Abstract
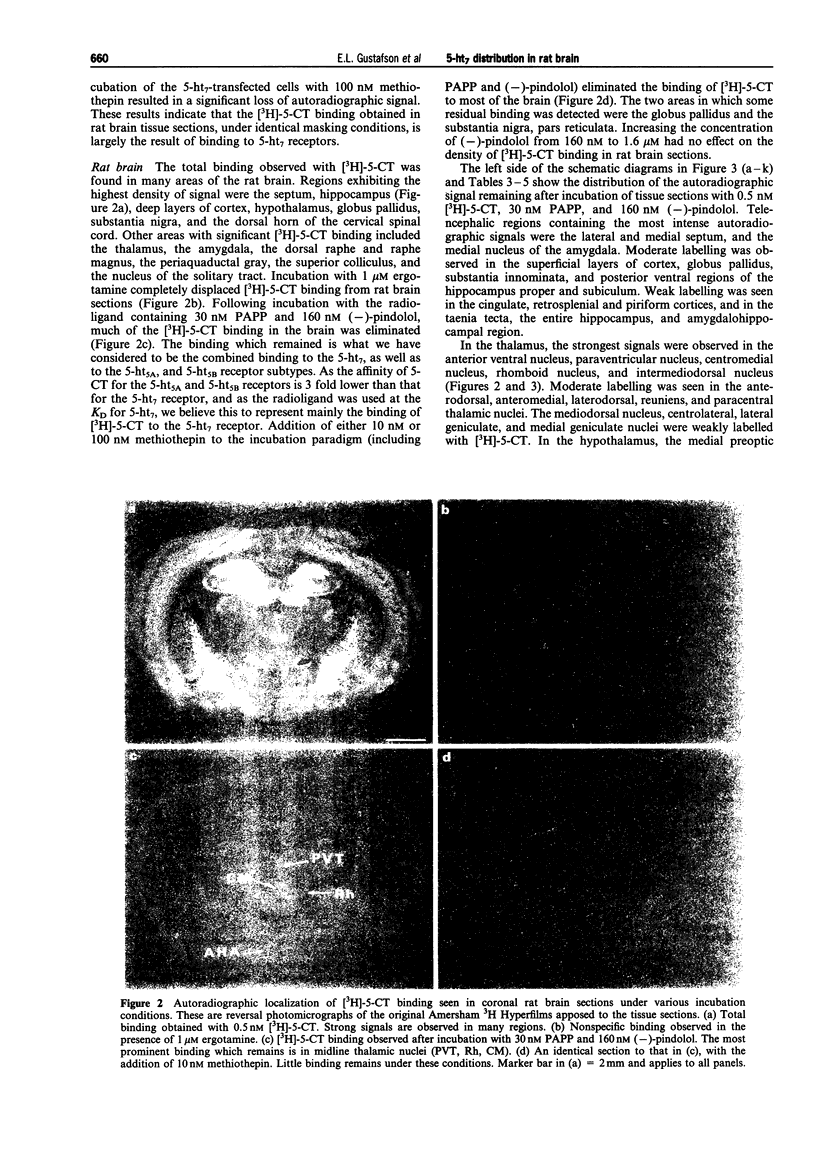
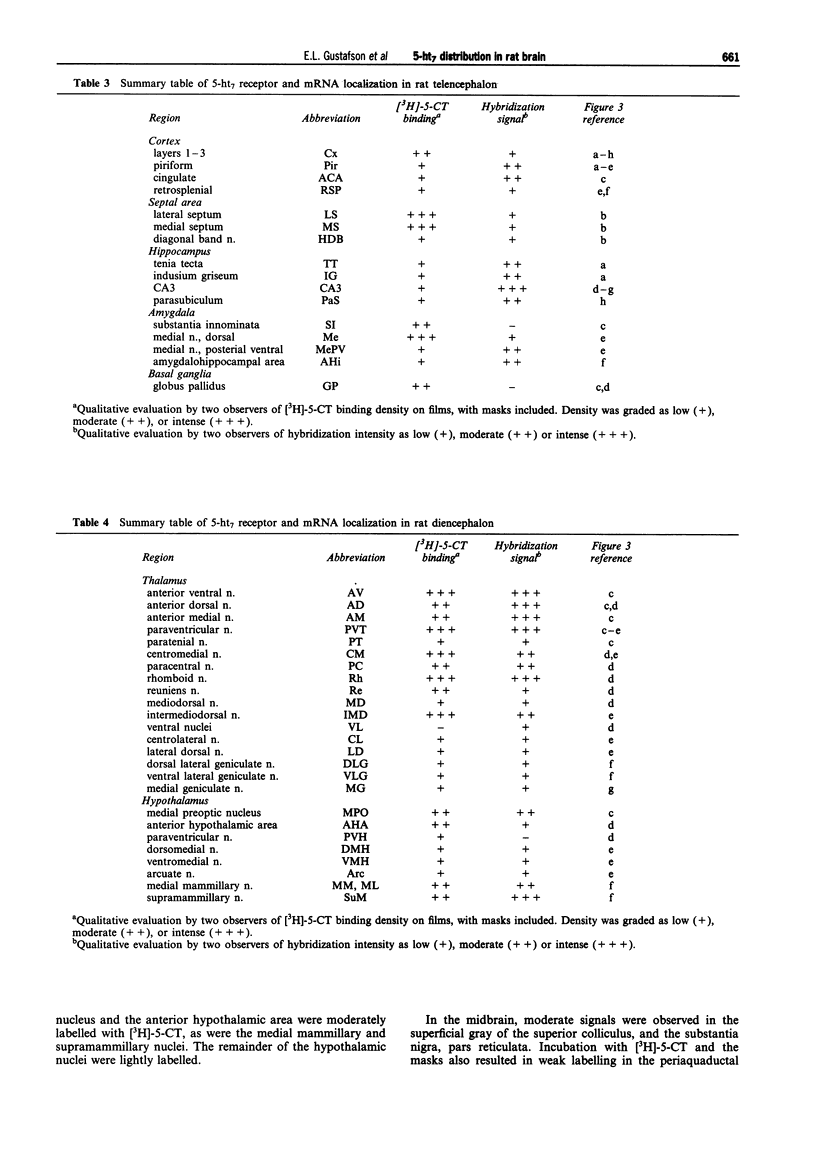
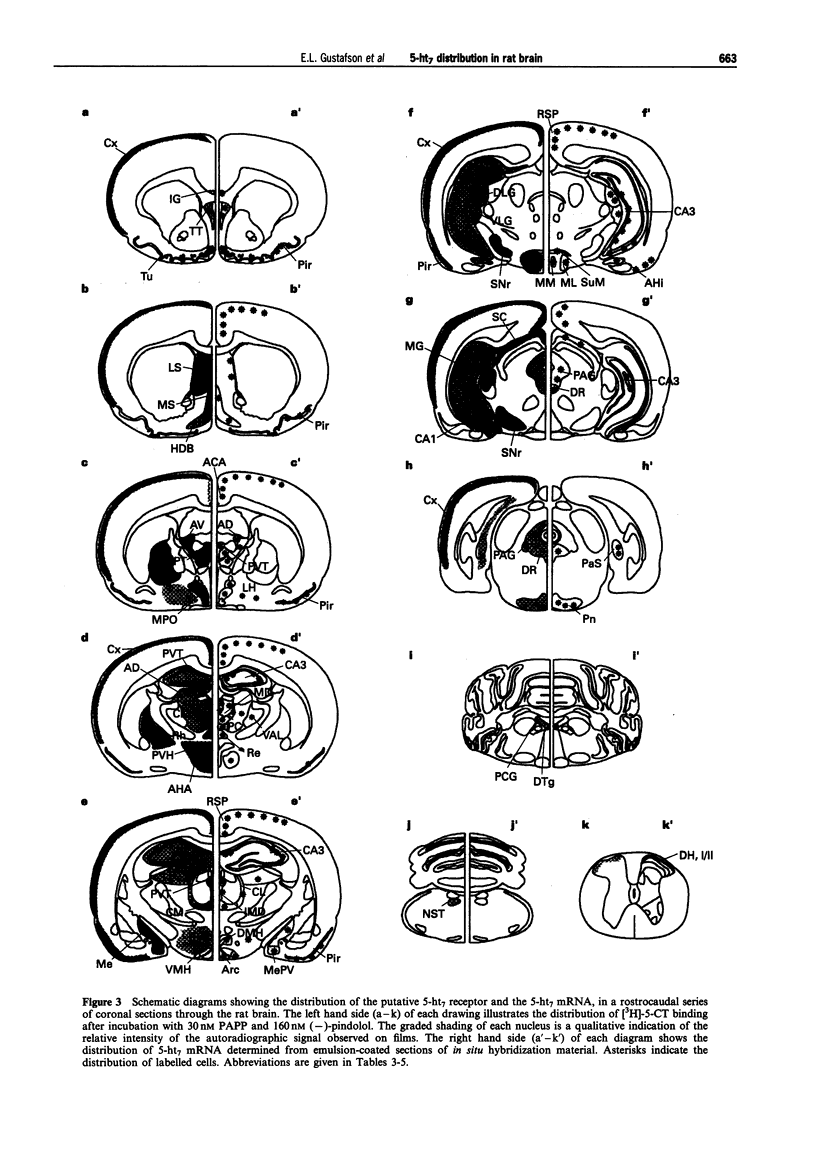
1. Receptor autoradiography and in situ hybridization histochemistry have been used to delineate the distribution of the 5-ht7 receptor and its mRNA in rat brain. Receptor autoradiographic studies were performed using [3H]-5-carboxamidotryptamine (5-CT) as the radioligand. The binding characteristics of the masking compounds were determined in Cos-7 cells transfected with a panel of 5-HT receptor subtype cDNAs, including the rat 5-ht7 cDNA. In situ hybridization studies were carried out with 35S-labelled oligonucleotide probes to the rat 5-ht7 mRNA. 2. Specific binding of [3H]-5-CT was observed in many areas of the rat brain. Following co-incubation with 1 microM ergotamine, this binding was completely eliminated. After addition of the masking ligands, [3H]-5-CT binding remained in layers 1-3 of cortex, septum, globus pallidus, thalamus, hypothalamus, centromedial amygdala, substantia nigra, periaquaductal gray, and superior colliculus. Addition of the antagonist, methiothepin, to the incubation regimen eliminated most of the remaining [3H]-5-CT binding in the brain, with the exception of the globus pallidus and substantia nigra. 3. The 5-ht7 mRNA was discretely localized in rat brain. The most intense hybridization signals were observed over the thalamus, the anterior hippocampal rudiment, and over the CA3 region of the hippocampus. Other regions containing hybridization signals included the septum, the hypothalamus, the centromedial amygdala and the periaquaductal gray. The regions exhibiting a modest receptor binding signal after methiothepin incubation, the globus pallidus and the substantia nigra, contained no 5-ht7 hybridization signals, suggesting a non-5-ht7 subtype in these two related structures. 4. The distribution of the 5-ht7 receptor and its mRNA is suggestive of multiple roles for this novel 5-HT receptor, within several brain systems. The limbic system (centromedial amygdala, anterior hippocampal rudiment, hypothalamus) is particularly well-represented, indicating a potential role for the 5-ht7 receptor in affective processes.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adham N., Ellerbrock B., Hartig P., Weinshank R. L., Branchek T. Receptor reserve masks partial agonist activity of drugs in a cloned rat 5-hydroxytryptamine1B receptor expression system. