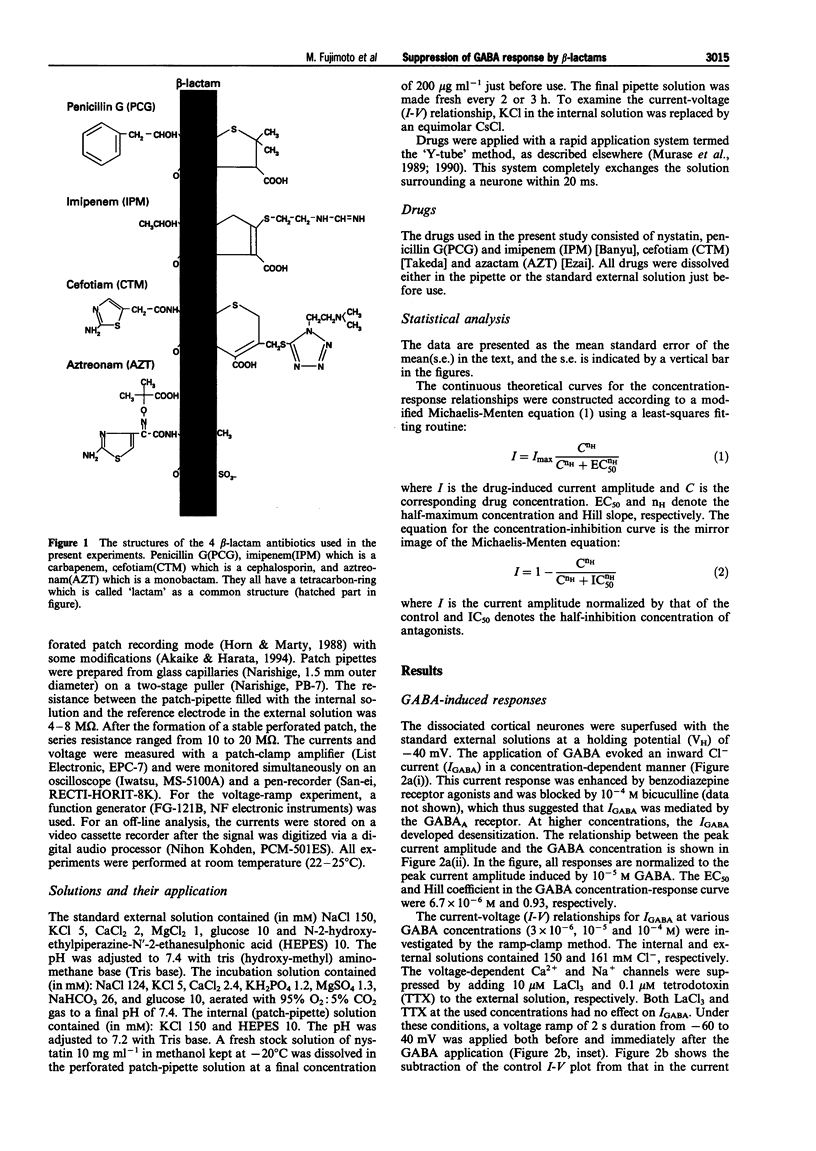
Abstract
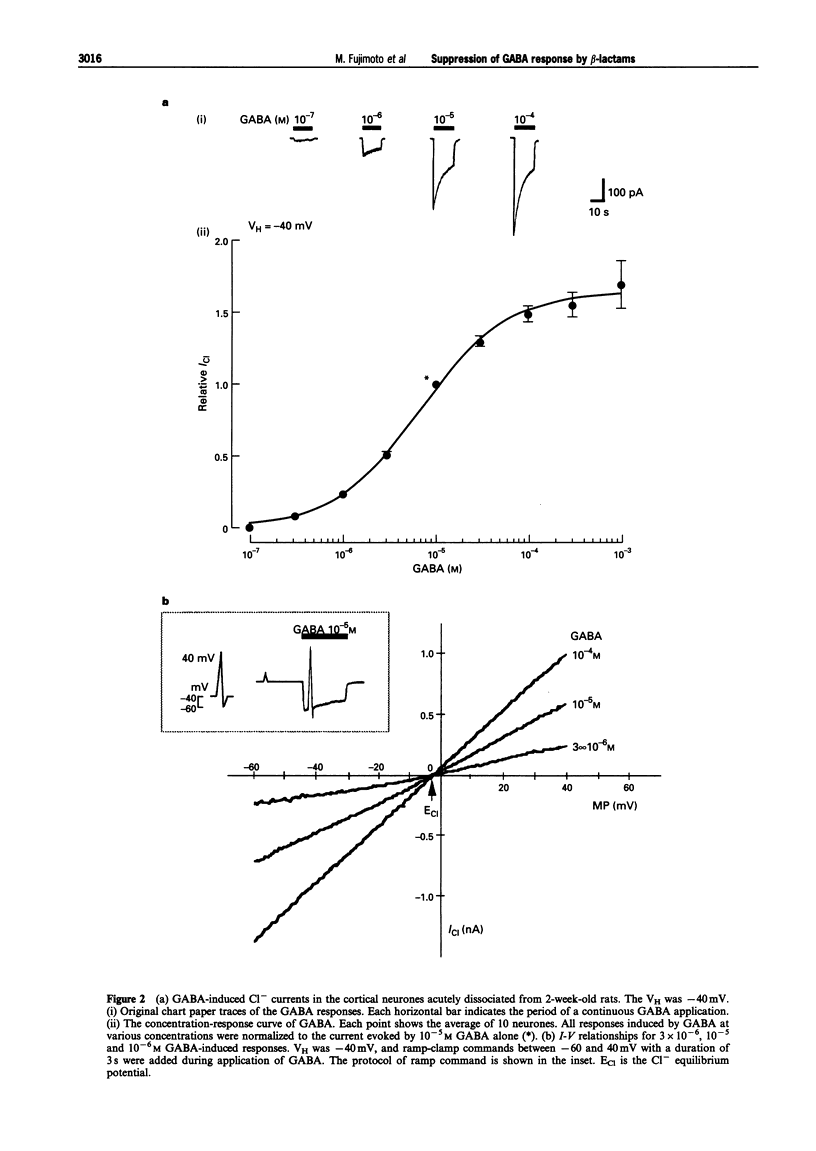
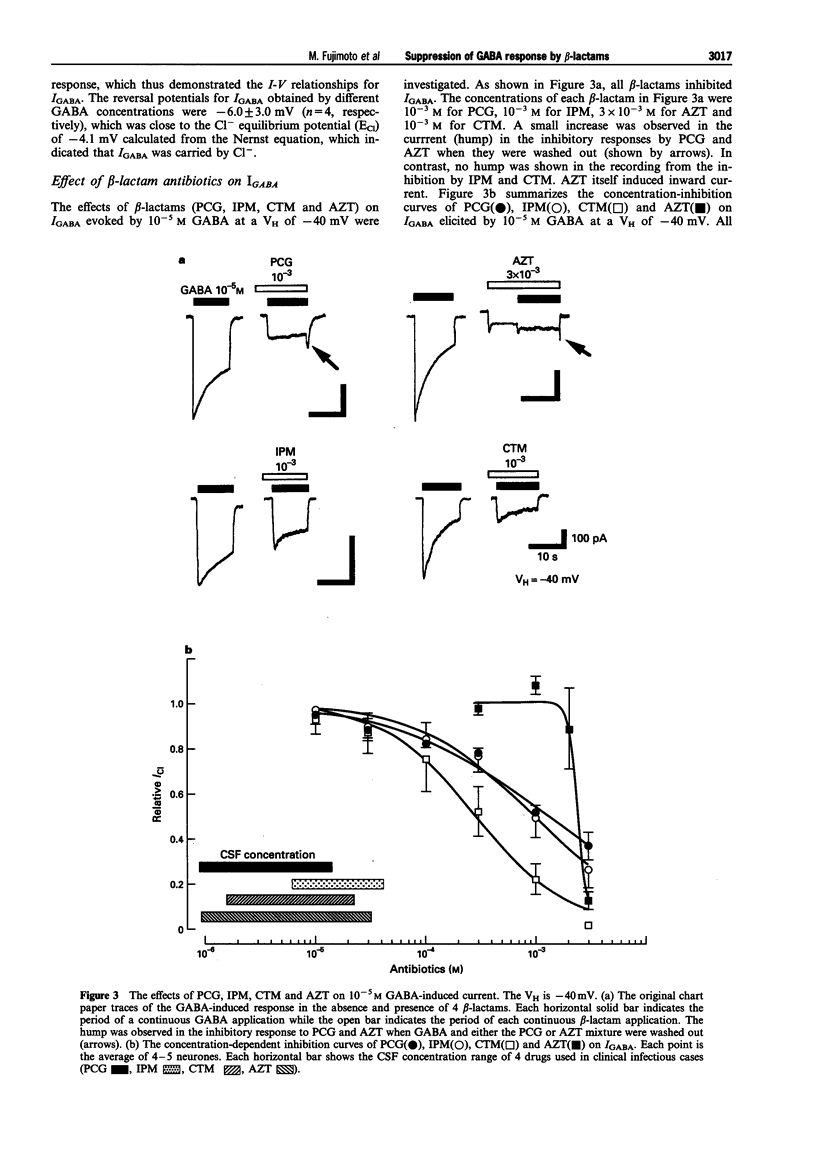
1. The effects of beta-lactam antibiotics on the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-induced Cl- current were investigated in pyramidal neurones freshly dissociated from the rat frontal cortex by the use of a nystatin-perforated patch recording mode under voltage-clamp conditions. 2. The GABA-induced inward current increased in a concentration-dependent manner with an EC50 of 6.7 x 10(-6) M at a holding potential of -40 mV. The GABA response was accompanied by an increase in the membrane conductance and reversed at near the Cl- equilibrium potential. 3. All beta-lactams (penicillin, imipenem, aztreonam and cefotiam) inhibited the 10(-5) M GABA-induced response in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC50 and Hill coefficient of 1.3 x 10(-3) M and 0.64 for penicillin, 9.6 x 10(-4) M and 0.83 for imipenem, 2.5 x 10(-3) M and 9.99 for aztreonam, and 2.9 x 10(-4) M and 1.03 for cefotiam. 4. Imipenem inhibited the GABA-response competitively while penicillin inhibited the same response in a noncompetitive fashion. 5. The inhibitory action of imipenem showed no voltage-dependency, whereas the effect of penicillin was voltage-dependent. 6. It is thus proposed that some classes of beta-lactams, including imipenem may have a mechanism that is different from penicillin and competitively affects the GABAA receptor.
