Abstract
1. The interaction between N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) and NK1 tachykinin receptors was analyzed isobolographically in rats with inflammatory hyperalgesia induced by intraplantar injection of complete Freund's adjuvant-saline emulsion (CFA, 100 micrograms Mycobacterium tuberculosis). 2. Thermal hyperalgesia of the inflamed paw, determined by paw withdrawal response to a heat stimulus, was dose-dependently attenuated by intrathecal administration of an NMDA receptor antagonist, dextrorphan (2.5-40 micrograms, ED50 = 7.2 micrograms), and two NK1 tachykinin receptor antagonists, WIN 51,708 (0.01-200 micrograms, ED50 = 10.4 micrograms) or CP-96,345 (5-200 micrograms, ED50 = 82.1 micrograms). There was no effect of these agents on the nociceptive threshold of the non-inflamed paw. CP-96,344, an enantiomer of CP-96,345 that is inactive as an NK1 tachykinin receptor antagonist, slightly attenuated hyperalgesia at a dose of 200 micrograms. 3. Combinations of dextrorphan and WIN 51,708 were administered at fixed ratios (10%:90%; 41%:59%; 90%:10%). Isobolographic analysis revealed that the ED50s obtained from the three combination ratios were not significantly different from those that were expected from a simple additive effect. 4. Thus, an additive interaction was demonstrated between NMDA and NK1 tachykinin receptor systems at the spinal level. These results suggest that both NMDA and NK1 tachykinin receptors are activated in response to peripheral inflammation, but that they may contribute independently to development of hyperalgesia.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aanonsen L. M., Wilcox G. L. Nociceptive action of excitatory amino acids in the mouse: effects of spinally administered opioids, phencyclidine and sigma agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Oct;243(1):9–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aanonsen L. M., Wilcox G. L. Phencyclidine selectively blocks a spinal action of N-methyl-D-aspartate in mice. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Jun 18;67(2):191–197. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90396-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams J. U., Tallarida R. J., Geller E. B., Adler M. W. Isobolographic superadditivity between delta and mu opioid agonists in the rat depends on the ratio of compounds, the mu agonist and the analgesic assay used. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1993 Sep;266(3):1261–1267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appell K. C., Fragale B. J., Loscig J., Singh S., Tomczuk B. E. Antagonists that demonstrate species differences in neurokinin-1 receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Apr;41(4):772–778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battaglia G., Rustioni A. Coexistence of glutamate and substance P in dorsal root ganglion neurons of the rat and monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Nov 8;277(2):302–312. doi: 10.1002/cne.902770210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beresford I. J., Birch P. J., Hagan R. M., Ireland S. J. Investigation into species variants in tachykinin NK1 receptors by use of the non-peptide antagonist, CP-96,345. Br J Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;104(2):292–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12423.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birch P. J., Harrison S. M., Hayes A. G., Rogers H., Tyers M. B. The non-peptide NK1 receptor antagonist, (+/-)-CP-96,345, produces antinociceptive and anti-oedema effects in the rat. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;105(3):508–510. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb09008.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caudle R. M., Williams G. M. The misuse of analysis of variance to detect synergy in combination drug studies. Pain. 1993 Dec;55(3):313–317. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(93)90006-B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman V., Dickenson A. H. The effect of intrathecal administration of RP67580, a potent neurokinin 1 antagonist on nociceptive transmission in the rat spinal cord. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Jul 23;157(2):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90724-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church J., Lodge D., Berry S. C. Differential effects of dextrorphan and levorphanol on the excitation of rat spinal neurons by amino acids. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 May 8;111(2):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90755-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coderre T. J., Melzack R. Central neural mediators of secondary hyperalgesia following heat injury in rats: neuropeptides and excitatory amino acids. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Sep 30;131(1):71–74. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90339-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Biasi S., Rustioni A. Glutamate and substance P coexist in primary afferent terminals in the superficial laminae of spinal cord. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(20):7820–7824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.20.7820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Koninck Y., Henry J. L. Substance P-mediated slow excitatory postsynaptic potential elicited in dorsal horn neurons in vivo by noxious stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11344–11348. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty P. M., Willis W. D. Enhancement of spinothalamic neuron responses to chemical and mechanical stimuli following combined micro-iontophoretic application of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid and substance P. Pain. 1991 Oct;47(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(91)90015-P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garces Y. I., Rabito S. F., Minshall R. D., Sagen J. Lack of potent antinociceptive activity by substance P antagonist CP-96,345 in the rat spinal cord. Life Sci. 1993;52(4):353–360. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(93)90148-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garret C., Carruette A., Fardin V., Moussaoui S., Peyronel J. F., Blanchard J. C., Laduron P. M. Pharmacological properties of a potent and selective nonpeptide substance P antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10208–10212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guard S., Boyle S. J., Tang K. W., Watling K. J., McKnight A. T., Woodruff G. N. The interaction of the NK1 receptor antagonist CP-96,345 with L-type calcium channels and its functional consequences. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Sep;110(1):385–391. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13821.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haley J. E., Sullivan A. F., Dickenson A. H. Evidence for spinal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor involvement in prolonged chemical nociception in the rat. Brain Res. 1990 Jun 4;518(1-2):218–226. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90975-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargreaves K., Dubner R., Brown F., Flores C., Joris J. A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain. 1988 Jan;32(1):77–88. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(88)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henley J. M., Jenkins R., Hunt S. P. Localisation of glutamate receptor binding sites and mRNAs to the dorsal horn of the rat spinal cord. Neuropharmacology. 1993 Jan;32(1):37–41. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(93)90127-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey A. D., Krause J. E. Molecular characterization of a functional cDNA encoding the rat substance P receptor. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):958–962. doi: 10.1126/science.2154852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylden J. L., Nahin R. L., Traub R. J., Dubner R. Expansion of receptive fields of spinal lamina I projection neurons in rats with unilateral adjuvant-induced inflammation: the contribution of dorsal horn mechanisms. Pain. 1989 May;37(2):229–243. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(89)90135-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylden J. L., Thomas D. A., Iadarola M. J., Nahin R. L., Dubner R. Spinal opioid analgesic effects are enhanced in a model of unilateral inflammation/hyperalgesia: possible involvement of noradrenergic mechanisms. Eur J Pharmacol. 1991 Mar 5;194(2-3):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(91)90097-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylden J. L., Wilcox G. L. Pharmacological characterization of substance P-induced nociception in mice: modulation by opioid and noradrenergic agonists at the spinal level. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Aug;226(2):398–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
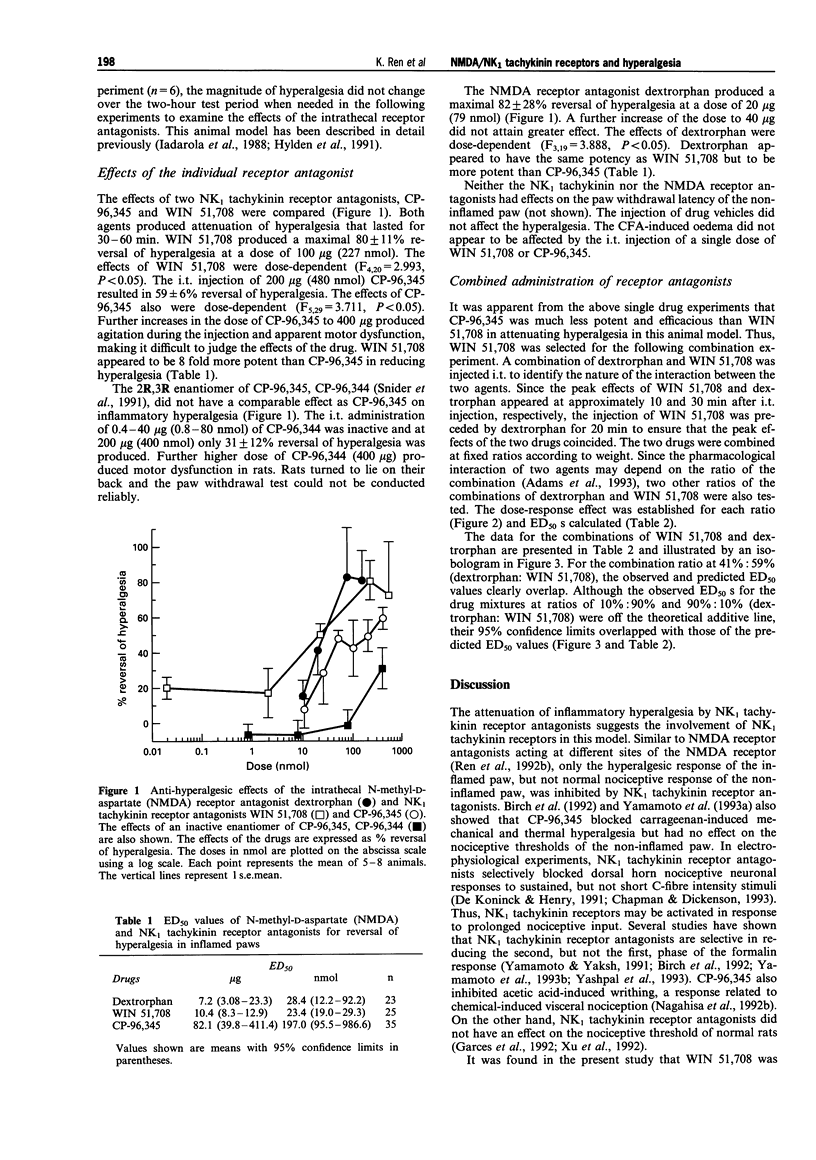
- Iadarola M. J., Brady L. S., Draisci G., Dubner R. Enhancement of dynorphin gene expression in spinal cord following experimental inflammation: stimulus specificity, behavioral parameters and opioid receptor binding. Pain. 1988 Dec;35(3):313–326. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(88)90141-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J., Price D. D., Hayes R. L., Lu J., Mayer D. J., Frenk H. Intrathecal treatment with dextrorphan or ketamine potently reduces pain-related behaviors in a rat model of peripheral mononeuropathy. Brain Res. 1993 Mar 5;605(1):164–168. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)91368-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarson K. E., Krause J. E. NK-1 and NK-3 type tachykinin receptor mRNA expression in the rat spinal cord dorsal horn is increased during adjuvant or formalin-induced nociception. J Neurosci. 1994 Feb;14(2):712–720. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-02-00712.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn L. G., Kerchner G. A., Kalra V., Zimmerman D. M., Leander J. D. Phencyclidine receptors in rat brain cortex. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Nov 15;33(22):3529–3535. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90133-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
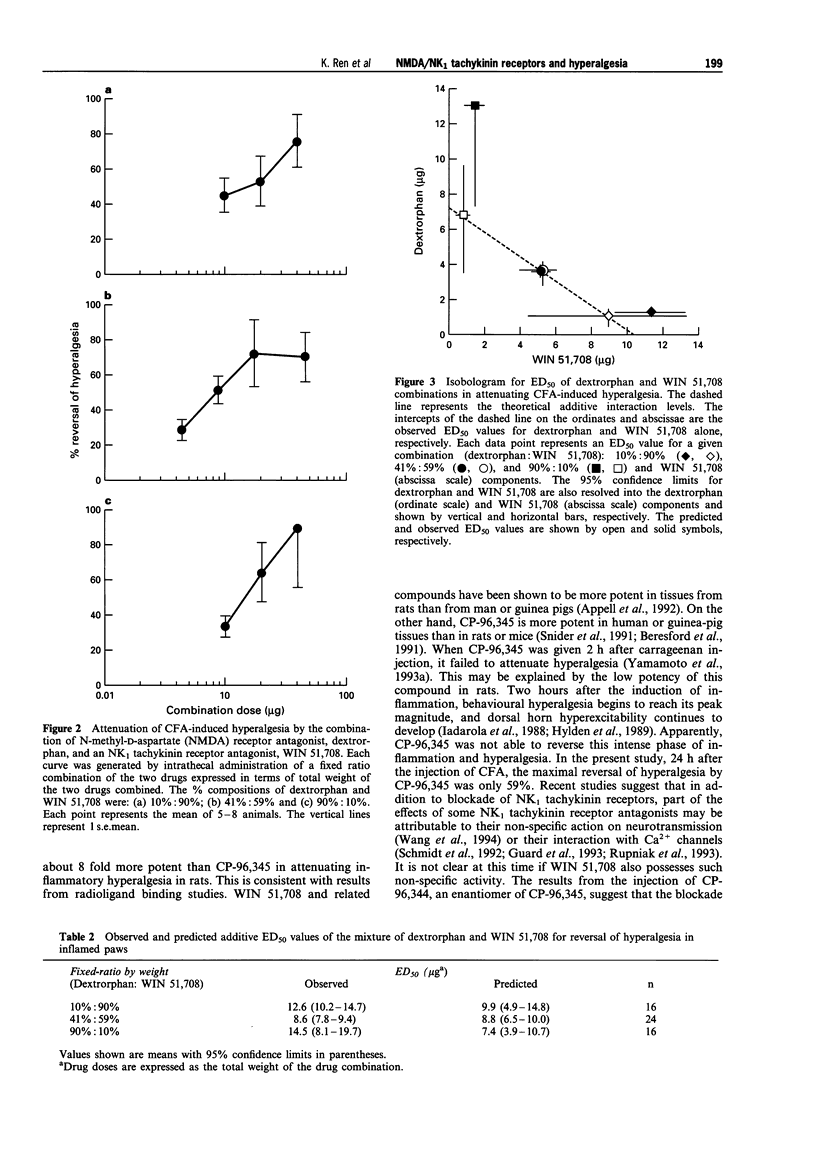
- Minami M., Kuraishi Y., Kawamura M., Yamaguchi T., Masu Y., Nakanishi S., Satoh M. Enhancement of preprotachykinin A gene expression by adjuvant-induced inflammation in the rat spinal cord: possible involvement of substance P-containing spinal neurons in nociception. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Mar 13;98(1):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mjellem-Joly N., Lund A., Berge O. G., Hole K. Intrathecal co-administration of substance P and NMDA augments nociceptive responses in the formalin test. Pain. 1992 Nov;51(2):195–198. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(92)90260-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mjellem-Joly N., Lund A., Berge O. G., Hole K. Potentiation of a behavioural response in mice by spinal coadministration of substance P and excitatory amino acid agonists. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Nov 25;133(1):121–124. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90072-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagahisa A., Asai R., Kanai Y., Murase A., Tsuchiya-Nakagaki M., Nakagaki T., Shieh T. C., Taniguchi K. Non-specific activity of (+/-)-CP-96,345 in models of pain and inflammation. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;107(2):273–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1992.tb12737.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagahisa A., Kanai Y., Suga O., Taniguchi K., Tsuchiya M., Lowe J. A., 3rd, Hess H. J. Antiinflammatory and analgesic activity of a non-peptide substance P receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jul 7;217(2-3):191–195. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90847-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neugebauer V., Weiretter F., Schaible H. G. Involvement of substance P and neurokinin-1 receptors in the hyperexcitability of dorsal horn neurons during development of acute arthritis in rat's knee joint. J Neurophysiol. 