., North R. A., Tatsumi H. Inhibition of calcium currents by noradrenaline, somatostatin and opioids in guinea-pig submucosal neurones. J Physiol. 1990 Dec;431:585–608. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. Purine receptors in mammalian tissues: pharmacology and functional significance. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1987;27:315–345. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.27.040187.001531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia Y., Baidan L. V., Fertel R. H., Wood J. D. Determination of levels of cyclic AMP in the myenteric plexus of guinea-pig small intestine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar 25;206(3):231–236. doi: 10.1016/s0922-4106(05)80023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Y., Ikeda S. R. Adenosine modulates voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in adult rat sympathetic neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1993 Aug;70(2):610–620. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.70.2.610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