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;43(3):427–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach A. W., Unger L., Sprengel R., Mengod G., Palacios J., Seeburg P. H., Voigt M. M. Structure functional expression and spatial distribution of a cloned cDNA encoding a rat 5-HT1D-like receptor. J Recept Res. 1993;13(1-4):479–502. doi: 10.3109/10799899309073674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bard J. A., Zgombick J., Adham N., Vaysse P., Branchek T. A., Weinshank R. L. Cloning of a novel human serotonin receptor (5-HT7) positively linked to adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 5;268(31):23422–23426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boddeke H. W., Fargin A., Raymond J. R., Schoeffter P., Hoyer D. Agonist/antagonist interactions with cloned human 5-HT1A receptors: variations in intrinsic activity studied in transfected HeLa cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;345(3):257–263. doi: 10.1007/BF00168684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boess F. G., Martin I. L. Molecular biology of 5-HT receptors. Neuropharmacology. 1994 Mar-Apr;33(3-4):275–317. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branchek T., Adham N., Macchi M., Kao H. T., Hartig P. R. [3H]-DOB(4-bromo-2,5-dimethoxyphenylisopropylamine) and [3H] ketanserin label two affinity states of the cloned human 5-hydroxytryptamine2 receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;38(5):604–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruinvels A. T., Palacios J. M., Hoyer D. Autoradiographic characterisation and localisation of 5-HT1D compared to 5-HT1B binding sites in rat brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1993 Jun;347(6):569–582. doi: 10.1007/BF00166939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerit M. B., Miquel M. C., Gozlan H., Hamon M. The GTP-insensitive component of high-affinity [3H]8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin binding in the rat hippocampus corresponds to an oxidized state of the 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor. J Neurochem. 1991 May;56(5):1705–1716. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb02071.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlander M. G., Lovenberg T. W., Baron B. M., de Lecea L., Danielson P. E., Racke M., Slone A. L., Siegel B. W., Foye P. E., Cannon K. Two members of a distinct subfamily of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors differentially expressed in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3452–3456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara Y., Tomita H., Hikiji M., Kashihara K., Otsuki S., Ohnuki T., Hamagishi Y., Oki T., Sora I., Roeske W. R. Characterization of a cloned rat serotonin 5-HT1A receptor expressed in the HeLa cell line. Life Sci. 1993;52(11):949–958. