Abstract
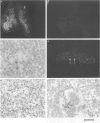
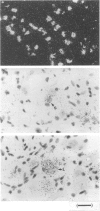
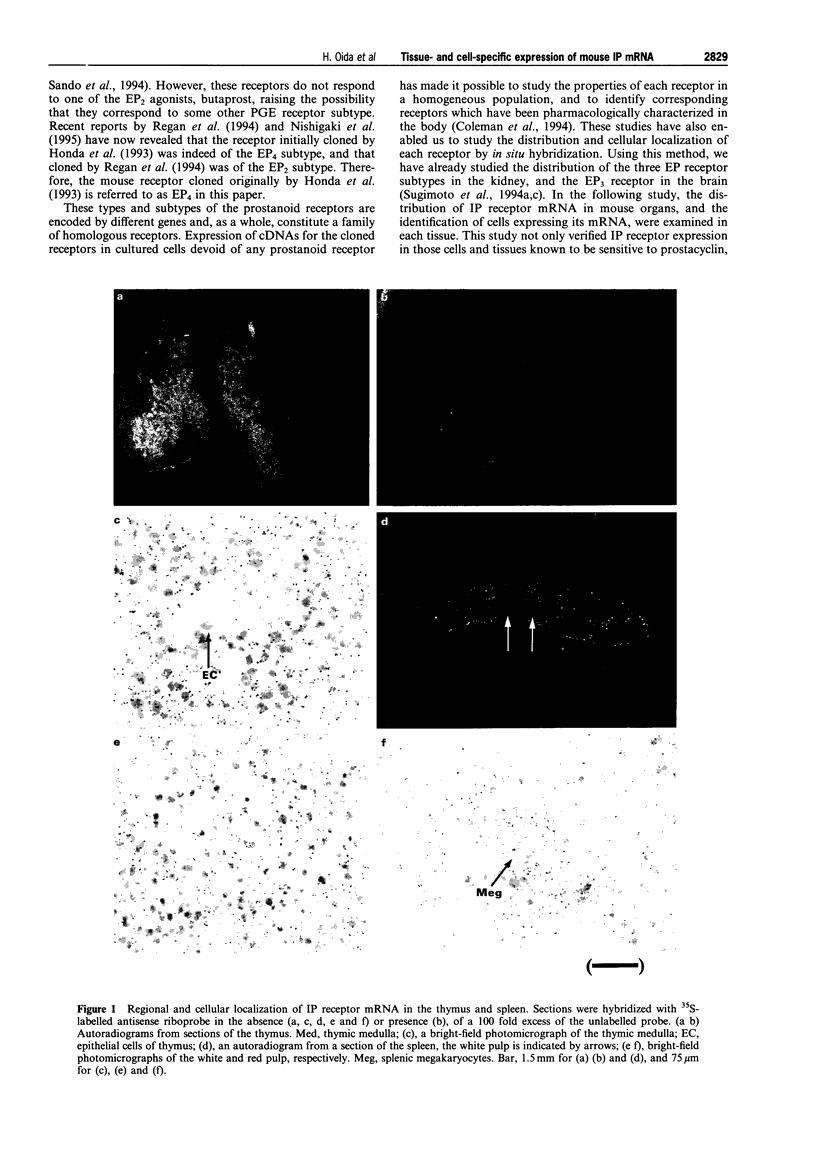
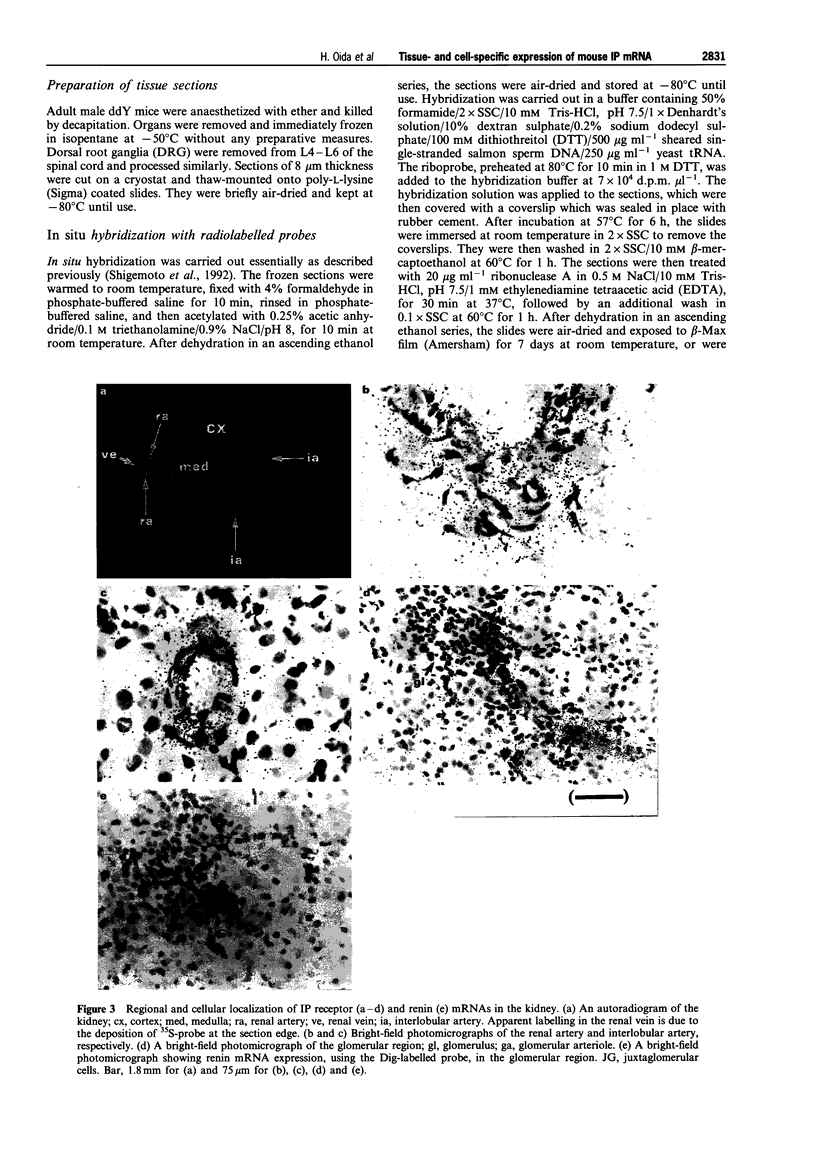
1. Expression of prostacyclin receptor (IP receptor) mRNA was examined in various mouse organs, and the cells expressing IP receptor mRNA were identified by in situ hybridization studies. Co-localization of mRNA for the IP receptor with that for preprotachykinin A (PPTA), a precursor protein for substance P, with mRNA for the prostaglandin E receptor subtypes (EP1, EP3 and EP4), and with renin mRNA, was examined by double in situ hybridization studies in the dorsal root ganglion and kidney, respectively. 2. IP receptor mRNA was expressed in the thymus and spleen. Expression in the thymus was found exclusively in the medulla, where mature thymocytes expressed transcripts for the IP receptor. Expression in the spleen was found as scattered signals over the white pulp and as punctate signals in the red pulp. The former was found in splenic lymphocytes and the latter in megakaryocytes. 3. IP receptor mRNA was also expressed in the vascular tissues of various organs such as the aorta, coronary arteries, pulmonary arteries and the cerebral arteries, where its expression was confined to smooth muscle cells. No expression was found in veins. In the kidney, IP receptor mRNA was detected in the interlobular arteries and glomerular arterioles but not in the juxtaglomerular (JG) cells which were labelled with the renin mRNA probe. 4. IP receptor mRNA was expressed in about 40% of the neurones in the dorsal root ganglion. Both small- and large-sized neurones were labelled but no labelling was found in the glia. Expression of PPTA mRNA was found in about 30% of total neurones. About 70% of these neurones expressed IP receptor mRNA, and about half of the IP receptor-positive neurones expressed PPTA mRNA. In addition to IP mRNA, mRNAs for EP1, EP3 and EP4 receptors were expressed in about 30%, 50% and 20%, respectively, of the dorsal root ganglion neurones. About 25%, 41% and 24% of the IP receptor-positive neurons co-expressed the EP1, EP3 and EP4 receptor, respectively. 5. These results not only verified IP receptor expression in various cells and tissues known to be sensitive to prostacyclin, but also revealed its expression in other systems, which urges the study of the actions of prostacyclin in these tissues. They also indicated that the actions of prostacyclin on blood vessels and platelets are mediated by the same type of receptor. Absence of IP receptor mRNA in the JG cells suggests that the action of prostacyclin on renin release may be indirect.
