Abstract
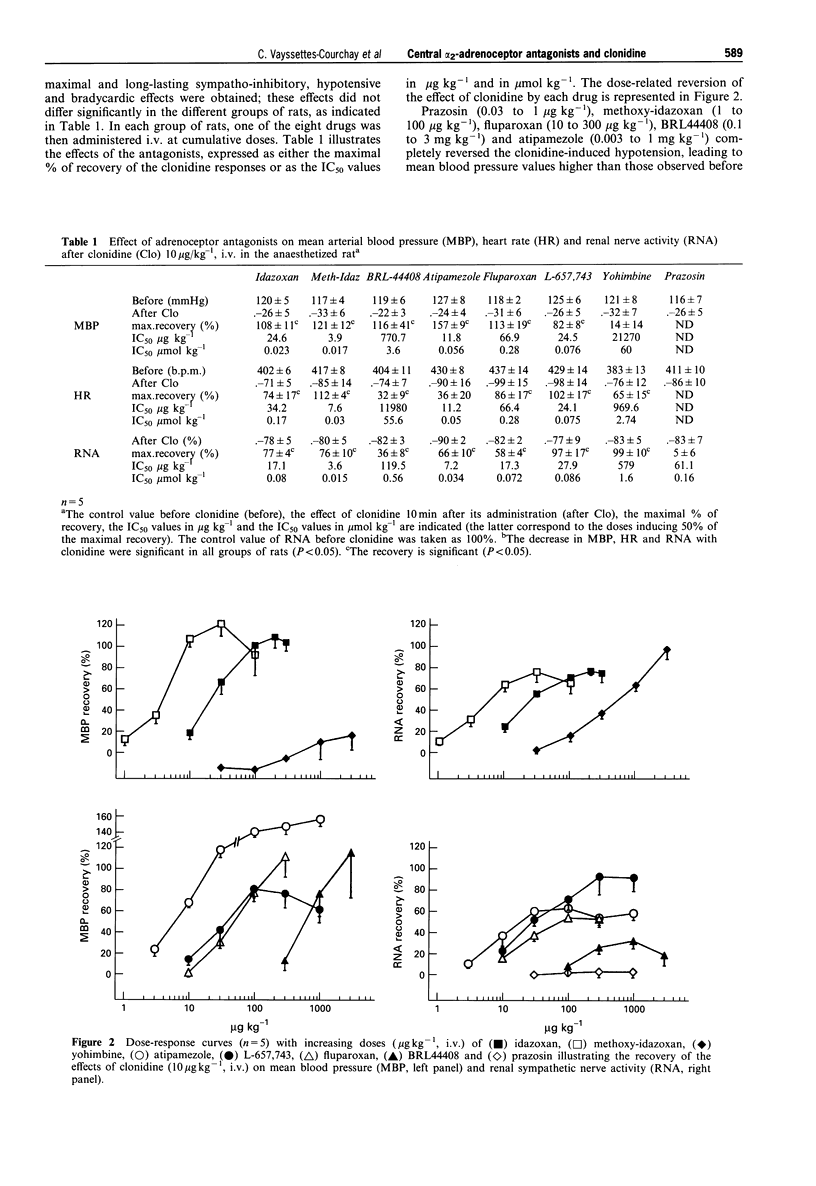
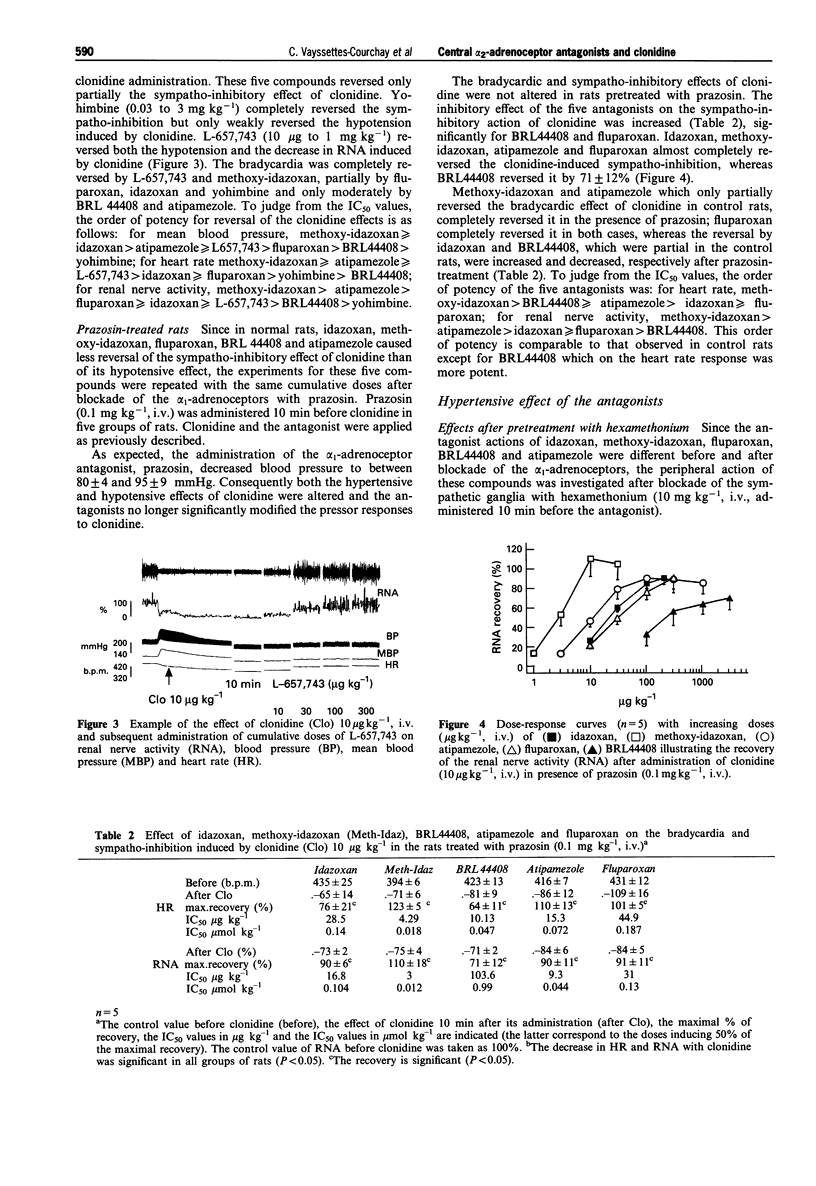
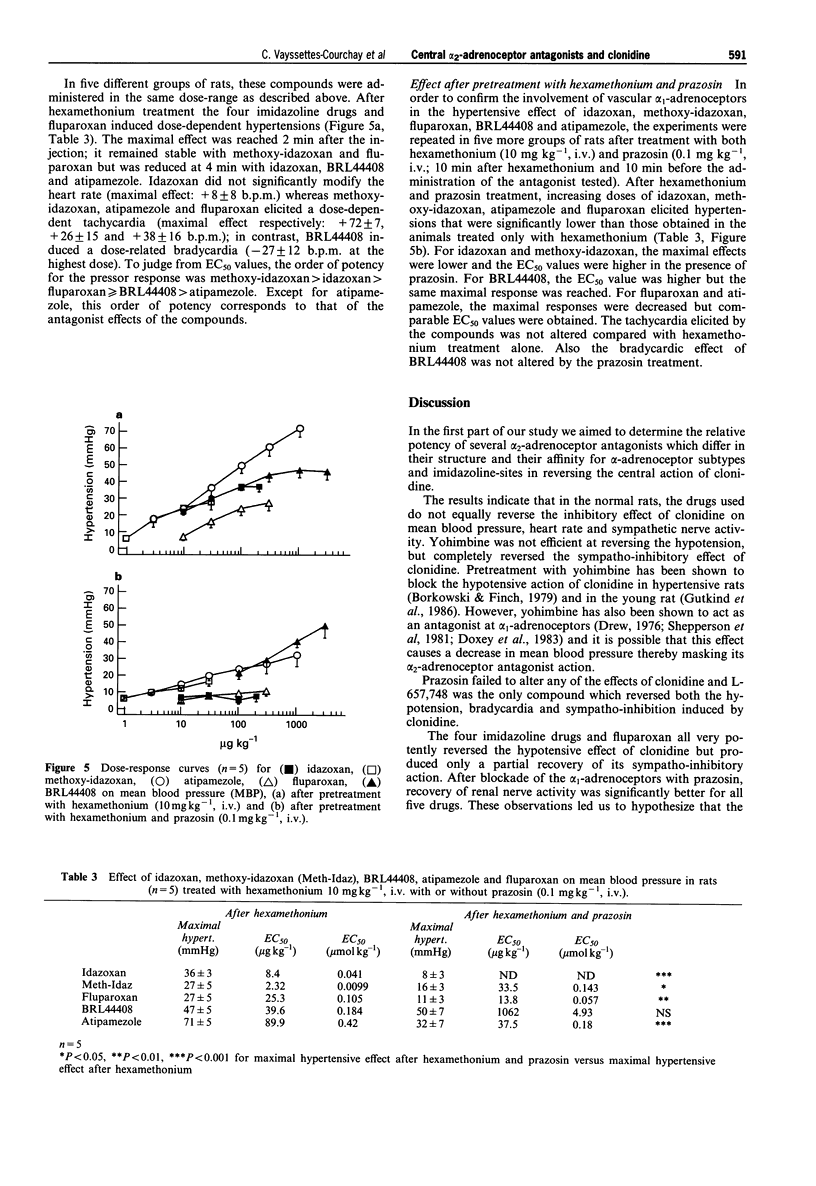
1. The recovery of the clonidine-induced hypotension, bradycardia and sympatho-inhibition produced by several putative alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonists was investigated in pentobarbitone anaesthetized rats. The activity of four substances containing an imidazoline structure: idazoxan, methoxy-idazoxan, BRL44408 and atipamezole was compared with the effect of fluparoxan, yohimbine and L-657,743; in addition the effect of the alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonist, prazosin, was also studied. 2. Prazosin (0.03-1 mg kg-1, i.v.) failed to alter the sympatho-inhibitory and hypotensive effects of clonidine (10 micrograms kg-1, i.v.). L-657,743 (0.01-1 mg kg-1, i.v.) induced a recovery of blood pressure, heart rate and renal sympathetic nerve activity. Yohimbine (0.03-3 mg kg-1, i.v.) completely reversed the sympatho-inhibitory effect of clonidine but did not alter its hypotensive effect. 3. The four imidazoline drugs: idazoxan (10-300 micrograms kg-1, i.v.), methoxy-idazoxan (1-100 micrograms kg-1, i.v.), BRL44408 (0.1-3 mg kg-1, i.v.) and atipamezole (0.03-1 mg kg-1, i.v.) and fluparoxan (10-300 micrograms kg-1, i.v.) reversed the clonidine-induced hypotension but produced only a partial recovery of the renal sympathetic nerve activity and of the heart rate. After pretreatment with prazosin (0.1 mg kg-1, i.v.), the recovery of the sympathetic nerve activity elicited by these compounds was significantly higher. In hexamethonium (10 mg kg-1, i.v.) pretreated rats, these five drugs induced dose-related hypertension which was reduced by pretreatment with prazosin (0.1 mg kg-1, i.v.). 4. Our results indicate that the putative alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonists idazoxan, methoxy-idazoxan, BRL44408, atipamezole and fluparoxan also have a peripheral hypertensive effect which is mediated through activation of vascular alpha 1-adrenoceptors; this property of the compounds may be partly responsible for the reversal of the hypotensive action of clonidine. Considering the structure and the affinities of the drugs tested, our data indirectly suggest that alpha 2A-adrenoceptors may be implicated in the central sympatho-inhibitory effects of clonidine.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blaxall H. S., Murphy T. J., Baker J. C., Ray C., Bylund D. B. Characterization of the alpha-2C adrenergic receptor subtype in the opossum kidney and in the OK cell line. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Oct;259(1):323–329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borkowski K. R., Finch L. A comparison of the cardiovascular effects of centrally administered clonidine and adrenaline in the anaesthetized rat. