Abstract
1. The effects of 5-HT1A antagonists on guinea-pig behaviour and dorsal raphe neuronal activity were investigated. 2. WAY100135 (10 mg kg-1, s.c.) and WAY100635 (1 mg kg-1, s.c.) significantly reduced the behaviours induced by 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino) tetralin (8-OHDPAT) (1 mg kg-1, s.c.) indicative of post-synaptic 5-HT1A receptor antagonism. WAY100635 (10 mg kg-1, s.c.) alone induced ear twitches, which were antagonized by ketanserin (1 mg kg-1, s.c.), but no other overt behaviours. 3. WAY100635 (0.125 mg kg-1, i.v.) produced a right-ward shift in the dose-related inhibition of neuronal firing by 8-OHDPAT (5-100 micrograms kg-1, i.v.) but did not affect the maximum inhibition induced by 8-OHDPAT indicating competitive antagonism between 8-OHDPAT and WAY100635 at the 5-HT1A somato-dendritic autoreceptor in the dorsal raphe nucleus of the guinea-pig. WAY100635 also produced a dose-related increase in the basal firing of 5-HT neurones in the dorsal raphe nucleus and restored the firing of dorsal raphe neurones previously inhibited by 8-OHDPAT (10 micrograms kg-1, i.v.). 4. The results indicate that WAY100635 is a competitive 5-HT1A antagonist in the guinea-pig. Furthermore WAY100635 can increase 5-HT neuronal firing, suggesting that it blocks a 5-HT1A receptor-mediated inhibitory tone acting on guinea-pig 5-HT neurones resulting in increased 5-HT release and 5-HT2 receptor-mediated behaviours.
Full text
PDF

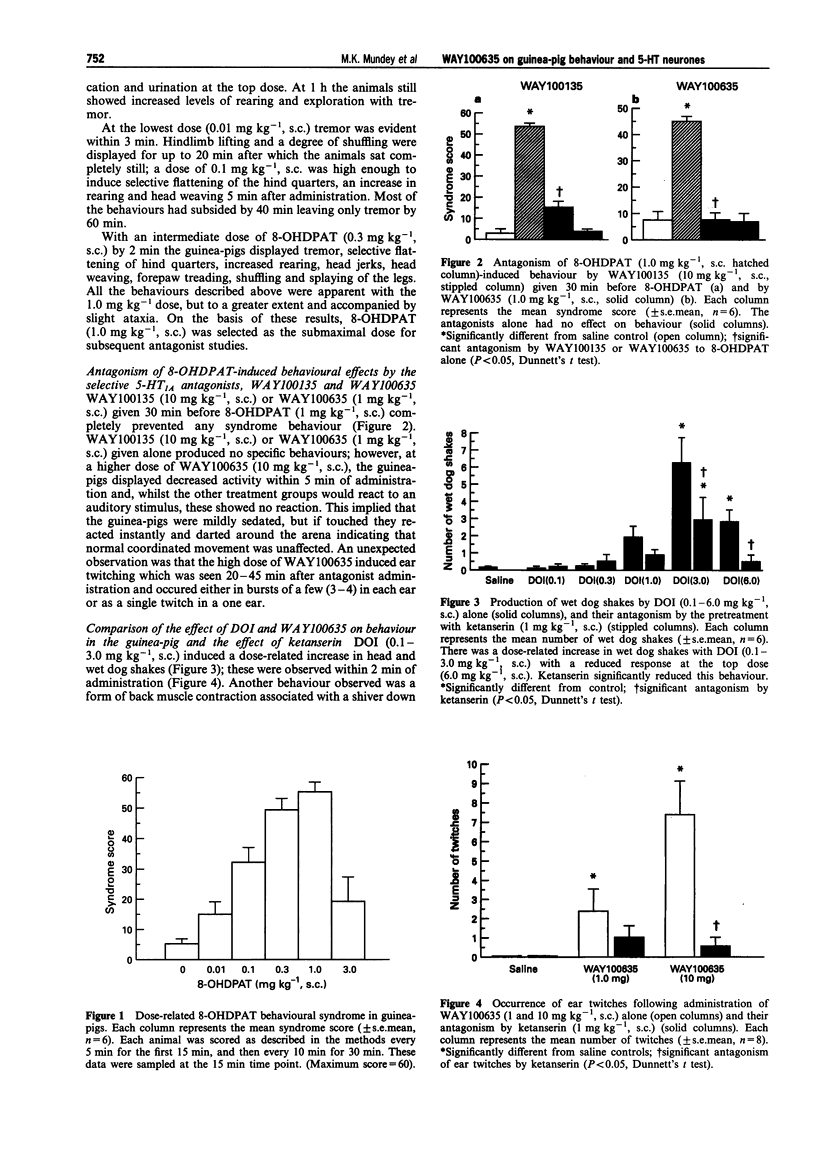
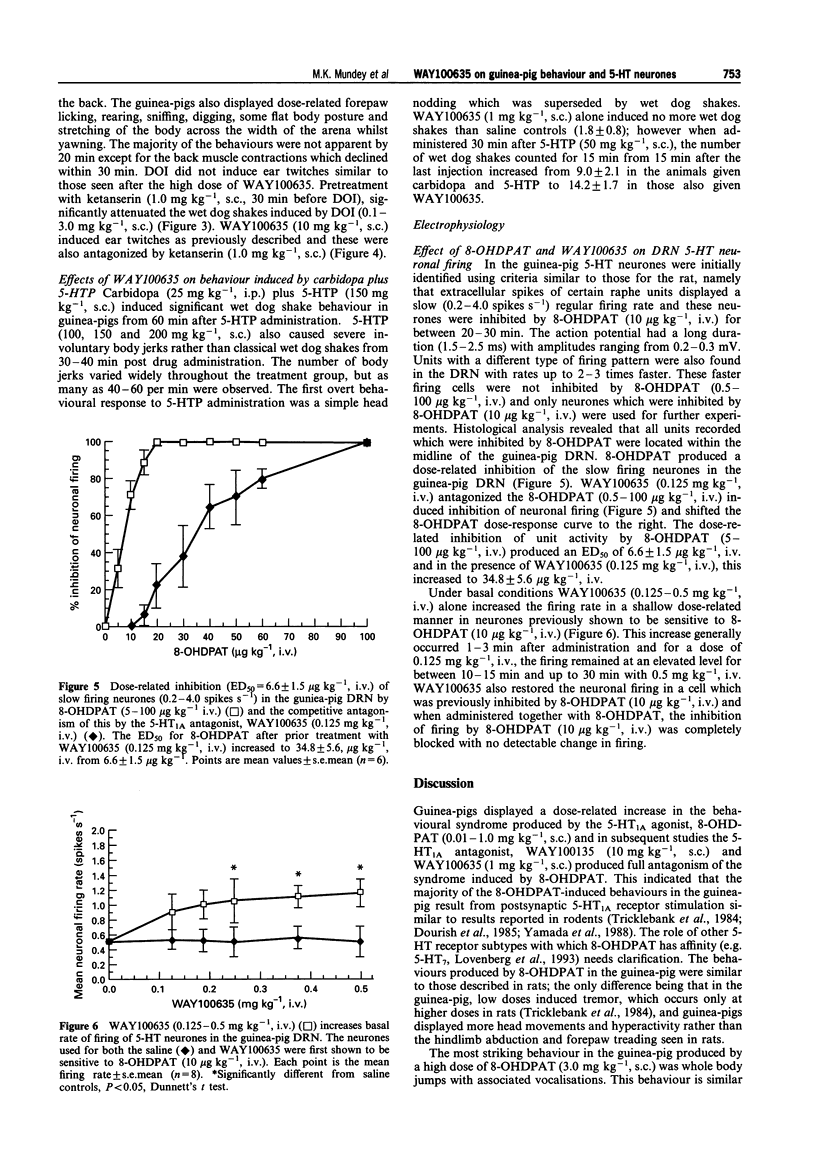



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvidsson L. E., Hacksell U., Nilsson J. L., Hjorth S., Carlsson A., Lindberg P., Sanchez D., Wikstrom H. 8-Hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin, a new centrally acting 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor agonist. J Med Chem. 1981 Aug;24(8):921–923. doi: 10.1021/jm00140a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter G., Kennett G., Blaney F., Blackburn T. 5-HT2 receptor subtypes: a family re-united? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1995 Mar;16(3):105–110. doi: 10.1016/s0165-6147(00)88991-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedard P., Pycock C. J. "Wet-dog" shake behaviour in the rat: a possible quantitative model of central 5-hydroxytryptamine activity. Neuropharmacology. 1977 Oct;16(10):663–670. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(77)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björk L., Cornfield L. J., Nelson D. L., Hillver S. E., Andén N. E., Lewander T., Hacksell U. Pharmacology of the novel 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor antagonist (S)-5-fluoro-8-hydroxy-2-(dipropylamino)tetralin: inhibition of (R)-8-hydroxy-2-(dipropylamino)tetralin-induced effects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1991 Jul 1;258(1):58–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deakin J. F., Green A. R. The effects of putative 5-hydroxytryptamine antagonists on the behaviour produced by administration of tranylcypromine and L-tryptophan or tranylcypromine and L-DOPA to rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1978 Oct;64(2):201–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1978.tb17290.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dourish C. T., Hutson P. H., Curzon G. Characteristics of feeding induced by the serotonin agonist 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino) tetralin (8-OH-DPAT). Brain Res Bull. 1985 Oct;15(4):377–384. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(85)90005-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher A., Bill D. J., Bill S. J., Cliffe I. A., Dover G. M., Forster E. A., Haskins J. T., Jones D., Mansell H. L., Reilly Y. WAY100135: a novel, selective antagonist at presynaptic and postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1993 Jun 24;237(2-3):283–291. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(93)90280-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fone K. C., Robinson A. J., Marsden C. A. Characterization of the 5-HT receptor subtypes involved in the motor behaviours produced by intrathecal administration of 5-HT agonists in rats. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Jun;103(2):1547–1555. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb09825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grahame-Smith D. G. Inhibitory effect of chlorpromazine on the syndrome of hyperactivity produced by L-tryptophan or 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine in rats treated with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor. Br J Pharmacol. 1971 Dec;43(4):856–864. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1971.tb07222.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grahame-Smith D. G. Studies in vivo on the relationship between brain tryptophan, brain 5-HT synthesis and hyperactivity in rats treated with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor and L-tryptophan. J Neurochem. 1971 Jun;18(6):1053–1066. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1971.tb12034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A. R., Hall J. E., Rees A. R. A behavioural and biochemical study in rats of 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor agonists and antagonists, with observations on structure-activity requirements for the agonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1981 Jul;73(3):703–719. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1981.tb16806.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green A. R., Tordoff A. F., Bloomfield M. R. Elevation of brain GABA concentrations with amino-oxyacetic acid; effect on the hyperactivity syndrome produced by increased 5-hydroxytryptamine synthesis in rats. J Neural Transm. 1976;39(1-2):103–112. doi: 10.1007/BF01248769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESS S. M., DOEPFNER W. Behavioral effects and brain amine content in rats. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1961 Nov 1;134:89–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolas T., Haj-Dahmane S., Lanfumey L., Fattaccini C. M., Kidd E. J., Adrien J., Gozlan H., Guardiola-Lemaitre B., Hamon M. (-)Tertatolol is a potent antagonist at pre- and postsynaptic serotonin 5-HT1A receptors in the rat brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1993 May;347(5):453–463. doi: 10.1007/BF00166735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klawans H. L., Jr, Goetz C., Weiner W. J. 5-Hydroxytryptophan-induced myoclonus in guinea pigs and the possible role of serotonin in infantile myoclonus. Neurology. 1973 Nov;23(11):1234–1240. doi: 10.1212/wnl.23.11.1234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovenberg T. W., Baron B. M., de Lecea L., Miller J. D., Prosser R. A., Rea M. A., Foye P. E., Racke M., Slone A. L., Siegel B. W. A novel adenylyl cyclase-activating serotonin receptor (5-HT7) implicated in the regulation of mammalian circadian rhythms. Neuron. 1993 Sep;11(3):449–458. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90149-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luscombe G., Jenner P., Marsden C. D. Myoclonus in guniea pigs is induced by indole-containing but not piperazine-containing 5HT agonists. Life Sci. 1982 Apr 26;30(17):1487–1494. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90563-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luscombe G., Jenner P., Marsden C. D. Pharmacological analysis of the myoclonus induced by 5-hydroxytryptophan in the guinea pig suggests the presence of multiple 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors in the brain. Neuropharmacology. 1981 Sep;20(9):819–831. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(81)90074-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luscombe G., Jenner P., Marsden C. D. Tryptamine-induced myoclonus in guinea-pigs pretreated with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor indicates pre- and post-synaptic actions of tryptamine upon central indoleamine systems. Neuropharmacology. 1982 Dec;21(12):1257–1265. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(82)90130-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin L. L., Sanders-Bush E. Comparison of the pharmacological characteristics of 5 HT1 and 5 HT2 binding sites with those of serotonin autoreceptors which modulate serotonin release. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1982 Dec;321(3):165–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00505480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mundey M. K., Fletcher A., Marsden C. A. Effect of the putative 5-HT1A antagonists WAY100135 and SDZ 216-525 on 5-HT neuronal firing in the guinea-pig dorsal raphe nucleus. Neuropharmacology. 1994 Jan;33(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(94)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakahata N., Ishimoto H., Mizuno K., Ohizumi Y., Nakanishi H. Dual effects of mastoparan on intracellular free Ca2+ concentrations in human astrocytoma cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 May;112(1):299–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13068.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortmann R., Waldmeier P. C., Radeke E., Felner A., Delini-Stula A. The effects of 5-HT uptake- and MAO-inhibitors on L-5-HTP-induced excitation in rats. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 1980 Mar;311(2):185–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00510258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tricklebank M. D., Forler C., Fozard J. R. The involvement of subtypes of the 5-HT1 receptor and of catecholaminergic systems in the behavioural response to 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Nov 13;106(2):271–282. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90714-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trulson M. E., Jacobs B. L. Dose-response relationships between systemically administered L-tryptophan or L-5-hydroxytryptophan and raphe unit activity in the rat. Neuropharmacology. 1976 Jun;15(6):339–344. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(76)90080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkman P. H., Lorens S. A., Kindel G. H., Ginos J. Z. L-5-Hydroxytryptophan-induced myoclonus in guinea pigs: a model for the study of central serotonin-dopamine interactions. Neuropharmacology. 1978 Nov;17(11):947–955. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(78)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh N. J., Shankley N. P., Black J. W. Comparative analysis of the vagal stimulation of gastric acid secretion in rodent isolated stomach preparations. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 May;112(1):93–96. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb13035.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada J., Sugimoto Y., Horisaka K. The behavioural effects of 8-hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)tetralin (8-OH-DPAT) in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Sep 23;154(3):299–304. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90205-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