1995 Apr;73(4):1574–1583. doi: 10.1152/jn.1995.73.4.1574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi K., Ruda M. A. Gene regulation in an ascending nociceptive pathway: inflammation-induced increase in preprotachykinin mRNA in rat lamina I spinal projection neurons. J Neurosci. 1992 Jul;12(7):2563–2572. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-07-02563.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossipov M. H., Harris S., Lloyd P., Messineo E. An isobolographic analysis of the antinociceptive effect of systemically and intrathecally administered combinations of clonidine and opiates. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1990 Dec;255(3):1107–1116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. D., Mao J., Frenk H., Mayer D. J. The N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist dextromethorphan selectively reduces temporal summation of second pain in man. Pain. 1994 Nov;59(2):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(94)90069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radhakrishnan V., Henry J. L. Antagonism of nociceptive responses of cat spinal dorsal horn neurons in vivo by the NK-1 receptor antagonists CP-96,345 and CP-99,994, but not by CP-96,344. Neuroscience. 1995 Feb;64(4):943–958. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)00440-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radhakrishnan V., Henry J. L. Novel substance P antagonist, CP-96,345, blocks responses of cat spinal dorsal horn neurons to noxious cutaneous stimulation and to substance P. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Oct 28;132(1):39–43. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90428-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren K., Hylden J. L., Williams G. M., Ruda M. A., Dubner R. The effects of a non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist, MK-801, on behavioral hyperalgesia and dorsal horn neuronal activity in rats with unilateral inflammation. Pain. 1992 Sep;50(3):331–344. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(92)90039-E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren K., Williams G. M., Hylden J. L., Ruda M. A., Dubner R. The intrathecal administration of excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists selectively attenuated carrageenan-induced behavioral hyperalgesia in rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Aug 25;219(2):235–243. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(92)90301-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rokkas C. K., Helfrich L. R., Jr, Lobner D. C., Choi D. W., Kouchoukos N. T. Dextrorphan inhibits the release of excitatory amino acids during spinal cord ischemia. Ann Thorac Surg. 1994 Aug;58(2):312–320. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(94)92200-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupniak N. M., Boyce S., Williams A. R., Cook G., Longmore J., Seabrook G. R., Caeser M., Iversen S. D., Hill R. G. Antinociceptive activity of NK1 receptor antagonists: non-specific effects of racemic RP67580. Br J Pharmacol. 1993 Dec;110(4):1607–1613. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb14008.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusin K. I., Bleakman D., Chard P. S., Randic M., Miller R. J. Tachykinins potentiate N-methyl-D-aspartate responses in acutely isolated neurons from the dorsal horn. J Neurochem. 1993 Mar;60(3):952–960. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03242.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh M., Kuraishi Y., Kawamura M. Effects of intrathecal antibodies to substance P, calcitonin gene-related peptide and galanin on repeated cold stress-induced hyperalgesia: comparison with carrageenan-induced hyperalgesia. Pain. 1992 May;49(2):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(92)90151-Z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer M. K., Nohr D., Krause J. E., Weihe E. Inflammation-induced upregulation of NK1 receptor mRNA in dorsal horn neurones. Neuroreport. 1993 Aug;4(8):1007–1010. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199308000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer E. A., Sperk G., Schmid R. Capsaicin does not change tissue levels of glutamic acid, its uptake, or release in the rat spinal cord. J Neurochem. 