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1979 Jan;31(1):16–19. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1979.tb13413.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bousquet P., Feldman J., Bloch R., Schwartz J. The nucleus reticularis lateralis: a region highly sensitive to clonidine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Jan 29;69(3):389–392. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90490-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bousquet P., Feldman J., Schwartz J. Central cardiovascular effects of alpha adrenergic drugs: differences between catecholamines and imidazolines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1984 Jul;230(1):232–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown C. M., MacKinnon A. C., McGrath J. C., Spedding M., Kilpatrick A. T. Alpha 2-adrenoceptor subtypes and imidazoline-like binding sites in the rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Apr;99(4):803–809. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1990.tb13010.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B., Eikenberg D. C., Hieble J. P., Langer S. Z., Lefkowitz R. J., Minneman K. P., Molinoff P. B., Ruffolo R. R., Jr, Trendelenburg U. International Union of Pharmacology nomenclature of adrenoceptors. Pharmacol Rev. 1994 Jun;46(2):121–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B. Heterogeneity of alpha-2 adrenergic receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1985 May;22(5):835–843. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(85)90536-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bylund D. B., Ray-Prenger C., Murphy T. J. Alpha-2A and alpha-2B adrenergic receptor subtypes: antagonist binding in tissues and cell lines containing only one subtype. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1988 May;245(2):600–607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doxey J. C., Roach A. G., Smith C. F. Studies on RX 781094: a selective, potent and specific antagonist of alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Mar;78(3):489–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb08809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew G. M. Effects of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists on pre- and postsynaptically located alpha-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1976 Apr;36(2):313–320. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(76)90084-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernsberger P., Giuliano R., Willette R. N., Granata A. R., Reis D. J. Hypotensive action of clonidine analogues correlates with binding affinity at imidazole and not alpha-2-adrenergic receptors in the rostral ventrolateral medulla. J Hypertens Suppl. 