Full text
PDF
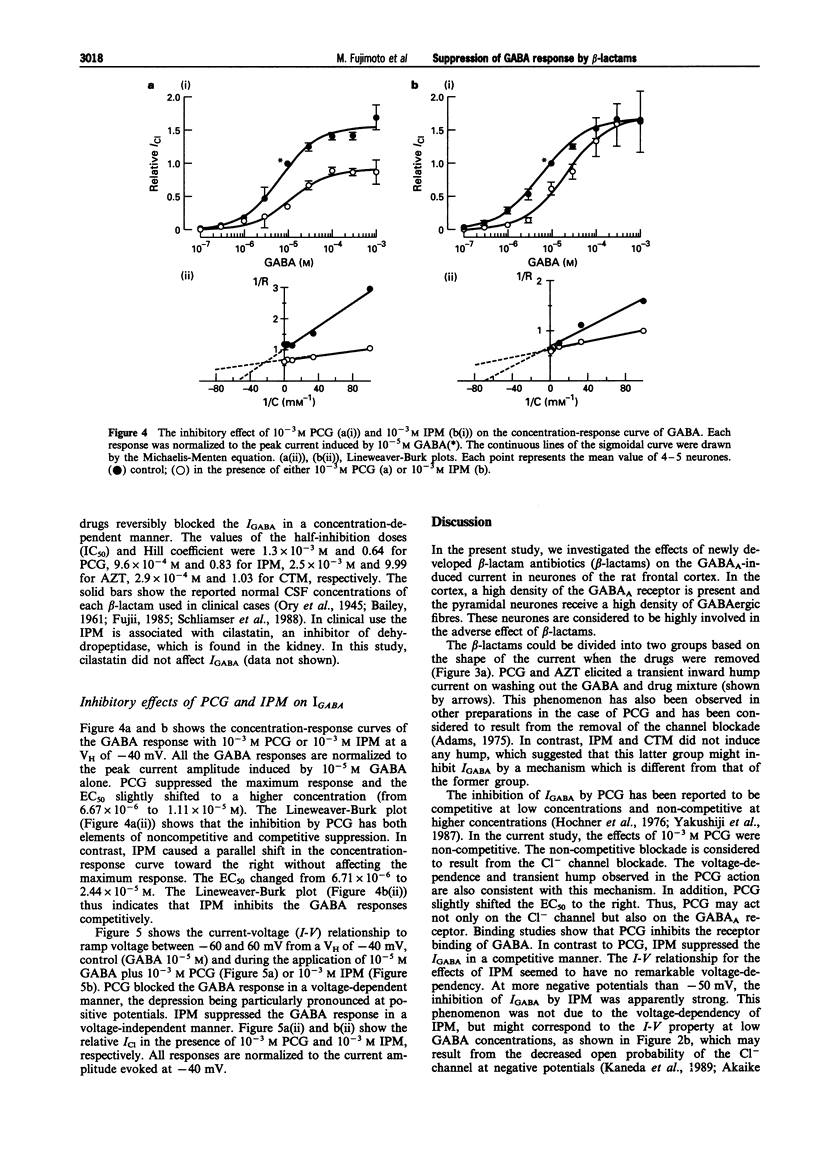
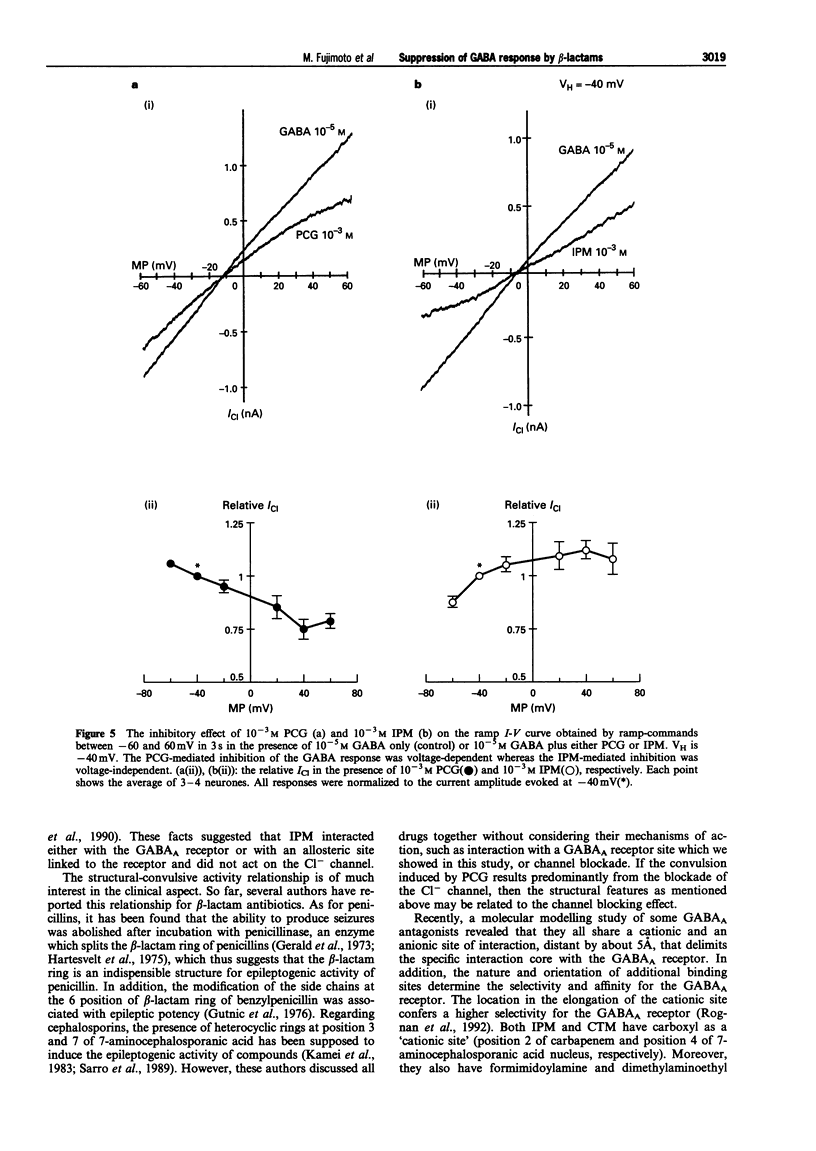

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R. A study of desensitization using voltage clamp. Pflugers Arch. 1975 Oct 28;360(2):135–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00580536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akaike N., Harata N. Nystatin perforated patch recording and its applications to analyses of intracellular mechanisms. Jpn J Physiol. 1994;44(5):433–473. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.44.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akaike N., Tokutomi N., Ikemoto Y. Augmentation of GABA-induced current in frog sensory neurons by pentobarbital. Am J Physiol. 1990 Mar;258(3 Pt 1):C452–C460. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.258.3.C452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avoli M. Penicillin induced hyperexcitability in the in vitro hippocampal slice can be unrelated to impairment of somatic inhibition. Brain Res. 1984 Dec 3;323(1):154–158. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90279-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAILEY D. J., Jr Passage of penicillin across the blood-brain barrier in adults. J Lab Clin Med. 1961 Aug;58:305–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calandra G. B., Brown K. R., Grad L. C., Ahonkhai V. I., Wang C., Aziz M. A. Review of adverse experiences and tolerability in the first 2,516 patients treated with imipenem/cilastatin. Am J Med. 1985 Jun 7;78(6A):73–78. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff R. A. Gamma-aminobutyric acid antagonism and presynaptic inhibition in the frog spinal cord. Science. 1972 Jan 21;175(4019):331–333. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4019.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Sarro A., De Sarro G. B., Ascioti C., Nisticó G. Epileptogenic activity of some beta-lactam derivatives: structure-activity relationship. Neuropharmacology. 1989 Apr;28(4):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(89)90030-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn P. F., Somjen G. G. Membrane resistance, monosynaptic EPSPs, and the epileptogenic action of penicillin in spinal motoneurons. Brain Res. 1977 Jun 17;128(3):569–574. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90184-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuyii R., Meguro H., Arimasu O., Sunakawa K., Ishizuka Y., Nakazawa S., Sato H., Narita A., Matsumoto K., Suzuki H. [Bacteriological, pharmacokinetic and clinical studies on aztreonam in the pediatric field. Pediatric Study Group of Aztreonam]. Jpn J Antibiot. 1985 Nov;38(11):3195–3216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerald M. C., Massey J., Spadaro D. C. Comparative convulsant activity of various penicillins after intracerebral injection in mice. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1973 Feb;25(2):104–108. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1973.tb10602.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutnick M. J., Van Duijn H., Citri N. Relative convulsant potencies of structural analogues of penicillin. Brain Res. 1976 Sep 10;114(1):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)91015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochner B., Spira M. E., Werman R. Penicillin decreases chloride conductance in crustacean muscle: a model for the epileptic neuron. Brain Res. 1976 Apr 30;107(1):85–103. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)90097-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Marty A. Muscarinic activation of ionic currents measured by a new whole-cell recording method. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Aug;92(2):145–159. doi: 10.1085/jgp.92.2.145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito C., Wakamori M., Akaike N. Dual effect of glycine on isolated rat suprachiasmatic neurons. Am J Physiol. 1991 Feb;260(2 Pt 1):C213–C218. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.2.C213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamei C., Sunami A., Tasaka K. Epileptogenic activity of cephalosporins in rats and their structure-activity relationship. Epilepsia. 1983 Aug;24(4):431–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1983.tb04913.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneda M., Wakamori M., Akaike N. GABA-induced chloride current in rat isolated Purkinje cells. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 1):C1153–C1159. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.6.C1153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Puil E., Werman R. Bicuculline, benzyl penicillin, and inhibitory amino acids in the spinal cord of the cat. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1977 Jun;55(3):670–680. doi: 10.1139/y77-091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer H., Prince D. Convulsant actions of penicillin: effects on inhibitory mechanisms. Brain Res. 1973 Apr 27;53(2):477–482. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90237-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murase K., Randic M., Shirasaki T., Nakagawa T., Akaike N. Serotonin suppresses N-methyl-D-aspartate responses in acutely isolated spinal dorsal horn neurons of the rat. Brain Res. 1990 Aug 13;525(1):84–91. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91323-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murase K., Ryu P. D., Randic M. Excitatory and inhibitory amino acids and peptide-induced responses in acutely isolated rat spinal dorsal horn neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Aug 14;103(1):56–63. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90485-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickles H. G., Simmonds M. A. Antagonism by penicillin of gamma-aminobutyric acid depolarizations at presynaptic sites in rat olfactory cortex and cuneate nucleus in vitro. Neuropharmacology. 1980 Jan;19(1):35–38. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(80)90163-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince D. A. The depolarization shift in "epileptic" neurons. Exp Neurol. 1968 Aug;21(4):467–485. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(68)90066-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rognan D., Boulanger T., Hoffmann R., Vercauteren D. P., Andre J. M., Durant F., Wermuth C. G. Structure and molecular modeling of GABAA receptor antagonists. J Med Chem. 1992 May 29;35(11):1969–1977. doi: 10.1021/jm00089a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schliamser S. E., Broholm K. A., Liljedahl A. L., Norrby S. R. Comparative neurotoxicity of benzylpenicillin, imipenem/cilastatin and FCE 22101, a new injectible penem. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Nov;22(5):687–695. doi: 10.1093/jac/22.5.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada J., Hori S., Kanemitsu K., Shoji Y., Nakashio S., Yanagawa A. A comparative study on the convulsant activity of carbapenems and beta-lactams. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1992;18(9):377–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse C. S., Hernandez Vera F., Desai D. V. Seizure-like activity associated with imipenem-cilastatin. Drug Intell Clin Pharm. 1987 Jul-Aug;21(7-8):659–660. doi: 10.1177/1060028087021007-820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twyman R. E., Green R. M., MacDonald R. L. Kinetics of open channel block by penicillin of single GABAA receptor channels from mouse spinal cord neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1992 Jan;445:97–127. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp018914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Hartesveldt C., Petit T. L., Isaacson R. L. Epileptogenic effects of several penicillins and penicillin-related compounds in rat neocortex. Epilepsia. 1975 Sep;16(3):449–455. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1157.1975.tb06072.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yakushiji T., Tokutomi N., Akaike N., Carpenter D. O. Antagonists of GABA responses, studied using internally perfused frog dorsal root ganglion neurons. Neuroscience. 1987 Sep;22(3):1123–1133. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)92987-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]