Full text
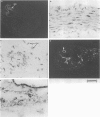
PDF



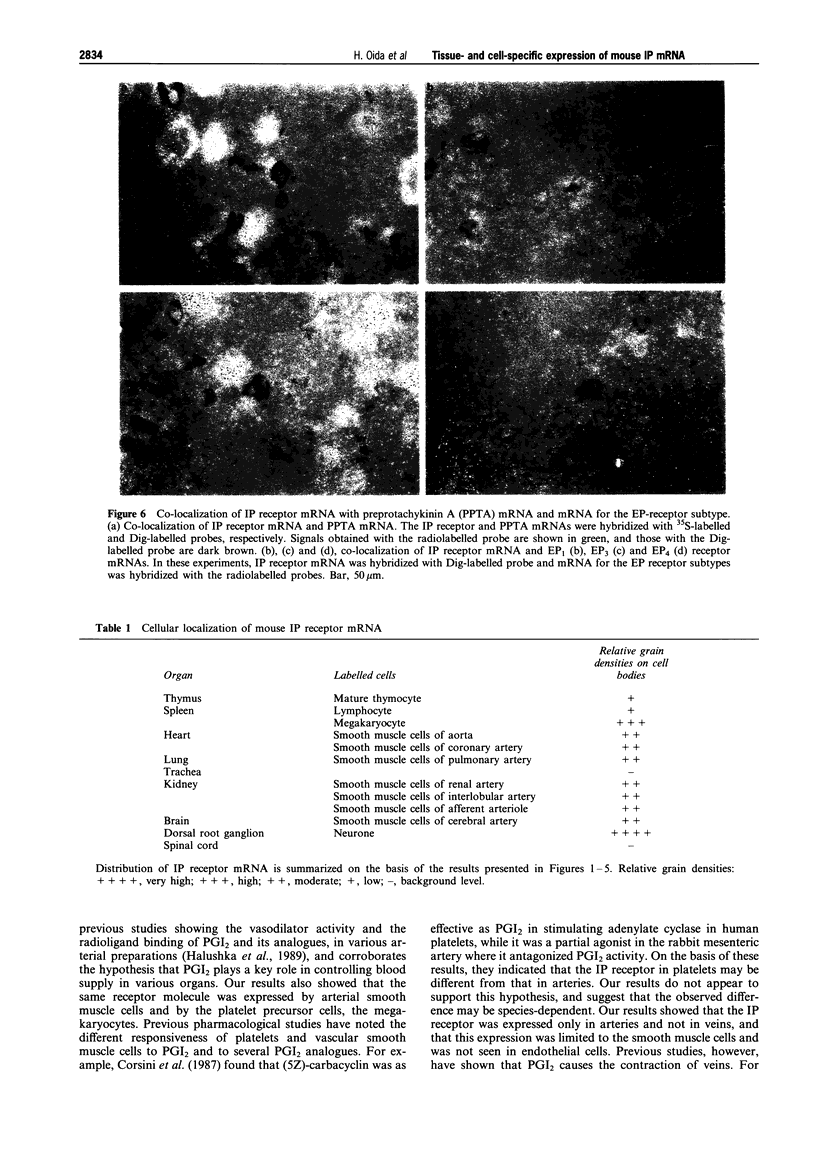



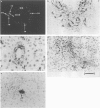
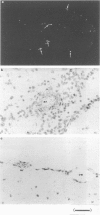
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alloatti G., Serazzi L., Levi R. C. Prostaglandin I2 (PGI2) enhances calcium current in guinea-pig ventricular heart cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1991 Jul;23(7):851–860. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(91)90218-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- An S., Yang J., Xia M., Goetzl E. J. Cloning and expression of the EP2 subtype of human receptors for prostaglandin E2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Nov 30;197(1):263–270. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong R. A., Lawrence R. A., Jones R. L., Wilson N. H., Collier A. Functional and ligand binding studies suggest heterogeneity of platelet prostacyclin receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;97(3):657–668. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb12001.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastien L., Sawyer N., Grygorczyk R., Metters K. M., Adam M. Cloning, functional expression, and characterization of the human prostaglandin E2 receptor EP2 subtype. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 22;269(16):11873–11877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolger P. M., Eisner G. M., Ramwell P. W., Slotkoff L. M. Renal actions of prostacyclin. Nature. 1978 Feb 2;271(5644):467–469. doi: 10.1038/271467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman R. A., Smith W. L., Narumiya S. International Union of Pharmacology classification of prostanoid receptors: properties, distribution, and structure of the receptors and their subtypes. Pharmacol Rev. 1994 Jun;46(2):205–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corsini A., Folco G. C., Fumagalli R., Nicosia S., Noe M. A., Oliva D. (5Z)-carbacyclin discriminates between prostacyclin-receptors coupled to adenylate cyclase in vascular smooth muscle and platelets. Br J Pharmacol. 1987 Jan;90(1):255–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1987.tb16847.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong Y. J., Jones R. L., Wilson N. H. Prostaglandin E receptor subtypes in smooth muscle: agonist activities of stable prostacyclin analogues. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Jan;87(1):97–107. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10161.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halushka P. V., Mais D. E., Mayeux P. R., Morinelli T. A. Thromboxane, prostaglandin and leukotriene receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1989;29:213–239. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.29.040189.001241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata M., Hayashi Y., Ushikubi F., Yokota Y., Kageyama R., Nakanishi S., Narumiya S. Cloning and expression of cDNA for a human thromboxane A2 receptor. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):617–620. doi: 10.1038/349617a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata M., Kakizuka A., Aizawa M., Ushikubi F., Narumiya S. Molecular characterization of a mouse prostaglandin D receptor and functional expression of the cloned gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):11192–11196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.11192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homo-Delarche F., Duval D., Papiernik M. Prostaglandin production by phagocytic cells of the mouse thymic reticulum in culture and its modulation by indomethacin and corticosteroids. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):506–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda A., Sugimoto Y., Namba T., Watabe A., Irie A., Negishi M., Narumiya S., Ichikawa A. Cloning and expression of a cDNA for mouse prostaglandin E receptor EP2 subtype. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):7759–7762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juan H. The pain enhancing effect of PGI2. Agents Actions Suppl. 