1988 Dec;6(4):S554–S557. doi: 10.1097/00004872-198812040-00174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernsberger P., Giuliano R., Willette R. N., Reis D. J. Role of imidazole receptors in the vasodepressor response to clonidine analogs in the rostral ventrolateral medulla. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Apr;253(1):408–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernsberger P., Meeley M. P., Mann J. J., Reis D. J. Clonidine binds to imidazole binding sites as well as alpha 2-adrenoceptors in the ventrolateral medulla. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jan 28;134(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90125-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutkind J. S., Kazanietz M., Enero M. A. Cardiovascular effects of alpha-adrenergic drugs: differences between clonidine and guanabenz. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;332(4):370–375. doi: 10.1007/BF00500089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guyenet P. G., Stornetta R. L., Riley T., Norton F. R., Rosin D. L., Lynch K. R. Alpha 2A-adrenergic receptors are present in lower brainstem catecholaminergic and serotonergic neurons innervating spinal cord. Brain Res. 1994 Feb 28;638(1-2):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(94)90661-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton C. A., Reid J. L., Yakubu M. A. [3H]yohimbine and [3H]idazoxan bind to different sites on rabbit forebrain and kidney membranes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Feb 9;146(2-3):345–348. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90314-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison J. K., D'Angelo D. D., Zeng D. W., Lynch K. R. Pharmacological characterization of rat alpha 2-adrenergic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Sep;40(3):407–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieble J. P., Kolpak D. C. Mediation of the hypotensive action of systemic clonidine in the rat by alpha 2-adrenoceptors. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;110(4):1635–1639. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb14012.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langin D., Lafontan M., Stillings M. R., Paris H. [3H]RX821002: a new tool for the identification of alpha 2A-adrenoceptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Aug 11;167(1):95–104. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90751-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langin D., Paris H., Lafontan M. Binding of [3H]idazoxan and of its methoxy derivative [3H] RX821002 in human fat cells: [3H]idazoxan but not [3H] RX821002 labels additional non-alpha 2-adrenergic binding sites. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Jun;37(6):876–885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laubie M., Delbarre B., Bogaievsky D., Bogaievsky Y., Tsoucaris-Kupfer D., Senon D., Schmitt H., Schmitt H. Pharmacological evidence for a central alpha-sympathomimetic mechanism controlling blood pressure and heart rate. Circ Res. 1976 Jun;38(6 Suppl 2):35–41. doi: 10.1161/01.res.38.6.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link R., Daunt D., Barsh G., Chruscinski A., Kobilka B. Cloning of two mouse genes encoding alpha 2-adrenergic receptor subtypes and identification of a single amino acid in the mouse alpha 2-C10 homolog responsible for an interspecies variation in antagonist binding. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Jul;42(1):16–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallard N. J., Hudson A. L., Nutt D. J. Characterization and autoradiographical localization of non-adrenoceptor idazoxan binding sites in the rat brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Aug;106(4):1019–1027. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14450.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Ernsberger P. Keeping an eye on the I site: imidazoline-preferring receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1992 Oct;13(10):369–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Insel P. A. Are there multiple imidazoline binding sites? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1989 Sep;10(9):342–344. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(89)90002-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosin D. L., Zeng D., Stornetta R. L., Norton F. R., Riley T., Okusa M. D., Guyenet P. G., Lynch K. R. Immunohistochemical localization of alpha 2A-adrenergic receptors in catecholaminergic and other brainstem neurons in the rat. Neuroscience. 1993 Sep;56(1):139–155. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90569-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt H., Fénard S. Action of -adrenergic blocking drugs on the sympathetic centres and their interactions with the central sympatho-inhibitory effect of clonidine. Arzneimittelforschung. 1973 Jan;23(1):40–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepperson N. B., Duval N., Massingham R., Langer S. Z. Pre- and postsynaptic alpha adrenoceptor selectivity studies with yohimbine and its two diastereoisomers rauwolscine and corynanthine in the anesthetized dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Nov;219(2):540–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun M. K., Guyenet P. G. Effect of clonidine and gamma-aminobutyric acid on the discharges of medullo-spinal sympathoexcitatory neurons in the rat. Brain Res. 1986 Mar 12;368(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmermans P. B., Schoop A. M., Kwa H. Y., Van Zwieten P. A. Characterization of alpha-adrenoceptors participating in the central hypotensive and sedative effects of clonidine using yohimbine, rauwolscine and corynanthine. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Mar 5;70(1):7–15. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90426-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlén S., Wikberg J. E. Delineation of three pharmacological subtypes of alpha 2-adrenoceptor in the rat kidney. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;104(3):657–664. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12485.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlén S., Xia Y., Chhajlani V., Felder C. C., Wikberg J. E. [3H]-MK 912 binding delineates two alpha 2-adrenoceptor subtypes in rat CNS one of which is identical with the cloned pA2d alpha 2-adrenoceptor. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Aug;106(4):986–995. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb14446.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vayssettes-Courchay C., Bouysset F., Verbeuren T. J., Laubie M., Schmitt H. The cardiovascular effects of quipazine are mediated by peripheral 5-HT2 and 5-HT3 receptors in anaesthetized rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1990 Aug 2;184(1):75–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(90)90668-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vayssettes-Courchay C., offysset F., Verbeuren T. J., Laubie M. Role of the lateral tegmental field in the central sympatho-inhibitory effect of 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin in the cat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 May 12;236(1):121–130. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90234-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikberg J. E. High affinity binding of idazoxan to a non-catecholaminergic binding site in the central nervous system: description of a putative idazoxan-receptor. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1989 Jan;64(1):152–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1989.tb00620.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wikberg J. E., Uhlén S., Chhajlani V. Medetomidine stereoisomers delineate two closely related subtypes of idazoxan (imidazoline) I-receptors in the guinea pig. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Feb 14;193(3):335–340. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90148-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young P., Berge J., Chapman H., Cawthorne M. A. Novel alpha 2-adrenoceptor antagonists show selectivity for alpha 2A- and alpha 2B-adrenoceptor subtypes. Eur J Pharmacol. 1989 Sep 22;168(3):381–386. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(89)90801-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