1982 May;38(5):1383–1386. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb07916.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider R. M., Constantine J. W., Lowe J. A., 3rd, Longo K. P., Lebel W. S., Woody H. A., Drozda S. E., Desai M. C., Vinick F. J., Spencer R. W. A potent nonpeptide antagonist of the substance P (NK1) receptor. Science. 1991 Jan 25;251(4992):435–437. doi: 10.1126/science.1703323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song X. J., Zhao Z. Q. Interaction between substance P and excitatory amino acid receptors in modulation of nociceptive responses of cat spinal dorsal horn neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1994 Feb 28;168(1-2):49–52. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)90413-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tal M., Bennett G. J. Dextrorphan relieves neuropathic heat-evoked hyperalgesia in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Mar 5;151(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90058-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tallarida R. J. Statistical analysis of drug combinations for synergism. Pain. 1992 Apr;49(1):93–97. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(92)90193-F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venepalli B. R., Aimone L. D., Appell K. C., Bell M. R., Dority J. A., Goswami R., Hall P. L., Kumar V., Lawrence K. B., Logan M. E. Synthesis and substance P receptor binding activity of androstano[3,2-b]pyrimido[1,2-a]benzimidazoles. J Med Chem. 1992 Jan 24;35(2):374–378. doi: 10.1021/jm00080a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z. Y., Tung S. R., Strichartz G. R., Håkanson R. Non-specific actions of the non-peptide tachykinin receptor antagonists, CP-96,345, RP 67580 and SR 48968, on neurotransmission. Br J Pharmacol. 1994 Jan;111(1):179–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb14041.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X. J., Dalsgaard C. J., Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z. Spinal substance P and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors are coactivated in the induction of central sensitization of the nociceptive flexor reflex. Neuroscience. 1992 Dec;51(3):641–648. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90303-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaksh T. L., Rudy T. A. Chronic catheterization of the spinal subarachnoid space. Physiol Behav. 1976 Dec;17(6):1031–1036. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(76)90029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Shimoyama N., Mizuguchi T. Effects of FK224, a novel cyclopeptide NK1 and NK2 antagonist, and CP-96,345, a nonpeptide NK1 antagonist, on development and maintenance of thermal hyperesthesia evoked by carrageenan injection in the rat paw. Anesthesiology. 1993 Nov;79(5):1042–1050. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199311000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Shimoyama N., Mizuguchi T. Effects of intrathecal FK888, a novel dipeptide NK1 receptor antagonist, on the formalin test in the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1993 Oct 14;161(1):57–59. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(93)90139-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Yaksh T. L. Stereospecific effects of a nonpeptidic NK1 selective antagonist, CP-96,345: antinociception in the absence of motor dysfunction. Life Sci. 1991;49(26):1955–1963. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(91)90637-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yashpal K., Radhakrishnan V., Coderre T. J., Henry J. L. CP-96,345, but not its stereoisomer, CP-96,344, blocks the nociceptive responses to intrathecally administered substance P and to noxious thermal and chemical stimuli in the rat. Neuroscience. 1993 Feb;52(4):1039–1047. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(93)90550-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann M. Ethical guidelines for investigations of experimental pain in conscious animals. Pain. 1983 Jun;16(2):109–110. doi: 10.1016/0304-3959(83)90201-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