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(93)90530-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer D., Clarke D. E., Fozard J. R., Hartig P. R., Martin G. R., Mylecharane E. J., Saxena P. R., Humphrey P. P. International Union of Pharmacology classification of receptors for 5-hydroxytryptamine (Serotonin). Pharmacol Rev. 1994 Jun;46(2):157–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S. T., Shibata S. Neurochemical organization of circadian rhythm in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Neurosci Res. 1994 Aug;20(2):109–130. doi: 10.1016/0168-0102(94)90029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawahara F., Saito H., Katsuki H. Inhibition by 5-HT7 receptor stimulation of GABAA receptor-activated current in cultured rat suprachiasmatic neurones. J Physiol. 1994 Jul 1;478(Pt 1):67–73. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovenberg T. W., Baron B. M., de Lecea L., Miller J. D., Prosser R. A., Rea M. A., Foye P. E., Racke M., Slone A. L., Siegel B. W. A novel adenylyl cyclase-activating serotonin receptor (5-HT7) implicated in the regulation of mammalian circadian rhythms. Neuron. 1993 Sep;11(3):449–458. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90149-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthes H., Boschert U., Amlaiky N., Grailhe R., Plassat J. L., Muscatelli F., Mattei M. G., Hen R. Mouse 5-hydroxytryptamine5A and 5-hydroxytryptamine5B receptors define a new family of serotonin receptors: cloning, functional expression, and chromosomal localization. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Mar;43(3):313–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medanic M., Gillette M. U. Serotonin regulates the phase of the rat suprachiasmatic circadian pacemaker in vitro only during the subjective day. J Physiol. 1992 May;450:629–642. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerhof W., Obermüller F., Fehr S., Richter D. A novel rat serotonin receptor: primary structure, pharmacology, and expression pattern in distinct brain regions. DNA Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;12(5):401–409. doi: 10.1089/dna.1993.12.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. Y. Organization and function of a central nervous system circadian oscillator: the suprachiasmatic hypothalamic nucleus. Fed Proc. 1983 Aug;42(11):2783–2789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morin L. P., Michels K. M., Smale L., Moore R. Y. Serotonin regulation of circadian rhythmicity. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;600:418–426. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb16898.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C. S., Cone R. D., Robbins L. S., Allen C. N., Adelman J. P. Cloning and expression of a 5HT7 receptor from Xenopus laevis. Receptors Channels. 1995;3(1):61–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peroutka S. J. Phylogenetic tree analysis of G protein-coupled 5-HT receptors: implications for receptor nomenclature. Neuropharmacology. 1992 Jul;31(7):609–613. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(92)90138-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plassat J. L., Amlaiky N., Hen R. Molecular cloning of a mammalian serotonin receptor that activates adenylate cyclase. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Aug;44(2):229–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prosser R. A., Miller J. D., Heller H. C. A serotonin agonist phase-shifts the circadian clock in the suprachiasmatic nuclei in vitro. Brain Res. 1990 Nov 26;534(1-2):336–339. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90153-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ransom R. W., Asarch K. B., Shih J. C. [3H]1-[2-(4-aminophenyl)ethyl]-4-(3-trifluoromethylphenyl)piperazine: a selective radioligand for 5-HT1A receptors in rat brain. J Neurochem. 1986 Jan;46(1):68–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb12926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roca A. L., Weaver D. R., Reppert S. M. Serotonin receptor gene expression in the rat suprachiasmatic nuclei. Brain Res. 1993 Apr 9;608(1):159–165. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90789-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth B. L., Craigo S. C., Choudhary M. S., Uluer A., Monsma F. J., Jr, Shen Y., Meltzer H. Y., Sibley D. R. Binding of typical and atypical antipsychotic agents to 5-hydroxytryptamine-6 and 5-hydroxytryptamine-7 receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1994 Mar;268(3):1403–1410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruat M., Traiffort E., Leurs R., Tardivel-Lacombe J., Diaz J., Arrang J. M., Schwartz J. C. Molecular cloning, characterization, and localization of a high-affinity serotonin receptor (5-HT7) activating cAMP formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8547–8551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saudou F., Hen R. 5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor subtypes in vertebrates and invertebrates. Neurochem Int. 1994 Dec;25(6):503–532. doi: 10.1016/0197-0186(94)90150-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen Y., Monsma F. J., Jr, Metcalf M. A., Jose P. A., Hamblin M. W., Sibley D. R. Molecular cloning and expression of a 5-hydroxytryptamine7 serotonin receptor subtype. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 25;268(24):18200–18204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleight A. J., Carolo C., Petit N., Zwingelstein C., Bourson A. Identification of 5-hydroxytryptamine7 receptor binding sites in rat hypothalamus: sensitivity to chronic antidepressant treatment. Mol Pharmacol. 1995 Jan;47(1):99–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- To Z. P., Bonhaus D. W., Eglen R. M., Jakeman L. B. Characterization and distribution of putative 5-ht7 receptors in guinea-pig brain. Br J Pharmacol. 1995 May;115(1):107–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1995.tb16327.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsou A. P., Kosaka A., Bach C., Zuppan P., Yee C., Tom L., Alvarez R., Ramsey S., Bonhaus D. W., Stefanich E. Cloning and expression of a 5-hydroxytryptamine7 receptor positively coupled to adenylyl cyclase. J Neurochem. 1994 Aug;63(2):456–464. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1994.63020456.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voigt M. M., Laurie D. J., Seeburg P. H., Bach A. Molecular cloning and characterization of a rat brain cDNA encoding a 5-hydroxytryptamine1B receptor. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4017–4023. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04977.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waeber C., Moskowitz M. A. Autoradiographic visualisation of [3H]5-carboxamidotryptamine binding sites in the guinea pig and rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1995 Sep 5;283(1-3):31–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(95)00275-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisden W., Parker E. M., Mahle C. D., Grisel D. A., Nowak H. P., Yocca F. D., Felder C. C., Seeburg P. H., Voigt M. M. Cloning and characterization of the rat 5-HT5B receptor. Evidence that the 5-HT5B receptor couples to a G protein in mammalian cell membranes. FEBS Lett. 1993 Oct 25;333(1-2):25–31. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80368-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zgombick J. M., Weinshank R. L., Macchi M., Schechter L. E., Branchek T. A., Hartig P. R. Expression and pharmacological characterization of a canine 5-hydroxytryptamine1D receptor subtype. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Dec;40(6):1036–1042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]