1979;(4):204–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi Y., Hoshimaru M., Nawa H., Nakanishi S. Sequence analysis of cloned cDNA for rat substance P precursor: existence of a third substance P precursor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 30;139(3):1040–1046. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80282-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Källskog O., Lindbrom L. O., Ulfendahl H. R., Wolgast M. Hydrostatic pressures within the vascular structures of the rat kidney. Pflugers Arch. 1976 Jun 22;363(3):205–210. doi: 10.1007/BF00594602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefer A. M., Smith E. F., 3rd, Araki H., Smith J. B., Aharony D., Claremon D. A., Magolda R. L., Nicolaou K. C. Dissociation of vasoconstrictor and platelet aggregatory activities of thromboxane by carbocyclic thromboxane A2, a stable analog of thromboxane A2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1706–1710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifschitz M. D. Prostaglandins and renal blood flow: in vivo studies. Kidney Int. 1981 Jun;19(6):781–785. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mais D. E., Saussy D. L., Jr, Chaikhouni A., Kochel P. J., Knapp D. R., Hamanaka N., Halushka P. V. Pharmacologic characterization of human and canine thromboxane A2/prostaglandin H2 receptors in platelets and blood vessels: evidence for different receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 May;233(2):418–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malmberg A. B., Yaksh T. L. Hyperalgesia mediated by spinal glutamate or substance P receptor blocked by spinal cyclooxygenase inhibition. Science. 1992 Aug 28;257(5074):1276–1279. doi: 10.1126/science.1381521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack J. E., Kappler J., Marrack P., Westcott J. Y. Production of prostaglandin E2 and prostacyclin by thymic nurse cells in culture. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):239–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morinelli T. A., Okwu A. K., Mais D. E., Halushka P. V., John V., Chen C. K., Fried J. Difluorothromboxane A2 and stereoisomers: stable derivatives of thromboxane A2 with differential effects on platelets and blood vessels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5600–5604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa O., Tanaka I., Usui T., Harada M., Sasaki Y., Itoh H., Yoshimasa T., Namba T., Narumiya S., Nakao K. Molecular cloning of human prostacyclin receptor cDNA and its gene expression in the cardiovascular system. Circulation. 1994 Oct;90(4):1643–1647. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.90.4.1643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba T., Oida H., Sugimoto Y., Kakizuka A., Negishi M., Ichikawa A., Narumiya S. cDNA cloning of a mouse prostacyclin receptor. Multiple signaling pathways and expression in thymic medulla. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):9986–9992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba T., Sugimoto Y., Hirata M., Hayashi Y., Honda A., Watabe A., Negishi M., Ichikawa A., Narumiya S. Mouse thromboxane A2 receptor: cDNA cloning, expression and northern blot analysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 May 15;184(3):1197–1203. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishigaki N., Negishi M., Honda A., Sugimoto Y., Namba T., Narumiya S., Ichikawa A. Identification of prostaglandin E receptor 'EP2' cloned from mastocytoma cells EP4 subtype. FEBS Lett. 1995 May 15;364(3):339–341. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00421-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka M., Yoshioka K. Neurotransmitter functions of mammalian tachykinins. Physiol Rev. 1993 Apr;73(2):229–308. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1993.73.2.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regan J. W., Bailey T. J., Pepperl D. J., Pierce K. L., Bogardus A. M., Donello J. E., Fairbairn C. E., Kedzie K. M., Woodward D. F., Gil D. W. Cloning of a novel human prostaglandin receptor with characteristics of the pharmacologically defined EP2 subtype. Mol Pharmacol. 1994 Aug;46(2):213–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sando T., Usui T., Tanaka I., Mori K., Sasaki Y., Fukuda Y., Namba T., Sugimoto Y., Ichikawa A., Narumiya S. Molecular cloning and expression of rat prostaglandin E receptor EP2 subtype. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 May 16;200(3):1329–1333. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki Y., Usui T., Tanaka I., Nakagawa O., Sando T., Takahashi T., Namba T., Narumiya S., Nakao K. Cloning and expression of a cDNA for rat prostacyclin receptor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Dec 30;1224(3):601–605. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(94)90300-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schor N., Ichikawa I., Brenner B. M. Mechanisms of action of various hormones and vasoactive substances on glomerular ultrafiltration in the rat. Kidney Int. 1981 Oct;20(4):442–451. doi: 10.1038/ki.1981.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrör K., Darius H., Matzky R., Ohlendorf R. The antiplatelet and cardiovascular actions of a new carbacyclin derivative (ZK 36 374)--equipotent to PGI2 in vitro. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1981 Jun;316(3):252–255. doi: 10.1007/BF00505658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigemoto R., Nakanishi S., Mizuno N. Distribution of the mRNA for a metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR1) in the central nervous system: an in situ hybridization study in adult and developing rat. J Comp Neurol. 1992 Aug 1;322(1):121–135. doi: 10.1002/cne.903220110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimokawa H., Flavahan N. A., Lorenz R. R., Vanhoutte P. M. Prostacyclin releases endothelium-derived relaxing factor and potentiates its action in coronary arteries of the pig. Br J Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;95(4):1197–1203. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1988.tb11756.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto Y., Hasumoto K., Namba T., Irie A., Katsuyama M., Negishi M., Kakizuka A., Narumiya S., Ichikawa A. Cloning and expression of a cDNA for mouse prostaglandin F receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 14;269(2):1356–1360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto Y., Namba T., Honda A., Hayashi Y., Negishi M., Ichikawa A., Narumiya S. Cloning and expression of a cDNA for mouse prostaglandin E receptor EP3 subtype. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):6463–6466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto Y., Namba T., Shigemoto R., Negishi M., Ichikawa A., Narumiya S. Distinct cellular localization of mRNAs for three subtypes of prostaglandin E receptor in kidney. Am J Physiol. 1994 May;266(5 Pt 2):F823–F828. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1994.266.5.F823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto Y., Shigemoto R., Namba T., Negishi M., Mizuno N., Narumiya S., Ichikawa A. Distribution of the messenger RNA for the prostaglandin E receptor subtype EP3 in the mouse nervous system. Neuroscience. 1994 Oct;62(3):919–928. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)90483-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahara K., Murray R., FitzGerald G. A., Fitzgerald D. J. The response to thromboxane A2 analogues in human platelets. Discrimination of two binding sites linked to distinct effector systems. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6836–6844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watabe A., Sugimoto Y., Honda A., Irie A., Namba T., Negishi M., Ito S., Narumiya S., Ichikawa A. Cloning and expression of cDNA for a mouse EP1 subtype of prostaglandin E receptor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):20175–20178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]